Pregnancy, children > Need to know > The placenta is located on the back wall of the uterus: features of the condition
The placenta is an organ that appears in the body of the expectant mother and functions until she gives birth to a child.
The placenta completely stops forming between 15 and 16 weeks of pregnancy. After this, it will carry out its main functions: serve as a barrier to the penetration of various harmful substances and infections, and also provide nutrition to the fetus.
Where exactly the placenta is located will influence the course of the pregnancy. For example, there are situations when the placenta is located along the posterior wall of the uterus.
Is this normal?
The placenta forms during pregnancy to provide nutrition to the fetus. It is a temporary organ that can be called a connecting link between mother and child. Thanks to the placenta, the fetus receives all the necessary nutrients, as well as oxygen. The baby's lungs are not yet functioning, and nature has come up with a simple method of life support.
The attachment of the placenta matters - there are several options. The most optimal of them is along the back wall, at the bottom of the uterus. Read more about the placenta during pregnancy→
The more the pregnancy progresses, the more the walls stretch, and the process occurs unevenly. The front is more stretchable, while the back is less elastic. Thanks to this fact, the fetus is well supported and protected.
It is still unknown why the placenta attaches along the back wall and closer to the fundus of the uterus. But there are several assumptions:
- This area is equipped with a large number of vessels, and the temperature there is higher than anywhere else.
- Nearby is the exit from the fallopian tubes. The egg cannot move on its own, so it remains where the contractions of the fallopian tubes brought it.
- Inside it are the mechanisms that are responsible for choosing a place for fastening.
Doctors' recommendations
The location of the placenta on the posterior wall makes it easier for a specialist to diagnose
The main thing while waiting for a baby is not on which wall the placenta is localized, but how high the lower edge of this organ is located from the pharynx of the uterine cervix, located inside. The placenta, which is located at the back of the uterus and partially covers the os, can cause problems in women.
If there are no changes in this situation throughout the pregnancy, then most often specialists decide to perform a cesarean section. It should be remembered that due to the general stretching of the uterus, the placenta can rise to the upper part.
The placenta covers the cervix completely or partially until the birth process only in 10% of cases.
Even if the placenta has a normal location along the posterior uterine wall, complications may arise that are associated with the functioning of such an organ. We are talking about placenta abruption or placenta accreta. The growth of this organ occurs when the baby is just born. In this case, a specialist will have to separate it manually.
Advantages of this location
It is easy for obstetricians to control the pregnancy process if the placenta is located on the posterior wall of the uterus - the fetus is accessible for palpation, ultrasound and a stethoscope. Even if there are some physical impacts on this area, amniotic fluid will soften them.
There are several points according to which it is proven that the placenta along the back wall of the uterus is the best option:
- The immobility of the placenta is ensured. The back wall can remain dense for a long time and is little subject to change. It increases slightly in size, which reduces the level of stress on the placenta.
- The risk of injury is reduced. If the placenta is localized along the posterior wall, then we can talk about less susceptibility to external factors and pushes from the child.
- The risk of placenta previa is reduced. Very often, in the early stages of pregnancy, posterior placenta previa is detected by ultrasound. She gradually rises up and assumes a normal position. When attachment occurs to the anterior wall, this process does not exist.
- The risk of premature detachment is reduced.
- The likelihood of placenta accreta and tight attachment is reduced. This point applies only to those cases where a woman had to undergo surgery with the formation of a scar on the anterior wall. If during pregnancy it is discovered that the placenta is attached there, there is a risk of true accreta.
In all respects, the location of the placenta along the posterior wall is better than along the anterior wall. Indeed, in the second case, it may not have time to react to changes, and hematomas may form. These 2-3 cm compactions interfere with listening to the fetal heartbeat, and the woman later begins to feel movements.
Causes
The mechanism of prolapse of the posterior wall of the uterus is based on two phenomena. The first is increased intra-abdominal pressure, which inevitably moves the genital organ down. The second phenomenon is a weakening of the ligamentous or muscular apparatus of the pelvis, due to which the support of the uterus weakens and it sinks under its own weight.
Let's look at the main factors that increase the risk of genital prolapse:
- difficult childbirth, complicated by perineal ruptures;
- multiple pregnancies occurring at short intervals;
- genital injuries;
- surgical operations performed on the organs of the reproductive system;
- advanced age and age-related weakening of the pelvic floor muscles;
- constant or frequent heavy physical activity (especially heavy lifting);
- muscle diseases leading to muscle dystrophy or atrophy;
- overweight, obesity;
- chronic diseases of the respiratory system, accompanied by a strong cough (frequent coughing increases the load placed on the muscles of the abdominal cavity and pelvis);
- hormonal imbalances, characterized by a decrease in estrogen concentration.
Features of the condition
It happens that the placenta is located low on the back wall. The doctor understands that its edge lags behind the internal pharynx by less than 6 cm. The reasons for this condition are frequent pregnancies, the presence of abortions, and inflammatory diseases of the endometrium of an infectious nature. A dangerous diagnosis is posterior placenta previa. In this case, the distance between its edge and the internal os is less than 6 cm. Because of this, there is a risk of premature placental abruption. As a result of this condition, heavy bleeding occurs.
Women whose placenta is low-lying should undergo an ultrasound scan at certain dates. Sometimes this is necessary more often than during normal pregnancy. If the diagnosis is confirmed at 36 weeks, hospitalization and surgical delivery are required. However, most cases end favorably.
There are factors that prevent the placenta from attaching to the optimal location:
- Defects in the area of the egg shell.
- The presence of fibroids, inflammatory, purulent phenomena in a woman, the presence of physical deformations of the uterus.
- An unproven factor is the effect of gravity during sleep.
More often, abnormal attachment is observed in women who have given birth.
It is important to remember that the posterior location of the placenta is not something for which all expert recommendations should be avoided. An ultrasound scan once per trimester allows you to determine whether a woman has a problem. If presentation is diagnosed, the doctor carefully plans monitoring of the pregnant woman.
As the size of the uterus increases, presentation may go away on its own, but how the placenta behaves cannot be predicted or controlled. It is important that there is no tone in the area where the fetus is attached, as this increases the likelihood of abruption.
In case of pathology, it is necessary to identify the problem in time and constantly see a doctor. Even with full presentation, women have the opportunity to hear the cry of their baby. But to do this, you need to follow the advice of your doctor and check your condition more often using ultrasound. It is impossible to “feel” the placenta on your own - it can only cause harm.
It is possible to save the life of the baby and mother by caesarean section if the presentation continues to persist. In this case, none of the dangers that exist during natural childbirth will be avoided. In most women, the placenta is attached along the posterior wall, and its development occurs normally. But even if a pathological picture is identified, in 90% of cases the diagnosis is removed by the end of pregnancy due to the fact that the uterus is actively growing.
Author: Irina Levchenko, doctor, especially for Mama66.ru
What does it mean?
Placental tissue is formed quite early during pregnancy. Already in the second trimester of pregnancy, it begins to function fully. The placenta contains various blood vessels through which the fetus receives the nutrients necessary for its growth and development, as well as dissolved oxygen.
How the placenta is attached to the uterine wall determines how the baby’s intrauterine development will proceed, as well as the course of pregnancy as a whole.
The location of the placenta and its initial localization are determined almost from the first days after conception. It all depends on where the fertilized egg will be located. In most cases, it is implanted (tightly attached) into the inner wall of the uterus in the area of its fundus along the back wall. This feature of implantation is due to nature. It has been established that this area has the best blood flow.
The presence of blood vessels in this anatomical zone of the uterus also contributes to the physiological growth of the chorion. In such a situation, it grows and develops quite quickly and fully. Let us note that in most clinical cases, the placenta on the posterior wall of the uterus is located quite high - almost in the area of the uterine fundus, that is, in its upper section. The distance to the internal uterine os is quite large.
In certain situations, the fertilized egg changes its attachment site and is implanted in the lower parts of the uterus. This situation can be dangerous and usually leads to the development of a low-lying placenta or previa.
Normally, there is a certain distance between the placental tissue and the internal os. It is different at each stage of pregnancy. So, normally in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy it is 5 cm, and by the third it changes to 7 cm.
If the placental tissue is almost completely adjacent to the internal uterine os and even directly touches it, then this pathology is called presentation.
Doctors distinguish several clinical variants of placenta previa: it can be central, lateral or marginal. It all depends on the zone in which the placental tissue shifts to the area of the internal uterine os.
Thus, central presentation is characterized by a displacement of the central part of the placenta to the area of the internal os. With lateral presentation, the placenta comes into contact with the pharynx from the area of the lateral walls, and with marginal presentation, only with separate edges.
Also, placenta previa can be complete or partial. With complete presentation, almost all the placental tissue is located in the area of the internal uterine os. If the placenta is in contact only in separate areas (parts), then such a presentation is called partial or incomplete.
The severity of adverse symptoms and possible complications in this case significantly depends on how the placental tissue is located relative to the internal uterine os. This also determines the nature of the pregnancy. Experts note that attachment of the placenta to the posterior wall of the uterus occurs in most clinical cases.
Prolapse of the posterior wall of the uterus and pregnancy
With genital prolapse, the functioning of the entire reproductive system is disrupted. The structure and location of the external and internal genital organs change, which affects the ability to procreate.
Firstly, when the posterior wall of the uterus prolapses, complexes develop that prevent a woman from building relationships and leading a full sex life. Sexual intercourse is limited or stopped, and this minimizes the chances of conception.
Secondly, even if sperm penetrate the uterine cavity and fertilize the egg, the fertilized egg will not be able to implant into the displaced walls of the uterus, resulting in a miscarriage.
Thirdly, in the case of successful and reliable fixation of the fertilized egg, the risk of its detachment will always remain. At later stages (in the second and third trimesters), the placenta will exfoliate, and this condition also threatens miscarriage or premature birth.
Fourthly, due to prolapse and displacement, the volume of the uterine cavity decreases, which affects the location of the fetus in it, the amount of amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid) and the functioning of the placenta. The development of the unborn child may be disrupted, and due to oligohydramnios and fetoplacental insufficiency, nutritional deficiency and hypoxia - lack of oxygen - will occur.
With moderate prolapse of the posterior wall, pregnancy can aggravate the situation and accelerate the process of displacement. Childbirth will also have a negative impact on the condition.
Features of pregnancy
With the normal location of the placental tissue along the posterior wall of the uterus at a considerable distance from the uterine os, the course of pregnancy usually proceeds quite physiologically. Good blood flow in the area of the uterine fundus and its posterior wall ensures optimal fetal growth. In such a situation, the risk of developing any complications and adverse consequences is quite low.
If for some reason the placental tissue moves lower along the back wall and reaches the internal os, then the course of pregnancy is already complicated by the development of presentation. In such a situation, the risk of developing unwanted complications increases significantly.
It is important to note that placenta previa along the posterior wall of the uterus is more favorable. The prognosis for pregnancy in this case is quite good.
Thus, the risk of developing mechanical damage to the placental tissue, which is located on the posterior wall, is much lower. This is due to certain anatomical features of the structure of the female body. The placenta is protected in front by the anterior abdominal wall and pelvic bones, and in the back by the skeleton of the spine. Such reliable protection minimizes possible trauma to delicate placental tissue.
Features of the pathology
Posterior wall fibroids are most often diagnosed in women aged 35 to 50 years, but can be much earlier. The main reason for its appearance is considered to be the influence of a sex hormone such as estrogen. A benign tumor is a small node that is located on the wall of the reproductive organ and has a round shape. The neoplasm can be located on a pedicle or have a wide base, and can also be multiple or local.
There are several types of uterine fibroids depending on their location, and each of them has certain symptoms. Myoma can be located in the muscular, subserous or submucosal layer, and has a different histological composition. Some nodes contain only connective tissue, while others consist of fibrous tissue, nerve cells and blood vessels.
The following types of fibroids are distinguished:
- subserous;
- submucous;
- interstitial;
- intramural.
When the hormonal levels of the female body are disrupted, the myomatous node begins to actively grow and reach several centimeters (cm) in diameter. Experience shows that the size of a benign neoplasm can greatly increase and reach the fundus of the uterus. Myoma is a hormone-dependent tumor, so upon the onset of menopause it can regress on its own. Given this feature of the myomatous node in older people, treatment is usually not prescribed.
Is placenta migration possible?
Even more interesting:
Sores around the head
Mouth ulcers hiv
A change in the initial localization of placental tissue is called migration by specialists. It usually lasts for several weeks and is not accompanied by the development of adverse symptoms. However, during pregnancy occurring with placenta previa along the posterior wall of the uterus, the possibility of migration of placental tissue, unfortunately, is extremely low.
Many obstetricians and gynecologists believe that in this position, the placental tissue practically does not change its original location. Only in extremely rare cases is migration possible.
In this case, it is very important for a pregnant woman to monitor her well-being. The appearance of bleeding during the 2-3 trimester of pregnancy, especially if it develops spontaneously, should be a good reason for urgently contacting a specialist. In this case, there is a high risk of bleeding or even placental abruption.
Possible complications during pregnancy
If a pregnant woman has uterine fibroids along the posterior wall, it is recommended to regularly visit a gynecologist, which will prevent the development of many complications. What unpleasant consequences can such a benign neoplasm in the uterus lead to?
- in the last weeks of pregnancy, rapid growth of nodes is possible due to increased blood flow;
- when problems arise with the blood supply to the nodes, necrosis or peritonitis may develop;
- high risk of opening of the uterine pharynx and miscarriage;
- torsion of a thin node and tissue necrosis;
- previous removal of nodes can cause rupture of the reproductive organ.
Intrauterine development of the fetus is determined by normal blood flow in the placental system, therefore ultrasound examinations must be performed throughout the entire pregnancy.
With small fibroids located on the front and back walls, a woman can give birth naturally. If the pregnancy has complications, a caesarean section is usually performed. The following pathological conditions may be indications for such an operation:
- fibroids are too large;
- problems with the blood supply to the node and tissue necrosis;
- breech presentation of the fetus;
- identifying pathologies in the patient that place her at risk.
Important: Many experts recommend that a woman not plan a pregnancy if she has fibroids on the anterior or posterior wall of the reproductive organ. With this pathology, the risk of developing anemia is too great, so in such situations they resort to artificial termination of pregnancy.
How to determine?
The location of the placenta can be determined in various ways. Thus, the localization of the placental tissue is determined by conducting a routine vaginal examination. When conducting such an examination, the doctor must evaluate where the placenta is located.
If the placental tissue is too low and its presentation develops, then too frequent vaginal examinations should not be performed. In this case, the delicate tissue of the placenta can be easily damaged. It is also very important that vaginal examinations are performed by a qualified professional. Accuracy in carrying out such gynecological examinations is very important.
A more accurate way to determine the location of the placenta is to conduct an ultrasound examination. With the help of modern equipment, it is quite easy and accurate to determine where the placental tissue is located. An experienced and qualified specialist can also quite easily determine the distance from the placenta to the uterine os.
If during pregnancy a diagnosis of “placenta previa” is established, then in this situation the expectant mother is prescribed several more repeated ultrasound examinations. This allows doctors to monitor the dynamics of pregnancy, as well as timely determine the onset of possible complications. Such dynamic ultrasound examinations also make it possible to evaluate the migration of placental tissue, if it does occur.
If there is placenta previa, then preference is given to transabdominal ultrasound techniques. During these procedures, the ultrasound sensor is located on the surface of the anterior abdominal wall.
Performing a transvaginal ultrasound, when the sensor is inserted into the vagina, can lead to bleeding. As a rule, this examination is not carried out during presentation.
What should you consider?
Pregnancies in which the placenta is located on the back wall of the uterus usually proceed well. However, this does not at all exclude scheduled visits to the doctor and undergoing screening examinations recommended by him.
During pregnancy, numerous changes can occur in a woman's body. At any time, the course of even a physiological pregnancy can be complicated by the development of complications. In order for them to be identified on time, the expectant mother should regularly visit her obstetrician-gynecologist.
If, during examinations, the doctor determines placenta previa, then, first of all, you should be very careful about this. The behavior of the expectant mother and her attitude towards her own health are a very important component for carrying such a pregnancy to term.
The appearance of bloody discharge from the genital tract, the occurrence of sudden and severe pain in the abdomen should be important reasons for contacting a specialist for advice.
When placenta previa occurs on the posterior wall of the uterus, doctors make a number of recommendations. They are mainly aimed at reducing the development of dangerous complications, such as bleeding or placental abruption. An expectant mother who has placenta previa should not lift heavy objects or engage in vigorous physical activity. Also, to improve her overall well-being, she should eat well and get enough sleep, and, if possible, limit as much as possible any stress and nervous shock.
You will learn more about the importance of the location of the placenta in the following video.
Expectant mothers, while carrying a baby, often ask questions about the normal and peculiarities of pregnancy. It also does not go unnoticed that during routine ultrasound examinations, doctors must look at the condition and location of the placenta. What is this miracle organ that was not previously in the female body? What functions does it perform and what is the area where the placenta is attached?
Symptoms
Unfortunately, pronounced symptoms begin to appear only with the progression of genital prolapse , and the initial stages of prolapse of the posterior wall of the uterus are often asymptomatic or have vague nonspecific manifestations.
Female Reproductive System 3D Model
As the posterior wall of the main reproductive organ descends, the following symptoms occur:
- pain of a dull, pulling or aching nature, localized in the lower abdomen;
- feeling of the presence of a foreign object in the vagina, bloating, discomfort and heaviness in this area;
- bowel disorders: frequent or persistent constipation;
- changes in the nature of menstruation: increased duration, increased discharge, pain during menstrual periods;
- pain that occurs during sex;
- bulging of the vagina (not noticeable in the first stages).
The listed signs worsen a woman’s quality of life, reduce and dull libido, and provoke the development of complexes. This affects self-esteem, mental state and emotional background. Negative influence affects all areas of life: professional activity, family or personal relationships, communication with loved ones.
What is the placenta and why is it needed?
Despite the availability of information on any issues related to pregnancy, many expectant mothers still believe that the placenta is the baby’s “house”. What misleads women is that it is often called a “children’s place.” In fact, this is not so; the child’s temporary “home” is the uterus and the bladder with amniotic fluid. The placenta is a unique organ that forms in a woman’s body only during pregnancy, which has the shape of a flat disk or a thick pancake. It is densely supplied with blood vessels through which the fetus is nourished.
In the “baby place” the blood of mother and child circulates simultaneously, but it does not mix due to the placental barrier
The placenta begins to form from the moment the embryo attaches to the uterine cavity. At first it looks like villi, which penetrate the mucous membrane and continue to develop until 15–16 weeks of pregnancy. After the 20th week, the most active exchange begins with the help of its blood vessels. Through the placenta, oxygen flows from the mother's blood to the fetus, and carbon dioxide flows back, replacing the baby's breathing through the lungs. Also, thanks to this organ, the child is supplied with the necessary nutrients, ensuring his growth and development.
Although the blood of the pregnant woman and the fetus are exchanged in the “baby place”, they do not mix, thanks to a special membrane called the placental barrier. Thanks to this, the placenta also acts as a filter, protecting the baby from harmful substances and viruses that can come from the mother’s blood, and also prevents the penetration of antibodies during Rh conflict.
In addition to the above functions, this organ is assigned the important hormonal task of maintaining pregnancy. About 15 types of different hormones are synthesized in the placenta, among them human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), prolactin and others.
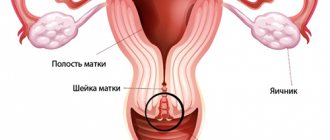
How can the placenta be located?
"Children's place" has several location options. Normally, it can be attached to the back wall of the uterus, along the front and in the fundus. There is also the concept of placenta previa, when it is located at the bottom of the uterus, blocking the exit to the cervical canal. This arrangement is considered pathological.
It is impossible to independently determine where exactly this organ is located. The attachment site is determined exclusively by ultrasound. Most often, the placenta is located on the back wall, less often - on the front.
It should be noted that the placenta is not always located along one wall. It can be slightly shifted to the left or right, and also located simultaneously on part of the back or front wall and in the bottom; less often, a completely lateral attachment is observed. These variations are normal and should not cause concern.
Photo gallery: placenta location options
During the examination, the main attention of doctors is drawn to the proximity of the location of the “baby spot” to the internal os of the cervix. If the presentation is marginal, that is, the placenta only touches the pharynx on the edge, then this situation is not too critical and the expectant mother should not panic ahead of time. You need to undergo examinations more carefully, and not overload yourself with physical labor, because as the uterus grows, the situation may change and the placenta will rise to a distance sufficient for a safe natural birth.
Consequences
If prolapse of the posterior wall of the uterus was noticed in time, it is reversible and removable, sometimes even without surgical intervention. But as the pathology progresses, the anterior wall begins to shift. The uterus literally pushes the vagina out and deforms it, which causes damage and sometimes erosion of the mucous membranes, which can lead to tissue infection.
The pathologically located uterus puts pressure on the rectum and provokes the development of constipation. Due to constant tension during bowel movements, hemorrhoids occur, and partial prolapse of the intestine is also likely. This is accompanied by severe discomfort, pain and stool disturbances.
When the anterior wall of the uterus prolapses, the bladder is compressed: its walls can become deformed, which entails the development of cystitis - inflammation of the mucous membranes. In addition, the bladder cannot hold the usual volume of urine, and if the sphincter of the organ is involved in the process, incontinence will occur.
Often, prolapse of the posterior uterine wall is accompanied by varicose veins of the external genitalia. Dilatation of the veins of the lower extremities may also be observed due to compression of the inferior vena cava by the displaced uterus, through which blood flows out from the lower part of the human body.
The placenta is located on the posterior wall - is it normal or not?
Attachment of the placenta to the posterior wall is one of the normal options. In addition, many doctors consider this arrangement to be the most physiological and safe. Why is embryo implantation into the posterior surface of the uterus more common? There is no proven information on this yet, but there are a number of factors that can contribute to the attachment of the placenta in this particular place. Thus, the posterior wall of the uterus has the greatest thickness of the endometrium and high temperature due to the abundant blood supply, which has a beneficial effect on the development of pregnancy in the short term. Also, do not forget that the egg itself cannot move and the fallopian tubes, contracting, push it into the uterine cavity, precisely closer to the back wall and bottom. Another assumption is that in the fertilized egg there are certain mechanisms responsible for choosing the most successful and favorable place for attachment.
Degrees of genital prolapse
Degrees of uterine prolapse in women.
There are four degrees of prolapse of the posterior wall of the uterus:
- I – prolapse of the external os of the uterus occurs, but it does not move beyond the middle of the vagina.
- II – the uterus is significantly lowered, located at the level of the entrance to the vagina, but does not protrude from the genital slit.
- III – incomplete prolapse of the organ occurs, in which its external os emerges from the genital slit, but the uterine cavity continues to remain in the vagina.
- IV – the uterus falls out completely.
Advantages of posterior placement, impact on childbirth
Placing a child's seat on the rear wall has a number of advantages compared to its attachment in front:
- This attachment reduces the risk of injury to the placenta in the event of an external impact on the expectant mother’s abdomen. Of course, this does not mean that pregnancy with an anterior position of the “baby seat” is more dangerous and it can be damaged if a woman, for example, hits her stomach. No, and in this case the placenta and the fetus itself are well protected. But still, the further location of this organ from external stimuli can play a decisive role in severe abdominal injuries.
- When located posteriorly, placenta previa is less likely to occur. In the case of a low attachment, there is a chance that during the growth of the uterus and the increase in the “baby spot” itself, it will rise to a height sufficient for a safe natural birth. This process usually occurs before 32 weeks of pregnancy. Since the anterior wall stretches much faster, such active migration of the placenta, alas, is not observed.
- The posterior wall of the uterus is less susceptible to stretching, which reduces the risk of abruption. This is especially important with low placentation or posterior placenta previa.
- If a woman has had surgical interventions in the uterus and scars remain on it, then they are located in the front part of it. In this case, the attachment of the embryo in this place can be dangerous due to placenta accreta - when the chorionic villi (placenta in the initial stage) grow not only to the mucous membrane of the uterus, but also to its walls and even to the abdominal cavity. This may lead to complications in the form that after childbirth the placenta does not separate on its own, and there is a risk of bleeding. This situation is life-threatening for the woman and may require removal of the uterus.
- An important confirmation of the advantage of placing the placenta in the back is the convenience for the obstetrician-gynecologist during examination. So, with this attachment, the vessels of the “baby seat” will not interfere with listening to the child’s heart, as well as more accessible palpation of parts of the body, determining its presentation by external palpation of the abdomen.
- If a cesarean section is necessary, the risk of damage to the placenta during the uterine incision is reduced.
When the placenta is located along the posterior wall, the doctor is less likely to damage this organ when making an incision
- Some pregnant women note that with posterior attachment, fetal movements can be felt earlier and much more clearly. This advantage cannot be proven, since, in addition to the location of the placenta, this is influenced by the individual sensitivity of the mother and what kind of child she is carrying.
During the second pregnancy, the first movements of the baby were felt at the 17th week. In this case, the location of the placenta was along the posterior wall and in the bottom. At the same time, a friend with the same term and anterior placenta began to feel movements at the 16th week, although this was her first pregnancy. Unfortunately, no one can confirm whether a woman really feels movements at the moment. Here you have to rely only on your own feelings and try not to confuse the first light kicks with intestinal peristalsis.
Therapy
The first and second stages of genital prolapse require conservative treatment, and surgical interventions can be avoided. Therapy includes areas:
- Gynecological massage performed with the aim of returning the uterus to its physiologically correct anatomical position.
- The use of bandages to support the abdominal organs and prevent further prolapse of the uterine walls.
- Gymnastics performed to strengthen the muscular system of the pelvic floor. Well-proven Kegel exercises can be performed, which involve alternating tension and relaxation of the vaginal muscles.
- Hormonal therapy is prescribed in case of failures to normalize the concentration of estrogen in the female body.
In the third and fourth stages of genital prolapse, conservative therapy is meaningless, and therefore surgical treatment is always prescribed. The operation involves narrowing the lumen of the vagina by suturing its walls and fixing the uterus in a physiologically correct position through the use of medical materials with a mesh structure (they form a frame and guarantee support). Surgical interventions are performed using vaginal access or laparoscopic method.
Exercises for prolapse of the uterus (Kegel exercises).
Educational video, a must watch !
Elderly patients are sometimes advised to have support rings implanted into the vagina to prevent further prolapse of the walls. If there is complete prolapse of the uterus, a hysterectomy - removal of the organ - may be necessary.
Video: location of the placenta, placenta previa
The most important thing for a successful and easy pregnancy is the health and peace of mind of the expectant mother. The location of the placenta not on the back wall should not cause concern for a woman, this is just her feature. Currently, all pregnant women undergo mandatory examinations, during which the condition and place of attachment of the placenta are established; this information is very important for the obstetrician-gynecologist who delivers the baby. And it is important to remember that even the presence of complete placenta previa does not exclude a successful pregnancy; you just need to be more attentive to your health during this period. Enjoy your position, capture wonderful moments, feeling the life inside you, and in due time you will definitely hold your baby in your arms. Be healthy!
Prevention
Prevention of prolapse of the posterior wall of the uterus includes following the recommendations:
- Regularly scheduled visits to the gynecologist for examinations.
- Body weight control.
- Limiting physical activity, avoiding sudden heavy lifting.
- Sufficient intervals between births are at least two to three years.
- Be attentive to your health and contact medical institutions if any alarming symptoms arise.
- Performing exercises that strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. Kegel exercises are useful: first tense your vagina, as if holding back the urge to urinate, then relax.
Genital prolapse is not only an unpleasant and delicate problem, but also a very serious problem. And if you want to avoid serious consequences, contact your doctor in a timely manner and follow his recommendations.
(Rate this article)
Share the news on social networks
Ask a Question! You have questions? Feel free to ask any questions! And our staff specialist will help you. Go>>
- Recommended Articles
- Hyperpolymenorrhea
- What causes thrush?
- Ovarian dysfunction
« Previous entry