The most common gynecological diseases among middle-aged females are adenomyosis and uterine fibroids. The parallel development of both diseases is often diagnosed.
This phenomenon is due to the fact that under the influence of these ailments, hormonal levels are disrupted, the uterus is affected, which causes changes in it.
Uterine fibroids with nodular adenomyosis are often diagnosed. Let's get acquainted with the reasons for the formation of these diseases, their symptoms and treatment methods.
General information about diseases
Myoma and adenomyosis are gynecological diseases that are provoked by hormonal imbalance. They differ in:
- cause of origin (pathogenesis);
- symptoms;
- probable complications.
General characteristics of hormonal-dependent diseases of the uterus
| Name of pathology | Peculiarities |
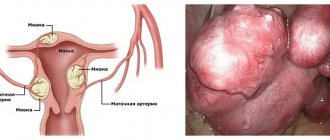
| Myoma (fibro-, leiomyoma) | A hormone-dependent tumor forms in the thickness of the muscle layer (myometrium). It consists primarily of smooth muscle and connective tissue cells. It is diagnosed in 20% of women when visiting a gynecologist. Depending on the direction of tumor growth (neoplasia), several forms of pathology are distinguished: subserous, intraligamentary, interstitial and submucosal. |
| Adenomyosis (endometriosis of the uterus) | The disease is characterized by the growth of the mucous layer (endometrium) into the thickness of the wall. Structural changes occur only within the body of the organ. Adenomyosis is the third most frequently diagnosed gynecological disease after leiomyoma and adnexitis. During menstruation, the overgrown uterine lining is shed, leading to the formation of cysts. |
| Endometriosis | The pathology is manifested by the growth of the endometrium outside the uterine cavity. Lesions form in the fallopian tubes, gonads, peritoneum, intestines, bladder, and respiratory system. Endometrial cells spread primarily through the blood and lymph. |
Adenomyosis is a type of endometriosis in which neoplasia does not extend beyond the uterine cavity. The disease cannot be called a tumor, since the cells in the overgrown tissue have a normal structure.
Often, patients are diagnosed with uterine fibroids against the background of internal endometriosis. The diseases manifest themselves with similar symptoms, so to accurately determine the cause of ill health, a histological analysis is performed.
Causes of development and risk factors for pathology
According to most experts, fibroids and endometriosis occur due to an imbalance of steroid hormones. This is indicated by the accelerated growth of neoplasia when taking hormonal contraceptives and their resorption after menopause. Leiomyoma, together with endometriosis, occurs due to excessive functional activity of the ovaries.
Factors provoking fibromyoma with adenomyosis:
- surgical termination of pregnancy;
- gonadal cysts;
- damage to the birth canal during delivery;
- abuse of hormonal contraceptives;
- myometrial injuries during diagnostic curettage;
- prolonged insolation;
- inflammation of the internal genital organs;
- genetic predisposition;
- endocrine and metabolic disorders;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- malfunctions of the immune system;
- use of intrauterine devices;
- obesity.
Fibroids in combination with endometriosis are provoked by long-term treatment with hormonal pills. The likelihood of neoplasia increases with autoimmune disorders, unbalanced nutrition, regular stress, and poor environmental conditions.
Clinical picture: how to distinguish fibroids from adenomyosis?
Symptoms for endometriosis and fibroids are similar. Both diseases occur when the gonads are overactive. Therefore, they are accompanied by disruption of the menstrual cycle and reproductive function.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids and adenomyosis
| Symptoms | Myoma | Endometriosis |
| Pain in the lower abdomen | + | + |
| Spotting a couple of days before menstruation | – | + |
| Painful intercourse | + | + |
| Heavy menstruation | + | + |
| Problems with conception | + | + |
| Painful periods | + | + |
| Dull pain in the lower back | + | – |
| Spontaneous abortion | + | + |
| Intermenstrual bleeding | + | + |
| Symptoms of anemia (drowsiness, pale skin, chronic fatigue) | + | + |
Uterine fibroids with internal endometriosis have a bright course. The severity of symptoms increases before menstruation. An increase in the level of estrogen in the blood leads to swelling of the endometrium and a decrease in uterine patency.
Distinctive features of diseases
| Characteristic | Internal endometriosis | Fibroids |
| At what age is it most often diagnosed? | After 27-29 years | After 30-35 years |
| Damage area | All layers of the uterus | myometrium |
| Pelvic pain | Aching or pulling | Cramping or sharp |
| Possibility of malignancy | High (at 3-4 degrees) | Very low |
| Characteristic complications |
|
|
It is impossible to distinguish fibroids from adenomyosis and endometriosis by external signs. Therefore, at the first symptoms of the disease, make an appointment with a gynecologist.
Reproductive function: possible problems and ways to solve them
Uterine fibroids in combination with adenomyosis reduce fertility - the ability to conceive a child. Due to diseases, the genital organ becomes deformed and its patency decreases. Therefore, the likelihood of sperm entering the fallopian tube to fertilize the egg is sharply reduced.
Endometriosis of the uterus with fibroids poses a serious threat during pregnancy. After conception, the level of estrogen in the body increases, so hormone-dependent tumors begin to grow faster. Myoma in combination with adenomyosis is dangerous:
- spontaneous abortion;
- deformation of the fetal skeleton;
- premature birth;
- fading of pregnancy;
- uterine ruptures;
- placental abruption;
- weakness of the ancestral forces.
At the initial stage, the disease can be treated with medication. Fibroids and endometriosis are treated with hormonal drugs. They inhibit the activity of the sex glands, provoke artificial menopause, so the neoplasms resolve. For large fibroids and endometrial growths, surgical intervention is recommended.
Surgical treatment of uterine fibroids is performed for necrosis of neoplasia, infertility, and tumors with a diameter of more than 5-7 cm.
What is uterine fibroid
The term uterine fibroids refers to a benign tumor created from the muscle layer lining the uterine cavity. The pathology is characterized by the formation of multiple or single nodes. The size of pseudotumor varies from several millimeters in diameter, but individual formations can grow up to several centimeters. The disease is often diagnosed in women aged 35 to 55 years.
The danger of the disease is that it can be asymptomatic. In this case, the tumor can only be detected during a regular examination by a gynecologist. This course is called hidden, it is quite rare, most often the disease has pronounced symptoms. In this case, the woman should consult a doctor with complaints of feeling unwell.
Attention! During the menstrual cycle, rapid growth of the tumor is observed. During menopause, the tumor stops developing and sometimes resolves on its own.
The list of main reasons provoking the development of the disease includes:
- hormonal disorders and imbalance of estrogen and progesterone in the body;
- infectious pathologies occurring in a chronic form;
- constant psycho-emotional stress and diseases of the endocrine system;
- hereditary predisposition;
- metabolic disease.
The following symptoms are characteristic of uterine fibroids:
- intense bleeding during menstruation;
- problems with bowel movements;
- frequent urge to empty the bladder, which occurs even at night;
- recurrent headaches;
- discomfort in the mammary glands;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- general deterioration of health.
Medium and large uterine fibroids often prevent conception. Successful fertilization is possible only after removal of the tumor. If a neoplasm is formed during pregnancy, it can negatively affect the development of the fetus, and myomatous nodes can also cause premature birth.
The treatment regimen for uterine fibroids is determined depending on the severity of the pathological process. If a woman feels discomfort due to a tumor, the doctor resorts to surgical action. At the initial stage, when the nodes are small, experts recommend the use of drug therapy. If the tumor is formed during pregnancy, the doctor selects safe drugs that ensure the resorption of the tumor.
Attention! The danger of the disease manifests itself if the patient delays its treatment. This often happens when small fibroids are detected. In the absence of timely qualified assistance, the pseudotumor will grow and can cause unpredictable consequences and complications.
Other dangerous complications
Estrogen-dependent diseases not only disrupt reproductive function, but also negatively affect the quality of life. Without proper treatment, they lead to life-threatening complications.
Consequences of uterine fibroids in combination with internal endometriosis:
- acyclic uterine bleeding;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- emotional lability;
- torsion and necrosis of neoplasia;
- pain syndrome;
- compression of the pelvic organs;
- neurological disorders;
- uterine deformation.
Large fibroids sometimes develop into malignant tumors. Without proper treatment, they are fatal.
Diagnosis and treatment
Before making a diagnosis, the doctor performs a standard gynecological examination and collects anamnesis. Then the woman is given directions for the following examinations:
- Ultrasound of the uterus and pelvic organs;
- hysteroscopy;
- laparoscopy;
- CT (computed tomography);
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- taking samples of affected tissues for histological examination.
Only after a complete comprehensive examination, the doctor chooses treatment tactics, which depend on many factors. The choice of therapeutic regimen is influenced by the size of the fibroids, the number of adenomyotic nodes, the degree of progress of adenomyosis, the presence of concomitant diseases, as well as the general health of the patient.
Conservative treatment
At the initial stage of the disease or women over the age of 40 years, as a rule, treatment with medications is prescribed. The thing is that in young women, the ovaries intensively produce estrogen, which enhances the growth of tumors. Therefore, drug treatment of fibroids with adenomyosis is often ineffective. At the same time, with the onset of menopause, pathological growths can begin to resolve on their own, precisely due to a decrease in estrogen production.
Conservative treatment is based on taking medications that help reduce growth and reduce the size of tumors. For this, doctors use hormonal, antibacterial and decongestant drugs, and immunomodulatory agents. This therapy allows you to stop the inflammatory process, normalize hormone levels and strengthen the immune system.
In advanced cases, in order to stop the progress of adenomyosis in combination with fibroids, surgical intervention may be required, including complete removal of the uterus. Therefore, timely diagnosis of these diseases is so important.
Important! With uterine fibroids and adenomyosis, any thermal effect on the pelvic organs is strictly prohibited.
That is why physiotherapy procedures such as:
- mud therapy;
- paraffin therapy;
- phonophoresis;
- warm sand treatment;
- laser and ultrasound therapy;
- ultraviolet irradiation.
For fibroids with adenomyosis, radon and iodine-bromine baths , as well as magnetic therapy, will be effective. But just like any treatment, physiotherapy should be prescribed only by the attending physician.
Surgery
As already mentioned, drug treatment is most often prescribed to older women. The thing is that it is impossible to completely get rid of uterine fibroids using drugs alone. Therefore, doctors advise young women with fibroids larger than 10 mm in diameter to undergo surgery.
In addition, surgery is performed in the following situations:
- with uterine bleeding;
- During the examination, necrotic foci were found;
- at risk of degeneration of the neoplasm into a malignant tumor;
- with severe pain;
- with adenomyosis combined with sumbocous fibroids;
- with the development of anemia;
- with rapid tumor growth.
Surgery is performed using instruments such as a laparoscope and a hysteroscope. Depending on the size of the tumor and the advanced stage of the disease, either partial excision or complete resection of the uterus.
Share the article on social media. networks:
Differential diagnosis
The clinical picture of fibroids on the background of endometriosis is similar to other tumor diseases. Therefore, to make a diagnosis, differential diagnostics is carried out, which involves conducting hardware examinations and taking tests.
Gynecological examination
Suspicions of nodular uterine fibroids in combination with adenomyosis arise already during the initial examination of the patient. The gynecologist performs a bimanual (two-handed) examination and assesses the condition of the genital organs using mirrors. With fibroids and endometriosis, the following are found:
- swelling and darkening of the cervix;
- organ enlargement;
- tuberosity in the uterine area.
On palpation, patients complain of increased pain in the pelvis and tension in the abdominal muscles.
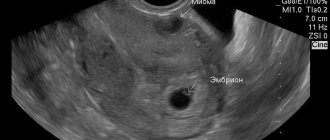
Ultrasonography
Even if myomatous nodes are located deep in the thickness of the myometrium, they are detected during transvaginal ultrasound. Estrogen-dependent diseases are indicated by:
- thickening of the endometrium;
- endometrioid cysts;
- nodules with a clear contour in the myometrium;
- deformation and enlargement of the uterus.
With cysts and tissue necrosis, hypoechoic areas are found. They appear as dark areas on the screen.
If the fibroid contains a lot of connective tissue, it reflects most of the ultrasound wave. Therefore, on the monitor screen the tumor looks like a white, hyperechoic inclusion of a round shape.
Hysteroscopy
The essence of the hardware study is to visualize the walls of the uterus using a hysteroscope - an optical device. Hysteroscopy is performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. If malignancy of neoplasms due to adenomyosis and fibroids is suspected, the doctor takes tissue samples for histological analysis.
Magnetic resonance imaging
To determine the extent of the lesions, obtaining from a three-dimensional image, MRI of the pelvic organs is used. Based on the data obtained, the feasibility of the operation is assessed.
Laboratory research methods
At the final stage of diagnosis, it is necessary to confirm the diagnosis using laboratory data. Therefore, during a gynecological examination, a smear is taken from the vagina and os of the uterus to detect sexually transmitted infections. Additionally, patients are prescribed:
- clinical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- test for steroid hormone levels.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor makes a diagnosis and determines the cause of fibroids with adenomyosis.
Diagnostics
The drug treatment regimen is established after correct determination of the form of the disease and stage of development. Due to the similarity of symptoms of adenomyosis and fibroids, there is a risk of misdiagnosis during examination in a gynecological chair. Examination of the cervix is uninformative.
If specialists suspect a cumulative course of diseases, they use various diagnostic methods, which include:
- Ultrasonography. The most favorable period for identifying the stage of the pathological process is 24-25 days of the menstrual cycle. The accuracy of the method is about 95% and depends on the degree of damage to the uterine body. Imaging may be complicated by the large size of the fibroid and other features of the disease. A doctor will be able to classify echo signs.
- MRI. This method is defined as more informative due to the ability to identify the internal structure of the tumor. An accurate result is guaranteed for nodular adenomyosis.
- Hysteroscopy. Allows for differential diagnosis of uterine fibroids and adenomyosis.
- Laparoscopy. Used to clarify the diagnosis or to identify difficulties in determining it.
- Biopsy. It is used when a cumulative course of diseases is suspected, when it is impossible to confirm the diagnosis by other methods.
During the first examination, the doctor must take a smear for flora and cytology. A prerequisite is a colposcopy. Uterine fibroids with signs of adenomyosis are diagnosed in several stages. Thanks to this approach, the gynecologist will be able to select an individual treatment regimen.
Principles of treatment for combination of fibroids and adenomyosis
The features of therapy depend on many factors - the extent of the lesions, the severity of symptoms, the age of the patient, and the size of the neoplasia. Fibroids in combination with uterine endometriosis can be treated using both conservative and surgical methods.
Conservative treatment
Drug therapy with hormonal drugs is effective for tumors with a diameter of up to 3 cm. To stop uterine fibroids in combination with adenomyosis from progressing, different groups of drugs are used:
- Gonadotropic releasing hormone agonists (Zoladex, Goserelin) – provoke pharmacological menopause, which leads to a reduction in foci of endometriosis and leiomyoma.
- Antigonadotropins (Gestrinone, Danazol) - suppress the synthesis of pituitary hormones that stimulate the ovaries. With a course of medication, foci of adenomyosis decrease.
- Progesterone antagonists (Pencrofton, Genale) – competitively bind to progesterone receptors. Slows down the progression of estrogen-dependent diseases.
For fibroids against the background of adenomyosis, vitamin-mineral complexes, immunostimulants, antispasmodics, etc. are additionally prescribed.
Additionally, contraindications for uterine fibroids are taken into account. During the entire therapy, they follow a diet, avoid stress, give up bad habits and visits to the solarium.
Surgery
Depending on the stage of adenomyosis and uterine fibroids, the surgeon determines the scope of surgical interventions. If the tumors are small, organ-preserving operations are performed. For large fibroids with a high risk of malignant degeneration, the uterus is removed.
Methods of surgical treatment
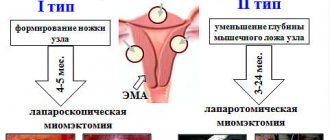
- myomectomy is an organ-sparing operation in which fibroids are removed from the myometrium;
- myometrectomy – removal of tumors followed by reconstruction of the uterus;
- total hysterectomy - excision of tumors along with the affected organ.
Conservative myomectomy is performed laparoscopically or laparotomically. In the first case, access to the uterus is gained through a puncture in the abdominal wall, and in the second, through an incision in the lower abdomen.
When is surgery needed?
The doctor prescribes surgical intervention only if there are direct indications:
- fibroids from 5 cm in size;
- constant uterine bleeding;
- necrosis of neoplasms in the uterus;
- reproductive dysfunction;
- combination of fibroids with endometriosis of the gonads;
- suspected malignant degeneration of neoplasia.
The scope of surgical interventions for leiomyoma combined with endometriosis depends on:
- reproductive health conditions;
- woman's age;
- neglect of the disease;
- the rate of increase in neoplasia.
If surgery is contraindicated, minimally invasive procedures are used - embolization of the uterine arteries, cryodestruction of small neoplasias.
Combination of pathologies
Interestingly, it is adenomyosis that often becomes a provoking factor for the occurrence of fibroids . At the same time, one of the most popular causes of these pathologies remains hormonal imbalance. Hormonal imbalance can be triggered by both the genitals and the endocrine system.
Another interesting fact is that a woman suffering from a combination of adenomyosis and uterine fibroids is often diagnosed with liver problems. It is this organ that is responsible for introducing excess estrogen.
Uncontrolled cell division leads to the fact that the size of the uterus increases to the same size as in healthy women at 10–12 weeks. In addition, with adenomyosis in combination with fibroids, the following symptoms may occur :
- dyspareunia (pain during sexual intercourse);
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- bleeding from the vagina;
- pain in the pelvic area, aggravation of which occurs with the arrival of menstrual flow;
- pain and problems when urinating;
- flatulence, constipation;
- pale skin;
- general weakness.
Attention, if the described symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor. Only timely diagnosis and properly selected treatment will avoid the development of complications.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine offers many recipes for herbal remedies that prevent the progression of estrogen-dependent diseases. Folk remedies do not eliminate fibroids or adenomyosis, but only alleviate symptoms, normalize hormonal levels and reproductive function.
Remedies for fibroids due to endometriosis:
- Flax seeds. 4 tbsp. l. raw materials are poured with ½ liter of water. Boil over low heat for 5 minutes. The strained broth is taken half a glass three times a day, half an hour before meals.
- Borovaya uterus. 2 tsp. herbs are poured with 250 ml of water. Simmer in a water bath for 10 minutes. The filtered drink is taken 15 ml 1 hour after meals up to 4 times a day.
Treatment with folk remedies should be agreed with a doctor. Irrational use of herbal medicines is dangerous due to allergic reactions.