Adenomyosis is a form of endometriosis. In most cases, diagnosis reveals diffuse changes in the myometrium like adenomyosis, accompanied by pathological growth of the endometrium. As a result of diffuse changes, irregularities in the menstrual cycle appear, long, painful periods, as well as bleeding not associated with menstruation, are a concern. The disease is diagnosed mainly in women of reproductive age, and regression often occurs during the postmenopausal period. If you do not treat the pathology in a timely manner or self-medicate, the risk of developing serious complications, such as female infertility and even uterine cancer, increases. Experienced gynecologists at the Healthy Family medical clinic have all the knowledge and the latest methods of treating this common gynecological disease. Our doctors will provide professional assistance to all patients, regardless of the degree of advanced adenomyosis.
Causes of adenomyosis
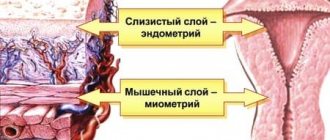
The body of the uterus consists of three membranes:
- internal mucosa or endometrium;
- intermediate layer;
- muscle.
The disease is characterized by the proliferation of endometrial cells with damage to the intermediate and muscular layers. Diffuse adenomyosis differs from other forms in that the structure of endometriotic tissue is changed due to the uniform growth of cells into the thickness of the uterine body. In this case, clearly defined foci are not formed.
The exact causes of this pathology have not been fully established. But scientists were able to identify a number of predisposing factors that increase the risk of encountering adenomyosis. Among the most common are the following:
- hormonal disorders;
- hereditary predisposition;
- violation of the timing of the menstrual cycle;
- often exacerbating chronic diseases that weaken the body’s immunity and resistance;
- infectious, viral, inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- traumatic manipulations on the uterus: operations, caesarean section, abortion;
- endometritis;
- use of an intrauterine device;
- chronic stress, psycho-emotional overload;
- heavy physical activity;
- complicated childbirth;
- obesity;
- uncontrolled use of hormone-containing drugs;
- unfavorable environmental conditions.
Each of these factors can become a trigger for the development of different forms of adenomyosis. Therefore, every woman should monitor the health of the organs of the reproductive system and, as a preventive measure, undergo a routine gynecological examination at least once a year, which will help identify the disease at an early stage and quickly, without consequences, cure it.
Diffuse changes in the uterus
During a diagnostic examination by a gynecologist, the doctor may detect diffuse changes in the uterus. Not every woman knows what this condition is, so she may begin to worry about her health.
Experts note that such features of the reproductive organ are not a pathology, but act as a diagnostic sign, which is determined through an ultrasound scan of the pelvic organs.
The uterus consists of several layers, among which there is the myometrium, which, in turn, is completely penetrated by muscles and vessels, which allows it to perform contractile actions.
The function of the myometrium is also that it is responsible for the rejection of the endometrium if pregnancy does not occur in the current cycle, and also pushes out the child during labor.
Let us consider in more detail why diffuse changes in the uterine myometrium occur.
- 1 Reasons
- 2 Diseases
- 3 During pregnancy
- 4 Diagnostics
- 5 Therapy
Causes
The myometrium acts as the muscular layer of the reproductive organ. It contains several types of fibers, a characteristic structure, and three shells. The first layer consists of the serosa and circular muscle fibers.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fI0oEDQ1fEw
The middle part of the myometrium is the most powerful, since it contains only muscle tissue, while the structure is supplemented by large main vessels. The inner layer consists only of longitudinal fibers.
Anatomy of the uterus. Source: pervenets.com
The structure of the uterus is heterogeneous precisely due to the fact that the myometrium is quite diverse in terms of its constituent elements. There may be several reasons for the development of diffuse changes, and they are divided into traumatic and less traumatic.
In the first case, the heterogeneous structure in the uterus may be due to previous abortions, against the background of which pathological foci appeared. Low-traumatic causes include childbirth, or spontaneous termination of pregnancy, in which a miscarriage occurs.
Diseases
If the structure of the uterus is heterogeneous, what this means should be explained by the attending physician. The fact is that such a condition of the lining layer of the reproductive organ can develop as a result of the progression of gynecological diseases. Let's consider several of the most common pathologies in which the structure of the uterus is revealed to be heterogeneous, what this can mean.
Endometriosis. The presented disease is quite often diagnosed in women of different ages. The main feature of the pathology is that as it progresses, there is a diffuse enlargement of the uterus, namely, the endometrial layer.
Violations are detected through a diagnostic procedure such as ultrasound. It is this procedure that makes it possible to notice that the endometrium has begun to grow beyond the reproductive organ, and the echostructure is heterogeneous.
Endomyometritis. With the development of the inflammatory process, diffuse changes in the myometrium of the uterine body may be observed. The pathological focus is located on the mucous membrane of the reproductive organ, as well as in the muscle layer. A distinctive feature of the disease is that it develops with severe symptoms.
Since there are pathogenic bacteria in the uterus, the woman complains of a high degree of painful syndrome. Microorganisms can penetrate the reproductive organ during artificial abortion, labor, or during diagnostic gynecological procedures.
Myoma. Considering the conditions in which there is a diffusely heterogeneous structure of the uterus, what it is and how it manifests itself, it is necessary to remember about fibroids, which are represented by a benign tumor.
As this disease progresses, the patient experiences changes in the homogeneity of the myometrium and also develops calcification.
To confirm the diagnosis, vaginal ultrasound screening or three-dimensional echography is performed.
Myometritis. A pathological process in which the structure of the uterus is diffusely heterogeneous can also develop as a result of oversaturation of the vaginal environment with infections, in which bacteria settle on the mucous membrane of the reproductive organ. With the development of this disease, a woman will experience symptoms similar to endometriosis, so differential diagnosis is required.
During pregnancy
Women carrying a child may experience signs of diffuse changes in the uterus. What this is should be determined by the attending physician, since such a condition is not the root cause of pregnancy, but acts as a sign or complication of a concomitant disease.
In order to monitor the process of fetal development, a woman is prescribed ultrasound diagnostics. Thanks to this procedure, the doctor can also monitor the condition of the uterine walls. That is why, if the patient is at risk with an increased likelihood of developing diffuse changes in the uterus, she is recommended to undergo regular ultrasound examinations.
This will help to promptly recognize the progression of the pathology and prescribe the necessary treatment. As for the prognosis for recovery, it directly depends on how correctly the doctor chose the treatment, as well as whether the woman listened to the specialist’s recommendations.
If a diffuse change in the uterus is discovered in a woman during pregnancy, only the leading specialist can discuss what this means.
However, she needs to understand that such a condition can cause premature birth or miscarriage. If the pregnancy was nevertheless carried to term, the type of delivery will also determine the lie.
If there is an increased likelihood of myometrial rupture, a Caesarean section is recommended.
It is strictly forbidden to make a diagnosis on your own, as well as interpret the results of ultrasound examinations. If diffuse changes in the uterus have been identified, what it is, and whether it is necessary to immediately carry out therapy, should be determined by a gynecologist. In some cases, there is no need to start treatment immediately.
The doctor will definitely have to take into account all the features of the clinical case, establish the reasons for the development of this symptom, as well as the severity of the symptoms. Only after this can a decision be made as to how best to influence the body of a pregnant woman.
Understanding such a condition as diffuse changes in the uterus, what it is, it is necessary to say that the pathology can be detected even before pregnancy.
In this case, the woman is necessarily identified as a risk group, which includes patients who have a high probability of primary miscarriage, spontaneous abortion, or may develop placental insufficiency.
The doctor will have to make sure that the woman does not have uterine fibroids. If a benign tumor is detected, the pregnancy should also be placed under special registration, since the development of abnormal conditions during labor is possible, including a high probability of severe bleeding.
The same applies to patients who have a history of fibrosis or scarring. All this can cause the birth canal to rupture during pushing.
Diagnostics
Nowadays, there are many techniques that can help identify diffuse changes in the uterus in the early stages, which will allow timely treatment to begin and quickly get rid of the disease.
Ultrasound examination is considered the main method for identifying a pathological condition. During the diagnostic procedure, the doctor has the opportunity to determine the echostructure of the layer. If an atypical condition of muscle tissue is detected, this will become a direct signal to a specialist who will be able to suspect the development of endometriosis or other concomitant pathology.
Ultrasound screening is a fairly simple procedure, so the patient does not need to undergo lengthy preparations before undergoing it. Diagnosis is performed using a transvaginal sensor. During the examination, the patient may feel slight discomfort, since the sensor penetrates quite deeply.
How is an intravaginal ultrasound performed? Source: uzibook.ru
The main reasons for prescribing an ultrasound are the following conditions:
After the doctor carefully examines the uterine cavity, he will be able to accurately determine the size of the reproductive organ, how it is located, whether there are structural anomalies and other factors that may indicate the development of pathology.
If during diagnosis the myometrium was characterized as homogeneous, then the possibility of diffuse changes is excluded. However, if an atypical structure or thickening of the muscle layer is detected, additional examination will be carried out, which will help to accurately make a diagnosis.
In addition to ultrasound screening, a specialist may recommend the following medical procedures:
- Magnetic resonance imaging, which will help evaluate the structure of the uterine walls;
- Performing a bimanual examination, through which the condition of the reproductive organ is determined;
- Donating blood to perform a biochemical analysis, which will determine the level of hormones in a woman’s body;
- Standard gynecological examination on a chair to determine the condition of the cervix and vagina;
- A thorough history taking will make it possible to identify accompanying symptoms, as well as determine how long ago the woman started having them.
Such a complete diagnostic examination is necessary in order to accurately determine the type of pathological process, the degree of its neglect, and also to develop the most complete and correct treatment regimen.
Therapy
If a woman has been diagnosed with diffusely heterogeneous changes in the myometrium, then treatment should be developed exclusively by a doctor, based on the individual characteristics of the clinical case, and only after a thorough diagnosis.
When a set of treatment measures is drawn up, the specialist must take into account the woman’s age, the degree of neglect of the pathological process, the presence of children, childbirth, and abortions.
As for conservative treatment, the patient is prescribed hormonal drugs, since these drugs can help reduce the production of certain hormones in the body, which stops the active process of proliferation of endometrial cells.
This method of influencing pathology will be justified only in a situation where the disease occurs without symptoms, as well as in patients with a history of infertility, and if it is necessary to restore fertility. The likelihood of developing side effects during therapy is extremely low.
Surgical treatment is also possible. In this case, the doctor will perform the intervention through laparotomy or laparoscopy. This method of solving the problem is necessary only in a situation where other methods of therapy have not given the expected effect, the patient has intolerance to hormonal drugs, or extensive damage to the uterus has been detected.
In the case of constant progression of the pathology, complete removal of the organ is necessary, which is often performed by women aged 40 years and older.
Almost every disease is easier to prevent than to carry out long and complex treatment later. Changes in the structure of the myometrium can also be predicted. To do this, women are advised not to neglect regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
This is especially true for teenage girls if their menstrual bleeding is accompanied by severe pain. Older patients need to visit their doctor more often if they have previously undergone gynecological surgery.
It is necessary to understand that the risk group for the development of diffuse changes in the endometrium includes women aged 30 to 45 years. That is why they need to be as attentive as possible to the health of their reproductive system.
If a girl notices that she has atypical symptoms, or there is pain in the lower abdomen, she should visit a gynecologist as soon as possible. This will help to identify pathology at an early stage of development and carry out its proper treatment.
Source: https://uterus2.ru/disease/diffuznye-izmeneniya-matki.html
Symptoms and signs of adenomyosis
At the initial stage of development of adenomyosis, a specific, pronounced clinical picture is almost completely absent. But as it progresses, suspicious symptoms appear, which should alert you and cause a visit to the doctor.
Significant signs of adenomyosis are long, heavy, painful menstruation. Periodically, intermenstrual brown or bloody discharge may appear, which is associated with the emptying of endometriotic cysts or pockets. Other symptoms of pathology:
- menstrual irregularities, in which the intervals between periods become longer or shorter;
- intense pain during intimacy;
- pain syndrome of varying intensity in the lower abdomen, lumbar region, perineum, inner thighs.
Another noticeable sign of adenomyosis is secondary iron deficiency anemia, which develops against the background of heavy menstrual and intermenstrual blood loss. Characteristic symptoms of anemia:
- general weakness, lethargy, drowsiness;
- headaches, dizziness;
- numbness of the lower extremities;
- memory loss;
- partial or complete loss of performance;
- frequent fainting;
- paleness of the skin and mucous membranes.
In advanced stages, menstrual pain becomes unbearable. Uncontrolled growth of the endometrium leads to an increase in the size of the uterus. It begins to compress nearby organs, leading to their dysfunction. Therefore, women at stages 3–4 complain of problems with urination and bowel movements, increased gas formation, and an increase in abdominal volume. Also, in advanced cases, a woman cannot conceive and carry a child to term, because overgrown endometrial tissue prevents the fertilized egg from implanting into the uterine wall.
Heterogeneous structure of the endometrium: normal or pathological
Women's reproductive health depends on the condition of the endometrium.
This term usually refers to the tissue covering the inner layer of the uterus. Throughout the entire menstrual cycle, changes in the mucous membrane are observed, and in many cases this is considered a physiological norm.
But pathological structural disorders are also possible, when heterogeneous endometrium is a sign of abnormalities in the body. Most often this occurs under the influence of hormonal disorders and inflammatory processes.
Characteristic
In the female reproductive system, the endometrium plays a special role. For successful embryo implantation and normal development of the embryo, the inner layer of the reproductive organ must have sufficient maturity and an appropriate structure.
Thanks to uterine changes, the female body prepares for possible fertilization. The heterogeneous structure of the endometrium and the different thickness of the inner layer in certain phases of the cycle create comfortable conditions for conception.
The mucous membrane is very sensitive to hormonal levels. It is this feature that is reflected in the size of the endometrium. Immediately after menstruation, the tissue thickens, which facilitates the successful attachment of the egg to the villi of the inner layer of the uterus.
The embryo receives the amount of oxygen molecules and nutrients necessary for growth. If pregnancy does not occur, the functional layer of tissue is torn away and comes out with blood.
The woman begins her period, and the remaining basal layer is restored by the onset of the next menstrual cycle.
A physiologically normal process is characterized by a change in the thickness of the inner layer of the uterus only during certain phases of the cycle. If a failure occurs and the doctor diagnoses untimely structural disorders, diffuse changes in the mucosa are possible.
The pathological proliferation of epithelial cells and glands over the entire uterine surface leads to the ingrowth of the endometrium into the adjacent muscle layer (myometrium). Such conditions must be corrected at the initial stage, otherwise the woman may have problems conceiving.
Diffuse changes in the myometrium are one of the most common gynecological problems, but this is far from the only cause of disruption of the endometrial structure. Before we deal with abnormal conditions, we will outline situations when you don’t have to fear for your health.
Standard indicators
An atypical structure of the uterine mucosa may be congenital, but such cases are rarely detected. Normal heterogeneity of the endometrial structure is diagnosed:
- Endometrium during pregnancy. When carrying a child, progesterone dominates in a woman’s body, causing endometrial growth. The hormone level increases gradually and reaches a maximum at the time of birth.
- During menopause. With age and the approach of menopause, the structure of the endometrium changes. The functional layer gradually becomes thinner, and with the onset of menopause, only the basal layer remains. The tissue has a homogeneous structure and is normally 5–6 mm.
- Specific phases of the menstrual cycle. In a healthy woman, in the first days of menstruation, the thickness of the mucous membrane is 5–8 mm. Around the 3rd day, the endometrium transforms and acquires good echogenicity. During this period, the size of the surface tissue varies from 3 to 5 mm. By the end of menstruation, the inner layer of the uterus increases, thickens and reaches a thickness of 7–9 mm. On the 8th day, the size of the mucosa is 8–10 mm.
The development of the endometrium throughout the cycle allows us to identify the presence of severe disturbances in the functioning of the body. The thickness should vary from 5 to 17 mm. If changes are not detected by ultrasound, treatment is prescribed. Women whose condition of the uterine mucosa does not correspond to the norms of a particular phase also need therapy.
Transformations associated with loss of endometrial homogeneity during menopause and pregnancy do not cause discomfort and are not treated. These are normal conditions, but medical supervision and preventive measures should not be excluded. The situation can change at any moment, and it is only possible to identify blood supply disturbances and other abnormalities with regular ultrasound scans.
Reasons for deviations
The main cause of endometrial heterogeneity is hormonal disorders. During menstruation, progesterone is active. Under its influence, the inner layer of the uterus increases and is renewed several times. Estrogen plays a different role.
This hormone prevents the proliferation of mucous tissue. With a balanced, healthy hormonal background, the density, thickness and structure of the endometrium correspond to normal values.
If one of the hormones begins to predominate, a malfunction occurs, the likelihood of the appearance and progression of diseases of the reproductive system increases.
Other reasons that provoke deviations in the structure of the inner layer include:
- disturbances in the blood supply to the mucous membrane;
- curettage, abortion, endoscopic operations;
- hypoplasia (underdevelopment) and uterine fibroids;
- long-term use of antibiotics.
In cases where endometrial heterogeneity is not a physiologically temporary phenomenon, doctors assess the condition as pathological. The final conclusion is made only after an ultrasound scan.
Pathological conditions
Violation of the structure and thickness of the uterine mucosa can be caused by diseases such as:
- submucous fibroid (benign neoplasm);
- adenomyosis (cellular growth in the muscle layer of the uterus);
- polyps and cystic formations;
- endometriosis and endometritis;
- hyperplasia (structural deformation and pathological growth of the glands of the functional layer);
- malignant tumors.
Inflamed, uneven endometrium negatively affects the well-being and health of women. Many of the identified pathologies interfere with normal conception and pregnancy. Cancers can be life-threatening and require immediate treatment.
Symptoms
The heterogeneous state of the endometrium, like any disease, is characterized by symptomatic manifestations. There are few of them and most are non-specific. Abdominal pain, no menstruation, weakness - all these are common symptoms that characterize a variety of pathologies of the uterine cavity, including heterogeneity of its mucous membrane.
In the initial stages, signs rarely appear. Changes in the structure of mucous tissues may not appear clinically, but as the pathology progresses, the symptoms become noticeable and noticeable. Typically, a woman is bothered by acute pain during menstruation and regular irregularities in the menstrual cycle.
The intensity and severity of symptoms depend on the causative factor that provoked the heterogeneity of the endometrium.
Research and diagnostics
During a routine examination, the condition of the endometrium is difficult to determine. Pathological changes are detected by ultrasound examination, which is done after menstruation.
A detailed analysis allows us to determine the density, thickness and structure of the endometrium.
During the examination, the doctor examines the echogenicity of the structure of the uterine mucosa and can identify neoplasms and other problems that affect reproductive functions.
In addition to local ultrasound, the doctor may prescribe curettage. If thickening and structural heterogeneity are detected, this type of surgical intervention is used for treatment and diagnosis.
In addition, for a more complete and detailed analysis, specialists from various fields can be involved in the diagnostic examination. This is due to the fact that the cause of many gynecological diseases are disorders of other systems and organs.
Preventive actions
In order to prevent the development of heterogeneity of the uterine mucosa, gynecologists recommend being more attentive to your health. Do not ignore painful symptoms, missed periods, cycle disruptions and other alarming symptoms. A late visit to the doctor can cause heavy bleeding, endometrial rupture, infertility and other complications.
It is very important to take timely tests, undergo ultrasound examinations and responsibly take prescribed medications to restore the endometrium.
These recommendations apply to women of any age.
Regular visits to the doctor and professional diagnostics reduce the likelihood of developing pathological disorders, and in cases of identified deviations, they allow you to cope with the disease faster and without serious complications.
Source: https://TopGinekolog.ru/zdorove/neodnorodnyj-endometrij
Degrees and forms of adenomyosis
According to the criterion of progression of pathological processes, 4 stages of adenomyosis are distinguished:
- First. Endometrial cells are spread to the lining of the uterus, other tissues are not affected. The clinical picture is completely absent.
- Second. Pathological processes spread to the muscle layers. The first suspicious symptoms may appear: an increase in the volume of menstrual bleeding, spotting in the middle of the cycle, mild abdominal pain.
- Third. Endometrial cells affect the entire thickness of the muscle wall, right down to the serous layer. Symptoms intensify and become pronounced.
- Fourth. The body of the uterus is completely affected by pathological endometrial tissues with possible spread to nearby tissues and organs. The clinical picture is pronounced, the condition is rapidly deteriorating.
Based on morphological characteristics, there are 4 forms of adenomyosis:
- Focal. In this case, endometrial cells grow into the muscular lining of the uterine body in the form of localized foci. The pathological process does not extend to the entire surface of the myometrium.
- Nodal. This variety is characterized by damage to the muscle layer by glandular epithelium in the form of multiple nodes. The cavity of the formations is filled with fluid and menstrual blood, which is still produced by the body in accordance with the menstrual cycle.
- Diffuse. Diffuse changes in the myometrium are characterized by the proliferation of endometrial tissue to different depths. As a result, depressions, pockets, winding and diverging passages, lined with glandular epithelium, are formed. With deeper growth, fistula tracts can form that open into the abdominal cavity. With diffuse changes, the myometrial wall becomes thickened and spongy-cellular.
- Diffuse nodular. Combines signs of diffuse and nodular forms of adenomyosis.
What causes diffuse changes in the myometrium?
Myometrium is one of the linings of the uterus, which consists of smooth muscle fibers with a small content of fibrocytes - connective tissue cells. It includes three layers - subserosal, submucosal and middle circular.
If ultrasound reveals diffuse changes in the myometrium, most often this indicates a benign disease.
It is manifested by heavy menstrual bleeding, pain in the lower abdomen, infertility, and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
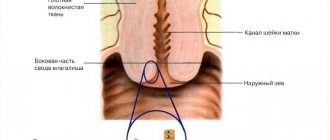
Features of the structure of the layers of the uterus
The uterus is a smooth muscle organ designed to bear a fetus during pregnancy. It is located in the middle part of the pelvis between the bladder and the rectum. The walls of the uterus consist of three layers:
- The perimetry is the serous membrane, which is a continuation of the serous cover of the urinary tract. This layer is tightly fused with the muscular layer. At the border of the peritoneal covering, the perimeter is attached very loosely.
- Myometrium is a muscular membrane capable of contraction. It, in turn, also consists of three layers, providing the organ with sufficient rigidity.
- The endometrium is the mucous membrane that forms the inner layer of the organ. It consists of two layers - basal and functional. The endometrium includes cells of columnar epithelium, connective tissue and glands.
The myometrium is the thickest lining of the uterus, which consists primarily of muscle cells. It includes 3 layers:
- Subserosal - the outer layer with longitudinally arranged fibers, which fits tightly to the serous membrane.
- Circular - the middle most powerful layer, consisting of a large number of rings. They are located in oblique and circular directions in the body of the smooth muscle organ. This layer contains many blood vessels. It is best developed in the cervical area.
- Submucosal is the inner thinnest layer in which muscle fibers are located in the longitudinal direction.
Thanks to this structure of the myometrium, the uterus is able to contract. Spasms prevent blood stagnation during menstruation.
A powerful muscle layer serves as a frame and “storage” during pregnancy. The uterus enlarges as the fetus grows, and after the amniotic fluid is released, it literally pushes it into the birth canal.
What are diffuse changes in the myometrium?
Normally, the myometrium has a homogeneous structure. In the last period of the cycle - the secretory phase - the level of steroid hormones in the body increases. Therefore, the endometrium thickens and loosens.
Diffuse changes in the myometrium are heterogeneity in the structure of the muscular layer of the uterus, which is associated with two types of reasons:
- Physiological. Natural transformations in the wall of the organ are caused by the extinction of ovarian function during menopause. Due to a decrease in the level of steroid hormones, the endometrium and other membranes become thinner, sometimes unevenly.
- Pathological. A diffuse heterogeneous structure of the myometrium is detected by ultrasound of the pelvic organs. During the examination, the following are taken into account: wall thickness, echogenicity and tone of the uterus.
If pathological inclusions are detected in the muscle layer of the organ, patients are prescribed additional hardware tests and laboratory tests. Based on their results, the severity of the disease is assessed and a treatment regimen is drawn up.
Reasons for changes in the myometrium
Hormonal imbalance is one of the key causes of diffuse changes in the structure of the myometrium. An increase in the concentration of steroid hormones leads to uncontrolled division of endometrial cells, its germination into the muscular lining of the uterus.
Specialists in the field of gynecology identify a number of factors that provoke tumor changes in the organ:
- uterine injuries during childbirth;
- artificial termination of pregnancy;
- chronic inflammation in the genitals;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- abdominal operations;
- cauterization of endometrial erosions;
- overactive thyroid gland;
- unbalanced diet;
- metabolic disorders (obesity, diabetes);
- frequent childbirth;
- uterine fibroids;
- use of intrauterine contraceptives;
- ovarian cysts and polyps;
- abuse of sunbathing;
- chronic stress;
- sexual infections;
- hereditary predisposition to tumor diseases;
- abuse of hormonal contraceptives;
- endometrial damage during instrumental examination.
Diffuse heterogeneity of the structure of the genital organ is one of the signs of a tumor disease that requires timely treatment. Ignoring the problem is fraught with uterine bleeding and infertility.
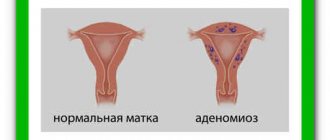
Adenomyosis and endometriosis: what is the difference?
Endometriosis can be differentiated from adenomyosis using ultrasound examination.
Both diseases are characterized by the proliferation of the mucous membrane of the genital organ, but there are serious differences between them:
- Adenomyosis is a localized form of endometriosis in which the endometrium grows into the myometrium but remains within the uterine body. Its structure changes under the influence of monthly hormonal fluctuations.
- Endometriosis is a tumor disease in which the mucous membrane extends beyond the uterus. Usually the organs of the woman's reproductive system are affected - the fallopian tubes, vagina, ovaries. But it is possible that the endometrium may grow into the abdominal cavity, bladder, and intestines.
Endometriosis poses a particular health hazard. Without proper treatment, diffuse changes affect not only the reproductive organs, but also other vital systems.
When diagnosing gynecological diseases, an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is performed. The doctor determines the homogeneity of the structure of the uterus by characteristic echo signs. The examination is performed using a transvaginal, transabdominal or combined method.
Echogenicity is the ability of soft tissues to reflect ultrasound waves, which are recorded by a special sensor. The echographic method allows:
- identify structural changes in organs;
- determine the localization of pathological inclusions;
- assess the size of tumors, etc.
Normally, the myometrium absorbs most of the ultrasound waves, that is, its echogenicity is low. With diffuse heterogeneity of the layer, this parameter changes.
But in order to conduct a differential diagnosis, the doctor performs additional studies and takes tissue samples for histological analysis.
Based on the data obtained, the gynecologist distinguishes endometriosis from other tumor diseases and establishes a final diagnosis.
A change in the echogenicity of the myometrium is an echographic sign of diffuse heterogeneity of the muscular layer of the uterus.
Echo signs and types of endometriosis
Hyperechogenicity of the myometrium is an echo sign of diffuse changes, indicating thickening of the muscle layer. Due to the growth of the endometrium into the surrounding tissues, the wall of the organ becomes denser, and therefore reflects most of the ultrasound waves. On the screen, these areas appear as white inclusions.
Ultrasound additionally determines:
- myometrial thickness;
- the vastness of the diffuse heterogeneity of the structure;
- presence of endometrioid cysts.
Main types of endometriosis
| Type of disease | Characteristic |
| Diffuse | Extensive changes associated with endometriotic growths are found in the myometrium. With moderate endometriosis, the uterus enlarges, and with diffuse endometriosis, it becomes deformed. In women with advanced pathology, the size of the organ corresponds to the 9th week of pregnancy and takes on the shape of a ball |
| Focal | In the thickness of the muscle layer, individual pathological inclusions are found. Their diameter varies from 2 to 15 mm. If the changes affect the narrow part of the uterus in front of the cervix, then it takes on a spherical shape. As a result, organ mobility decreases |
| Nodal | Pathological inclusions look like nodules with a diameter of 2-6 mm. Because of them, the inner surface of the organ becomes lumpy. The nodules do not have a shell, so there is no clear separation from the myometrium |
Changes in the myometrium according to the type of adenomyosis are fraught with serious complications. Therefore, immediately after diagnosis, the doctor develops treatment tactics and assesses the feasibility of surgical intervention. If the disease manifests itself with clear symptoms and interferes with reproductive function, surgery is required.
Symptoms of diffuse changes in the myometrium
The clinical picture depends on the form of the disease. With moderate diffuse changes in the myometrium, most patients do not complain about their health status. As the pathology progresses, the functions of the reproductive system are disrupted.
Diffuse heterogeneity of the myometrium sharply reduces the chances of conception and pregnancy. The probability of pregnancy does not exceed 56%.
The main signs of diffuse changes in the myometrium:
- Painful menstruation. More than 60% of patients complain of discomfort in the lower abdomen. Due to diffuse changes, the myometrium swells, so blood does not exit into the vagina. Due to increased pressure in the uterine cavity, the pain intensifies.
- Anemia. Women with adenomyosis often experience acyclic bleeding, which causes a decrease in hemoglobin levels in the blood. Therefore, there are complaints of weakness, pale skin, dizziness, and drowsiness.
- Infertility. Diffuse changes in the myometrium are the cause of ovulation disorders and impossibility of conception. Infertility is found in 25-40% of patients with an advanced form of the disease.
- Pelvic pain. The symptom occurs in 16-24% of patients. The pain is localized in the lower abdomen or diffuse in nature. They intensify a few days before menstruation, which is associated with swelling of the endometrium due to an increase in the amount of estrogen in the body.
In the focal form of the pathology, the symptoms are moderate. If diffuse changes affect the bladder or intestines, the clinical picture is replenished with new symptoms - painful urination, frequent urge to go to the toilet, constipation.
Consequences
The likelihood of complications and their diversity depends on the form of the disease. With diffuse changes in the structure of the myometrium, the following are possible:
- heavy uterine bleeding;
- adhesions in the peritoneum and pelvic organs;
- neurological disorders;
- endometrioid ovarian cysts.
Large blood losses lead to iron deficiency anemia, which causes:
- chronic fatigue;
- emotional lability;
- aggressiveness.
If diffuse changes in the myometrium occur during pregnancy, this increases the risk of spontaneous abortion, placental abruption, and premature birth.
Treatment
When determining treatment tactics, several parameters are taken into account - the size of the uterus, the prevalence of lesions, the patient’s age, plans for pregnancy. Treatment methods are divided into:
- Medication. With relatively minor changes in the myometrium, they limit themselves to taking medications that prevent the growth of the endometrium.
- Surgical. Depending on the lesions, organ-preserving or radical surgery is prescribed.
Often, after completing a course of therapy, diffuse changes are detected again. Relapses of endometriosis occur in 15-40% of cases and depend on the radicalness of the previous treatment and the prevalence of pathological foci.
Drug therapy
With moderate diffuse changes in the myometrium, conservative therapy is limited. It is aimed not only at eliminating endometrioid lesions, but also at preventing complications.
Standard therapy regimen
| Group of drugs | Peculiarities | Names of drugs |
| Estrogen-progestogen | They suppress the synthesis of steroid hormones, which prevents diffuse changes in the organ. Used only at the initial stage of adenomyosis |
|
| Gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists | Reduce the content of estrogen in the body, so the growth of the endometrium stops |
|
| Gestagens | Inhibits the functions of the ovaries. Used for any diffuse changes in the myometrium. The course of therapy lasts up to 6 months |
|
Taking hormonal medications for diffuse changes in the uterus is accompanied by side effects - chest pain, hot flashes, sweating, weight gain.
Surgery
At the initial stage of adenomyosis, cryodestruction of cells of the overgrown endometrium is indicated - freezing of pathological foci. For moderate forms of the disease, the following operations are recommended:
- Laparoscopic is a minimally invasive intervention in which pathological inclusions are removed through a puncture in the skin. It is performed for minor diffuse changes, when the diameter of the tumors does not exceed 3 cm.
- Hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing the uterus. Indicated for diffuse endometriosis and relapses of the disease.
Radical surgery to remove the organ is recommended for women of late reproductive age who are not planning a pregnancy.
Conclusion
Diffuse changes in the uterine myometrium are a sign of tumor damage to the organ associated with the proliferation of the endometrium. It manifests itself as heavy bleeding during menstruation, infertility, pelvic pain, and anemia. Depending on the stage of the disease, treatment is carried out using conservative or surgical methods.
Source: https://ginekologius.ru/diffuznye-izmenenija-miometrija
Adenomyosis during pregnancy
Advanced adenomyosis becomes one of the main causes of female infertility. But in the early stages of development, when the uterus is still functioning normally and there are no complications, most women get pregnant without problems and carry the child safely. To prevent complications and miscarriage in the early stages, a woman diagnosed with adenomyosis is carefully monitored throughout her pregnancy by a doctor who, if necessary, prescribes appropriate treatment and periodically adjusts the regimen.
In later stages, adenomyosis negatively affects a woman's ability to conceive. The fact is that with this disease, the transport function of the fallopian tubes is impaired, which is why the fertilized egg cannot enter the uterine cavity and gain a foothold there. Also, women with this diagnosis experience serious hormonal disruptions, which also prevents ovulation. Increased contractility of the uterus, caused by an inflammatory complication, causes spontaneous abortion.
Many pregnant women are concerned about the effect of adenomyosis on the intrauterine development of the child. Doctors say that the pathology does not affect the condition of the fetus, especially if treatment is prescribed on time and the woman is constantly monitored by a specialist.
Treatment at the clinic on Barclay
Therapy for endometrial hyperplasia is quite complex and depends on the patient’s age, the severity of the disease, the severity of its symptoms, the ability to take medications, their tolerability and many other factors. Such a woman needs regular monitoring and treatment by a gynecologist.
The clinic on Barclay offers:
- consultations and treatment from qualified doctors;
- thorough diagnostic examination;
- dynamic observation and evaluation of treatment effectiveness;
- selection of the most modern and effective hormonal drug;
- psychological comfort for patients, attentive attitude of all staff;
- affordable prices for services.
Make an appointment with a gynecologist by calling the clinic. Remember that with proper treatment, all patients with endometrial hyperplasia avoid the malignant transformation of this disease.
Reasons for the development of pathology
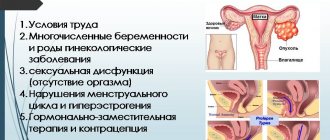
The exact causes of the development of the disease have not been fully established. Doctors say that adenomyosis occurs against the background of hormonal disorders, but there are other predisposing factors that can trigger the pathological process of endometrial growth. These include:
- any traumatic manipulations in the uterine cavity that violate the so-called protective zone between the endometrium and myometrium;
- early or late sexual life;
- complicated childbirth;
- long-term and uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs;
- physical inactivity, obesity;
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- abortions;
- use of an intrauterine device.
Hyperplastic processes of the endometrium
Hyperplasia is an increase in the number of cells in any tissue (except tumor) or organ, resulting in an increase in the volume of this anatomical formation or organ.
Histologically (according to cellular composition), several types are distinguished:
- glandular endometrial hyperplasia
- glandular cystic hyperplasia
- atypical endometrial hyperplasia (synonym – adenomatosis, adenomatous hyperplasia)
- endometrial polyps
According to most authors, the first two types of hyperplasia are not a precancerous disease. The third type, atypical hyperplasia, is a precancerous disease. If present, the risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor (endometrial cancer) in the absence of therapy ranges from 1 to 14% and is most often observed during menopause (cessation of menstrual function due to age).
Precancerous hyperplastic processes develop into endometrial cancer in approximately 10% of patients (according to various authors, from 2 to 50%), they often persist for a long time, and sometimes undergo reverse development. However, taking into account the real threat of the process progressing to endometrial cancer, a doctor’s attentive attitude towards patients with endometrial adenomatosis and adenomatous polyps is necessary.
There are opinions about the possibility of considering glandular hyperplasia and hyperplastic processes that arise again (recur) after endometrial curettage or are not amenable to hormone therapy as precancer of the endometrium. The risk of malignancy (malignancy) of hyperplastic processes increases with metabolic disorders caused by extragenital disease (obesity, impaired carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, dysfunction of the hepatobiliary system and gastrointestinal tract), concomitant with the development of endometrial pathology.
A localized, localized form of endometrial hyperplasia is called an endometrial polyp. Histologically, they are also divided into several types depending on the cells that predominate in their structure: glandular; glandular fibrous and fibrous polyps.
Clinical manifestations of the diffuse form of the disease
Like other forms of adenomyosis, diffuse does not cause any suspicious symptoms at the initial stage of development. As the endometrium spreads into deeper structures, a pronounced clinical picture develops. Since the endometrial cells growing into the body of the uterus continue to function, at the end of the cycle bleeding occurs in the formed cavities and passages. Diffuse changes in the myometrium are accompanied by heavy, prolonged, painful menstruation, spotting in the middle of the cycle. Also a common sign of diffuse damage to the uterus is intense pain during intercourse.
Adenomyosis of the diffuse form is characterized by a recurrent course, developing into a chronic form, which, in the absence of adequate treatment, can be accompanied by frequent exacerbations. This course of the pathology significantly complicates therapy.
Consequences and complications
Timely detection and treatment of the heterogeneous structure of the myometrium or foci of diffuse changes has a favorable prognosis. Women of reproductive age, with a competent approach, can quite easily get rid of the existing problem. If you do not look for the causes of diffuse changes, then the formation of a heterogeneous structure of the muscle layer will continue. The result of this may be:
- infertility;
- progression of fibroid growth;
- severe adenomyosis;
- malignant neoplasms of the muscle layer;
- lack of sex life (due to pain);
- menstrual irregularities;
- bleeding leading to fainting and other problems.
It will not be possible to independently detect the diffusely heterogeneous structure of the myometrium. A woman may suspect the presence of a problem based on her symptoms. If you are concerned, you should definitely get examined, since adenomyosis and endometriosis are progressive pathologies. The more extensive the damage to the myometrial structure, the more difficult it will be to get rid of the problem.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of pathology is carried out using the following methods:
- Gynecological examination. During the procedure, the doctor assesses the size of the uterus and determines characteristic changes associated with the disease.
- Colposcopy. The walls of the cervix are examined for pathological changes.
- Biopsy. A histological analysis of uterine tissue is performed.
- Hysteroscopy. During the procedure, the uterine cavity is examined.
- Laparoscopy. Helps determine the degree of growth of the endometrium and diffuse changes in the myometrium.
- Ultrasound. In the presence of adenomyosis, echographic signs of altered tissues are revealed.
- MRI. Helps to clarify the localization, form and extent of the pathological process, as well as to carry out differential diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis of pathological changes in the uterine wall, what is it and how does it go?
Often, this disease is detected simultaneously with a number of other pathologies. Most often, a woman encounters a disease with problems such as a cyst in the cervical area, metritis in the chronic stage, proliferation of the follicular apparatus and other diseases in the female genital area. If you have each of your diseases mentioned, you can note the presence of changes occurring in the area of the uterus and other genital organs.
What to do, how to treat endometriosis?
If a woman has been diagnosed with this, then it is necessary to begin timely treatment.
Therapy is necessary not only to eliminate unpleasant symptoms, but also if there are problems conceiving a child. If we talk about treatment options, then in this case it may turn out to be scarce:
- Treatment using hormonal drugs. This action is necessary in order to return to normal the balance of hormones that were disturbed as a result of the disease. Unfortunately, such therapy does not always boast effective results;
- To prevent the disease from spreading further to the uterine mucosa, the affected areas are cauterized. This therapy method is the most effective way to get rid of the disease.
When choosing one or another method of therapy, in this case it is very important to exclude the likelihood of certain complications. These pathologies can arise as a result of diffuse changes in the myometrium. In any case, you should not delay treatment, because this can lead to very negative consequences.
Source: womanchoise.ru
Similar articles
- Fluid in the uterine tube (hydrosalpinsk), causes and treatment As a result of the fact that the fallopian tube is greatly narrowed, fluid may begin to accumulate, an adhesive process begins, as a result of which a certain bag appears in which all the fluid collects. If we talk about the varieties of this disease,...
- Pathology of the endometrium of the uterus, causes, types and treatment Recently, many women have encountered diseases of the uterine mucosa. Pathologies of the endometrium of the uterus are observed in representatives of the fairer sex, regardless of their age, and they can lead to very negative consequences. Often…
- Itching under the testicles: causes and treatment of symptoms Severe itching under the testicles is a delicate and very common problem. With this condition, a man feels itching and discomfort in the genital area. Sometimes this condition may be accompanied by visual manifestations of redness of the skin,…
Treatment methods
Treatment of diffuse adenomyosis can be carried out in two ways:
- conservative;
- surgical.
Conservative drug therapy is carried out in the initial stages of the disease, when pathological processes have not yet affected a large area and the function of the organ is not impaired. Since adenomyosis is a hormone-dependent tumor, hormonal drugs are used for its treatment, the main task of which is:
- normalize the menstrual cycle;
- reduce the heaviness of menstruation;
- improve the condition of the myometrium;
- stop the uncontrolled proliferation of the endometrium;
- reduce pathological symptoms.
In addition to hormonal drugs, the following groups of drugs may be additionally prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- painkillers;
- immunomodulators;
- vitamin and mineral complexes.
If the disease is advanced and conservative methods have not brought the desired therapeutic effect, surgical treatment of adenomyosis is prescribed. Effective surgical procedures for treating diffuse adenomyosis are:
- electrocoagulation;
- embolization;
- ablation
These operations are classified as organ-preserving. If stage 4 adenomyosis is diagnosed and the risks of tumor degeneration into malignancy are high, complete removal of the uterus may be required. A radical method will completely eliminate the focus of endometriosis and prevent dangerous complications, but after removing the uterus, a woman will never be able to get pregnant. Therefore, this method of surgical treatment is used only in extreme cases.
How to treat uterine adenomyosis?
The gynecologist will answer this question after making a diagnosis and determining the stage of the pathology. It is important to distinguish adenomyosis from endometriosis and uterine fibroids. Although these diseases are similar, they are different and require different approaches.
The disease can be diagnosed through a gynecological examination with colposcopy. To understand how to treat adenomyosis and its stage, the following is carried out:
- laboratory tests - blood tests (clinical, biochemical, hormones), smear (flora and cytology);
- instrumental studies - ultrasound (the uterus looks spherical, unevenly enlarged, cystic formations are visible), hysteroscopy, MRI.
For the treatment of adenomyosis the following are used:
- drug therapy – hormonal, painkillers, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory drugs;
- physiotherapy - blockage, cauterization of blood vessels, ablation;
- surgical removal of pathological nodes or the uterus (last resort).
Successful treatment of uterine adenomyosis in the early stages is possible using conservative methods.
The key to health is timely consultation with a doctor and annual preventive examinations by a gynecologist. Diffuse changes in the endometrium
Prevention of internal diffuse endometriosis
Preventive measures used to prevent endometriosis are as follows:
- conducting a thorough examination of adolescent girls of reproductive age;
- systematic observation of women who experience excessively heavy discharge during menstruation;
- after medical abortions and gynecological operations, long-term follow-up of the patient is necessary;
- timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system;
- systematically carrying out the necessary laboratory tests and taking a smear.
The main thing is to remember that it is easier to prevent a disease than to eliminate symptoms and treat complications later. That is why timely gynecological examination is a way to prevent the development and progression of diffuse endometriosis.
Video: surgery to remove endometriosis
Endometriosis. Operation. Adamyan L.V.
Video: endometriosis - symptoms and treatment
Endometriosis - symptoms, causes and treatment
Video: nutrition for endometriosis
NUTRITION for ENDOMETRIOSIS
Treatment tactics for internal diffuse endometriosis
To treat this disease, conservative therapy is used, as a rule, it is based on the use of hormones. During the period of treatment, the woman is artificially delayed for up to six months. During such a stop, the body independently copes with the proliferation of cells of the functional layer of the uterus. The use of hormonal drugs is carried out in combination with immunomodulatory agents that increase the body's protective properties. Advanced forms of endometriosis may contribute to the need for hysterectomy. Timely detection of the disease and high-quality prescribed therapy can preserve a woman’s health and normal functioning of the reproductive system.
Etiology of internal diffuse endometriosis
Endometriosis of the uterus - photo
At the moment, experts cannot attribute any of the factors of internal or external influence to the most common causes of the development of diffuse endometriosis, but there are several theories:
- According to the implantation hypothesis, pathological areas of epithelial growth are formed as a result of blood reflux into the abdominal cavity through the fallopian tubes;
- According to the hypothesis of metaplasia of the coelomic epithelium, this disease develops due to the lack of regression of embryonic tissue remains that were preserved during the formation of organs and systems.
- According to the induction hypothesis, the previous theory and the impact of negative environmental factors or the body are combined together.
The main problem of the inability to determine the true cause of the disease is the inability to prevent its impact on the woman’s body and the lack of a plan for prescribing etiotropic therapy.