A healthy woman gets her period once a month. The condition is generally satisfactory. Spontaneously occurring vaginal bleeding, which is accompanied by discomfort, is not normal. The causes and symptoms of the disorder may vary. You can't do without visiting a doctor. Discharge also occurs between periods. Such unscheduled bleeding is the most dangerous and may indicate, for example, the development of an ectopic pregnancy. Causes also include hormonal disorders and uterine diseases.
Normal periods occur once a month
Types of dysfunction
In gynecology, there are several possible types of this pathology. Depending on them, the intensity of bleeding and its consequences may vary. First of all, bleeding can be vaginal or uterine, depending on the place of origin. The former most often occur when the walls of the vagina and vulva are injured or become infected with infectious diseases. The second – for pathologies in the development of pregnancy, labor, and in the early postpartum period.
The nature of the discharge is possible:
- acyclic - in which blood from the vagina appears spontaneously and does not correspond to the expected time of menstruation, in this case we are talking about metrorrhagia;
- cyclical - discharge begins at regular intervals, then they talk about menorrhagia.
Menstruation accompanies women from adolescence, and up to 80 ml of blood is lost monthly. If your periods come irregularly and the volume of blood released exceeds the mentioned norm, it is necessary to be examined to identify the cause of the dysfunction.
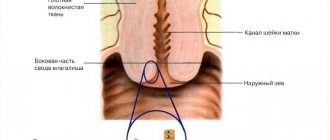
Uterine bleeding
Signs
A symptom of uterine bleeding is the discharge of blood from the uterus outside of menstruation.
Moreover, the intensity of the discharge can be different - from heavy bleeding to spotting. However, abnormal bleeding can also occur during menstruation. In this case, it differs from the normal physiological process in intensity (sometimes a woman has to change pads or tampons every hour), duration (more than seven days) and uncharacteristic pain in the lower abdomen. A woman suffering from uterine bleeding is usually pale, feels weak, and has low blood pressure.
Description
Almost any disease of the uterus or dysfunction of the ovaries can lead to uterine bleeding. There are several types of uterine bleeding - dysfunctional uterine bleeding, bleeding due to cancer, bleeding due to uterine fibroids, uterine polyps, endometrial and cervical canal polyps and endometriosis, bleeding after abortion, bleeding in the postpartum period, obstetric bleeding,
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding occurs due to dysfunction of organs in the absence of any organic pathology. Most often they occur during puberty and menopause. Moreover, in girls, bleeding most often occurs due to hormonal imbalance, in middle-aged women - due to infections of the genital organs, in women who have entered menopause - due to natural changes in hormonal balance. They are never caused by pregnancy or neoplasms. They develop due to:
- hormonal imbalance;
- too much weight;
- stress, overwork;
- heavy physical work;
- blood diseases;
- taking certain medications;
- genital infections;
- strict diets;
- sudden climate change.
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is divided into polymenorrhea (menstruation with an interval of less than 21 days), menometrorrhagia (prolonged irregular bleeding that occurs between menstruation) and menorrhagia (menstruation with a normal interval but long - more than 7 days and heavy, when more than 80 ml of blood is released).
These bleedings are also divided into ovulatory in a two-phase cycle (with ovulation) and anovulatory (without ovulation). Most often, anovulatory bleeding occurs, that is, without ovulation.
Some experts classify bleeding during menopause as a separate group, since it is a natural physiological process. However, there is no need to relax. Even if a woman knows for sure that she is currently experiencing menopause, it is better for her to still see a doctor to rule out cancer.
Bleeding in cancer is one of the first signs of this disease. However, the pathological process may already be at a late stage. Even if the bleeding is minor and does not cause inconvenience or discomfort, you still need to contact an oncologist.
Bleeding due to uterine fibroids, polyps, endometriosis and other benign growths of uterine tissue most often appear during the reproductive period. These diseases are easily diagnosed and treated quite simply. You shouldn’t wait for it to go away on its own; it’s better to see a doctor and get rid of both the disease and the bleeding once and for all.
Bleeding after an abortion always happens, this is normal. It is not normal if the bleeding is too heavy and prolonged. If there is too much blood or the bleeding is not severe, but continues for more than a month, you need to consult a gynecologist. It is possible that the cervix was injured during the manipulation. Bleeding can also occur after an abortion if fetal tissue remains in the body of the uterus.
Postpartum bleeding is small and can bother a woman for up to two months. However, if it continues longer, you should definitely consult a doctor. There may be an infection in the uterus or there may be remains of the placenta in it.
Obstetric hemorrhage occurs immediately after childbirth. It occurs due to a violation of the contractility of the uterus or due to a disruption of the blood coagulation system. This is a very dangerous condition and often causes the death of a woman after childbirth. It is for this reason that women are not recommended to give birth without the participation of doctors.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing uterine bleeding is not difficult. It is much more difficult and important to find out why it happened. To do this, you will need consultations with an obstetrician-gynecologist, an endocrinologist, an oncologist; if the bleeding occurred in a teenager, then you need a consultation with a teenage therapist.
Need to do:
- blood test for hormones (thyroxine, estrogens, testosterone, luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones, cortisol and progesterone);
- clinical blood test;
- blood chemistry;
- general urine analysis.
Instrumental research data is also needed:
- ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages;
- electroencephalography with orthostatic tests;
- rheoencephalography;
- vaginoscopy;
- vulvoscopy;
- hysterosalpingography;
- cervical biopsy;
- puncture of the posterior vaginal vault.
Treatment
It is very important for successful treatment to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Treatment of uterine bleeding depends on its cause. If the bleeding is caused by stress, sedatives and psychotherapy are prescribed; if it is caused by dysfunction of the hormonal system, appropriate hormones are prescribed; if it occurs as a result of taking medications, the medications are discontinued. If you are overweight or severely underweight, appropriate diets are prescribed. If it is caused by infectious diseases, antibacterial therapy is prescribed taking into account the pathogen. If the bleeding is caused by cancer, the oncologist prescribes appropriate treatment or palliative care.
To stop uterine bleeding, tampons and hemostatic sponges are used.
In some cases, physical therapy provides a good therapeutic effect - electrophoresis of medicinal solutions, magnetic therapy, transcutaneous short-pulse electrical stimulation.
In some cases, surgery is necessary. If the bleeding is caused by the growth of uterine tissue or a neoplasm, it is removed. In case of obstetric hemorrhage, a hysterectomy - removal of the uterus - is possible. Often this is the only way to save a woman.
In case of large blood loss, the blood volume must be replenished. For this purpose, a blood transfusion or infusion of physiological solutions is prescribed.
Prevention
Prevention of uterine bleeding involves preventing the diseases that cause it. That is, you need to undergo regular and timely examinations by a gynecologist, maintain intimate hygiene, and protect yourself from sexually transmitted diseases. It is important to monitor your weight, promptly treat hormonal diseases, and avoid stress and physical strain.
© Dr. Peter
Causes
To accurately determine the causes of vaginal bleeding, you need to undergo a full range of diagnostic procedures. Dysfunction is usually caused by:
- hormonal disorders leading to pathological bleeding;
- iatrogenic causes, which include coils installed in the uterine cavity, long-term use of oral contraceptives or drugs that protect against the formation of blood clots;
- pathologies of pregnancy or labor;
- pathologies in the development of the internal genital organs of women;
- disorders during the postpartum period;
- pathologies that develop during menopause;
- injuries to the cervix or uterine body.
Often the problem is discovered after sexual intercourse or during it - uncharacteristic discharge and soreness in the vagina appear. Most often this is caused by insufficient hydration of the area. This can happen with menopause, hormonal problems, or poor functioning of the glands responsible for secreting vaginal fluid.
During pregnancy, pain and discharge indicate pathologies, and symptoms can appear both in the early stages and before childbirth. In most cases, this is an alarm bell indicating the possibility of a miscarriage.
Only implantation bleeding is considered normal, but it is short-term and occurs even before the delay. When infected with an STD, similar complaints are also typical. Sometimes the signs become apparent only some time after the unprotected act, and the woman does not connect these events with each other. Vaginal dryness is felt.
The appearance of erosions, polyps and even cancer is also accompanied by blood from the vagina. The process of their occurrence and the development of the disease can lead to problems with urination. Sometimes you can also notice red inclusions in your urine. Even ordinary stress, which every person experiences at different stages of life, can lead to irregularities in the menstrual cycle and bleeding. In any case, this alarming symptom should be taken seriously and seek medical help immediately.
Important! When bleeding, there are no cases where medical intervention can wait. The sooner a woman visits the clinic, the better.
Risk scale
If patients have an unfavorable underlying disease or a reason why the effect of the anticoagulant may be greater than predicted, the risk of bleeding must be determined. For this purpose, a medical calculator is used - the HAS-BLED scale.
Expert opinion
Alena Ariko
Expert in Cardiology
It must be taken into account that there are practically no patients without concomitant conditions leading to bleeding. Often the same risk factors cause strokes, heart attacks and similar diseases that require reducing blood clots.
Using this scale, the doctor can determine the most significant pathologies for a particular patient that need to be corrected, select a safe dose and the optimal drug. The likelihood of developing major bleeding during a year of taking anticoagulants is assessed.
Any hemorrhage in the brain, blood loss that requires hospitalization, and also causes:
- cardiac, respiratory failure;
- the need for surgery or endoscopy, angiography to make a diagnosis;
- drop in blood pressure to 90 mm Hg. Art. or less;
- decrease in hematocrit below 20%;
- the need for three or more units of blood transfusion;
- acute violation of cerebral, coronary circulation;
- loss of vision;
- obvious or hidden gastrointestinal bleeding.
For each existing risk factor, the patient is assigned one point. The probability of blood loss is assessed as the total positive assessments of the following conditions:
- systolic blood pressure above 160 mm Hg. Art.;
- the patient is on constant hemodialysis (artificial kidney), blood creatinine is above 200 µmol/l, he has undergone a kidney transplant;
- there is a chronic liver disease, in the blood test bilirubin is 2 times higher than normal and/or transferases ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase – 3 times;
- there was an acute disturbance of cerebral hemodynamics, especially a lacunar stroke;
- in the past there was bleeding from an ulcer, hemorrhoids, uterine, pulmonary, renal, or there is anemia of unknown origin;
- The INR should be maintained at a level greater than 3;
- age after 65 years;
- long-term use of other medications that reduce blood clotting is prescribed;
- the patient abuses alcohol (more than 8 glasses per week).
If the patient scores more than three points, then he is included in the high-risk group, which means that he needs constant and frequent INR monitoring.
Diagnostics
The fastest way to conduct an examination, establish a diagnosis and begin treatment is to use a woman’s menstrual calendar. Some neglect its management, and then the doctor’s office cannot compare the timing, duration and intensity of discharge over recent years.
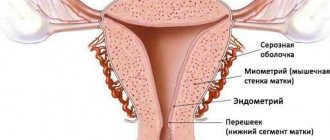
In addition to studying the menstrual cycles characteristic of the patient, the doctor examines her in a gynecological chair. He takes a smear from the cervix to make sure there is no dysplasia or cancer. An ultrasound examination is also indicated, during which the thickness of the endometrium is measured - the inner layer of the uterus, which comes off during menstruation. Often, gynecologists also prescribe blood donation for hormones. If the patient is over 45 years old, an endometrial biopsy must be performed. When making a diagnosis, the results of all of the above studies, as well as the woman’s complaints, are taken into account.
When and which doctor to contact
Not every woman can understand in time that there is blood from the vagina, but not menstruation. Therefore, it is worth knowing the conditions in which you need to see a doctor:
- the presence of clots in the blood during menstruation;
- spotting during or after sex;
- hypotension, weakness, established anemia;
- increased pain during menstruation;
- increased body temperature due to blood from the genitals;
- menstruation lasting more than 7 days;
- the appearance of blood between periods - in the middle of the cycle.
If complaints appear after a cesarean section, you must inform your obstetrician-gynecologist about this.
Bright scarlet blood in large volumes may indicate that epithelial restoration is going poorly. Then the doctor conducts additional examinations designed to exclude ruptures in the cervical area, poorly placed sutures, violations in the cleaning procedure and placenta remains in the uterine cavity.
Important! Initially, the patient must make an appointment with a therapist, who will refer her for an examination by a gynecologist. But if the blood loss is great, the first thing they do is call an ambulance.
What you need to know about the effects of oral contraceptives on the body
Effect of birth control pills
As you know, the main hormones of the female reproductive system are progesterone and estrogen. They regulate the course of the menstrual cycle, influence the process of ovulation and the possibility of conception.
All hormonal pills for pregnancy are divided into two main types according to their chemical composition and mechanism of action. If the capsules consist of only progesterone, pharmacists and gynecologists call them “mini-pills” among themselves. The main function of these drugs is to increase the resistance of the cervical canal of the uterus to the movement of sperm. This becomes possible by increasing the viscosity of the secreted mucus.
In addition to interfering with the movement of male reproductive cells, drugs consisting of progesterone change the structure of the mucous membrane of the uterine wall. This process reduces the possibility of complete attachment of the egg by approximately 40%.
TO
Stronger contraceptives include combined contraceptives consisting of progesterone and estrogen. In addition to creating mechanical obstacles to fertilization with progesterone, estrogen suppresses the process of egg maturation itself. It is these double-acting drugs for preventing pregnancy that can cause bleeding in the middle of the cycle.
Menorrhagia
If blood is released from the vagina cyclically, menorrhagia is diagnosed. There can be many causes for this condition, the most common of which are endometritis, mimoma and endometriosis. These pathologies lead to the fact that the walls of the uterus lose their ability to contract normally. As a result, bleeding during menstruation, which should have lasted 4-7 days, continues much longer.
Menorrhagia is distinguished by the nature of the discharge - it contains blood clots. During such bleeding, a woman experiences loss of strength, weakness, and may complain of frequent dizziness, which sometimes leads to fainting. If you do not consult a doctor for a long time and do not stop the bleeding from the vagina, a severe form of anemia may develop.
Metrorrhagia
With acyclic bleeding that occurs spontaneously, doctors note metrorrhagia. In this case, the appearance of bloody discharge has nothing to do with the date of the expected menstruation. Bleeding often occurs during physical and psycho-emotional overload, living in unfavorable environmental conditions, as well as due to tumors and disorders of the endocrine system.
The first such bleeding indicates the acute stage of the disease. If left untreated, it becomes chronic, and intermenstrual bleeding becomes frequent.
Anovulatory metrorrhagia
This form is typical for teenage girls with an unsteady menstrual cycle, as well as for women experiencing menopause. The name itself indicates the absence of ovulation. This is caused by the fact that the corpus luteum is no longer formed, menstruation does not come on time, but lasts longer than expected.
Postmenopausal metrorrhagia
When ovarian function begins to fade and reproductive function is lost, women notice irregular menstrual flow. After some time they stop completely. If menopause has already occurred and bleeding from the vaginal cavity occurs against its background, this is a serious reason to immediately consult a doctor. Pathology can indicate tumors, both benign and malignant.
Bleeding during postmenopause should include all spotting if there has been no menstruation for one year or more.
Causes of bleeding when taking birth control pills
The process of egg maturation, the period of ovulation and the removal of rejected female reproductive cells from the body is controlled and regulated by hormones of the female reproductive system. The fluctuation in the content of progesterone and estrogen in the patient’s blood is quite large and depends on the phase of the reproductive cycle.
In the first half of the monthly cycle of egg maturation, estrogen is more active. Its maximum effect on the female body occurs during ovulation. If fertilization does not occur, progesterone comes into play. It is this hormone that is responsible for the rejection and removal of the egg from the woman’s body.
The natural percentage of sex hormones in a woman’s body will always be much greater than the dosage of active substances in the recommended medications. It takes some time to adapt to their action.
A normal reaction of the patient's body is spotting during 2-3 months of taking birth control pills. If the spotting does not increase and the endometrium of the uterus does not reject the egg ahead of time, then the dose of contraceptives has been selected successfully. Bleeding in the middle of taking the pills indicates the need to adjust the dose of hormones in this particular case.
Treatment
If the diagnosis is correct, timely treatment will help quickly improve the woman’s condition. But when vaginal bleeding has just been detected and blood loss is profuse, calling an ambulance may be necessary.
How to stop quickly
To reduce or stop blood loss from the vagina, you must:
- Take the correct position: stretch out on your back, put your feet on a pillow or other fairly high object.
- Place a damp, cold towel or a bottle of cold water on the lower abdomen area. This will help narrow the blood vessels and thereby reduce bleeding.
- Drink sweet tea or just plenty of warm water to replenish your body's fluids and prevent dehydration.
- Take ascorbic acid and Dicinone to stop bleeding from the uterus.
Important! Under no circumstances should you get into a hot bath if you are bleeding, or continue any treatment without consulting your doctor.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment is aimed at stopping the bleeding, eliminating its causes and combating the anemia that arises as a result of it. In addition, doctors prescribe vitamin complexes and fluid intake (tea with decoction or rose hips is especially recommended).
The course of treatment necessarily includes means to stimulate the muscles of the uterus, such as Oxytocin and Ergotamine. To these are added hormonal drugs that normalize the cyclicity of menstruation - Duphaston and Norkolut.