Definition
The endometrium of the gravidary type is the uterine layer, the formation of which is observed from the moment of successful fertilization and is considered the norm. Sometimes it is also found in women who do not intend to become mothers in the near future.
The process of such changes in the structure of stromal cells is decidualization. For this reason, this type of uterine layer is often called decidual tissue.
The formation of the endometrium does not occur in certain areas, but immediately throughout the entire cavity of the reproductive organ. As a rule, certain changes in the appendages are also noted.
If fertilization is successful, changes in the uterine layer are not dangerous. This process is considered natural and necessary for implantation of the fertilized egg. For this reason, it is considered acceptable and safe. So, after a spontaneous miscarriage, a similar transformation can normally be observed. As soon as the hormonal levels are restored, the endometrium acquires its previous structure.
There is a danger in the situation when the gravid membrane is detected in the absence of pregnancy. Such changes provoke strong hormonal fluctuations that can lead to serious complications, including infertility. Pregnancy in this condition becomes problematic. It is very difficult for the fertilized egg to implant into the transformed mucosa.
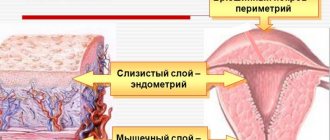
What is endometrium
This is the mucous membrane that is located inside the reproductive organ. The uterus is a complex mechanism in which changes constantly occur. This may be related:
- with pregnancy;
- cycle change;
- termination of pregnancy.
The organ requires close attention, good control and support for functioning at the proper level. This is due to the fact that the tissues are completely dependent on hormonal levels.
The uterine layer has several types, each of which has its own characteristics, depending on the degree of hormonal changes. Gravid endometrium is often noticed.
The doctor will explain what it is, why it appeared, whether the established diagnosis is dangerous, whether it is worth resorting to treatment and which methods will be more effective.
Kinds
Gravid endometrium with signs of reverse development sometimes poses a serious danger. Taking into account the reasons that led to the transformation of the uterine layer, two types of pathology are distinguished. With properly selected therapy, they can be eliminated, and a normal pregnancy can occur in the future.
Pathology of the corpus luteum
This type of disease occurs quite often. Pathology develops due to hormonal imbalance and is diagnosed if persistence of the corpus luteum is detected. At the same time, the concentration of progesterone produced by it becomes significantly less. If this continues for a long period, then a pathological process begins.
The gravid uterine layer is rejected and renewed much more slowly, since a considerable part of it is subject to reverse development. The size of the uterus increases, menstruation takes a long time. Necrosis of tissues of the appendages affected by pathological changes cannot be excluded in the future.
Disturbed pregnancy
The pathological condition often develops against the background of a disrupted pregnancy. As a rule, the process of reverse development of the endometrium does not begin immediately, but after several weeks. Such changes may occur in the following cases:
- incomplete spontaneous miscarriage;
- incomplete removal of the fertilized egg as a result of abortion procedures;
- death of the embryo shortly after conception.
The size and shape of the uterus changes as a result. The mucous membranes of the reproductive organ cease to be decidual and go into a state of rest. As a result, the process of endometrial proliferation begins.
As a rule, it is possible to diagnose such changes after taking a scraping from the uterine cavity, when the process of decomposition of the tissues of the dead embryo has already begun.
Description of the pathology
Pathological thickening of the endometrium is caused by increased proliferation of its cells.
As a result, the internal space of the uterus decreases, and the external dimensions of the organ increase. Hyperplasia is very often detected in women with elevated levels of male sex hormones and low levels of progesterone.
This imbalance is observed in the following diseases:
- Mastopathy.
- Uterine fibroids.
- Endometriosis.
- Obesity.
- Liver failure.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Diabetes.
Women with these diseases are at risk. In addition, the likelihood of endometrial hyperplasia increases significantly during menopause or early menopause.
The most dangerous complication of hyperplasia is the malignant degeneration of cellular structures, causing the appearance of a cancerous tumor. The likelihood of such a development of events depends on the type of hypertrophy of endometrial cells, the age of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases and the rate of thickening of the endometrium of the uterus.
A woman's body changes cyclically throughout most of her life. The greatest changes occur in the ovaries and endometrium. From the first day of menstruation, the endometrium prepares for possible conception. During the entire cycle, its cells actively grow. If pregnancy does not occur, then the excess mucous layer is rejected by the uterus.
Normally, hypertrophy occurs not due to an increase in the number of cells, but due to an increase in the size of cellular structures, intercellular substance, connective and glandular tissues.
When the hormonal balance is disturbed, the amount of estrogen in a woman’s body increases, and the proportion of progesterone decreases significantly. This immediately affects the cyclic processes in the endometrium of the uterus. It begins to increase at the beginning of the cycle, but not due to an increase in cell size, but due to their reduplication.
The level of estrogen in a woman’s body can be increased not only due to internal processes, but also due to external influences. For example, hormonal imbalance can be caused by taking hormonal contraceptives that do not contain progesterone.
In addition, the disease can be caused by the following reasons:
- Abortion.
- Leiomyoma of the uterus.
- Diagnostic curettage.
- Congenital uterine dysplasia.
- Inflammatory diseases of the genital tract.
The disease also often manifests itself during menopause. This is explained by the extinction of ovarian functions followed by hormonal changes in the entire body.
The latter is very similar to what happened to a woman during puberty.
Symptoms and treatment of sore throat in children
The ovaries gradually become thinner, the number of ovular cycles is reduced to nothing. If the body is weakened by any chronic disease during this period, then a hormone imbalance always appears.
Since the endometrium becomes very sensitive to hormones during menopause, it begins to gradually change.
Almost 70% of all identified cases of endometrial hyperplasia occur in menopausal women. In most cases, hypertrophy phenomena are accompanied by severe uterine bleeding.
Doctors distinguish several types of endometrial hyperplasia. The division is based on knowledge of the mechanism of occurrence of pathology and the type of its development. The following types of disease are distinguished:
- Glandular. It is considered a background process occurring in a woman’s body against the background of proliferation of the glands of the inner layer of the uterus. Glandular hyperplasia manifests itself in thickening of the mucous cells and abnormal location of the glands in the stroma of the uterus. The glands themselves become tortuous. Pathology in its form can be acute or chronic. In the acute stage, the growth of endometrial cells is stimulated by estrogens. In the chronic stage, the endometrium may thicken due to a lack of these hormones. The degeneration of this type of hyperplasia occurs most often during menopause.
- Glandular-cystic. This is a type of glandular hypertrophy. Characterized by the appearance of cysts in the glands.
- Cystic. The glands become so enlarged that they turn into cysts. Their cavities are lined with ordinary epithelial cells.
- Basal. This is a rare type of hyperplasia. It manifests itself as hypertrophy of the deep layer of the endometrium and the appearance of multiple nuclei in the stromal cells. It is considered a precancerous condition. The likelihood of malignant degeneration is very high.
- Atypical. The pathology is characterized by a rapid enlargement of the glands, changes in their structure and the appearance of fibrous formations in the uterus. Atypical hyperplasia due to significant changes in cell nuclei is considered by doctors as the initial stage of oncology. It captures both layers of the endometrium at once. The diffuse form of the disease is especially dangerous. Atypical hyperplasia can occur in both hypertrophied and thinned endometrium.
Separately, it is worth mentioning gravid hyperplasia. It appears only in pregnant women against the background of hormonal changes characteristic of pregnancy.
Gravid endometrium has specific echographic signs and is therefore easily detected by ultrasound.
Unlike other types of hyperplasia, the gravidar variety is not considered a pathological condition and does not pose a serious danger.
Taking into account the localization of hypertrophy of the endometrial layer, doctors distinguish 2 forms of pathology:
- Diffuse. With this form, all cells of the endometrial layer grow evenly.
- Focal. This form is manifested by the proliferation of cells in a small area in the uterine cavity. The focal form is most often detected with glandular hyperplasia.
Causes of cervical cysts in women
In some cases, foci of growth take the form of polyps.
Polypous formations can be fibrous, glandular and adenomatous. In fibrous formations, connective tissue predominates.
Adenomatous polyps have more glandular structures and are more prone to degeneration.
There is another type of classification - simplified. Many doctors call it modern because it is the most commonly used today. According to this classification, the disease can be simple or complex.
Simple hyperplasia
It is characterized by an excessive amount of stromal and glandular structures in the endometrial layer. This leads to an increase in the size of the latter.
The location of the glands is disrupted. Their activity increases significantly. In some of them, cystic expansion is formed. Within the stroma there is a uniform arrangement of vessels. Cell nuclei do not change their shape.
The likelihood of malignant degeneration of simple hyperplasia is low. Cancer develops in only 3% of identified cases of the disease.
With atypical hyperplasia, on the contrary, a change in the position and shape of cell nuclei is observed.
Many glandular cells become multinucleated. An increase in vacuoles occurs inside cellular structures. Red blood cells are detected in the patient’s blood, the size of which significantly exceeds the norm. Eosinophilia of the cytoplasm develops. This may mean the development of cancer.
Complex growth
A complex type of disease can be typical or atypical. In the typical form, the glands are located very tightly to each other. This arrangement can be observed throughout the entire endometrial layer or in individual foci.
Complex growth is characterized by a more pronounced change in the glands: they not only increase, but also change their shape. A significant imbalance between the stroma and glands is revealed. In most epithelial cells, multinucleation is detected. No change in the shape and size of the nuclei is observed.
An atypical type of complex hyperplasia develops into oncology in approximately 40% of cases. Atypia manifests itself both at the cellular and tissue levels. Glands take on a variety of shapes and sizes. The regularity in their arrangement is disrupted.
Very often, symptoms of uterine endometrial hyperplasia appear only in the later stages of the disease. In the early stages, the pathology does not manifest itself in any way.
The most common symptoms accompanying this disease:
- Menstruation becomes more abundant. Blood discharge may continue after the end of menstruation.
- Delay of menstruation. As a rule, after their return, the woman develops prolonged and heavy uterine bleeding.
- Regular and irregular bleeding from the uterus. They most often appear in women over 45 years of age.
- Infertility. Due to endometrial dysfunction, the fertilized egg cannot implant in the uterus.
- Severe pain during menstruation. You should pay attention to this if previously menstruation was not accompanied by pain.
The appearance of any of these signs is a reason to consult a doctor. Until the disease reaches an advanced stage, it can be dealt with with the help of medications.
Establishing diagnosis
The most common diagnostic method is ultrasound. Ultrasound allows the doctor to personally assess the degree of endometrial thickening and the localization of the pathological process. But there is one problem: with moderate hypertrophy, echo signs of endometrial hyperplasia do not allow the doctor to accurately diagnose the pathology.
Lump in the mammary gland near the nipple: causes and treatment
Therefore, doctors use additional diagnostic methods:
- Echosalpingography. This method allows you to determine the patency of the fallopian tubes.
- Biopsy. Necessary for differentiating typical and atypical hypertrophy.
- Diagnostic curettage followed by histology of the resulting material.
A radioisotope study of the uterus can also be performed. It is rarely used, but allows you to quickly and accurately identify focal endometrial hyperplasia.
- Therapy is prescribed only after the doctor determines why the pathology appeared.
- In the initial stages, doctors may limit themselves to drug treatment.
- For this purpose, hormonal drugs are mainly used.
- At the same time, doctors select dosages so that patients do not gain excess weight, do not develop acne, and do not grow excess hair.
To restore hormonal balance, combined oral contraceptives are prescribed: Janine and Regulon. Girls take these medications for 6 months. Progesterone drugs can also be prescribed: Duphaston and Norkolut.
- When it is necessary to reduce the production of female sex hormones, Goselerin, Buselerin, Leuprorelin, Nafarelin are prescribed.
- When using these drugs, a woman may feel a worsening of her condition, but then she will feel much better.
- If medications do not help, doctors resort to surgical treatment.
- The following methods are usually used:
- Cryodestruction. The doctor locally removes areas of enlarged endometrium using cold.
- Hysteroscopy. This therapeutic and diagnostic procedure is often used as a method of treating polypous hyperplasia. During the operation, the doctor uses a hysteroscope to find the attachment point of the polyp and cuts it with flexible scissors. After this, the tumor is removed outside the uterus.
- Cauterization with laser. The surgeon burns out local areas of hyperplastic endometrium.
- Uterus removal. This operation is resorted to when there is a threat of cancer.
Detection methods
Decidualization is a natural reaction of the endometrium to the attachment of the fertilized egg. In the absence of pregnancy, the gravid layer peels off at the end of the menstrual cycle, and after completion the regulus begins to grow again.
It can be detected by performing an ultrasound examination. The most accurate results can be obtained using three-dimensional ultrasonography, which uses Doppler. In addition, a blood test for hCG is prescribed.
If the fact of conception has not been confirmed, then angiography is additionally performed. In this case, the uterine layer is assessed according to the following parameters:
- the number of blood vessels in the area being examined;
- blood flow speed;
- pulsation strength.
Thanks to this, it is possible to determine how sensitive the endometrium is.
Finally, an endometrial biopsy is performed, and the tissue taken is sent for cytological examination.
During pregnancy
Immediately after successful fertilization, the fact of conception cannot be confirmed even by performing an ultrasound examination. Changes in the endometrium occur from the very first days, so a transvaginal (inside the vagina) ultrasound will immediately show what the condition of the uterine layer is. In this way, pregnancy is diagnosed even at the earliest stages.
Diagnostic methods
The normal reaction of the gravid endometrium to the fixation of a fertilized egg (also called a zygote) is decidualization. If conception does not occur and pregnancy does not occur, then the gravid layer of the lining of the reproductive organ begins to actively peel off at the end of the menstrual cycle.
After the final completion of menstruation occurs, the uterus is cleared of unnecessary secretions, and the tissue begins to grow again. This process is absolutely normal and is repeated every month.
Diagnostics
It is possible to determine that a transformation of the endometrium has occurred using ultrasound. At conception, the fertilized egg attaches to it and provokes the onset of decidualization. After an abortion or childbirth, the tissues gradually acquire their previous structure.
To identify pathology of the corpus luteum and disrupted pregnancy, a scraping is taken, since ultrasound turns out to be uninformative. In this case, a loop or curette is inserted into the cervix through the cervical canal and tissue is collected. This method is low-traumatic and safe, the mucous membranes are practically not damaged.
During a histological examination on a glass slide, one can see that areas of the uterine layer with signs of reverse development are in close proximity to the secretory ones. If such changes appear against the background of a disturbed pregnancy, then it is often possible to detect a fertilized egg or its particles.
In case of spontaneous miscarriage, a scraping is prescribed. In this way it is possible to identify its cause. If signs of reverse development are detected, the doctor gives recommendations on further therapy.
Endometrial hyperplasia: is it possible to get pregnant?
For a long period, it was believed that it was impossible to get pregnant with hyperplasia. But as a result of the development of medicine, methods for effective treatment of this pathology have been developed. After completing the full treatment course, the woman’s body completely restores reproductive function, and it becomes possible to give birth to a healthy baby.
To increase the likelihood of a successful pregnancy, a woman must undergo a medical examination to identify the form of hyperplasia and the stage of its development. Based on the diagnostic data obtained, the physician will prescribe effective treatment and advise on the elimination of all factors that provoke the occurrence of this pathology.
With glandular-cystic form
Glandular hyperplasia of the endometrium of the uterus is a relatively safe type of pathology, characterized by a slight thickening of the mucous layer. Uterine discharge in this case is minimal. Doctors say that with this disease it is impossible to get pregnant.
The same applies to the glandular-cystic type. It is characterized by vivid symptoms; the endometrium begins to grow, forming cysts and polyps that interfere with conception.
With atypical form
This type of pathology is considered the most dangerous. It is characterized by a change in the structure of the tissue cells of the glandular layer. It is impossible to get pregnant with the atypical form. Moreover, this form of the disease often develops into a cancerous tumor.
If the pathology is not recognized in time, this can lead not only to the impossibility of conception, but also to the need for anti-cancer therapy and removal of the uterus. Pathology can be recognized by the irregularity of menstruation and changes in their character.
In focal form
This form of pathology is compatible with pregnancy. This is due to the fact that the endometrium grows in patches. But it is worth considering that the likelihood of conception is very low.
Women with focal hyperplasia who suspect signs of pregnancy should urgently register with a gynecologist and be regularly monitored by him, since in this case the following are possible:
- formation of fetal pathologies;
- the occurrence of uterine endometriosis;
- degeneration of altered areas into cancer;
- early miscarriage.
Complications can be suspected by the spread of pain in the lower abdomen.
In exceptional cases, pregnancy can cure the disease. This happens when, under the influence of conception, progesterone levels return to normal.
With diffuse form
Diffuse glandular hyperplasia of the endometrium does not allow a woman to become pregnant, since it covers almost the entire organ cavity. Even if the possibility of ovulation remains, the fertilized egg loses the ability to attach to the uterine walls.
The difficulty of conception also lies in the fact that the diffuse form of the pathology also affects the menstrual cycle, making it irregular.
Methods for detecting decidual tissue
Most often, gravid endometrium is detected during ultrasound. The most accurate results are shown by three-dimensional ultrasonography using Doppler. If a routine ultrasound showed the presence of gravid endometrium in a non-pregnant woman, then angiography may be additionally prescribed.
The endometrium will be assessed according to the following parameters:
- Vascularity Index (represents the number of blood vessels in the measured area);
- Blood flow index (speed);
- Perfusion index (pulsation strength of the measured area).
These three parameters will allow you to assess the sensitivity of the endometrium. Additionally, a specialist can perform a biopsy and cytological examination of endometrial tissue.
Treatment
If the condition is diagnosed after childbirth, it is not treated. It should go away on its own as soon as the woman’s hormonal levels return to normal. If at this stage she is worried about severe bleeding, then drugs that stop them can be prescribed - Oxytocin, Vikasol, etc. However, if this endometrial condition does not go away for a long time, then hormonal treatment can be prescribed, but it is strictly individual , and is based on what type of malfunction persisted in the woman after pregnancy.
They act in a similar way for changes resulting from a disturbed pregnancy. It is important to quickly remove the fertilized egg and embryo if it remains in the uterus. Then its hormonal activity will completely disappear and the body will return to normal quickly (even faster than after childbirth). Treatment is also carried out individually only if the hormonal imbalance persists. The same drugs are prescribed to stop bleeding.
If the process is not associated with pregnancy, but is associated with low concentrations of progesterone in the body, then it is treated accordingly. Progesterone drugs are prescribed in individual dosages. These are such products as Norkolut, Utrozhestan, Duphaston. They are taken for a period of about 3 months, and if necessary, longer.
Therapy
If gravid endometrium is detected during pregnancy, then this is normal and no treatment is needed. Everything goes away on its own as soon as the woman’s hormone balance returns to normal.
But if the uterus spontaneously rejects the child or during an abortion, the woman will need an ultrasound examination in a month. Thanks to him, it will become clear in what condition the lining of the reproductive organ is.
In case of severe bleeding during this period, the doctor prescribes some medications belonging to the group of hemostatic agents, the main function of which is to accelerate blood clotting:
- "Vikasol".
- “Etamzilat.”
- “Oxytocin.”
- “Ergometrine.”
If such treatment does not produce the desired results, and the endometrium does not reach a satisfactory state, then hormonal therapy is prescribed. They will help restore the level of substances. The treatment regimen for correcting the balance of hormones is used only as prescribed by a doctor, strictly observing the dosage and recommended time of use. The doctor takes into account:
- ultrasound results;
- histology results;
- reasons for the failure.
Similar treatment regimens are followed if a woman has had a miscarriage. Medical care begins with the mandatory removal of the zygote or its remains from the uterus. Thus, hormonal activity is suppressed, and the body begins to recover.
Tissue decidualization is a natural process in the event of successful fertilization of the egg. This phenomenon helps to establish conception at very early stages. If such changes occur in the body of non-pregnant patients, then treatment should begin immediately.
Is it dangerous?
The gravid endometrium itself plays a very important role during pregnancy and is an integral part of the body, since it is to it that the fertilized egg clings. That is why this endometrial condition is safe and completely acceptable. Also, the situation in which a miscarriage occurs does not pose any danger, since after time the hormone levels will return to normal and the mucous layer will become normal again. But still, doctors strongly recommend conducting a control ultrasound in order to assess how quickly the endometrium will return to normal and whether it will return at all.
Treatment in Israel
Israeli gynecologists have significant experience in treating various diseases of the uterus. Using modern technologies, doctors at the Top Ichilov Clinic accurately determine the likelihood of malignant degeneration of tumors and carry out their excision using minimally invasive methods.
To find out more detailed information regarding your case, fill out the form below.
For non-surgical treatment, Top Ichilov uses the latest drugs, the effectiveness of which exceeds 90%, and advanced techniques: brachytherapy, photodynamic therapy, radiotherapy using the TrueBeam and many others.
If there is no choice left and it is necessary to surgically remove a tumor or even the uterus, Top Ichilov often uses a Da Vinci . This operation completely eliminates the possibility of medical error and prevents complications.
The endometrium is the inner layer of the reproductive organ, which undergoes changes in different phases of the cycle, during pregnancy and in the event of its termination. This is due to the fact that the tissues are completely dependent on the level of hormones. There are several types of the uterine layer, which have certain characteristics depending on the nature of hormonal fluctuations. Gravid endometrium is often found. It is worth immediately understanding what it is and what danger it poses.
Danger
Gravid endometrium during pregnancy is a necessary and natural phenomenon, and therefore does not pose a danger. If it appears, but a miscarriage occurs, then this condition also does not pose a significant danger, since in most cases the level of hormones normalizes over time on its own. However, control ultrasounds are recommended to assess the rate of normalization of the condition.
The danger is when such mucous membrane appears outside of pregnancy. This indicates a significant hormonal imbalance in the body, which can cause problems with conception and even infertility. And, in addition, the fertilized egg is, in principle, poorly attached to such endometrium. Therefore, the condition must be treated.
Corpus luteum and its pathology
Often this type of disease is diagnosed in patients. The problem develops due to hormonal disorders, and is determined if persistence of the corpus luteum is detected. The corpus luteum produces progesterone, but with this pathology the hormone becomes much smaller. If this period continues for a long time, the development of the disease will not take long.
It appears this way:
- menstrual bleeding becomes longer;
- gravid endometrium is poorly rejected and is reluctant to renew itself, since most of it is prone to reverse development;
- the size of the uterus increases.
If treatment is not started in time, the process is fraught with necrosis of tissue of the appendages, subject to pathological transformations. The reasons lie in the methodical decrease in the functioning of one or two ovaries. Typically, this condition distinguishes the health of a woman before menopause and during menopause.
In women of reproductive age, the appearance of such a problem may be associated with other pathologies:
- oncological;
- from the endocrine system;
- inflammatory processes in the ovaries and other ailments.
Lost pregnancy
Another source of development of reverse gravid endometrium is a failed pregnancy. The process does not develop immediately, but after several weeks. Alarming symptoms arise, and when you consult a doctor, a similar illness is diagnosed. Such changes may manifest themselves under the following circumstances:
- spontaneous rejection of the child occurred in a short period of time, but not everything came out with blood;
- during mechanical abortion – the fertilized egg was poorly cleaned and removed;
- a miscarriage with the help of medications that was not as successful as planned;
- death of the baby in the first half of the first trimester.
The pathology of the gravid endometrium can manifest itself in both uterine and ectopic terminated pregnancies. The process of disease formation is carried out as follows:
- changes occur in the structure of the endometrium - it ceases to be decidual;
- the mucous membrane is not renewed and goes into an inactive state;
- the formation of endometrial proliferation occurs.
It will be possible to establish such tissue deformation only after examining scrapings from the cavity of the reproductive organ. At this time, the remaining tissues of the dead fetus begin to decompose, causing harm to the woman’s body.
Gravid endometrium: causes, symptoms and treatment
Women's health is not just about caring for the figure, skin and hair, but also about the internal organs, including the genitals. Sometimes a gynecologist discovers gravid endometrium. So, if a representative of the fair sex does not experience pain or discomfort, this is not a guarantee of good health.
What is endometrium
This is the mucous membrane that is located inside the reproductive organ. The uterus is a complex mechanism in which changes constantly occur. This may be related:
- with pregnancy;
- cycle change;
- termination of pregnancy.
The organ requires close attention, good control and support for functioning at the proper level. This is due to the fact that the tissues are completely dependent on hormonal levels.
The uterine layer has several types, each of which has its own characteristics, depending on the degree of hormonal changes. Gravid endometrium is often noticed.
The doctor will explain what it is, why it appeared, whether the established diagnosis is dangerous, whether it is worth resorting to treatment and which methods will be more effective.
Definition
The functional layer lining the reproductive organ that forms in the early stages of conception can be detected during an ultrasound examination. This coating is the endometrium of the gravidar type. Sometimes it is noticed in women who are not planning a pregnancy.
This process of transformation into stromal cell constructs is called decidualization. Therefore, this type of uterine covering is called decidual tissue.
The process of change occurs throughout the entire covering of the organ, and not partially. At the same time, some changes are noted in the appendages themselves.
Causes
The gravid reaction of the endometrium is hormonal transformations and changes in the body. A change in the uterine layer occurs when successful fertilization has occurred. The endometrium becomes fuller and more loose, so that the fertilized egg is more comfortable. Therefore, it is considered appropriate and harmless.
The same can be said if there was a spontaneous loss of the baby. As soon as the hormone levels are restored, the endometrium returns to its previous state.
Danger
If a woman is not pregnant, and the doctor notices fragments of the gravid endometrium, then this is fraught with strong hormonal surges leading to poor results - problems with conception will arise and even infertility threatens. The fertilized egg does not attach well to this kind of endometrium. It is advisable to treat this condition, and the sooner the better.
Kinds
The disease can manifest itself in two different directions, it all depends on the reasons that provoked its occurrence. What kind of malfunctions caused the pathology indicates that completely different treatments are prescribed. Efficiency depends on the degree of neglect of the disease.
Often this type of disease is diagnosed in patients. The problem develops due to hormonal disorders, and is determined if persistence of the corpus luteum is detected. The corpus luteum produces progesterone, but with this pathology the hormone becomes much smaller. If this period continues for a long time, the development of the disease will not take long.
It appears this way:
- menstrual bleeding becomes longer;
- gravid endometrium is poorly rejected and is reluctant to renew itself, since most of it is prone to reverse development;
- the size of the uterus increases.
If treatment is not started in time, the process is fraught with necrosis of tissue of the appendages, subject to pathological transformations. The reasons lie in the methodical decrease in the functioning of one or two ovaries. Typically, this condition distinguishes the health of a woman before menopause and during menopause.
In women of reproductive age, the appearance of such a problem may be associated with other pathologies:
- oncological;
- from the endocrine system;
- inflammatory processes in the ovaries and other ailments.
At the first bell, you should not hesitate, but turn to a specialist for help - the sooner it arrives, the greater the chances of a speedy recovery.
Lost pregnancy
Another source of development of reverse gravid endometrium is a failed pregnancy. The process does not develop immediately, but after several weeks. Alarming symptoms arise, and when you consult a doctor, a similar illness is diagnosed. Such changes may manifest themselves under the following circumstances:
- spontaneous rejection of the child occurred in a short period of time, but not everything came out with blood;
- during mechanical abortion – the fertilized egg was poorly cleaned and removed;
- a miscarriage with the help of medications that was not as successful as planned;
- death of the baby in the first half of the first trimester.
The pathology of the gravid endometrium can manifest itself in both uterine and ectopic terminated pregnancies. The process of disease formation is carried out as follows:
- changes occur in the structure of the endometrium - it ceases to be decidual;
- the mucous membrane is not renewed and goes into an inactive state;
- the formation of endometrial proliferation occurs.
It will be possible to establish such tissue deformation only after examining scrapings from the cavity of the reproductive organ. At this time, the remaining tissues of the dead fetus begin to decompose, causing harm to the woman’s body.
Diagnostic methods
The normal reaction of the gravid endometrium to the fixation of a fertilized egg (also called a zygote) is decidualization. If conception does not occur and pregnancy does not occur, then the gravid layer of the lining of the reproductive organ begins to actively peel off at the end of the menstrual cycle.
After the final completion of menstruation occurs, the uterus is cleared of unnecessary secretions, and the tissue begins to grow again. This process is absolutely normal and is repeated every month.
The ability to diagnose reverse development of the endometrium exists only after taking a scraping from the uterus for histology and studying it.
The scraping is taken at an appointment with a gynecologist - in the office. The procedure is not very pleasant, but not painful:
- performed with a curette or loop;
- the instrument is inserted through the cervical canal into the cervix;
- a small area of tissue is collected in such a way that the mucous membrane is almost not damaged;
- the resulting material is sent to the laboratory.
When performed professionally, this procedure is completed without negative consequences for the woman.
During histological studies, the picture of the endometrium on a glass slide appears ambiguous. Parts of the gravid endometrium of reverse development can be located next to an area with the properties of secretory development and much more. If the condition was formed due to an interrupted pregnancy, then there is a possibility of noticing the fertilized egg or its elements.
Usually, scraping is done after a miscarriage - this allows, in some cases, to determine the cause of the problem.
Therapy
If gravid endometrium is detected during pregnancy, then this is normal and no treatment is needed. Everything goes away on its own as soon as the woman’s hormone balance returns to normal.
But if the uterus spontaneously rejects the child or during an abortion, the woman will need an ultrasound examination in a month. Thanks to him, it will become clear in what condition the lining of the reproductive organ is.
In case of severe bleeding during this period, the doctor prescribes some medications belonging to the group of hemostatic agents, the main function of which is to accelerate blood clotting:
- "Vikasol".
- “Etamzilat.”
- “Oxytocin.”
- “Ergometrine.”
If such treatment does not produce the desired results, and the endometrium does not reach a satisfactory state, then hormonal therapy is prescribed. They will help restore the level of substances. The treatment regimen for correcting the balance of hormones is used only as prescribed by a doctor, strictly observing the dosage and recommended time of use. The doctor takes into account:
- ultrasound results;
- histology results;
- reasons for the failure.
Similar treatment regimens are followed if a woman has had a miscarriage. Medical care begins with the mandatory removal of the zygote or its remains from the uterus. Thus, hormonal activity is suppressed, and the body begins to recover.
Tissue decidualization is a natural process in the event of successful fertilization of the egg. This phenomenon helps to establish conception at very early stages. If such changes occur in the body of non-pregnant patients, then treatment should begin immediately.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/466340/endometriy-gravidarnyiy-prichinyi-poyavleniya-simptomyi-i-lechenie
Causes
The reason for this condition, like any other change in the structure of the endometrium, is hormonal changes and changes in the body. Gravid endometrium appears when hormonal levels change, characteristic of pregnancy. That is, such a condition can appear exclusively during pregnancy, as a result of the mutual influence of progesterone and estrogen and changes in their content.
At the same time, at the initial stages the pregnancy itself may not be diagnosed by ultrasound. The mucous layer undergoes changes from the first day of conception. Therefore, with a delay of 1 day, its changes are already noticeable on ultrasound, although the self-fertile egg is not yet visible - it is visualized much later. In this case, doctors usually recommend that patients take a venous blood test to determine the content of the hCG hormone in the body. This hormone begins to be produced immediately upon pregnancy and its level helps diagnose this condition with high accuracy.
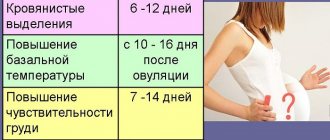
Endometrial thickness by cycle phases
Only a healthy endometrium is able to create conditions for the emergence and full course of pregnancy. When a woman finds out that the size of the uterine lining detected during diagnosis does not correspond to the norm for the days of the menstrual cycle, she understands that this is a pathological process that can cause infertility. Therefore, when planning conception, it is very important to check the condition of the mucous membrane of the female reproductive organ.
If deviations are detected, then it is imperative to undergo a course of treatment that stabilizes the thickness of the lining, since changes in its structure during pregnancy can affect the formation of the child.
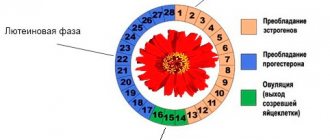
First phase
It begins on the first day of menstruation. During this period, the functional layer of the endometrium is rejected with bleeding. On average, the process lasts from 4 to 7 days. Of these, on days 1 and 2, the thickness of the mucosa is 5–9 mm.
Second
This is called the proliferation phase. It lasts from the 5th to the 15th day of the menstrual cycle. During this time, the endometrial layer increases. In the early period of this stage, lasting from the 5th to the 7th day, the normal layer of the uterine mucosa is 5–7 mm. On the average - from the 8th to the 10th day - the endometrium dynamically grows and thickens. During this time it increases from 8 to 12 mm. In the final period – from the 10th to the 14th day – the lining of the reproductive organ is normally 10–12 mm.
In accordance with these indicators, the condition of the endometrium is diagnosed. If the data obtained as a result of an ultrasound is normal, then the inner lining of the genital organ is functioning properly, and during the period of ovulation the woman will be able to become pregnant. And if there are significant discrepancies, then it is worth consulting with a gynecologist to see what medications can correct the situation.
How does the process of decidualization work?
The process of decidualization begins in the first days after fertilization of the egg. The newly formed tissue is characterized by increased vascularity and the presence of a large number of polygonal and white blood cells (leukocytes).
Vascularization (the process of active proliferation of blood vessels) is the most significant change that can be quite easily detected using ultrasound.
Initially thin endometrial arterioles undergo a process of endothelial proliferation (the walls of the vessels become significantly thicker, and the blood network itself grows).
It is the arterioles that play a decisive role in the process of normal decidualization: without a sufficient amount of arterial blood, the endometrium cannot degenerate.
Important! In a healthy woman, the decidual endometrium cannot be focal, but should line the entire internal cavity of the uterus.
Conventionally, the process of decidualization goes through the following stages:
- After the implantation process begins (at the site of attachment of the fertilized egg), functional and morphological changes begin;
- The changed cells send a signal to begin changing the surrounding tissues;
- Glycogen accumulates in the tissues of the uterus;
- Primary “anchor” villi are formed, ensuring normal fixation of the zygote to the uterine wall.
The process of complete transformation of all endometrial stromal cells into decidual cells is completed in approximately 8-10 days.
Pregnancy after treatment of hyperplasia
With proper and timely treatment, reproductive function can be restored. At the same time, there is a high probability of having a completely healthy child. If difficulties with fertilizing the egg still persist, a woman can give birth to a child using one of the following methods:
- carrying out artificial insemination IVF;
- the use of intracytoplasmic injection of sperm into the cytoplasm of the egg.
These procedures increase the likelihood of successful conception even after curing a severe form of hyperplasia.
It is worth considering that after therapy, pregnancy needs to be planned. The period of possible conception can be determined based on the techniques used in the treatment process.
If a woman took hormones that normalize the levels of progesterone and estrogen, conception can be planned 4 weeks after they are discontinued and the menstrual cycle is restored. If the therapy involved surgery, you will need to undergo a full rehabilitation course, lasting at least 6 months.
To increase the likelihood of a successful pregnancy, a woman should follow several rules:
- be sure to visit the gynecological office twice a year;
- If you notice any disturbing discharge, itching, burning, bleeding, or disruption of the menstrual cycle, consult a doctor immediately;
- Do not allow weight gain under any circumstances;
- avoid stress and emotional experiences;
- completely give up bad habits;
- organize a proper diet;
- engage in sports characterized by moderate physical activity.
If a woman plans to become a mother, she should follow all the above rules and adhere to the full list of recommendations from her doctor. At the end of treatment, it is necessary to consult a doctor in order to re-diagnose the presence of pathology and the likelihood of its development. This will eliminate any risks of complications during pregnancy.
Why is endometrial gravidar needed?
Pregnant women should not worry about the presence of decidual tissue: this means that the body has prepared to bear a child. In addition, the increased number of white blood cells prevents embryo rejection.
Because the fertilized egg contains the DNA of the baby's father, there is a risk that the body will perceive the fertilized egg as a hostile foreign body. It is decidual leukocytes that suppress the mother’s negative immune reaction to a cell with foreign DNA.