Transition from lactostasis to mastitis
Incomplete pumping or a long break in feeding the baby leads to milk retention. The same thing happens with hyperlactation, spasm or blockage of the excretory duct or compression by tight underwear. The breasts begin to hurt, in the morning they look more swollen, lumps can be felt in them, and the skin becomes hot. These symptoms indicate lactostasis, which goes away on its own after several feedings or pumping. If after a day no improvement is felt, then there is every reason to suspect the onset of mastitis.
Staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli and other pathogens of infectious inflammation enter the breast tissue with blood and lymph or through skin cracks or nipple ducts. While there are no problems with the outflow of milk, the immune system of a nursing mother successfully fights a small amount of infection. But its stagnation creates favorable conditions in the ducts for the proliferation of bacteria.
Symptoms of postpartum mastitis
Symptoms of mastitis depend on the stage of inflammation of the mammary gland. The onset of the disease is announced by the rapid appearance of signs of serous mastitis:
- a sharp increase in general body temperature, no difference when measuring it from the healthy and affected breasts, which is typical for lactostasis;
- chills, headache and general weakness;
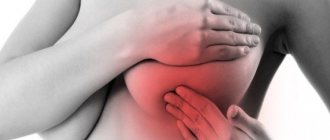
- aching pain in the chest does not ease after expressing milk;
- the chest becomes hot, dense, blood vessels are visible through the skin;
- milk removal is painful and difficult;
- the child is capricious when applied to the affected breast.
The infiltrative stage begins after 1-2 days. It is characterized by:
- the appearance in the mammary gland of one or more lumps that do not have clear boundaries;
- preservation and intensification of a feverish state;
- enlarged axillary lymph nodes on the side of the inflamed breast.
Insufficient therapy for this form of the disease leads to its transition to purulent mastitis:
- body temperature during fever exceeds 39º C;
- infiltrate in the internal seals is replaced by pus;
- against the background of hyperemic skin, even darker areas stand out above the foci of inflammation;
- the breast greatly increases in size, and a noticeable swelling forms above the abscess;
- Constant pain in the mammary gland can take on a throbbing character.
Causes of the disease
For a nursing mother, mastitis is a serious disease that can occur under the influence of the following harmful factors:
- During feeding, small cracks appeared on the nipples. Through them, harmful bacteria penetrated into the mammary gland. That is why a woman should treat all infectious diseases of the breast. For example, during thrush, the risk of spreading the infection increases several times. Treatment must be started immediately. In this case, most of the negative consequences will be avoided.
- Mastitis in newborns can also develop if the nipples have not been properly prepared for the lactation period.
- After the birth of a child, hormonal changes begin to actively occur in a woman’s body, and the protective functions of the immune system decrease. A combination of external negative factors can lead to the development of mastitis in the postpartum period.
- When breastfeeding, the mother does not adhere to the basic norms and rules of personal hygiene.
- A woman has to deal with constant hypothermia.
- Previously, malignant or benign tumors were identified in the mammary gland.
- After the birth of a child, a woman’s body undergoes a natural process of breast swelling. If the baby does not drink enough milk, stagnation may occur. Against the background of this situation, the woman develops lactostasis. It is necessary to proceed to treatment in time, otherwise the pathology will develop into mastitis.
It is important to start treating mastitis within 48 hours
Diagnosis of mastitis
Making a diagnosis for lactation mastitis is usually not difficult, since the signs of inflammation of the mammary gland are pronounced and develop quickly. The difficulty lies in diagnosing the early stage of the disease, when nursing mothers delay visiting a gynecologist, believing that breast pain is associated with stagnation of milk.
To differentiate mastitis from lactostasis, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- visual inspection and palpation of the breast and adjacent lymph nodes;
- general blood analysis;
- sowing milk for microflora (milk is taken from the affected and healthy breast);
Ultrasound of the mammary glands is the most informative way to obtain information about the current inflammatory process, since both the onset of mastitis and its purulent form can be equally represented on a general blood test.
Women who care about their health and the health of their baby need to contact their gynecologist in a timely manner, avoiding self-medication and traditional methods of combating mastitis. Although the prognosis for treatment of the disease is usually favorable, purulent complications can lead to deformation of the breast, destruction of its tissue, and pose a threat to the life of the mother if pus enters the blood.
Is it possible to breastfeed with mastitis?
There is no general consensus yet on whether breastfeeding can be continued during mastitis.
In the manual of the World Health Organization “Mastitis. Causes and management" (2000) states that in most cases it is possible and necessary to continue breastfeeding during mastitis, since the risk of infection of the child is minimal. And this risk is much less than the damage that forced weaning will cause to the baby’s health.
Some “advanced” Russian pediatricians support this point of view: they argue that feeding with mastitis is possible, even at the treatment stage. After all, for example, amoxiclav is compatible with hepatitis B. Moreover, you can feed not only healthy, but also sick breasts.
Some doctors recommend pumping the sore breast regularly and feeding the baby only from healthy breasts. In some cases, milk is advised to be expressed and pasteurized.
A significant part of Russian doctors believe that breastfeeding during mastitis is prohibited from any breast and at any stage, since staphylococcus can be transmitted to the baby and cause serious health problems. They claim that if purulent mastitis develops, feeding is stopped, including from the healthy breast.
Is it possible to resume feeding after treatment (conservative or surgical) or will it have to be stopped? Most modern doctors say that it is possible, but provided that:
- inflammation is eliminated;
- Bacteriological tests of milk gave a negative result.
However, there are also adherents of a categorical ban on breastfeeding. They believe that after surgery they have to stop lactation, even if mastitis has been cured.
What should a nursing mother do? Weigh the pros and cons, consult with a good pediatrician and make a decision together with him.
Most breastfeeding consultants believe that feeding should be continued. For example, watch this video.
Treatment of inflammation of the mammary glands in a nursing mother
As with any infectious disease, antibacterial therapy is the most important part of the conservative treatment of postpartum mastitis. They resort to it in the first days of the disease before it turns into a purulent form.
The choice of antibiotic is made by the doctor based on three parameters:
- the sensitivity of the infectious agent to the components of the drug is determined by the results of milk culture;
- maximum concentration in the breast area (preferably intravenous or intramuscular administration of the drug, tablets are prescribed very rarely);
- safety for the health of the child and mother.
To avoid the transition of incipient inflammation into purulent breast lesions, medications are prescribed without waiting for the results of a milk test. Usually these are penicillin antibiotics (Oxacillin) or cephalosporins (Cefazolin), effective against the main causative agent of mastitis, Staphylococcus aureus. If necessary, the drug is replaced. Swelling, pain and body temperature are reduced with anti-inflammatory drugs.
The second important part of the treatment is aimed at emptying the mammary gland and reducing lactation. Unlike lactostasis, feeding during mastitis is contraindicated in order to protect the child’s body from the effects of medications and the ingestion of infectious agents along with milk. Reducing milk production and improving its outflow is achieved with hormonal drugs. Regular pumping helps prevent stagnation, which also maintains lactation until you return to breastfeeding.
In case of pronounced symptoms of intoxication of the body, which is more typical for purulent mastitis, infusion therapy is carried out: droppers with solutions of Ringer, Remaberin and others.
The course of antibacterial therapy takes 5-10 days, medication is stopped after a stable result that lasts 2-3 days. Resumption of breastfeeding of the child is allowed a week after discontinuation of medications and confirmation of the effectiveness of treatment by test results.
Treatment of purulent inflammation of the mammary gland requires surgical intervention. In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed, but if there is no improvement within 2-3 days, then while continuing to take medications, the abscesses are opened and the source of inflammation is thoroughly drained. If mastitis has passed into the phlegmonous or gangrenous stage, then necrotic tissue is removed.
Good results are shown by supplementing the drug treatment of serous and infiltrative mastitis with physiotherapy: ultrasound, ultraviolet rays. They are also used during postoperative rehabilitation.
Basics of treating the disease
Treatment of mastitis during breastfeeding is effective if therapy is started in a timely manner. You should consult a doctor within two days after the first symptoms appear. In this case, the likelihood of surgical intervention is minimized. The operation will be mandatory only in case of purulent mastitis. Most often, therapy is performed on an outpatient basis. With her, breastfeeding is allowed. In some cases, on the contrary, refusal may lead to aggravation of the situation.
How to treat mastitis in a nursing mother so that the disease recedes quickly:
- You cannot stop the flow of milk from the gland. Doctors recommend feeding girls or boys from the sore breast. It is important to remove as much liquid as possible from it. If feeding is not possible, pumping should be done regularly. In this case, it will be possible to prevent the formation of stagnation. Refusal to feed should only be done if the woman has been prescribed antibiotics for mastitis. Today, doctors have more effective, albeit conservative, treatment methods in their arsenal.
- First aid for mastitis is regular breast massage. Thanks to simple manipulations, it is possible to improve the flow of milk.
- Additionally, it is allowed to apply a heating pad with ice to the breast for a quarter of an hour after finishing feeding. Before the procedure, it should be wrapped in cloth.
- You can improve the movement and flow of milk by taking a special solution. Your doctor will prescribe four drops of oxytocin five to six times a day.
Cabbage leaves help against mastitis
The treatment as described above should be used every two hours. Procedures should also be carried out at night. Only in this case will it be possible to achieve a positive effect.
- The source of inflammation must also be treated from the outside. To eliminate cracks and inflammatory processes, it is advisable to use Bepanten or Purelan-100. The attending physician, at his discretion, may recommend using a different ointment.
- Antipyretic drugs should be used only if the body temperature rises above thirty-eight degrees.
- It makes sense to prescribe antibiotics only if the inflammatory or infectious process is prolonged. The course of treatment will be from five to ten days. Antibiotics are harmful for a child, so breastfeeding should be suspended during this period. Artificial mixtures will be used as a food source. It will be possible to continue feeding only after the end of the course of treatment.
Prevention of inflammation of the mammary glands after childbirth
It is no coincidence that postpartum mastitis in most cases occurs in women who have given birth for the first time. Lack of breast care skills, inability to properly feed a child, neglect of the importance of emptying the milk ducts are the first reasons for the development of pathological lactostasis. It is not far from infectious inflammation of the mammary gland. Therefore, prevention begins during pregnancy, when young mothers become familiar with the features of personal hygiene during lactation. Advice on breast care is given by obstetricians in maternity hospitals, and they also teach basic feeding skills.
Care includes rinsing your hands and breasts before and after feeding, and choosing underwear that doesn't compress your breasts. Feeding itself should take place at the baby’s request, and expression of excess milk is carried out only if necessary, until the nursing mother’s body adapts to the baby’s diet. To protect against cracked nipples, make sure that the baby attaches correctly so that the baby grasps the entire nipple, along with the areola. After feeding, the nipples are lubricated with wound-healing ointments or moisturizers with lanolin and air-dried for several minutes. A light massage of the mammary glands copes with mild stagnation in the ducts and helps to notice in time the signs of lactostasis or incipient mastitis.
Caring for the health of a nursing mother means paying attention to detail. The slightest discomfort that hygiene procedures cannot cope with: fever, the appearance of redness or cracks in the skin and nipples, painful lumps that last for several days is a reason to contact your doctor, antenatal clinic, or maternity hospital.