Women's breasts are one of the most delicate and vulnerable parts of the body, the condition of which depends on many factors. That is why most often problems with the mammary glands arise during menopause, when serious hormonal changes occur in the body. One of the most common diseases in women over 45 is breast fibrolipoma. This is a benign formation that forms in fatty tissues. It may not cause any concern until it is discovered during a routine examination or grows to a fairly large size. Having learned about such a diagnosis, a woman must quickly begin treatment, otherwise there is a high risk of the fatty tumor degenerating into a cancerous one.
General characteristics of the disease
Breast lipoma is a benign lump in the subcutaneous tissue. Pathology is formed from adipose and connective tissue. An atypical cell grows slowly. Lipoma sizes are diagnosed from 25 mm to 20 cm. With volumes exceeding 20 mm, pathological compression of the nearest blood vessels and milk ducts with nerve processes occurs, which can lead to stagnation of blood and subsequent tissue necrosis.
The formation in the sternum is located in a special capsule made of connective fiber. The soft node is mobile and can be easily felt during palpation of the organ. It is difficult to determine the disease on your own. To confirm the diagnosis, you need to see a doctor and undergo a detailed examination of the body.
Based on the structure of the neoplasm, the following types are distinguished:
- myxolipoma consists of adipose epithelium interspersed with mucus produced by the lipoma;
- fibrolipoma contains connective fibers with adipose tissue;
- angiolipoma is characterized by a high content of blood capillaries with a fatty layer of tissue;
- myolipoma consists of a small amount of fatty epithelium;
- lipofibroma is characterized by a predominance of the fat layer with minor inclusions of connective fiber.
Depending on the location of the tumor, superficial, intermuscular and subcutaneous forms are distinguished.
Breast lipoma
The wen looks like a rounded neoplasm with clear boundaries. Sometimes there are seals with blurred edges. The tumor developing in the capsule consists of a fibrous membrane.
The ICD-10 code for the disease is D17.9 “Benign neoplasm of adipose tissue of unspecified localization.” Women over 25 years of age are at risk of developing pathology.
Treatment with traditional methods
Depending on the severity of the disease, a suitable method of therapy is selected.
Conservative treatment:
- Puncture. Under anesthesia, a thin needle is inserted into the formation in the mammary gland, through which the contents are sucked out. The danger of the technique is that the capsule remains in place, and relapses of the disease are possible.
- Radio wave method. Using a radio knife, the lipoma is quickly removed. Due to the high temperature, the wen is practically “burned”, leaving a crust that quickly falls off. This method is very fast, relapses are unlikely. Prohibited for use if the body has metal prostheses.
- Using a laser to remove breast tissue is one of the safest methods. With the help of a laser, the lipoma is completely removed, practically no traces remain, and the risk of relapse is minimal.
- Injection into the tumor of a special substance that has a resolving effect. However, such therapy continues for at least two months.
It is worth noting that conservative treatment methods are used if the formation is small. In other cases, surgical removal is used.
When prescribed:
- Rapid increase in size
- Lipoma puts pressure on glandular tissues,
- Education deforms the shape of the breast,
- Constant presence of painful sensations.
The surgery is performed under local anesthesia. Using a scalpel, the doctor removes the formation along with the capsule, and the wound is sutured. Recently, endoscopy is often used - removal of lipoma through small incisions in the mammary gland.
The disadvantage of this type of therapy is the possible appearance of scars after treatment. However, with this method, relapses of the disease rarely occur.
Causes of the disease
Reasons for the appearance of a wen on the mammary gland:
- pathologies of an endocrine nature - diabetes mellitus, pancreatic tumors;
- metabolic problems;
- hereditary predisposition;
- disturbances in the production of sex hormones;
- state of stress for a long period of time;
- excess body weight;
- lack of physical activity - sedentary work;
- unbalanced diet – deficiency of plant fiber and vitamins and microelements;
- injury to chest tissue;
- abuse of alcohol and nicotine.
Lipoma occurs in the sternum due to blockage of the ducts of the sweat glands. A disruption in the functioning of the gland leads to the formation of a capsule filled with fatty fiber. Many doctors consider hormonal and metabolic disorders in the body to be the main factor of the disease - this is accompanied by tissue replacement with a predominance of the glandular type. The fibrous epithelium is actively growing. Lipofibromatosis must be treated urgently to avoid degeneration into cancer.
Clinical picture
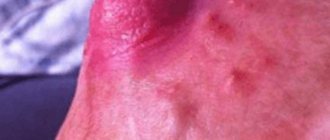
When palpated, fatty deposits in the mammary gland are defined as painless, soft protruding lumps. A lipoma can be located in any part of the chest. This tumor can be distinguished from other tumors by certain characteristics. For example, the skin over the lipoma does not change. The only exception is a wen on the nipple, in which the skin in the area around the nipple becomes covered with a small white rash.
Symptoms in the form of a feeling of fullness and pain in the chest can appear only with large tumors. The pain is a consequence of the pressure of the wen on the surrounding tissues and vessels. If the wen grows, then the shape of the glands may change and its asymmetry appears.
Nodules, as a rule, do not grow and appear only with certain movements. Despite the benign nature of the process and the lack of growth, constant trauma to the tumor with underwear, solar radiation and excessive stay in the solarium can lead to its malignancy (transformation into liposarcoma).
The diffuse form of the disease is found much less frequently. The most dangerous process is the spread of the tumor to connective tissue fibers (that is, the formation of fibrolipoma). Often such tumors become calcified and touching the breast causes pain. The average tumor size is usually 1-5 cm, but lipoma can grow up to 12 cm.
Signs of pathology
A suspicious lump in the chest cavity can be felt independently through the skin. During the rapid growth of atypical tissue, the tumor can be diagnosed without palpation. Lipoma is characterized by a dense consistency with a movable capsule in the subcutaneous layer. At the initial stage of formation, the disease has no symptoms. The first signs appear when the node increases to 15 mm and above.
Due to the structural features and characteristic mobility under the skin, there is systematic contact with the upper layer of the dermis and the internal epithelium in the chest. Often women are diagnosed with lobular compaction with no clear boundaries. The formation often protrudes above the skin surface.
Localization of the wen in the deep layers of tissue develops secretly - without the presence of external signs and the ability to palpate the node. Characterized by germination into muscle fibers. In this case, a pain symptom appears with internal discomfort in the mammary gland.
It is possible for a single lipoma to form in one breast or on both sides at once - a bilateral variant of the pathology.
Classification of lipomas
The main component of lipomas in the mammary glands is fat, however, in addition to it, other tissues may be present in the tumor. In accordance with external signs and composition, these neoplasms are divided into different types.
So, depending on the number of nodes, lipomas are divided into:
- Single. Present exclusively in the chest, they are not found in other organs.
- Multiple (lipomatosis). Present in the mammary gland and several other organs. Typically, this condition is hereditary. In this case, the removal of one node activates the growth of the tumor in other organs.
According to the structure and form:
- Nodal. They have clearly defined (due to the capsule) rounded edges.
- Diffuse. They are shapeless compactions formed due to the growth of adipocytes outside the capsule.
Depending on the quality composition:
- Myolipoma. The tumor contains adipose tissue and muscle fibers.
- Lipofibroma (lipofibrosis). The node is adipose tissue with fibrous (connective tissue) inclusions.
- Myxolipoma. Lumps of mucus are present among the fat cells.
- Fibrolipoma. The basis of the tumor is represented by connective tissue interspersed with fat.
- Angiolipoma. A tumor of fat cells, penetrated by a whole network of blood vessels. During surgical removal of such a wen from the mammary gland, massive bleeding may occur.
Diagnosis of the disease
The breasts perform important functions in the female body, so doctors advise closely monitoring the appearance of suspicious tumors. If a node is detected inside the mammary gland, you should consult a doctor for a full examination.
At the clinic, the patient will be prescribed a number of procedures to clarify the diagnosis and select the correct course of therapy. The disease is dangerous due to the active growth and compression of blood vessels with nerve endings, which can lead to necrosis of damaged tissues.
Diagnostics includes the following activities:
- The doctor conducts a physical examination of a woman with breast palpation and collects a complete medical history.
- Ultrasound (ultrasound) examines the shape and size of the tumor with the depth of penetration into the subcutaneous layers of the organ.
- The mammography procedure allows you to examine the structure of the mammary gland affected by the wen.
- A general analysis of blood and urine is carried out to determine the indicators of the main elements.
- The patient is prescribed a puncture to collect biological material for a biopsy of the lipoma.
- To exclude a malignant form, cytology is prescribed with a histological examination of the tumor cell sample.
- The doctor may suggest computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging as an additional procedure to clarify the extent of damage to the body.
After receiving the test results, the doctor will be able to assess the woman’s condition and choose the right treatment. The fatty tissue must be removed at any stage of the development of the pathology. As the tumor grows, the milk ducts and blood vessels are compressed, which can cause serious consequences for a woman’s health.
Symptoms
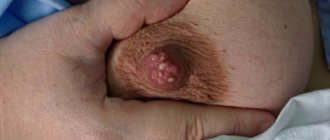
The main sign of a lipoma is the presence of a tumor-like formation. It is often discovered accidentally during an ultrasound examination of the breast. A woman feels a nodule when its diameter is at least 1.5-2 cm. The favorite localization of the tumor is the upper outer quadrant of the breast. Usually the formations are single, but cases of paired symmetrical development also occur.
Main palpation characteristics of the breast wen:
- round, oval shape;
- the surface is smooth, the contours are clearly defined;
- the consistency of a classic wen is soft-elastic, fibrous lipomas are dense, mixolipomas are doughy;
- pressure is painless.
The disease has no general symptoms. The occurrence of pain syndrome is possible, but extremely rare:
- when squeezing muscle membranes or vascular bundles;
- “old” lipomas with calcification;
- local disturbance of blood flow, which leads to ischemia and necrosis.
In most cases, lipoma does not manifest itself at all. Palpation of the breast reveals oval or round mobile formations with a diameter of 1-1.5 cm, which may increase in size over time. If nerve fibers were involved in the process of lipoma growth, then pain may occur upon palpation. In some cases, swelling of the mammary gland, changes in skin pigmentation, and clearly localized wen may be observed.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fyfTYxdXq1I
Breast lipoma can be encapsulated or diffuse. In the first case, the wen is localized in one place, it is soft and mobile. In the second, the lipoma does not have a clear shape; it is surrounded by diffuse growths of adipose tissue.
Based on consistency, breast lipomas are divided into:
- Myxolipomas. They are characterized by a predominance of mucous adipose tissue;
- Lipofibromas. They include adipose and connective tissue. In this case, fatty tissue predominates;
- Myolipomas. Fat formations with a predominance of muscle fibers;
- Fibrolipomas. Formations consisting of adipose and connective tissue with a predominance of connective tissue;
- Angiolipomas. They are characterized by the presence of a large number of blood vessels;
Breast lipomas can also be single or multiple, in some cases there are symmetrically located lipomas.
Most often, lipomas measure 1-2 cm, but over time they can increase to 5-10 cm.
You can detect a lipoma, if it has appeared recently, by palpating the breast. According to experts, small tumors practically do not manifest themselves in any way (there is no pain or any discomfort). When a breast lipoma “grows”, it can displace nearby tissues, which leads to breast deformation. Visually, these kinds of changes are clearly visible.
If the neoplasm is localized in the nipple area, it looks like a small light rash.
A giant tumor (occurs extremely rarely) constantly puts pressure on tissues and blood vessels, as a result, the woman is haunted by a feeling of fullness in her chest, and sometimes even pain.
Experts strongly recommend that all women regularly visit a mammologist in order to take all necessary measures against such a disease as breast lipoma in the early stages. Symptoms, as noted above, most often appear when the tumor begins to grow. In such a situation, it will simply be impossible to do without surgical intervention.
Lipoma in the breast is an independent disease, but in rare cases it is part of a multiple lesion - lipomatosis. The disease is characterized by a dense elastic consistency, mobility, clear demarcation, and non-invasive growth.
Fats that reach large sizes, cause tissue deformation or interfere with the function of the mammary gland are removed surgically.
Education grows slowly and painlessly. Discomfort occurs only when surrounding tissues, blood vessels or nerve bundles are compressed. Lumps in the mammary gland are rare; most often the problem is localized in areas with a low percentage of fat.
- nodular, delimited by a dense connective tissue capsule;
- diffuse - cluster-shaped accumulations of lipocytes without clear boundaries.
Treatment of breast lipoma
After diagnosis, the patient prepares for treatment. Breast lipoma can be removed using conservative therapy, surgical excision and traditional medicine. Drug treatment is used in the early stages of lipomatosis, when the tumor is within 10 mm. The wen does not resolve on its own.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the woman is under close medical supervision with any method of therapy. An ultrasound procedure is performed once every 3 months and mammography annually.
Conservative treatment is accompanied by regular blood tests for the presence of tumor markers CA-15-13. If the tumor is actively growing, it must be urgently removed by surgery. There is a risk of injury to nerve endings, accompanied by painful spasms.
A lipoma of gigantic size causes external deformation of the breast, noticeable to the naked eye. This also requires urgent surgery to excise the node.
Surgical excision of lipoma
The surgical method is recommended when diagnosing a large tumor in the breast or in the absence of effect from the conservative method of therapy. Sectoral resection is mainly used, which allows the tumor to be removed along with the capsule - this avoids relapse.
Small lumps are removed using enucleation (husking) - a method that is gentle and non-traumatic for the woman. A small node can be removed with a puncture biopsy. To do this, you will need a long thin needle, which is inserted into the capsule and the contents are brought out. After removal, no scars remain, but the lipoma shell remains inside, which can provoke a relapse.
Sectoral resection is a painful procedure for excision of the wen, but it gives a positive result for a complete recovery. The method is used in the presence of certain discomfort and other concomitant pathologies of the mammary gland - mastitis, fibroadenoma or granuloma.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia - depending on the area being operated on and the depth of the organ damage. Then cut marks are made using a cotton swab with brilliant green. The doctor makes an incision into the organ to access the lipoma and removes the capsule completely. If there is a risk of malignant degeneration, then partially healthy tissue is removed - this will help avoid recurrent pathology. After the operation, the edges of the wound are sutured.
It is impossible to leave empty cavities in the breast tissue, so it is possible to apply sutures above the subcutaneous fat layer. The removed biological material is sent to the laboratory for histological examination of the structure of the wen. The procedure lasts 20-30 minutes.
Complications after surgery are rare. Re-infection of the wound with an inflammatory process or a hematoma in the operated area is possible due to incomplete bleeding. If there are problems with blood clotting, internal bleeding may be diagnosed.
Stitches are usually removed within 7-8 days. After the procedure, there may be pain discomfort, so the patient is prescribed a course of painkillers and sedatives.
New growths in the mammary gland that do not exceed 50 mm in size can be removed using laser therapy. The operation is performed using local anesthesia for pain relief. The tumor is excised along with the capsule to prevent recurrence of the disease. The laser beam has antibacterial properties, which prevents re-infection of the wound. The operated area heals in 5-7 days. The skin recovers completely within 15 days.
The operation is considered safe in terms of no vascular damage or rapid wound coagulation. The disadvantage of the procedure is the inability to take biomaterial for histology.
Liposuction is rarely used due to the high risk of recurrence. Radio wave treatment is used when the node is small in size and accessible.
Drug treatment
Wen can be cured using conservative therapy. For a positive effect, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations. The method helps at the initial stage of the formation of the disease. Manipulations allow you to stop the growth of the node and reduce it in size until it completely resolves. The following medications are used for this:
- Vitaon is made from natural plant ingredients. The ointment does not irritate the skin and does not cause inflammatory processes. The presence of individual intolerance requires stopping use and replacing it with another product with a similar effect. The balm is applied to the sore spot and secured with an adhesive plaster or tight bandage. The bandage needs to be changed 2 times a day. The medicine has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties, which has a beneficial effect on the tumor.
- Vishnevsky ointment is made on the basis of birch tar, castor oil and xeroform. Recommended if there is an inflammatory process inside the lipoma. The substance is applied to the chest and fixed with a bandage for 2-3 hours. The procedure is repeated up to 3-4 times a day for a week. Side effects or an allergic reaction may occur, in which case the drug should be excluded from the course of therapy.
- Ichthyol ointment has an antiseptic effect. They prefer to prescribe when diagnosing infection of a wen inside the mammary gland. The drug eliminates the effect of itching, restores skin turgor and blocks further inflammation. A positive therapeutic effect after use is observed after 2-3 hours. It is forbidden to use by pregnant and breastfeeding women.
Treatment with drugs helps with early detection of the disease and small size of the tumor. Correct use of medications with precise dosage guarantees rapid recovery of the body and complete resorption of the wen.
Alternative medicine
Traditional medicine is considered an auxiliary method to the conservative method of therapy. Before using these recipes, you should consult your doctor and carry out the procedures under close medical supervision.
The following recipes are considered the most effective and popular in the treatment of breast lipoma:
- Grind 50-100 g of lard in a meat grinder with 1 head of garlic. Mix everything thoroughly and apply the finished mixture to the affected area. Repeat the procedure 3 times a day. The ointment can be secured with an adhesive plaster or bandage.
- Wash the Kalanchoe and cut into small pieces. Apply the resulting paste to the chest and secure with gauze overnight.
- The golden mustache is cut and applied to the tumor. Place cling film on top and secure with a tight bandage. Change the bandage 2 times a day. The course lasts 15 minutes.
- Bake a head of onion in the oven and crush it with 50 g of laundry soap. The compress is applied 2 times a day until the node is completely absorbed.
- Cinnamon should be added to coffee, porridge, and milk to cleanse the blood and stimulate the breakdown of fatty tissue.
- Mix 40 g of fresh or dried black currants with 50 grams of rose hips. Pour boiling water (350 ml) and leave for 30 minutes. Then strain, pour in beer (200 ml). Drink once a day until complete recovery on an empty stomach.
- Pour boiling water (300 ml) over fresh pine needles. Place in a water bath for up to 15 minutes. Cool and apply lotions 2 times a day.
Traditional medicine recipes cannot be used independently without consulting a doctor. This can cause serious consequences and deterioration in well-being.
Could it be cancer?
The lump is considered a benign formation, but we must not forget about the risk of cell mutation into cancer.
Liposarcoma and other types of fatty tissue cancer may be no different from a lipoma in the breast.
Any neoplasia after removal is subject to histological examination to exclude oncopathology at the cellular and tissue levels.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
A lipoma located in the mammary gland is dangerous if it is constantly traumatized. The risk of malignancy increases or the lump degenerates into oleogranuloma - focal necrosis of adipose tissue with the development of an inflammatory process. Macroscopically, it is similar to a malignant neoplasm and has no clear boundaries. The final diagnosis is made by a pathologist. Differential diagnosis must be carried out with lymphadenitis, hygroma, epidermal cyst, soft fibroma, leaf-shaped fibroadenoma.
Disease prevention
To prevent lipomas in the breast, you need to eliminate fatty foods and enrich your diet with plant fiber. The presence of physical exercise will reduce the risk of developing pathology. You also need to control your weight and emotional background. Self-examination of the breast will allow you to identify lumps at an early stage and provide timely treatment.
The presence of illness in the family requires close attention from doctors and the woman herself. It is necessary to regularly undergo scheduled examinations and diagnostic procedures.
Preventive measures
To avoid tumors, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle. It is recommended to play sports, since lack of physical activity is a predisposing factor to disease. Physical inactivity leads to excess weight, and accordingly, the patient has health problems. It is necessary to pay attention to changes in the mammary glands.
If close relatives have been diagnosed with a benign tumor, it is necessary to visit the doctor more often and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. Despite the fact that the formation is benign, the patient cannot distinguish it from cancer. The prognosis for lipoma is favorable. Surgical treatment is not always prescribed. However, if the invasive procedure was performed correctly and the doctor completely removed the capsule, relapse is unlikely.
Manifestation and features
Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in women over 40 years of age. If a neoplasm is detected in a young girl, this indicates a hereditary predisposition. Like other types of benign neoplasms, fibrolipomas can be transmitted from mother to daughter.
If we compare fibrolipoma with ordinary lipoma, their main difference is in size. In the first case, the size of the tumor can reach 10 cm in diameter. As a rule, growth does not stop on its own until quality treatment or surgery is carried out.
A diagnosed lipoma, if not properly treated, can progress to the next stage of its development – lipomatosis. This is a condition in which tumors form in all parts of the body in large numbers.
Also, for timely diagnosis, it is recommended to familiarize yourself with the features of the manifestation of the disease:
- The neoplasm is soft to the touch, but as it grows it becomes harder. Depending on the composition of the tumor, they are divided into lipofibromas, fibrolipomas, angioipomas, myolipomas and myxolipomas.
- This type of tumor rarely develops into liposarcoma, an oncological disease, but can contribute to the development of cancer. If the tumor reaches a large size, it displaces the surrounding tissue, which leads to breast deformation. A cosmetic defect, a rapid increase in size and suspicion of cancer are the main indications for surgery.
- If tumors form deep in the tissues, they cannot always be identified by palpation. In these cases, the tumors do not cause pain or discomfort. They are found during an instrumental diagnostic examination, for example, ultrasound or mammography.
The clinical picture of the disease is mild, however, with the rapid growth and deformation of the breast, the presence of pathology cannot be ignored. Leaving this state of affairs unattended is fraught with complications.
Why education is dangerous for women, men and children
Lipoma in the breast in most cases remains a benign formation. The risk that pathology will move into the field of oncology arises if:
- the formation is large in size;
- a wen on the nipple and there is a risk of mechanical damage to tissue (trauma, bruise);
- there is a chronic disease of internal organs;
- accompanied by decreased immunity or inflamed wen;
- During pregnancy, a woman developed clearly defined painful “bursting” sensations in the chest;
- on the man’s sternum, under the skin, a formed nodular formation of a spherical shape has formed, which increases in size and is accompanied by severe painful sensations.
It is important for men to pay no less attention to breast health than for women. In men, both benign formations (in the form of lumps, dense nodes) and malignant ones can form in the chest area, since in addition to fibrous tissue, the male mammary gland also consists of fatty tissue.
The chances of their development are higher in men suffering from gynecomastia - growth and thickening of breast tissue. The entire area may swell and become particularly painful. Infants also face a similar problem due to the effects of maternal hormones, as well as children during puberty.