Pregnancy for each woman is completely individual, although films always show how the newly-made expectant mother quickly runs to the toilet to get rid of the food she has eaten. This is toxicosis in pregnant women - morning vomiting and nausea. But you shouldn’t believe the cinema and, when two lines appear on the test, wait in horror for you to start feeling sick from just the sight of food. It is just as normal to experience toxicosis at the beginning of pregnancy as not to experience it.
Pregnancy not only proceeds in different ways, it can also end, unfortunately, in different ways, and this does not necessarily mean the birth of a small healthy person. One of the options for the development of events is the miscarriage of pregnancy; this does not happen very often, but, nevertheless, it does happen. Let’s try to figure it out together whether toxicosis continues during a frozen pregnancy.
Toxicosis during frozen pregnancy
Toxicosis: how to deal with it
So, some expectant mothers encounter toxicosis in the first trimester of pregnancy; by the second, it usually goes away on its own. Sometimes its symptoms manifest themselves in the third trimester, but this no longer applies to the normal course of pregnancy, and in this case we are talking about gestosis.
As for toxicosis, there is no way to get rid of it; it will go away on its own within the prescribed period. The only way to ease its course is to stubbornly wait for the second trimester. Due to constant vomiting and nausea, many expectant mothers do not gain weight, but, on the contrary, lose it. There is nothing terrible about this, but still the doctor must take control of this indicator.
In medicine, there are three stages of toxicosis, depending on the severity of its course: mild, moderate and severe.
Mild - the most typical, when nausea occurs up to 4 times a day, mainly in the morning or after meals.
Average characterizes attacks of vomiting, repeated up to 10 times a day. If it is not accompanied by an increase in temperature or an increased heart rate, then there is nothing terrible, although this form of toxicosis is difficult and very unpleasant to endure. In any case, the doctor monitors the condition of his ward and, if anything happens, can prescribe appropriate treatment.
The severe form is the rarest, but also the most dangerous. It is characterized by almost non-stop vomiting; any food is not retained in the body. In this case, urgent hospitalization is recommended.
In order to alleviate your condition and try to cope with the overwhelming toxicosis yourself, try following the following recommendations:
- Don't overeat. You need to eat often, but in small portions - these are the basics of proper nutrition, which do not allow the stomach to take on an extra load with all the ensuing consequences.
- Ventilate. Often, attacks of nausea and even vomiting are provoked by ordinary odors, so get into the habit of keeping the windows constantly open, at least when you are in the next room. Try not to cook strongly aromatic dishes now, listen to yourself and your feelings. It’s unlikely that even the most delicious homemade cutlets are worth at least a minute spent hugging the toilet.
- Drink more water, and let it be unboiled water from a proven source.
- Prepare a plate of crackers for yourself on the bedside table in advance the night before: if you suffer from toxicosis in the morning, chew them without getting out of bed!
Frozen pregnancy: signs and causes
As for frozen pregnancy, this condition is characterized by the cessation of fetal development in the womb, and a miscarriage is not at all necessary. This is the danger of miscarriage; a dead fetus can seriously infect a woman, and the longer it remains inside, the more dangerous the consequences. This is one of the reasons why the expectant mother should regularly visit an antenatal clinic and undergo all the necessary tests, because although this condition has some external signs, it is still extremely difficult to diagnose it yourself.
Most often, fading occurs in the first trimester of pregnancy, but sometimes it happens that the risk persists until delivery. In general, there are three most risky periods: 3-4, 8-11 and 16-18 weeks of pregnancy, and among them the 8th week is considered the most critical, when vital organs are formed in the fetus.
There can be many reasons for pregnancy failure, and these include, for example, pregnancy through IVF - artificial insemination increases the risk of developing pathology. Various genetic disorders, viral or infectious diseases, hormonal imbalance, depression, stress, excessive physical activity, smoking and drinking alcohol - all of these, even individually, can provoke a missed abortion, but some of the factors can occur simultaneously.
Obviously, the expectant mother can protect herself from such a deplorable event as pregnancy fading. To do this, you must first plan your pregnancy. This will allow us to study the genetic material of the spouses in advance and predict the course of a possible pregnancy, identify potential weaknesses in the development of the future baby and prepare in time for undesirable consequences, if any.
Having already become pregnant, the expectant mother should visit her doctor and get tested as often as the situation requires - an unexpected virus or infection can be caught in the bud, preventing it from negatively affecting the development of the baby.
And lastly, already at the pregnancy planning stage, future parents should lead a healthy lifestyle, spending more time in the fresh air and moderate exercise, forgetting about cigarettes and alcoholic drinks. Then the husband can relax, but the woman won’t have it any other way for the next 1.5 years!
It is clear that there are no 100% guarantees, even if a woman regularly visits a gynecologist, follows all his instructions and leads a healthy lifestyle, but at a minimum, she reduces the risk of such a terrifying outcome as miscarriage.
If this happens, the woman may not even realize that something went wrong, because at first signs of pregnancy, such as toxicosis or engorgement of the mammary glands, persist; they disappear only after some time. However, the disappearance of these signs, in turn, does not mean a terrible outcome. Signs of a frozen pregnancy include:
- A decrease in basal temperature can be noticed if it is regularly monitored, and it is measured in the morning without getting out of bed in the rectum.
- A decrease in the hCG value - in the first months of pregnancy it grows at a very rapid pace, and even a slight decrease in the indicator is a very alarming sign. You can track it by taking a general blood test on an empty stomach.
- Deterioration of the general condition - abdominal pain, spotting, increased body temperature - all this may indicate that the fetus is no longer developing. However, this can also indicate many other things - such an ambiguous sign!
Obviously, it is not possible to independently diagnose fading pregnancy, which is why it is so important to attend an antenatal clinic!
How to avoid fetal death?
To prevent fetal fading, a combination of factors that could provoke its undesirable termination should be eliminated before pregnancy occurs.
You should be tested for genetic abnormalities. Their result will allow the specialist to find out about the presence of weaknesses in the further development of the embryo, to predict as accurately as possible the likely difficulties in pregnancy and to prepare future parents for various consequences.
The expectant mother should introduce preventive measures so that the body acquires maximum resistance to infectious diseases. For example, strengthening the immune system with vitamins, doing daily exercises or jogging, it won’t hurt to just walk and breathe fresh air. You should avoid places where you are likely to get sick, such as infectious diseases departments of a hospital. If you have already visited one, you should take measures in the form of a face mask, and then wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
You should stop taking strong medications such as antidepressants or antibiotics. If the therapist has prescribed such medications, then warn him that you are planning to become a mother in the near future, and perhaps the doctor will recommend less aggressive medications.
In addition, future father and mother should lead a healthy lifestyle. You should give up cigarettes, alcohol and energy drinks, which have an adverse effect on the body.
While carrying a baby, avoid long-distance tourist trips or air travel. Prolonged exposure to the sun, as well as in a solarium and sauna, are not the best places for a pregnant woman to be.
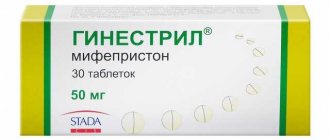
The answer to the question, does toxicosis occur when the fetus freezes? More than clear. Can not be. After fading, it lasts for a maximum of two days.
No one is immune from such an outcome, but over time a woman can become pregnant again. Further pregnancies often result in the birth of a healthy baby.
Does toxicosis occur during frozen pregnancy?
The fact is that toxicosis is one of the possible companions of pregnancy in the first three months, but if the fetus freezes, then there is no longer pregnancy, then toxicosis stops. Not sharply, but quite quickly - within a maximum of two days.
If toxicosis persists during a frozen pregnancy, then most likely either very little time has passed, or the condition is caused rather by psychological reasons.
How to identify a non-developing pregnancy
If the embryo has stopped developing, then there are two options for a woman’s behavior: she will either feel a problem or not. Much depends on the timing. In the first trimester, signs of a frozen pregnancy may not appear until the onset of intoxication. At later stages, the symptoms are more obvious, and the main one is the absence of fetal movement. Read more about the features of the manifestation of symptoms at different periods.
Early in the first trimester
How to determine a frozen pregnancy before 12 weeks? Facts that may indirectly indicate fetal death include:
- Sudden disappearance of toxicosis. Due to the death of the fetus, the woman loses nausea and dizziness.
- Painful sensations in the nipples disappear: due to a decrease in prolactin, they are no longer swollen.
- Heavy bleeding, similar to menstruation.
- Decrease in basal temperature.
In the second trimester
All of the above symptoms are possible. Changes occur in the uterus: when palpating, the doctor discovers that its size does not correspond to the gestational age. To clarify the diagnosis, an ultrasound scan is required. In the second trimester, many signs of toxicosis disappear, but when the child dies, they return and appear doubly stronger. The breasts become rough and intense discharge is possible. If you suspect fetal death, you should not run to the pharmacy for tests - even after his death, they can show positive results.
At a later date
The most important symptom during this period is the absence of fetal movement. He must push about 10 times a day, otherwise the pregnancy may be stopped. After the death of the fetus, the woman experiences a feeling of weakness, dizziness, drowsiness, and loss of appetite. Over time, the breasts become soft and lose their elasticity. Hormonal levels return to normal.
Toxicosis and fetal death
When the fetus in the uterus stops developing, the woman, of course, does not know about it. But all the signs of pregnancy that she experienced before stop. After all, they were associated with hormonal changes in the body. If she suffered from toxicosis, which was accompanied by vomiting, weakness, and a reaction to odors, then it stops - and her condition improves, and quite quickly, in a day or two. This is why toxicosis during fetal death is impossible. If a woman’s vomiting increases and her temperature rises, then most likely these are signs of infection. It is likely to spread rapidly, requiring immediate treatment.
If a woman experienced signs of toxicosis during pregnancy and suddenly began to feel well, then it makes sense to consult with a supervising gynecologist to eliminate possible risks. A frozen pregnancy that does not result in a miscarriage is dangerous. This is a risk of developing infection, suppuration, and sepsis. Then the apparent symptoms of toxicosis are actually signs of intoxication of the female body caused by the death of the fetus.