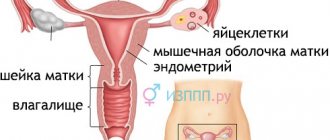
Sexually transmitted diseases or sexually transmitted infections are a group of diseases that are caused by bacteria and protozoa, fungi and viruses. This group of infections has become widespread among people who are promiscuous and do not use condoms, who are prone to an antisocial existence, alcoholism and drug addiction. Without exception, all STIs have long-term consequences, including damage to the central nervous system, liver, bones and other organs.
Causes of STIs
It is not for nothing that genital infections that are predominantly sexually transmitted are named after the goddess Venus - infection with them in most cases occurs during close contact with the carrier of the disease. Most often this occurs during sexual intercourse without the use of barrier contraceptives.
The causative agents of infection may be:
- in the host's saliva;
- on the skin (most often near the mouth, in the perianal area, in the perineum);
- in seminal fluid and vaginal secretions.
You can become infected with an STI without direct contact with a carrier. Infection often occurs when using shared utensils, towels, shaving machines, sponges and washcloths. This transmission route is called household.
Important! Even bar soap can become a source of infection. Despite its properties to destroy pollution, it is a good breeding ground for many STI pathogens.
Sexually transmitted infections are not as harmless as they might seem at first glance. Among the complications that arise after an STI are infertility and miscarriage in women, prostatitis and impotence in men, liver and central nervous system diseases.
What diseases are classified as STIs?
Sexually transmitted infections are numerous and varied. The modern classification contains at least 300 diseases that first affect the reproductive system and then other human organs. The causative agents of STIs can be bacteria, viruses, protozoa, protozoans, fungi and parasites.
Important! Candidal and nonspecific urethritis and colpitis, bacterial vaginosis, provoked by opportunistic microflora, do not belong to sexually transmitted diseases.
Bacterial infections
Bacterial infections, predominantly sexually transmitted, are considered the most numerous among all STIs. This category of diseases includes:
- inguinal and venereal granulomas;
- syphilis;
- chlamydia;
- gonorrhea;
- mycoplasmosis;
- ureaplasmosis.
There are other bacterial infections that are predominantly sexually transmitted, which are extremely rare in Russia and the post-Soviet space. For example, chancroid, caused by the bacterium Haemophilus ducreyi, is diagnosed mainly in the inhabitants of Africa and America.
Viral infections
Viral infections that are sexually transmitted are less numerous than bacterial ones, but the number of people infected by them reaches impressive figures.
According to statistics from the World Health Organization, at least 50% of sexually mature people on the planet are infected with the human papillomavirus, and this disease also falls under the category of STIs.
The peculiarity of viruses that can be infected during sexual intercourse is that they can remain in an inactive state for a long time, and appear when immunity decreases or against the background of other diseases. The most common are the following viral sexually transmitted infections:
- human immunodeficiency virus (HIV);
- herpes simplex virus;
- human papillomavirus (HPV);
- cytomegalovirus;
- Hepatitis B.
This is not a complete list of viral sexually transmitted infections. These also include Kaposi's sarcoma, Zika virus and other diseases that are diagnosed in a relatively small number of people.
Protozoal infections
Protozoal infections include diseases of the reproductive system, the causative agent of which is Trichomonas vaginalis. According to statistics, trichomoniasis is the most common disease among all sexually transmitted infections.
According to the World Health Organization in 2000, at least 10% of all people on Earth, including newborns and the elderly, are infected with these microorganisms.
Fungal infections
Fungal infections that are sexually transmitted are represented by thrush. Its occurrence is due to the increased activity of the opportunistic microorganism Candida albicans, a yeast-like fungus that lives on the mucous membranes of the mouth, vagina, and large intestine.
The disease develops against the background of a decrease in general and local immunity, microflora imbalance, and after long-term use of antibiotics.
Parasitic infections
Parasitic sexually transmitted infections are represented by two diseases:
- phthiriasis (pediculosis pubis), the causative agent of which is the pubic louse;
- scabies, the causative agent of which is the scabies mite.
Almost all sexually transmitted infections, even if they are asymptomatic, are fraught with complications. Most often they manifest themselves as infertility, miscarriage, chronic inflammation of the uterus and appendages, and prostate gland. Certain types of STIs provoke the formation of benign and malignant tumors.
List of hidden pathologies
In the list of hidden infections in women, the “leaders” are:
- Herpes virus;
- HPV (human papillomavirus);
- Gardnerellosis;
- Thrush (candidiasis);
- Microplasmosis;
- Ureaplasmosis;
- Chlamydia;
- Cytomegalovirus.
All of these gynecological infections have their own characteristics, they are defined differently, and each disease has its own treatment methods.
Herpes virus
The disease is caused by various viruses living in the female body. Doctors say that it is almost impossible to get rid of herpes forever, because the slightest decrease in immunity leads to a new round of symptoms of the disease.
Most often, women complain of red spots in the perineal area, pain and itching. Later, these bubbles burst, leaving small but very aching wounds in place.
Top article: Causes of pain and burning when urinating in men
If the problem is not solved for a long time, it can lead to:
- encephalitis;
- meningitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- keratitis;
- damage to the central nervous system.
Human papillomavirus
Female infections such as HPV lead to the appearance of warts and condylomas on the mucous membranes.
Often the disease occurs in a latent form, practically not manifesting itself at all. It is usually detected during a full examination.
The first alarming symptom of human papillomavirus infection is the appearance of genital warts or warts in the mouth, lips, and groin. If at the same time a woman is diagnosed with cervical erosion, she should immediately undergo an examination.
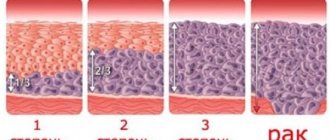
Without proper treatment, HPV very often leads to various types of cancer.
Gardnerellosis
Gardnerellosis or Gardnerella vaginalis is bacterial vaginosis or vaginal dysbiosis. The disease is caused by bacteria that are found in small quantities in the vagina of every representative of the fairer sex. Reproduction usually occurs either during a decrease in immunity, as well as during a period of hormonal imbalance.
These sexually transmitted infections in women are less dangerous, unlike HPV, but they must be diagnosed and treated.
Common symptoms indicating the presence of bacterial vaginosis include:
- copious discharge of white or grayish secretion with an unpleasant odor;
- itching in the genital area;
- pain during intercourse.
In advanced stages, the disease can lead to:
- The appearance of urethritis.
- Inflammation of the vagina.
- Premature contractions.
- Inflammation of the appendages, cervix and uterus.
- I'll miscarry.
Candidiasis (thrush)
Candida infection (Candidosis) is known to almost every girl. And, despite the fact that many people are familiar with the symptoms of the disease, they cannot be ignored.
The onset of candidiasis may be indicated by:
- Painful sensations during urination and lovemaking.
- White (curd-like) vaginal discharge.
- Itching and burning in the perineal area, increasing over time.
Candidiasis is not one of those hidden infections in women that poses some kind of threat to the woman’s health or life, but there is no point in delaying the solution to the problem.
Top article: Sexual infections in men: consequences of improper treatment
Mycoplasmosis
The disease is caused by microorganisms such as Genitalium or Mycoplasma hominis, which parasitize on the surface of cells of the genitourinary system.
A woman may not know for a long time that she has mycoplasmosis. Only in some cases, clear vaginal discharge may appear and pain may be felt during urination.
The danger lies in the fact that microorganisms lead to the appearance of other ailments affecting:
- vagina;
- urethra;
- appendages;
- cervix and uterine cavity;
- the development of the placenta is disrupted;
- infertility appears;
- polyhydramnios;
- miscarriages occur.
Ureaplasmosis
The development of the disease is provoked by the bacterium Ureaplasma urealyticum. As with mycoplasmosis, it is rare to experience any symptoms. This is actually why these are hidden infections that are important to recognize.
If the disease is not diagnosed in time, the following complications may appear:
- fetal pathology;
- inflammation of the fallopian tubes;
- narrowing of the urethra;
- formation of adhesions.
Chlamydia
Many people have heard about chlamydia. This is a disease caused by a microorganism such as Chlamydia Trachomatis. The disease is asymptomatic. Sometimes a woman may notice an increased need to go to the toilet, pain or pain during urination.
A disease that goes untreated for a long time leads to the appearance of more pronounced symptoms.
These are:
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- lower abdominal pain;
- weakness;
- temperature increase.
Chlamydia must be diagnosed and treated because it affects other organs.
And problems may already arise with:
- cervix;
- fallopian tubes;
- rectum peritoneum;
- ovaries;
- peritoneum of the fallopian tubes.
Cytomegalovirus
Cytomegaly is a disease that is provoked by a type of herpes virus type 5 - Cytomegalovirus (CMV). People with strong immunity may not know for years that they have the virus.
Very often, the symptoms of cytomegalovirus are similar to the symptoms of a common cold. Therefore, a hidden infection is not diagnosed immediately. The disease is most severely experienced by people with weak immune systems and in adulthood.
Sometimes the disease leads to complications such as
- gastroenteritis;
- premature birth;
- pneumonia;
- intrauterine fetal death;
- miscarriage;
- hepatitis;
- encephalitis;
- inflammation of the spleen;
- arthritis.
Top article: Miramistin and sexually transmitted infections
If a disease is detected, it should be treated immediately. Gynecological infections are a rather complex thing, but they can be diagnosed and eliminated. The most important thing is to contact medical specialists in a timely manner.
Diagnostics
To diagnose sexually transmitted infections, a standard set of methods is used:
- visual inspection;
- laboratory research;
- instrumental studies.
Based on complaints and the results of an external examination, the doctor can guess what kind of infection the patient has:
- Bacterial infections are characterized by the appearance of discharge from the genital tract and urethra, enlarged lymph nodes in the groin, inflammation of the mucous membranes of the genital tract, the formation of ulcers, buboes, rashes, condylomas lata, depending on the type of pathogen;
- Viral infections are characterized by an asymptomatic course; when infected with certain varieties of the virus in the groin and perianal area, growths, vesicles, and weeping ulcers appear on the external genitalia;
- fungal infection is expressed by itching, copious discharge from the genital tract, discomfort when urinating, plaque on the external genitalia;
- parasitic infections are expressed by severe, unremitting itching in the groin and perineum, scratches and rashes are visible on the skin.
Laboratory diagnosis of STIs includes a number of studies of biological samples:
- direct and fluorescent smear microscopy;
- cultural method of smear examination;
- detection of antigens of pathogens of sexually transmitted infections in the blood - direct immunofluorescence and enzyme-linked immunosorbent test;
- DNA detection of STI pathogens using polymerase chain reaction;
- detection of antibodies to pathogens of sexually transmitted infections in the blood.
Additionally, instrumental studies may be prescribed - ultrasound of the pelvic organs (uterus and appendages, prostate), liver and abdominal organs (if hepatitis is suspected) and others.
Treatment
Treatment methods for sexually transmitted infections depend on the type of disease and pathogens detected during diagnosis. The basis of therapy is taking medications internally and using them externally. Additionally, immunomodulatory and immunostimulating agents and drugs are prescribed to help restore the functions of organs and systems affected by the disease.
The groups and names of drugs used to treat sexually transmitted infections are given in the table:
| Types of pathogens | Drug groups | Names of medicines and scope of application |
| Bacterial genital infections | Antibiotics |
|
| Antiseptics | Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Betadine solution. | |
| Immunomodulators | Panavir, Interferon. | |
| Probiotics (prescribed additionally) | Probifor, Bifidumbacterin, Acylact, Linex, Bifiform and others. | |
| Viral STIs | Antiviral and antiretroviral drugs | Phosphazide, Abacavir, Zidovudine. |
| Immunomodulators | Herpferon, Viferon, Ribavirin, Acyclovir, Valtrex, Trizivir, Viramune. | |
| Hepatoprotectors (additionally prescribed) | Ursosan, Phosphogliv, Galstena, Essentiale Forte. | |
| Protozoal infections | Antibiotics and antiprotozoal drugs | Levomecitin, Metronidazole, Tenonitrozole (Atrican), Tinidazole, Nimorazole (Naxojin). |
| Hepatoprotectors (additionally prescribed) | Ursosan, Phosphogliv, Galstena, Essentiale Forte. | |
| Fungal infections | Antifungal agents | Fluconazole, Itraconazole, Clotrimazole, Pimafucin, |
| Probiotics | Probifor, Bifidumbacterin, Acylact, Linex, Bifiform. | |
| Immunostimulants | Viferon, Ribavirin, Acyclovir, Valtrex, Trizivir. | |
| Parasitic infections | Antiparasitic agents |
|
Treatment for sexually transmitted infections may also include surgery and minimally invasive interventions. They are especially often used when signs of HPV (genital warts) appear on the genitals and in the perianal area. New growths are removed with a laser, radio wave method, or excised with a regular scalpel.
Important! HIV, AIDS, herpes types I and II, HPV and hepatitis C cannot be cured forever. Patients will have to adapt to life with them and take special medications constantly or in separate courses.
Elimination of sexually transmitted infections will be effective only if both sexual partners undergo the course of therapy. During treatment, it is advisable to abstain from sex or use barrier contraceptives.
Symptoms of the disease
Doctors advise women to pay special attention to the following symptoms, which often appear after unprotected sex with a partner.
Namely:
- Itching and burning that appear in the labia area.
- Rash and redness on and near the genitals.
- Unusual discharge with an unpleasant odor.
- Unpleasant sensations during intimacy.
- Frequent urge to urinate, pain and cramping after urination.
Even a small symptom makes you think about a hidden infectious disease.
When women already have hidden infections, the symptoms are more serious, which gives reason to necessarily diagnose the disease and undergo a course of treatment.
What women should pay attention to first:
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- constant pain in the pelvis;
- infertility or miscarriage (repeating repeatedly).
The hidden danger of sexually transmitted diseases has a rather detrimental effect on women's health.
STI prevention
The first stage of preventive measures is to convey information to young people about what sexually transmitted infections are and the dangers of contracting them. According to statistics, more than 20% of venereologist patients do not know the basic rules of contraception or ignore them. Meanwhile, to avoid unpleasant diagnoses and their negative consequences, it is enough:
- use barrier contraceptives, preferably condoms;
- have an orderly sex life and do not change partners too often;
- avoid casual sexual contacts;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- do not use other people’s personal hygiene items (toothbrush, shaving machine, etc.).
In the prevention of infections that are predominantly sexually transmitted, timely detection of diseases plays a special role. Men and women of puberty are advised to regularly undergo tests for dangerous infections such as hepatitis C, HIV, syphilis and others. Such tests are considered mandatory for pregnant women and those whose work involves direct contact with people: doctors, cooks, service personnel, teachers, drivers and others.
If you suspect an STI infection, it is advisable to undergo a full examination. Today this can be done anonymously in private clinics and laboratories. It is necessary to treat sexually transmitted infections immediately after they are identified and only under the guidance and supervision of a venereologist.
STI test
Testing for sexually transmitted infections is the main diagnostic method in gynecology. These studies are completely safe and painless for a woman and very informative for a doctor.
What tests should be taken for sexually transmitted infections:
- Microflora smear
- Bacterial culture with selection of antibiotics
- Florocenosis
- PCR analysis 12-18
- NASBA RNA Assays
- Blood test ELISA and PCR.
How to prepare properly
- 1-2 days before visiting the doctor, refrain from intimacy;
- Before taking an STI test from the urethra, it is recommended not to urinate for 2 hours.
- On the eve of going to the clinic, it is recommended to carry out a provocation. The simplest and most reliable method is considered to be food (alcohol, salty, spicy).
- If possible, it is best for girls to get tested for sexually transmitted infections before or immediately after their period.
Places (points) of capture. Women (F), virgin girls (D) and men (M) can get tested for sexually transmitted infections from the following places:
| Take points | M | AND | D |
| "C" - cervix | — | + | — |
| "V" - vagina | — | + | + |
| "U" - urethra | + | + | + |
| "R" - rectum | + | + | + |
| "O" - oropharynx | — | + | + |
Diagnostics
How much does it cost to get tested for sexually transmitted infections, ₽
| List of studies | Price |
| STI smear | 550 |
| Gram microscopy | 750 |
| Sowing on flora and a/h | 1 750 |
| PCR tests | 450 |
| Florocenosis, from | 3 000 |
| NASBA | 1 300 |
| Blood test for syphilis | 750 |
| Test for HIV (AIDS) | 750 |
| Blood test hepatitis B, C | 750 |
| Rapid blood tests | 750 |
| Taking blood from a vein | 450 |
| Taking material | 450 |
home
Where to get tested for STIs
We invite women and men to get tested for STIs in our paid clinic in Moscow. During the consultation, the doctor will listen to your complaints and, based on them, recommend the optimal list of studies. Once the analysis result is ready, we can offer to draw up an individual treatment regimen for sexually transmitted infections. Remember that timely contacting a doctor when symptoms of ill health appear will allow you to solve the problem faster and with less loss of time and effort!