One of the reasons for disrupting the natural balance of microflora in the vagina is an imbalance of microflora in the intestines. E. coli can enter the genitals and provoke the development of inflammatory processes. To solve this problem, an integrated approach is required: in some situations, not only a consultation with a gynecologist is required, but also an appeal to a gastroenterologist.
Intestinal flora from the rectum can enter the vagina. This triggers inflammation, profuse discharge and a feeling of discomfort. This is how colpitis develops (it is also called vaginitis). More often, this pathology occurs during reproductive age. If treatment is not started in time, the inflammatory process can spread to the cervix, uterus and appendages.
Causes
The most common reason for getting e. coli in the vagina is an incorrect way to wash. If the hygiene procedure is carried out in a back and forth direction, then E. coli can enter the genitals. However, this is far from the only reason; the general list should also include:
- Wearing tight underwear made of synthetic materials, in particular thongs.
- Sexual contacts combining anal and vaginal sex. It cannot be said with certainty that E. coli is transmitted sexually, but such sexual activity contributes to the entry of one’s own e. coli in the vagina.
- Frequent douching.
- Metabolic and endocrine pathologies (diabetes mellitus).
- Reduced functionality of the immune system.
- Taking antibiotics.
- Chronic infectious diseases, both general and reproductive system.
- Sudden changes in ambient temperature (cold and hot).
The anatomical features of the location of the anus and the entrance to the vagina make it possible for Escherichia coli to enter the genitals. Therefore, to prevent infection, it is extremely important to maintain good hygiene.
Treatment options for infection
As during pregnancy, treatment should include several effective techniques . You should definitely use an antibiotic, since using diuretics exclusively does not give any result.
E. coli clings tightly to the walls of the vagina and urethra, which makes it impossible to wash it out. The use of an antibiotic weakens the grip, causes death and gradual elimination of bacteria from the body.
The anti-inflammatory drug relieves irritation, relieves pain and swelling of the genital organs.
Symptoms
The list of symptoms accompanying colpitis caused by E. coli infection includes the following:
- the appearance of vaginal discharge in a large volume, whitish or transparent, with an unpleasant odor;
- feeling of burning and itching;
- a feeling of constant discomfort, especially during sexual intercourse.
Active progression of the inflammatory process causes a sharp increase in the severity of clinical symptoms. The volume of discharge increases; from transparent or white, it can become purulent yellow-greenish.
Colpitis caused by E. coli is extremely dangerous during pregnancy. Escherichia coli is capable of crossing the placental barrier and causing meningitis in the fetus, which manifests itself after birth.
What is Escherichia coli?
This is a bacterium that lives in the human intestines and really looks like a small stick. It has many different strains that are involved in the synthesis of vitamin K and take care of human safety by destroying harmful bacteria. But some types of E. coli can be dangerous during pregnancy, especially if they enter the body orally.
For expectant mothers, E. coli is dangerous if it has settled on the vaginal mucosa or in the bladder. Since it causes inflammation, dysbiosis and other problems. Symptoms of vaginosis or colpitis caused by E. coli are itching, unpleasant odor of discharge and even burning.
Treatment
Treatment of colpitis involves an integrated approach and is prescribed by a gynecologist after a bacteriological examination of biomaterial obtained from the vagina. This diagnostic method allows you to identify a specific strain of the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to drugs. To remove E. coli from the vagina, a course of antibiotics is required.
Important! Under no circumstances should course therapy be interrupted, even if the symptoms have subsided. The duration of taking prescribed medications should be observed. You should not resort to folk remedies - this can significantly aggravate the condition.
In addition to antibiotics, comprehensive correction of colpitis caused by E. coli includes anti-inflammatory and probiotic drugs, as well as some local procedures. It is suggested to prescribe vaginal suppositories with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory components. We recommend washing with chamomile decoction, as well as physiotherapy (UV therapy).
How to treat inflammation in a specific clinical situation is determined by the doctor. Therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis and does not require hospitalization. Regular medical supervision is important. At the end of the course of treatment, diagnostics are required to confirm the effectiveness of the measures taken.
Medication
To suppress pathogenic microflora, the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics, namely:
- Oral preparations, the active components of which may be metronidazole, clindamycin phosphate, tinidazole.
- Vaginal suppositories, gels and creams for E. coli: Clindess, Metrogyl, Kleotsin.
In order to suppress the activity of the pathogen, an antiseptic agent for local treatment, Miramistin, is additionally prescribed. This medication helps reduce the resistance of flora to antibiotics.
To restore the natural balance of vaginal microflora after the use of antibiotics, it is necessary to prescribe antifungal, probiotic and immunomodulatory agents. It is rational to use such probiotics with lactobacilli:
With the help of these medications, it is possible to restore the balance of the vaginal microflora.
Kagocel, Likopid, Viferon can be prescribed as immunomodulators. Complex therapy also involves following a special diet including a sufficient amount of fermented milk products.
Prevention
In order to prevent infection, as well as to prevent the spread of the pathological process at the beginning of its development to the cervical canal and uterus, the following recommendations must be followed:
- Carry out proper hygiene procedures (washing should be done from front to back) and observe their frequency: at least twice a day. After the procedures, you should wear clean underwear.
- Use special intimate hygiene products. Lactacid, Epigen intimate can be purchased in pharmacies.
- Avoid too tight, synthetic underwear, as well as thongs.
- Do not exceed the frequency of douching prescribed by a specialist.
- Promptly treat chronic infectious diseases, as well as metabolic and endocrine pathologies.
Diagnostics
The therapeutic intervention regimen is determined after receiving the results of a smear taken from the cervix. In order for the examination result to be accurate, it is important to comply with the following conditions:
- one day before the examination, exclude sexual intercourse;
- stop using vaginal tablets and suppositories for 2-3 days;
- On the day of the smear test, carry out the hygienic procedure without using soap or any cosmetic chemicals.
A smear for Escherichia is considered positive when E. coli is detected in the cervical canal, provided that a trend towards a decrease in the number of lactobacilli is detected.
Causes of infection
E. coli can penetrate the vaginal cavity and actively multiply in it. If for the intestines the presence of a bacillus is considered a physiological norm, then for the genitals this becomes a prerequisite for the development of bacterial vaginosis, or vaginitis.
Most often, this pathology occurs in women of reproductive age. Infection from the vagina can spread to the bladder, urethra and genital skin. It is quite dangerous, and the chronic course of the disease can cause serious complications that are difficult to treat: endometritis, adnexitis, cervical erosion, cervicitis.
Anatomically, in women, the entrance to the vagina is located close to the anus, and therefore the spread of opportunistic E. coli occurs almost unhindered.
The reasons why infection occurs and the vaginal ecosystem changes:
E. coli in the vagina can colonize and actively multiply against the background of weakened immunity and sudden temperature changes (heat or cold), during menopause, from frequent douching, endocrine and metabolic disorders. Provokes the colonization of pathogenic microflora by long-term use of antibacterial drugs, chronic general and sexually transmitted infections.
Causes and classification
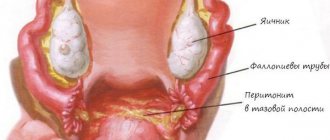
The cervix is the narrowest part of the uterus and communicates with the vagina. The cervix has the shape of a cylinder and is pierced through by a narrow cervical canal, which is like a continuation of the uterine cavity. Normally, it is closed by a dense mucous plug, which protects the overlying genital organs from the penetration of microorganisms from the external environment into them. It is produced by cells of the mucous layer of the cervical canal.
The structure of the female reproductive system
They are hormone-dependent, so the viscosity of the mucus depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. During ovulation, their secretions thin out to make it easier for sperm to penetrate from the vagina into the uterus. Accordingly, at the same time, the risk of infection of the overlying female genital organs increases.
Under the mucous layer there is a muscle layer - it is quite powerful, since during pregnancy it is responsible for holding the growing fetus in the uterine cavity. A dense serous membrane separates the cervix from other organs. The cervix has two parts:
- Ectocervix - it is seen by the gynecologist in the vagina when examined in the mirrors. This is the outer part of the neck, it looks like a dense disk with a hole in the middle. Covered with flat non-keratinizing epithelium, the same as the walls of the vagina.
- The endocervix is a part invisible to the eye during normal examination that directly passes into the uterus. From the inside it is lined with secretory columnar epithelium, into which microorganisms easily penetrate during various types of infections.
The inflammatory process can be localized in:
- Exocervix – exocervicitis;
- Endocervix – endocervicitis;
- In both parts of the cervix there is cervicitis.
Since the cervix and vagina are closely connected to each other, it is extremely rare that cervicitis develops in isolation. As a rule, it is a consequence of colpitis, bakvaginitis or vulvitis and easily turns into endometritis - inflammation of the mucous layer of the uterus.
Due to the inflammatory process there are:
- Nonspecific cervicitis - it is caused by opportunistic bacteria that live on the skin and in the rectum (Escherichia coli, staphylococci and streptococci) when they are introduced into the woman’s genital tract. In addition, it also develops under conditions of insufficient estrogen production during menopause and ovarian hypofunction.
- Specific - it occurs when exposed to STI pathogens, most often gonococcus, chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, genital herpes virus, yeast-like fungus candida. Tuberculous cervicitis of the cervix also occurs if Koch's bacillus penetrates it with the flow of blood or lymph from foci of tuberculosis.
According to the duration of the flow, they are distinguished:
- Acute cervicitis – lasts up to 2 weeks;
- Subacute – from 2 weeks to 6 months;
- Chronic – over six months. It is characterized by periods of remission - subsidence of the symptoms of the disease and exacerbation, when they gain strength again. The causes of chronic cervicitis are usually chlamydia, mycoplasma and ureaplasma, as well as hormonal imbalances.
In a healthy woman, the cervical canal is reliably protected from infectious agents, since its mucus contains lysozyme and immunoglobulins - substances that are harmful to them. The normal microflora of the vagina also plays an important role: it prevents the proliferation of pathogenic microbes, acidifying the environment. Cervicitis develops under the influence of provoking factors, which include:
- Childbirth, abortion;
- Invasive interventions (hysteroscopy, IVF);
- Infectious diseases;
- Exacerbations of chronic diseases;
- Hormonal disorders;
- Metabolic diseases;
- Injuries of the pelvis and female genital organs;
- Lack of personal hygiene.
All of them lead to local and general immune disorders and create a favorable situation for the introduction of the pathogen into the epithelium of the cervical canal.
Symptoms
Initial infection does not manifest itself with pronounced clinical signs.
At the stage of active reproduction, opportunistic E. coli produces abundant clear or white discharge. Their smell is pungent and unpleasant. With the development of the pathological process, vaginal mucus becomes purulent and foul-smelling. A woman complains of itching and burning of the mucous membranes and skin.
Colonization with opportunistic enterococcus is especially dangerous in pregnant women. Bacteria easily penetrate the placenta and can cause meningitis in a newborn.
Therapy
An E. coli infection should be treated by a specialist. Self-medication and traditional methods are completely excluded in the acute stage.
Before undergoing the necessary therapeutic course, the patient undergoes a bacterial culture. The study will accurately determine the strain of the pathogen, and this will determine the intensity and duration of drug therapy.
Comprehensive treatment of E. coli includes antibacterial drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, probiotics, and local procedures.
In gynecology, vaginosis caused by E. coli is treated on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a doctor. Local procedures include washing with chamomile infusion, medicinal douching, and administering vaginal suppositories with nystatin. The doctor prescribes a course of physiotherapy: ultraviolet irradiation on the genitals.
Antibacterial therapy
To suppress pathogenic microflora, a course of antibiotics is prescribed for 7 days. For vaginosis caused by E. coli, the following are indicated:
- Oral preparations based on clindamycin phosphate, metronidazole and tinidazole: Cleocin, Flagyl, Tindamax. Pros of taking: allowed for treatment during pregnancy. Disadvantage: drugs can cause side effects such as a metallic taste in the mouth and dyspepsia.
- Vaginal antibiotics (suppositories, creams, gels): Metro-gel, Kleotsin, Clindess. Advantages of local treatment: symptomatic side effects are excluded, the drug acts directly on pathogenic microflora. Disadvantage: vaginal route of administration is contraindicated during pregnancy.
To suppress pathogenic E. coli, the antiseptic Miramistin is additionally prescribed. The product reduces the resistance of flora, enhances the effect of antibiotics, and stimulates the body's immune response.
Maintenance therapy
In order to restore the vaginal microflora, probiotic and antifungal agents and immunomodulators are prescribed after antibacterial treatment. Medicines for maintenance therapy:
- Probiotics with lactobacilli: Laktogin, Vagilak, Gynoflor. The drugs restore normal pH levels and stimulate the development of healthy microflora.
- Immunomodulators Likopid, Kagocel, Viferon. The tablets prevent and stop purulent-septic processes and strengthen the immune system.
Complex treatment necessarily includes a diet with a sufficient amount of fermented milk products.
Prevention
To prevent infection of the vagina by pathogenic microflora, a woman must follow several important but basic rules. Points that must be observed:
To prevent the development of bacterial vaginosis, a woman should undergo regular examinations with a doctor. If the pathogen is identified in the early stages and treatment is started on time, the prognosis for full recovery will certainly be positive.
The human body contains a lot of positive and opportunistic microorganisms that are necessary for its normal functioning and the proper functioning of the immune system? synthesis of vitamins and a number of other necessary substances.
What it is
The microorganism was isolated back in 1885. Today many of its varieties are known. Their mass is harmless and necessary for the intestinal microflora. Escherichia coli is involved in the synthesis of a number of vitamins: K, group B.
But there are more than a hundred types of pathogenic microorganisms that can cause serious illness or poisoning.
Even opportunistic bacteria, getting from the intestines to other organs, can pose a danger.
The normal habitat of the stick is the area of the large intestine located closer to the anus.
In small quantities, this bacterium is present in the vagina, but when it multiplies, it leads to problems - bacterial vaginosis and others.
What happens in the body
Microorganisms enter the cervix through:
- Vagina - during unprotected sexual intercourse or with insufficient hygienic care;
- Blood or lymph - from foci of chronic inflammation that are located in any part of the body.
Having penetrated the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, the pathogen begins to actively multiply, releasing its metabolic products into the surrounding tissues. The latter cause cell death and a reaction of the immune system, and therefore an inflammatory process develops. At the injection site, blood stagnates, blood vessels dilate and their permeability increases. Liquid plasma, together with immune cells, enters the tissue and forms edema - this is how the source of inflammation is localized. If the first reaction is adequate, then the pathogen cannot spread beyond the mucous membrane and inflammation is limited only to it. After this, the foreign microflora is destroyed and removed from the cervical canal along with mucus, and the damaged tissue is gradually restored.
With an insufficient immune response or certain characteristics of the pathogen, inflammation becomes chronic. The microorganism remains in the body for a long time, as it is able to penetrate inside cells or evade the immune response and the action of antibiotics in other ways. From time to time it becomes active, destroys tissue, and causes inflammation. As a rule, exacerbations are of low intensity, but prolonged damage to the mucosa and deeper layers leads to excessive growth of connective tissue. As a result, the cavity of the cervical canal narrows, becomes deformed, or mucous cysts form in its thickness. They appear when the connective tissue elements close the excretory duct of the cervical gland. The cells of the latter continue to produce mucus, which accumulates inside the cavity, gradually stretching it. The cyst grows in size and can significantly disrupt the anatomy of the cervix. A chronic focus of inflammation is fraught with another danger. Damage to epithelial cells sooner or later leads to their degeneration - dysplasia followed by malignancy.
Reasons for appearance
Reasons why a microorganism can enter the vagina:
- Inadequate hygiene, improper washing . The vagina and anus are located nearby, so you need to wash yourself not from bottom to top, but from top to bottom to prevent the introduction of pathogenic microbes.
- Wrong underwear . Microorganisms can get into the vagina due to wearing tight underwear and thongs. Many people like the latter - it’s beautiful, sexy, but it’s still better not to abuse them, choosing health over beauty.
It is worth choosing underwear made from natural materials. Unprotected sex . You can get E. coli through combined anal-vaginal contact. Therefore, lovers of variety in bed need to be careful about protective equipment.
Constant change of sexual partners, weakened immunity and frequent douching increases the risk of getting the bacillus into the smear.
Menopause - what is it, how to determine its onset and how to relieve symptoms? We have a very interesting article on this topic on our portal.
About the symptoms and treatment of chronic urethritis in women; You can find out what medications are used for this here on the website.
Don’t know what colpitis is in women, what are the features of its treatment? We have an interesting article that is worth reading.
Associated symptoms and signs
The first signs of the presence of E. coli in a smear may appear a day or even a week after it enters. Characteristic symptoms:
- severe diarrhea;
- heat;
- vomiting with greenish impurities;
- unpleasant pulling sensations in the stomach;
- constant nausea;
- lack of appetite;
- general malaise.
Symptoms usually disappear on their own within a couple of days. The reason for this is spontaneous sanitation of the intestines . But if this condition does not go away for more than two days, consult a doctor.
How to get rid of an infection
If E. coli was detected in a vaginal smear, this is a serious reason to start treatment as early as possible . Of course, only a doctor can describe his tactics correctly. Antibacterial drugs are mainly used.
What drugs are prescribed
Sometimes local therapy is sufficient, but if the lesion is quite serious, more thorough treatment is required. Antibacterial correction is carried out on the basis of an antibiogram of the identified pathogen.
Often drugs from the fluoroquinolone group are used - Levofloxacin or Ciprofloxacin. The required dosage and duration of treatment is determined only by the doctor. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances, as this may cause the microorganism to become resistant to antibiotics.
Consider popular antibacterial drugs:
- Monural . Available in the form of a colorless granular powder, which must be taken after dissolution with water. The effect is determined by the presence of phosphonic acid derivatives. This remedy is a broad-spectrum antibiotic and can be prescribed to pregnant women.
It is usually recommended to consume 3 grams once a day. If the infection is severe, the drug may be combined with other antibiotics.
- Suprax . Available in capsule form. The main active substance is cifixime. Used for a number of infections, in particular E. coli. It is often prescribed together with Canephron, which simultaneously protects the urinary tract from infections. This is a strong antibiotic.
- Fosmicin . Also applies to broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs, an absolute analogue of Monural. Contraindications include pregnancy, age under 12 years. If the lesion is serious, symptoms of inflammation appear, there is a risk of intrauterine damage, this remedy is also prescribed to pregnant women with careful supervision of a specialist.
What to do if a woman’s smear contains E. coli
E. coli in a smear in women is a sign of a malfunction in the body that requires treatment. These bacteria not only prevent the proliferation of putrefactive microflora, but also participate in the synthesis of B vitamins.
However, E. coli (Escherichia coli) can become extremely dangerous if it leaves the digestive system.
General practitioner: Azalia Solntseva ✓ Article checked by doctor
Escherichia coli in a smear in women - treatment
Patients, especially adults, often do not need therapy, since many infections are localized and the body copes with them on its own. In addition, antibiotics were not helpful for the acute disorder.
In fact, some studies have shown that antimicrobials can increase the chances of developing a urinary tract infection (up to 17 times). This is thought to happen because the antibiotic damages the bacteria, causing them to release even more toxin.
Prescribing atropine, diphenoxylate, and other drugs commonly used to control diarrhea may also increase symptoms and cause complications.
Thus, some low-risk infections are treated as follows:
- rest;
- adequate fluid replacement;
- rarely, antibiotics.
How to treat severe symptoms of infection and complications:
- treatment in the intensive care unit;
- intravenous fluids and electrolytes;
- transfusion of plasma, platelets and red blood cells;
- kidney dialysis;
- medicines to increase blood pressure;
- medications to suppress seizures;
- kidney transplantation.
www.medicinenet.com
Characteristics of human pathology
If the bacterium leaves its habitat, even the normal, non-pathogenic form can cause serious problems. Its presence in a vaginal smear indicates that the healthy microbiota is disrupted, resulting in inflammation. It spreads to the uterus and ovaries, enters the urethra, bladder, urogenital tract and nearby organs.
To diagnose an infection caused by these microorganisms, you can use a regular smear from the vaginal mucosa, since bacteria are often detected when examining the vaginal flora.
If the answer to the test is positive, it can be assumed that it was E. coli that caused vaginitis, cervicitis, endometritis or other inflammatory disorder of the genitourinary system.
E. coli can be detected not only in vaginal contents, but also in a smear from the urethra. The infection often spreads from the intestines due to the anatomical structure of the genital organs in women.
This creates favorable conditions for the transfer of microorganisms from the rectum to the perineal organs. Women more often suffer from cystitis, due to the ability of the microbe to move upward.
www.mednotess.com
Reasons for the problem
The bacteria that cause the infection can enter the body in several ways.
Whether food is prepared at home, in a restaurant, or at the grocery store, improper handling and preparation can cause it to become contaminated.
Causes of food poisoning:
- poor hand washing before preparing food;
- using dirty dishes, cutlery and cutting boards;
- consumption of unpasteurized or expired dairy products and mayonnaise;
- eating food that has been stored or cooked at the wrong temperature or length of time, especially meat and poultry;
- consumption of raw seafood;
- use of unwashed vegetables and fruits.
Food processing. During the slaughter of poultry and animals, bacteria can spread from the intestines to the carcass.
Polluted water. Unsanitary conditions can cause the liquid to contain bacteria. You can become infected by drinking or swimming in such water.
People who work with animals, especially cows, goats and sheep, are at increased risk of infection. They should wash their hands regularly and thoroughly.
www.healthline.com
Disease in men - symptoms
If Escherichia coli is detected after tests, the question arises of what to do and how dangerous it is. Although E. coli is part of the body's normal microflora, infections with altered strains cause serious illness. Severe forms lead to death.
Most often, E. coli is found in a smear in those men who neglect the rules of personal hygiene and come into contact with infected sexual partners. The infection is also spread through food and liquids.
Usually, a positive urethral smear test result is detected by chance, since signs and symptoms of the disease are often absent in men. The urethra gradually becomes inflamed, causing severe disorders.
Possible symptoms of bacterial growth in the urethra:
- greenish coloration and cloudiness of urine;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- increased body temperature;
- nausea, poor appetite and exhaustion;
- severe diarrhea.
The described manifestations in men can disappear within 2 days, because the body has the ability to self-heal in this disease. If this does not happen, then you need to consult a doctor.
Bacteria in throat swab
Sometimes E. coli can be found in the mouth. This is usually confirmed by examining a smear from the throat, from the surface of the tonsils. In patients with such changes in the analysis, severe tonsillitis is often observed, prone to relapse.
The detection of microorganisms in a smear often becomes the reason for the initiation of special treatment. Its basis is the use of various antibiotics, after a course of which drugs are prescribed to restore the microflora.
www.mednotess.com
Pathology was detected in a child
The test is carried out to detect infection. For the purpose of diagnosing the disease, material for research can be taken from the mucous membrane of the mouth and pharynx, urethra in boys and vagina in girls. A stool test is performed to detect gastrointestinal distress caused by E. coli.
If there is a suspicion, even watery stool without the presence of blood is tested, which is not typical for these pathogens. Routine stool cultures typically test for Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter species.
Because E. coli is part of normal fecal flora, laboratories do a special test to detect pathogenic E coli subtype 0157:H7.
To accurately diagnose a urinary tract infection in a child, a properly collected urine sample that is clean and of sufficient volume is required. Otherwise, catheterization or aspiration of the bladder contents is necessary.
Symptoms of infection can be mild and nonspecific in infants, young children, and even older children, similar to symptoms of common viral diseases, which leads to incorrect diagnosis and treatment.
The following symptoms may occur in newborns and infants:
- lethargy;
- hypothermia (lower body temperature);
- diarrhea and/or vomiting;
- jaundice;
- fever;
- poor nutrition;
- attacks of suffocation and respiratory arrest;
- irritability or fussiness.
The treatment has a beneficial effect. It is aimed at replenishing fluid and electrolyte losses. Antibiotic therapy should be used after the results of the smear examination are received.
www.emedicine.medscape.com
How to treat an illness - effective suppositories
Most often, antiseptics and disinfectants are used to locally combat infection. The most popular representative prescribed by gynecologists is betadine, in the form of vaginal suppositories.
It blocks the development of microorganisms and causes their death. It has a wide spectrum of antimicrobial action against bacteria (including E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus), fungi, viruses, and protozoa.
It is recommended to moisten the suppositories with water and insert them deep into the vagina at night before bed. In case of acute vaginitis, you should use 1 suppository, 1-2 times a day for a week.
In the case of a chronic process, the course of treatment is about half a month, and longer if necessary. Since the pathology cannot be cured in a week, you should not stop using suppositories during menstruation.
www.dx-health.com/en/betadine-vaginal-suppositories-p-149 (Betadine Vaginal Suppositories)
Danger level during pregnancy
The issue of detecting a microorganism in a smear in pregnant women should be considered separately. At this time, the expectant mother’s body and her immunity are weakened, so the likelihood of various infections occurring is very high.
The rod can penetrate the placenta and infect the baby, which can cause meningitis..
The baby can become infected while passing through the birth canal.
E. coli can cause vaginosis, which can cause premature birth. Pregnant women also need to be careful with antibiotics. Under no circumstances take any medications without the permission of a specialist.
You need to go to the doctor as soon as possible - he will help you choose medications that will be safe for the development of the fetus, but will be able to normalize the microflora.
Prevention measures
Simple preventive measures will help prevent E. coli from entering the vagina:
- Wash yourself at least twice a day.
- Change your underwear every day.
- Wear the right underwear, try to avoid thongs and choose panties made from natural materials.
- Use protective equipment during intimate contact, and be careful when choosing sexual partners.
E. coli can cause a number of problems. But even if it is discovered, there is no need to panic. The main thing is to go to the doctor in a timely manner and begin treatment, avoiding dubious amateur activities.
Therapy with folk remedies
Boiled Jerusalem artichoke
Wash several fruits thoroughly with a brush and peel them. Boil them until ready and drain the resulting broth. The fruits must be cut into small pieces and filled with sour cream or kefir; you can use any fermented milk product . The broth remaining after cooking should also be drunk, adding a little salt and sour cream to it.
You should eat this dish once a day until the symptoms of E. coli infection disappear. More suitable for complex treatment, but not independent .
Kefir lotions
E. coli is very afraid of the healthy fermented milk environment. That is why they say to use kefir, sour cream and natural yogurt if it is present in the body.
Lotions with kefir can also give a good and noticeable result at minimal cost. It is enough to take a strictly sterile bandage or cotton wool and moisten them well with a fermented milk product. Ideally, it is better to make kefir yourself from village milk. Place the compress in your underwear and put it on. This is how you need to walk around, but it is better to take a horizontal position for 10 minutes. After this, the perineum is washed with clean water. Repeat for 7 days .
Washing with chamomile or calendula
This recipe will not help remove the E. coli itself, but it will perfectly cope with the symptoms of the lesion and will quickly wash away the dead organisms from the surface of the genital organs and mucous membranes . To prepare the mouthwash, you need to take 20 g of herbs and pour a liter of boiling water over them. Cover the container tightly with a lid and let the water cool. After this, carefully strain the grounds and use the decoction for its intended purpose. 7-10 daily procedures are enough .