Molluscum contagiosum on the genitals is a contagious (contagious) disease of smallpox nature. According to statistics, the inguinal localization of the pathological process is observed most often. The main category of patients are children under 5 years of age. Pubertal patients, and especially adult patients, are much less common. It is important to note that adult patients suffer exclusively from the genital form of the described pathology.
Very little is known about the causes of the development of molluscum contagiosum, as well as about the pathogenesis. It is known for certain that the causative agent of the disease is transmitted both through unprotected sexual contact and through interaction with infected objects (domestic route). What is it recommended for patients to know?
Symptoms
Signs of the disease appear two weeks after the infectious agent enters the body. Due to the low-symptomatic nature of the disease, patients rarely pay attention to the first signs. After the specified period, small red rashes are found on the pubis, in the area of the external genitalia, and in the lower abdomen. Their size varies from 1 to 3 mm. Over time, the localization of the process expands, covering the mucous membranes of the external genitalia (including the urethral canal). The shape of the formation is ovoid or oval.
The spots gradually increase in size, begin to rise above the skin and become pigmented (the color changes from flesh to bright crimson or pink). Subsequently, the number of formations of molluscum contagiosum in the groin increases, they become massive and, ultimately, merge into large focal structures. A few weeks after the onset of the pathological process, the pathogenic structures are filled with a whitish, curd-like liquid. The exudate includes dead skin cells, sebaceous gland secretions, dead lymphocytes, as well as pathogens.
All the described manifestations are not specific enough. The absence of characteristic symptoms does not give doctors and the patient the opportunity to make a correct diagnosis in a timely manner. Molluscum contagiosum on the pubis and other locations is often confused with allergic acne and other formations. Timely diagnosis guarantees relief from molluscum contagiosum.
How does the disease appear?
Based on the location of the rash, you can determine how the virus entered the body.
During sexual contact with an infected person, foci of neoplasms will appear around the genitals and on the genitals themselves. Nearby skin may also be damaged as the infection spreads. Usually the inner thighs are affected. After contact with a sick person, the first signs of infection will appear within a few weeks. Small punctate nodules from 1-2 mm, which quickly increase in size.
If infected through household contact, a rash can appear on any part of the body. Often in adults in the facial area.
Molluscum contagiosum in adults has the following symptoms:
- pink or flesh-colored papules with a depression in the center;
- protrude above the skin, when pressing on the papules, the contents are released in the form of a viscous mass;
- rashes may change color over time, become pink, pearlescent, and the contents become more liquid;
- in rare cases, as the inflammatory process progresses, an inflamed rim may form around the papule;
- the number of rashes from single to large clusters in diameter from 1 to 10 mm, can merge, forming a large plaque;
- Sometimes the rashes cause itching.
It should be noted that an infected person poses a danger to himself. If the papules are damaged by scratching or any other method, the rash can spread throughout the body and transfer to the face.
Molluscum contagiosum in adults is treated using various techniques and medications depending on the location of the nodules and papules.
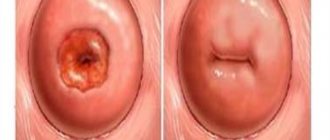
Photo of molluscum contagiosum on the genitals
Causes
This is a highly contagious disease. If there is contact with a carrier of infection or a contaminated household item, then the penetration of the virus into the body occurs with a very high degree of probability. Among adult women, the disease is mainly spread through unprotected sex with dubious partners. Moreover, even a condom does not always save you - cheap products can allow small amounts of natural fluids to pass through along with pathogenic microflora. You can also become infected by:
- using other people's personal belongings, such as underwear or bed linen;
- careless visits to public restrooms and solariums;
- swimming in natural reservoirs and pools that do not meet sanitary standards.
Please note that the pools themselves are safe - they are well cleaned, and antiseptics are added to the water. But if you visit a dubious sauna, you can catch more than just molluscum contagiosum.
But penetration of the virus into the body is small; it begins to develop only in the presence of provoking factors. The main one is problems with immunity, which arise due to:
- untreated colds;
- improper lifestyle;
- severe stress;
- frequent changes in time zones and climate zones.
If everything is fine with the immune system, then the virus will live in cells for years without causing any trouble to its carrier.
The household route of infection is most often found among children and adolescents. In the vast majority of cases, adult women become infected through sexual contact.
Examination methods
Since molluscum contagiosum of the genitals is not a sexually transmitted disease, diagnosis is carried out by dermatology specialists. At the initial consultation, the doctor conducts a survey of the patient to find out the nature of the complaints and their duration. A life history is being collected. Then comes the turn of visual assessment of the papules. For these purposes, a dermatoscope is used - a special magnifying device. It is not possible to determine the nature of the pathological process visually, “by eye”.
Molluscum contagiosum mimics psoriasis, tuberculous skin lesions, herpes and other diseases. Histological examination is intended to put an end to the question of the origin of red rashes. To carry it out, biological material is collected through a biopsy of the contagious node. Additionally, a study of a smear from the urethra is indicated in order to exclude diseases according to the profile of a dermatovenerologist.
The patient's general health is assessed by collecting venous blood, finger prick blood, and urine. In general, diagnosis does not present significant difficulties. However, this is only true for the developed stages of the mollusk.
Symptoms
The period from infection to the first signs of the disease is called incubation. Over the course of 14 days to several months, the virus accumulates in tissues, and this is asymptomatic. Then a very characteristic clinical picture unfolds.
Since sexual transmission of the virus predominates in adults, the manifestations of infection will primarily be in intimate places. A typical sign of molluscum contagiosum is papules (nodules) up to 8 mm in size with a depression in the center. They are flesh-colored or pearl-white in color and hemispherical in shape. The contents of the papules are cheesy in nature and consist of epithelial cells and viral particles.
The rash can be single, but in most cases you have to deal with multiple nodules. In women they are localized on the labia, and in men - on the penis. Patients of both sexes encounter papules on the pubis, thighs, and lower abdomen. In children, the localization of the rash is different: the skin of the face, neck and chest, and the back surfaces of the hands are mainly affected. Rashes can sometimes become generalized, spreading to other parts of the body.
Molluscum contagiosum does not produce subjective symptoms. Sometimes there may be an itching sensation in the areas where the rashes accumulate. If, after squeezing out the papules, a secondary infection occurs, then inflammatory phenomena occur (redness, swelling). However, the disease most often has a favorable course, and the papules disappear on their own in about six months in many patients.
If papules appear on the skin in the groin, and when pressed, a curd-like mass is released, then we are talking about molluscum contagiosum.
Treatment
The question of the fundamental need for treatment of molluscum contagiosum remains controversial in medical science and practice. Having brought all the arguments to a common denominator, we can say with certainty that treatment is still necessary. Yes, this disease does not pose any threat to life and health. However, papules do not look aesthetically pleasing. The treatment is designed to eliminate the proliferation of the pathogen, as well as remove the cosmetic defect.
Treatment measures, in most cases, are surgical (also cosmetic). Conducted:
- Curettage of cavities of formations using special tools. Squeezing out and combing papules on your own is strictly prohibited. This will lead to infection of even larger areas of the skin.
- Elimination of mollusks with a laser beam.
- Removal of affected skin areas through cryotreatment.
You can also help with medication. Used: zinc ointment, salicylic acid, antihistamines, tincture of iodine. In case of damage to the mucous membranes of the external genitalia, therapy is complicated, since treatment can be associated with significant discomfort for the patient.
Causes and mechanisms
The direct causative agent of molluscum contagiosum is considered to be poxvirus, which belongs to the smallpox group. It is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person through sexual or household contact. In the second case, infection occurs through common household items (towels, washcloths, bed linen). There is also a water method of transmission of the pathogen, when infection occurs when using the same bathroom and visiting swimming pools.
The virus is released from skin elements and can survive in room dust. The following factors contribute to the appearance of the disease:
- Violation of personal hygiene rules.
- Neglect of cleaning the home and washing clothes.
- Decreased general immunity (with chronic diseases, malnutrition, taking cytostatics and hormones, in the elderly).
Autoinfection can occur when papules are damaged (squeezing, shaving, rubbing with clothing). Mostly isolated (sporadic) cases are observed, but there are also outbreaks of molluscum contagiosum in children's groups. The latter confirms the epidemiological significance of the disease.
Molluscum contagiosum on the genitals is an infectious pathology of viral origin. Most often it is contracted through sexual contact or through everyday contact.
Complications and preventing further infection
With the exception of a cosmetic defect, there are no complications. You can stop the process by:
- You can’t touch the formations again.
- Under no circumstances should you comb them.
- You need to wash your hands more often.
- It is necessary to use emollient creams and ointments.
Molluscum contagiosum is not a dangerous, although unpleasant, disease. The main characteristic of the pathology is the occurrence of a cosmetic defect. The dermatologist decides whether to treat the molluscum or not, based on the prevalence of the process and the degree of discomfort experienced by the patient.
Description and methods of transmission
The rashes on the skin look like pink papules, very reminiscent of warts. As the infection spreads, the affected area increases. They do not itch, but if damaged, there is a risk of infection.
Molluscum contagiosum in adults most often appears as a result of non-compliance with hygiene rules and promiscuity. Location on the face, genitals and inner thighs. The disease is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact and through household objects. An infected person poses a threat to others. The risk increases if the rash is damaged.
Molluscum contagiosum during pregnancy
When a woman is pregnant, her immunity is weakened more than even with a cold in her normal state. At the same time, molluscum contagiosum does not pose a threat to the expectant mother herself, but the baby may not be well. The virus is able to penetrate the placental protection, introducing itself into fetal cells. Since his immunity is not yet working (at least not at full strength), there is no protection. The consequences are severe:
- miscarriage;
- congenital deformities;
- mental disabilities;
- heart and lung defects.
In addition, vertical infection, that is, infection from the mother during passage through the birth canal, is possible. There will not be such terrible consequences, and the disease will most likely not manifest itself soon, but in the future the mollusk will definitely affect the development of the child.
Molluscum contagiosum in the vast majority of cases occurs in children from 1 to 6 years old; adults encounter it extremely rarely. You can learn about the symptoms, causes of this disease, and how to avoid this insidious disease.
When planning a pregnancy, you must be examined for molluscum contagiosum and other sexually transmitted diseases. If the disease is identified, then it is better to avoid conception until it is cured (suppressed). In addition, while carrying a baby, you need to undergo periodic examinations and immediately begin treatment if the doctor makes an unpleasant diagnosis.
In rare cases, problems are possible for the expectant mother. Molluscum contagiosum that affects the fetus can cause sepsis and suppuration, which sometimes lead to death.