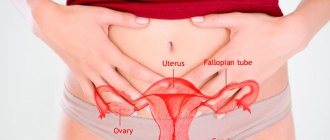
Women's tests for infections are quite traditional, as doctors note. At the same time, not all representatives of the fair sex know what exactly is being rented out and under what circumstances. Not everyone knows the indications for conducting research, although the list of them is described by doctors as extensive.
Representatives of the fair sex often ask their doctors where to get tested for infections, and how to prepare for various tests.
What are the normal indicators and signs of abnormalities, where can I get tested if it becomes necessary?
Blood tests for STIs
Blood tests for STIs
- examination using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Blood is donated on an empty stomach, taken from a vein.
The method is not applicable to all infections and may not always give an unambiguous result.
Only in the absence of all types of antibodies in the blood can we speak of a negative test.
All other options require further examination using the PCR method.
Molecular genetic examination
Molecular genetic examination (polymerase chain reaction)
– a method for detecting DNA or RNA of a specific pathogen.
The biological material obtained by scraping is placed in a special apparatus.
Specific reagents are added to the sample, which multiply the existing pathogen DNA many times over, which is then identified.
This method can detect genetic material even when the number of microbes in the sample taken for analysis is small.
Using PCR, you can identify a large number of microorganisms - chlamydia, trichomonas, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, human papillomavirus (oncogenic and non-oncogenic strains), candida, herpes viruses, etc.
To perform an examination using the PCR method, preparation is required.
48 hours before the test you need to abstain from sex, douching and vaginal suppositories should not be used.
It is also advisable not to urinate for 1.5-2 hours and not to perform other gynecological manipulations on the eve of the examination.
These include examination on a chair, insertion/removal of a coil, vacuum, transvaginal ultrasound of the pelvic organs, colposcopy, etc.
You can undergo a PCR examination for a number of pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases in our dermatovenerological clinic.
If it is necessary to prescribe treatment, you can be consulted by a highly qualified venereologist.
Preparing for tests
Proper preparation for the examination
A woman should understand that excessive attention to hygiene procedures can lead to a certain number of microorganisms being washed away or neutralized by the detergent. In order not to distort the test results, it is recommended not to use douching, not to use aggressive and disinfectant detergents, and not to wash too intensively, frequently and deeply before examining and taking biological material. To carry out intimate hygiene, it is enough to use a neutral substance, and immediately before the analysis do not use any drugs, using only clean boiled water.
Taking a variety of medications, especially those that can affect the state of the microflora of the vagina and other organs, can also distort the picture of infection.
We are not just talking about specific drugs, for example, those used to treat thrush or other STDs. Drugs that are usually used to treat colds, runny nose and cough can also affect test results. First of all, these are antibiotics, sulfonamide drugs, antiviral drugs, drugs aimed against fungal diseases, antitumor drugs and many others.
More information about infection tests can be found in the video.
To properly conduct gynecological tests for infections, you should stop drinking alcohol at least 24 hours before. This is especially important in cases where a blood test is also added to the examination. Alcohol, tobacco, medications and an abundance of heavy food can affect the results of the study, so a basic limitation of excesses will help to immediately get a clear and clear picture, the correct result.
If specific preparatory steps are required, the doctor will definitely explain to the patient what exactly she will need to do and what not to do.
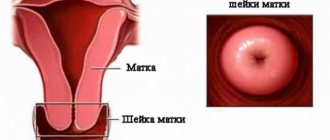
Microflora smear
Description and meaning of a smear on vaginal flora
One of the oldest methods of taking gynecological tests for infections is the so-called flora smear.
Purpose of analysis:
- It is usually taken during a gynecological examination in a chair, as well as in cases where the patient complains of excessive genital discharge, unpleasant odor, type and color of discharge, itching of the external genitalia and anus, redness of the vulva and vagina.
- Also, such an analysis is carried out in cases where gynecological surgery or any serious procedures are planned.
This method of taking tests is attractive because it is carried out very quickly and gives quick results, but it is already somewhat outdated. A smear shows only the presence of pathogenic microflora without specifying the results and their differentiation, which indicates the low information content of this method.
PCR method
Modern gynecological tests for infections include such an effective test as the PCR method. It helps to identify hidden infections that do not manifest themselves in any way. Unfortunately, most sexually transmitted infections develop very secretly, without showing themselves for months and sometimes years.
Using the PCR method, it is possible to identify even single cells of pathogenic microorganisms and quickly take action against them.
This method will help cope with a variety of diseases long before they develop into a dangerous condition.
Sowing tank
Description and meaning of seed tank
Gynecological tests for infections, such as bacteriological culture, give more accurate results than a smear for flora. For such an analysis as tank culture, you can take a variety of biological material. This could be a swab from the vagina or cervix, a urine or blood sample.
This analysis is called sowing because the resulting biological material is placed in a special nutrient medium. Microflora is grown in special, favorable conditions for a strictly defined time, and then analyzed.
A special feature of the culture tank is the fact that it can be used to “calculate” not only the causative agent of the disease, but also medicines that actively influence the development of microflora.
To do this, special tests and experiments are carried out with the resulting colony of microorganisms. They clearly and quickly show which medicine will be the most effective and will quickly help deal with pathogens.
Other types of tests for infections
Gynecological tests for infections may also include a blood test. It can show general results, for example, the presence of an obvious or hidden infection in the body, the intensity of the inflammatory process, and possibly its duration.
This analysis is rarely used on its own; it is usually used as an additional test to create a clearer picture of the disease.
Tests prescribed by a doctor help quickly and effectively identify the source of the disease and take adequate measures that will help the woman and her partner quickly recover and forget about their illness. Follow all the doctor’s instructions and your health will quickly return to normal, preserving the opportunity to have children and live a full, fulfilling life.
Read: What is dangerous and how is human papillomavirus of high oncogenic risk treated?
Women's tests for infections during pregnancy
The issue of conception must be approached with special attention.
It is recommended to be tested for infections while planning pregnancy.
Both partners need to do this.
This approach will avoid adverse consequences for the fetus and mother if the infection is detected later.
When registering with a antenatal clinic, the gynecologist will in any case issue a referral for STI tests.
This is a planned procedure and you should not be afraid of it.
A pregnant woman is prescribed not only tests for sexually transmitted infections, but also for syphilis, hepatitis, and HIV.
If an infection is detected in the biomaterial, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
Effective drugs are selected with minimal effect on the embryo.
Women's tests for infections: when to take them
When the first signs of an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system appear, you should not delay your visit to the doctor.
It is also necessary to take tests for infections for the purpose of prevention.
Some STDs have a long incubation period and are asymptomatic.
In this case, you may not suspect an infection for a long time.
If you have only one sexual partner, it is recommended to visit a gynecologist at least once a year.
Warning symptoms when you should get checked:
- 1.Discharge
- 2. Pain in the lower abdomen
- 3.Discomfort when urinating
- 4. Inability to get pregnant or miscarriage
Women's tests for infections: preparation
In order for the test results to be as reliable as possible, preparation is needed.
Following simple rules will allow you to get reliable results.
If a woman has to undergo a smear test for infections, she must:
- Avoid taking antibiotics
- Do not enter into sensual relationships a couple of days before the analysis
- Do not use antifungal or antibacterial agents
- Wash yourself the day before collecting biomaterial with warm water.
During menstruation, a smear for infection is not taken.
When you have taken antibiotics, consult your doctor.
It is recommended to take tests no earlier than after 2 weeks.
Blood is taken for venous examination.
To identify the inflammatory process in the body, urine must be collected in the morning.
To do this, use a sterile container.
What does a PAP test determine and how often should it be taken?
In many developed countries, a Pap test is recommended. It helps to identify the risks of cervical cancer, which allows timely and effective treatment.
After the start of sexual activity, regular PAP tests can help prevent cervical cancer, the Ministry of Health reports.
The best time to take a Pap test is during the first dry days after your period. Women who take birth control pills and women in menopause can come for examination any day.
Important! Two days before the test, you should not have sex, nor use vaginal suppositories, irrigations, gels and creams.
There is no need to be afraid of this procedure, because it is completely painless. Only a few women can feel discomfort and prolonged pain in the lower abdomen - everything, as during a routine examination by a gynecologist, is quite normal.
Who should get a Pap test every year?
- Women who smoke
- HIV-infected
- Immunocompromised due to corticosteroid use
- For those who frequently change sexual partners without using contraceptive methods
- Cervical cancer in mother, grandmother or sister
- If sexual relations began before age 16
If a woman has a high risk of cancer, then from the age of 30 she is recommended to undergo a combined test: a Pap test and a test for the human papillomavirus.
The PAP test is a painless smear; contact your gynecologist immediately if:
- Have irregular bleeding
- Any unusual vaginal discharge, including watery or bloody discharge after intercourse
- Frequent pain in the lower abdomen
- Feel pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse
Regular preventive medical examinations by a gynecologist are the main protection for every woman from serious diseases, which the doctor can notice at the very beginning or even before the main symptoms appear.
Small financial costs for research can be more than justified if they help to notice dangerous health changes in time. Here are the studies doctors recommend for women at different ages. Consult a specialist about possible contraindications.
Women over 20 years old
Inspection of the vagina and cervix for erosions, benign tumors - papillomas and condylomas (every 6 months)
- Breast examination (every 6 months)
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands (every 6 months). Early diagnosis of breast cancer significantly increases the effectiveness of its treatment
- Examination of scrapings from the cervix for the presence of precancerous and cancer cells (once a year). This test allows you to effectively detect cervical cancer in the initial stages, when the disease responds well to treatment. From 20 to 30 years of age, women are recommended to take this test every two years.
- PCR diagnostics (analysis for latent infections)
Women over 30 years old
Gynecological examination (every 6 months)
- Breast examination
- Examination of the vagina and cervix
- Vaginal microflora smear
- PCR – testing for STDs and various urogenital infections
- Examination of scrapings from the cervix for the presence of precancerous and cancer cells (once a year)
Women over 35 years old
Gynecological examination (once a year)
- Breast examination
- Examination of the vagina and cervix
- Smear for oncocytology
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Tumor markers
Women over 40 years old
Breast examination (once a year)
Examination of the vagina and cervix (once a year)
- Papanicolaou smear (if there is a possibility of disease, then such a smear should be done 3 times a year, it helps to identify precancerous as well as cancer cells of cervical tumors), examination of vaginal contents, determination of vaginal pH level
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (once a year)
- Mammography – to detect breast cancer (once a year). However, depending on your genetic makeup, family history, and other risk factors, your doctor may recommend more frequent mammograms. The X-ray machines used are low-dose radiation and can detect a tumor three years before you feel it.
Women over 45 years old
Breast examination (once a year)
- Examination of the vagina and cervix (once a year)
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (once a year)
- Mammography – to detect breast cancer (once a year)
- Examination of scrapings from the cervix for the presence of precancerous and cancer cells (once a year)
Women over 50 years old
- Examination of scrapings from the cervix for the presence of precancerous and cancer cells (once a year)
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (once every 2 years)
Analysis for human papillomavirus infection in women
If growths or warts are detected in the genital area, a woman is advised to visit an antenatal clinic.
The doctor will definitely examine the woman’s genitals and prescribe the following tests:
- Smear
- Scraping from the cervix
- Biopsy
- PCR diagnostics
- Research for the presence of cancer cells
Tests must be taken after menstruation, after 3-5 days.
It is important to understand that HPV is one of the causes of cancer in women.
It is necessary to find out the type of infection in time.
A qualified physician should interpret the results.
Analysis for bacterial culture in women: what infections
Cultures are taken from women to identify causative agents of the inflammatory process.
In addition, bacteriological culture determines the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics.
Discharge from the urethral canal using a urological instrument is used as a biomaterial for research.
The readiness of the results of bacteriological culture is a maximum of 7 days.
If bacteria, fungi, viruses are found in the culture and their number exceeds the limit values, treatment is prescribed.
To identify ureaplasma and mycoplasma, bacterial culture is not prescribed.
Smear assessment for infections in women
The female smear test is perhaps the most common and widely known test used in gynecology.
The technique is characterized by ease of execution, combined with high diagnostic value. With the help of a smear, a diagnosis can be made even in doubtful cases. True, as doctors note, a certain level of qualification is required from the attending doctor. He must ensure that the woman not only prepares correctly for the analysis, but also that the right way to evaluate the material is chosen. The smear, if used correctly, becomes an aid in making diagnoses related to sexually transmitted diseases.
Blood test for hidden infections in women
Using a venous blood test, you can determine the presence of pathogens such as:
- Herpes
- HPV
- HIV
- Hepatitis
- Ureaplasma and mycoplasma
A blood test determines immunoglobulins G and M.
If immunoglobulins G are detected in the blood, this indicates that the woman has had the disease and has antibodies to pathogens in her body.
In the presence of immunoglobulins M, an acute inflammatory process is detected.
Types and symptoms of sexually transmitted infections
Quite common female diseases include:
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasmosis;
- mycoplasmosis;
- candidiasis;
- gonorrhea;
- genital herpes.
What are the main symptoms of sexually transmitted infections? First of all, you should pay attention to the discharge. They can be either white or bloody, and sometimes even purulent and with a rather unpleasant odor. Burning, itching, severe redness, or small, bright sores in the genital area or anus can also be symptoms of infection.
Quite often, such diseases pass in a latent form without pronounced symptoms, and the carrier of a sexually transmitted infection may simply not be aware of the presence of a dangerous illness.
Therefore, regular scheduled examination by a gynecologist, testing for infections and sexual intercourse using a condom is a reliable prevention of many female diseases. Do not under any circumstances rely on your partner’s belief that you are not in danger, since he himself may not have accurate information about the state of his health.
You need to know that the risk of contracting various types of sexually transmitted infections increases if:
- you have had a blood transfusion;
- you change sexual partners very often;
- have unprotected sexual intercourse;
- use drugs.
Women's tests for infections: transcript
The interpretation of the results of smear tests must be entrusted to a qualified gynecologist.
The diagnosis of the disease and the prescription of a comprehensive course of treatment depend on this.
The smear results come in the form of a table with three columns: vagina, cervix, urethral canal.
Normal values should be as follows:
- Leukocytes: do not exceed 10 in the vagina; 30 – cervix; 5 – in the urethral tract
- Epithelium no more than 10 everywhere
- Mucus may be present in moderate amounts in the vagina and cervix, but should be absent in the urethra
- Trichomonas, gonococci, candida – normally should not be detected anywhere
It is not recommended to decipher the tests yourself when receiving the results.
This should be done by an experienced gynecologist, who will then prescribe effective treatment.
Features of gynecological tests for infections
Before taking the tests, it is necessary to conduct an examination. In gynecology, the following types of tests are distinguished:
- flora smear;
- bacteriological culture;
- PCR tests.
In modern medicine, taking a smear on the flora is the most ancient way to determine the presence of infection. In the laboratory, the doctor carefully examines the biomaterial and identifies the causative agent of the infection. The results of such an analysis are completely dependent on the human factor, which undoubtedly calls into question their accuracy.
Bacculture is a research process in which the taken biological material is grown in a special nutrient medium. The special environment promotes the rapid growth and reproduction of microorganisms. In this way, the cause of the disease can be identified.
PCR analysis is considered the most modern, fast and accurate method for diagnosing infectious diseases. It makes it possible to identify a fairly wide range of microbes.
In the medical center, which is located in the Eastern Administrative District of Moscow (Golyanovo, Izmailovo, Ivanovskoye districts) between the Novogireevo, Shchelkovskaya, Pervomaiskaya metro stations, you can take gynecological tests for any type of infection at the most affordable prices.
Under no circumstances should you try to treat yourself. By using antibiotics or other types of medications, you can worsen the problem, which will lead to irreversible consequences. Remember that in the early stages the disease is much easier to cope with.
Only a gynecologist after an examination can prescribe one or another antibiotic, taking into account the results of your tests and the individual characteristics of the body. Gynecological tests are taken from:
- vagina;
- cervix;
- urethra;
- anus.
The medical specialist is ready to conduct a high-quality analysis for any hidden infections in gynecology.
Entrust your precious health to professionals!
Our specialists can also take a smear for analysis.
Female smear: leukocytes are elevated
Leukocytes are an important component when deciphering a smear analysis in women.
A healthy woman's smear may show some white blood cells.
It is considered normal when the leukocyte count does not exceed 15 if the smear was taken from the vagina.
A normal indicator when collecting biomaterial from the cervix is considered to be an amount not exceeding 30.
From the urethral canal - no more than 10.
When the number of leukocytes exceeds the permissible values, an inflammatory process in the body is detected.
To find out the reasons, the doctor will prescribe additional tests.
How is a smear tested for infection in women?
Examining a woman's smear is not an easy task. It should only be trusted by an experienced doctor. You can find it in a private diagnostic center, or in a antenatal clinic.
There are several options for evaluating the obtained samples, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Microscopy
The simplest option for assessing a smear. The doctor examines the sample under a microscope, looking for bacteria that may be pathogenic. You can evaluate both a fresh smear and one painted in a special way. The method is simple. But with its help, viral infections, as well as a number of bacterial pathologies, are not diagnosed.
- Sowing
The second most common option. The samples are transferred to nutrient media and observed which colonies of microorganisms grow there. It is not possible to get results right away because the bacteria need time to grow. On average, the production time for seeding is a week, which is too long in some cases. However, the likelihood of error during sowing is minimal. Doctors note that it is impossible to diagnose viral infections using this method.
- PCR
Polymerase chain reaction is one of the modern diagnostic options. It is based on the determination of certain RNA or DNA fragments in samples. After their detection, identification occurs and a final diagnosis is made. PCR is expensive, but it is a way to get objective results in one or two days.
- ELISA
The ELISA technique exists to detect antibodies in biological material. There are several types of antibodies, based on the ratio of which it is concluded whether there is an infection in the body and at what stage it is. The method shows both viral and bacterial pathologies.
Women's tests for infections: sampling of material
Women's smears for flora are studies in which it is necessary to follow the technique of collecting material.
If the doctor violates the process, there is a possibility of getting results that are not true. Firstly, you need to remember that the smear is done strictly on a gynecological chair.
Thanks to its use, the doctor receives optimal access to the genitals. He can take samples not only from the vagina, but also from the urethra, from the area of the cervix.
Secondly, sampling should be carried out only with the help of sterile instruments. This will prevent the fair sex from becoming infected with other infections and will allow us to obtain objective data.
The resulting material should be quickly placed in a sealed tube or on a special glass in order to be successfully delivered to the laboratory.
Representatives of the fair sex may be afraid of the procedure. For women, unlike men, a smear is not difficult. The procedure is so common that it is used as a screening procedure.
There are absolutely no inconveniences. The most a woman can complain about is not very pleasant contact with the instrument, which can be cold.
After the material reaches the doctor, the woman can get dressed and leave the office. In the future, she will only need to get results.
Rules for preparing for women's tests for infections
A woman's smear test can be performed using several different techniques. However, none of them guarantee 100% results.
There is always a risk of both false positive and false negative results. This is explained not only by a violation of the smear collection technology, but also by the woman’s failure to comply with the preparation rules.
For material to be suitable for assessment, it is recommended that the following conditions be met:
- abstain from all sexual contacts for at least 24, and preferably 48 hours;
- for 2-3 hours before visiting the doctor, do not go to the toilet to relieve the bladder, so that urine does not wash away pathogenic microorganisms;
- do not douche with antibacterial solutions the day before visiting a medical professional to collect samples;
at least a week before taking the tests, you must stop taking all antibacterial drugs, including vaginal suppositories, used in the treatment of a number of diseases;
- on the eve of the study, do not use products to care for the intimate area, limiting yourself to light rinsing with plain water.
If the recommendations are followed correctly, it is much easier to obtain reliable results. Moreover, following the doctor’s recommendations will help avoid the need to undergo repeated tests. And the doctor, if he suspects false results, may well insist on repeat tests!
Interpretation of smear analysis in women
Interpretation of tests is a task that must be performed by the attending physician. Only a doctor who knows the patient can draw conclusions about how reliable the analysis is. And is there a need to retake it? The analysis pays attention to:
- the number of leukocytes, which is the main marker indicating that an active inflammatory process is occurring in the body, specifically affecting the genital organs;
- the number of red blood cells, an excess of which indicates damage to blood vessels and microcapillaries, from which blood is released;
- mucus, its nature and quantity (normally, mucus is present in the smear, but there is not too much of it; excess indicates the presence of pathology, rarely acting as a variant of the norm);
- the presence of epithelium, the presence of which in the smear also speaks primarily of an inflammatory process that provokes desquamation processes.
It is imperative to pay attention to the presence of pathological microorganisms, such as gonococci, chlamydia, trichomonas, etc. Their presence in the smear clearly indicates that the patient has a disease and needs competent medical treatment.
Women's tests for infections for the purpose of prevention
Preventive examinations and tests are carried out at least once a year.
More frequent screening is recommended for women at risk.
You need to follow simple rules to avoid infection:
- Have a permanent sexual partner
- Avoid accidental communication without barrier protection
- Don't forget about personal hygiene rules
- Support the immune system
It is worth getting tested for infections periodically.
This is recommended for both healthy women and those who have previously had sexually transmitted diseases.
Women's tests for infections: where to get them
A woman can get tested for infections either in a municipal hospital or in a paid center.
The main thing when choosing a medical institution is experienced and qualified doctors.
In a regular clinic, you can get smears for infections for free.
In this case, you will have to wait your turn.
The readiness of test results can take up to 1 - 2 weeks.
Commercial centers win in terms of the quality of gynecological services.
Appointments by phone are available, test results will be ready the same day or the next.
The research can be conducted anonymously.
Paid clinics are equipped with anonymous rooms, and complete confidentiality of the results is guaranteed.