Hormonal imbalances that cause infertility are detected through a series of specific tests.
Each hormone test for infertility is carried out strictly on a specific day of the cycle as prescribed by the doctor. The cycle count begins on the 1st day of menstrual bleeding.
Hormone analysis makes it possible to find out whether a woman is ovulating, and also allows us to predict a favorable period for conceiving a child.
Men need to follow a number of simple rules that serve as preparation before conducting the study, namely:
- refusal to drink alcohol;
- quit smoking if possible;
- If possible, you should avoid taking medications that may affect the results of your hormone test. If it is impossible to exclude taking medications, then the patient must inform the doctor about taking medications.
- abstaining from sexual intercourse several days before taking tests;
- a man needs to avoid strong emotional stress, spend more time outdoors, and stop going to the gym.
Analysis of hormones for infertility is very sensitive to the influence of factors of various nature. Therefore, compliance with the above conditions is necessary to obtain reliable results.
To determine the hormonal causes of infertility, it is necessary to undergo a series of mandatory tests.
Hormone analysis for infertility: determining the level of follicle-stimulating hormone
A man can take the test any day, and the results will be reliable. A woman undergoes similar tests only on certain days of the cycle - on days 3-8 or 19-21 of the cycle.
In men, follicle-stimulating hormone is responsible for the growth of the seminiferous tubules and increases the concentration of testosterone in the blood, while ensuring the maturation of sperm.
In women, follicle-stimulating hormone acts as a stimulator of follicle growth and also affects the production of estrogen.
Ovulation occurs when a critical level of follicle-stimulating hormone is reached in the middle of the cycle.
Other hormones
For infertility, check:
- Progesterone is a hormone that is produced by the corpus luteum, thus preparing the endometrium of the uterus for the attachment of an egg. For the study, an analysis is prescribed in the second half of the monthly period (after ovulation). If the egg is successfully implanted inside the uterus, the increased level of progesterone works to maintain pregnancy. It is also produced by the adrenal cortex and additionally by the placenta during pregnancy.
- DHEA sulfate is synthesized by the adrenal glands; its increased or decreased value makes it possible to diagnose various pathologies in hormonal synthesis. It is a “building material” in the production of sex and steroid hormones.
Increased concentrations of steroid hormones (for example, due to the use of steroid drugs in sports) inhibit the production of FSH and LH and over time can completely stop it.
Hormone analysis for infertility: determining the level of luteinizing hormone
Blood is taken for analysis from men on any day convenient for them; for women the situation is different. The analysis is carried out only on days 3-8 or 19-21 of the cycle.
In women, this hormone takes on the functions of stimulating the maturation of follicles, the onset of ovulation, the formation of the corpus luteum, and also ensures the production of estrogen hormones. The concentration of LH in the blood of women differs at different stages of the menstrual cycle.
In men, LH increases the permeability of the seminiferous tubules to testosterone by stimulating the production of globulin, which in turn binds sex hormones.
Treatment
Therapy includes several stages:
- Elimination of the cause of hormonal imbalance: selection of medications, surgical treatment.
- Correction of concomitant endocrine disorders (including normalization of body weight).
- Creating optimal conditions for conceiving a child.
In women, the main goal of therapy is to restore the menstrual cycle and ovulation . Hormonal drugs based on estrogens and gestagens are prescribed for a course of several months. Next, follicle maturation is monitored.
If there is no effect, drug stimulation of ovulation is indicated. If it is not possible to conceive a child within a year, a diagnostic laparoscopy is performed. Infertility is often caused by a combination of endocrine and tubo-peritoneal factors. IVF is possible.
In men, the main goal of therapy is to restore normal spermatogenesis . Hormonal medications are prescribed taking into account the identified cause of infertility and the level of one’s own hormones. Surgical correction is performed according to indications. If infertility cannot be treated, IVF + ICSI or IVF with donor sperm is indicated.
Hormone analysis for infertility: determination of estradiol levels
A woman is tested for this hormone throughout her menstrual cycle. Estradiol in the female body is responsible for the regulation of menstrual function and egg development. This hormone is secreted by the yellow corpuscle of the ovary, the maturing follicle, the adrenal glands, and adipose tissue under the influence of LH, FSH and prolactin.
After a significant peak in the level of estradiol in a woman’s blood, ovulation occurs within 24-36 hours. After ovulation, the concentration of the hormone decreases. Next, there is a rise and fall in estradiol levels. The decrease in hormone concentration continues until the end of the luteal phase. For the proper functioning of estradiol, an important factor is its relationship with testosterone concentration.
Prolactin
The third pituitary hormone that is required for testing in case of infertility. As the name suggests, it is responsible for lactation after childbirth, and also controls ovulation. In increased concentrations, it reduces the production of FSH, which necessarily occurs during pregnancy, but can be an obstacle to conception. Deviation from the norm in any direction leads to immaturity of the follicle.
For correct interpretation of the results, an important condition is to donate blood in the morning with a mandatory rest period of at least 30 minutes: anxiety, malaise, physical activity or recent sexual intercourse affect the test result. The level of the hormone fluctuates greatly during the day, the greatest production of prolactin occurs during sleep, therefore several hours must pass between awakening and the procedure.
The results of tests taken with a 2-week interval in both phases of the monthly cycle are considered reliable.
Hormone analysis for infertility: determination of testosterone levels
An analysis for the content of this hormone can be taken on any day. Testosterone is present in both female and male bodies, but is considered a male hormone.
In women, testosterone is secreted by the adrenal glands and ovaries. The maximum concentration of the hormone in the female body is observed in the luteal phase, as well as during ovulation. Exceeding the normal level of testosterone in a woman's blood can lead to miscarriage in early pregnancy.
Reduced testosterone levels in men lead to deterioration in sperm quality and decreased potency.
Causes of hormonal infertility
Hormonal infertility is associated with insufficient or excessive production of certain hormones that affect the functioning of the gonads.
Causes of female infertility
Insufficiency of the hypothalamic-pituitary system:
- damage to the pituitary gland or hypothalamus;
- hyperprolactinemia;
- luteal phase deficiency.
Ovarian insufficiency:
- gonadal dysgenesis;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- resistant ovarian syndrome;
- ovarian wasting syndrome;
- hyperandrogenism of ovarian origin;
- iatrogenic damage to the gonads.
Damage to other organs:
- congenital insufficiency of the adrenal cortex;
- thyroid diseases.
Causes of male infertility
Key factors:
- Damage to the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
- Testicular damage.
- Disruption of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
Common reasons
The direct damaging factor in men and women may be one of the following conditions:
- genetic abnormalities;
- injuries to the bones of the skull and genitals;
- tumors;
- infectious lesion;
- metabolic disorders;
- severe somatic diseases;
- radiation exposure;
- taking medications.
Indications for hormonal testing
These studies are carried out if the patient has:
- infertility;
- spontaneous abortions;
- menstrual disorders;
- delayed puberty or premature puberty;
- inter-cycle discharge;
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding;
- decreased sexual desire;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- dryness and atrophy of the vaginal mucosa;
- signs of endometriosis;
- hirsutism;
- anovulation;
- symptoms of polycystic ovaries;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the pelvis;
- galactorrhea;
- mastopathy;
- neoplasms in the uterus, ovaries and mammary glands;
- signs of sexual infantilism;
- obesity;
- cardiovascular pathologies at a young age;
- signs of osteoporosis;
- obesity;
- lactation disorders after childbirth;
- pain in the mammary glands;
- severe PMS;
- severe menopausal disorders;
- hair loss;
- acne, etc.
Hormonal levels are also examined to determine the ovulatory period, assess the control of ongoing hormonal therapy, control drug induction of ovulation, before in vitro fertilization, assess the condition of the feto-placental complexes, etc.
Necessary tests for women
Examination for infertility in women includes laboratory tests and instrumental research methods. The list of tests and procedures is determined by the doctor, who takes into account the woman’s age and medical history:
- past infections, inflammatory processes and surgical interventions;
- hereditary pathologies;
- presence of pregnancies in the past.
The first stage of the examination is a gynecological examination and study, analysis of the patient’s medical history. It is mandatory to perform a general smear and ultrasound examination in women. If cervical pathology is suspected, a simple and extended colposcopy is performed.
Examination for infertility in women also includes:
- determination of the concentration of sex steroids and thyroid hormones;
- performing immunological screening;
- testing for sexually transmitted infections;
- confirmation of ovulation;
- endometrial examination.
In some cases, consultation with specialized specialists, for example, an endocrinologist, may be required.
Often, the diagnosis of infertility includes a significant list of various laboratory and instrumental studies, which is associated with certain costs and discomfort. Some invasive diagnostic methods in women are factors in the development of infertility:
- diagnostic curettage of the cervix and uterine cavity (RDW);
- hysterosalpingography;
- hysteroresectoscopy;
- hysteroscopy.
These diagnostic methods are recommended for women only if there are serious indications, as they can cause the development of side effects and complications:
- chronic endometritis;
- salpingo-oophoritis;
- dysfunction of the receptive apparatus of the uterus.
The traumatic nature of invasive diagnostic methods increases the risk of infectious complications, which aggravates infertility in women. Gynecologists emphasize that tests to determine the cause of infertility should be as non-invasive as possible. The feasibility and compatibility of the research carried out is essential.
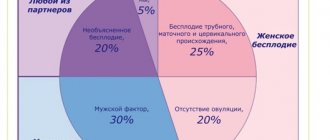
In recent years, there has been a tendency to increase the number of cases of infertility caused by male factor. The examination of men and women is carried out in parallel.
What hormones need to be tested for infertility?
Assessing a woman's hormonal levels is of particular importance in diagnosing infertility. Many processes occurring in a woman’s body are regulated and controlled by the required level of sex hormones. A decrease or increase in the concentration of sex hormones affects:
- ovulation mechanism;
- advancement of the egg into the uterine cavity;
- conception, gestation;
- childbirth and lactation;
- composition of cervical mucus.
The necessary physical and chemical properties of the secretion of the cervical canal, which is located in the cervix, provide a unique preparation of sperm for subsequent fertilization of the egg.
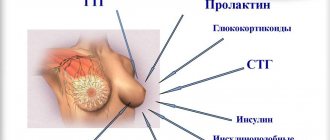
Hormone tests for infertility involve determining the concentration in the blood of:
- TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone), T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine), which are thyroid hormones;
- FSH (follicle stimulating hormone);
- LH (luteinizing hormone);
- prolactin;
- estradiol;
- testosterone;
- progesterone.
FSH
Follicle-stimulating hormone is produced by the pituitary gland. FSH causes the growth of follicles, stimulates the function of the corpus luteum by regulating the production of estrogens, which are sex hormones. It is advisable for women to perform the analysis at different phases during a particular cycle.
LH
Luteinizing hormone is produced in the anterior pituitary gland. LH stimulates estrogen production in the ovaries. When assessing the analysis, the doctor takes into account the correct ratio of the hormones LH and FSH.
Progesterone
The hormone is secreted in the second phase of the cycle due to the formation of the corpus luteum. Progesterone is considered the pregnancy hormone in women. The required concentration of progesterone ensures the preparation of the uterine mucosa for implantation of the fertilized egg. After pregnancy occurs, the hormone helps to prolong it until the formation of the placenta, which takes over the function of the corpus luteum.
Prolactin
The hormone is secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. Prolactin regulates the production of progesterone and FSH. The hormone provides the ovulation mechanism, which makes conception and pregnancy possible. After childbirth, prolactin promotes lactation.
Testosterone
This hormone is produced by the adrenal glands and ovaries in insignificant quantities. Testosterone is a male sex hormone. Excessive testosterone production causes disruption of the ovulation mechanism, miscarriage and early pregnancy loss.
DEA sulfate
It is an androgenic hormone produced by the adrenal glands. The concentration of the hormone allows us to judge the condition and functioning of the adrenal glands. Metabolic reactions lead to the formation of male sex hormones, in particular testosterone and dihydrotestosterone. Hormone production is stable under normal conditions. The hormone is excreted from the body in the urine, which prevents sharp fluctuations in the level of DHEA sulfate.
Estradiol
The sex hormone is produced by follicles that mature in the ovaries, the corpus luteum. The process of hormone production occurs under the influence of LH, prolactin and FSH. The concentration of estradiol affects the cycle and maturation of eggs in the ovaries.
Thyroid hormones
TSH is produced by the thyroid gland. The functioning of the thyroid gland is also ensured by the hormones T3 and T4. The concentration of hormones that are produced by the thyroid gland affects the adequate maturation of follicles in the ovaries and the mechanism of ovulation.
Immunological screening
With some disturbances in the functioning of a woman’s immune system, the production of antibodies is observed, which is a reaction to a protein present in sperm. Normally, women do not produce antisperm antibodies due to protective mechanisms.
The doctor prescribes a test to detect antisperm antibodies if there are no other factors of infertility. Detection of antibodies may indicate infertility that has an immune cause.
The presence of antisperm antibodies in women does not always lead to infertility. However, the likelihood of pregnancy is reduced by half.
To identify antisperm antibodies, a postcoital test is sometimes used, which involves examining the secretions of the cervical canal under a microscope a certain number of hours after sexual intercourse. The test sample must contain spermatozoa that move in a straight line. The number of male germ cells correlates with the norm. Immobility of sperm may indicate poor sperm quality and the presence of antisperm antibodies in a woman.
Endometrial examination
Chronic inflammatory processes in the uterus, hyperplasia and hypoplasia, fibroids, polyps and adenomyosis can cause infertility in women. The fertilized egg cannot implant and develop adequately in the altered inner layer of the uterus. Diagnosis of infertility necessarily includes examination of the endometrium or uterine mucosa.
Gynecologists call the simplest method of studying the condition of the endometrium an ultrasound examination of the internal genital organs, which is carried out both abdominally and transvaginally. Ultrasound allows you to measure the thickness of the endometrium, identify benign formations of the uterus, for example, polyps and fibroids, pathologies of the ovaries and tubes, and also suspect endometriosis. A discrepancy in the thickness of the inner layer of the uterus indicates hyperplasia and hypoplasia in women, which are often caused by an imbalance in hormones.
With endometrial hyperplasia, the thickness of the inner layer of the uterus exceeds normal. This pathology causes the formation of polyps and the need for surgical intervention.
The endometrium of the uterus can be examined through a biopsy. During this procedure, samples of the inner layer of the uterus are taken. The obtained samples are examined in the laboratory as part of histological analysis.
The analysis allows you to obtain information about the condition of the endometrium and increase the chances of embryo implantation. A biopsy reveals:
- the cause of infertility and miscarriage, bleeding;
- hormonal disorders;
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- uterine cancer.
Types of analysis:
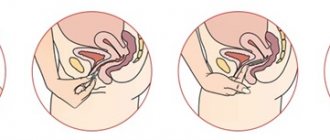
- pipel biopsy, performed using a thin tube with a piston to create negative pressure and suction pieces of the endometrium of the uterus;
- aspiration biopsy performed using a syringe or vacuum apparatus;
- curettage of the uterus with a curette as part of a minor surgical operation;
- hysteroscopy, performed using a hysteroscope with a video camera and a surgical instrument.
The feasibility and choice of anesthesia depends on the type of analysis. A biopsy is not performed if infections and inflammatory processes or blood clotting disorders are detected.
The process of preparing and studying the material takes 7-10 days. In conclusion, the structural features of the inner layer of the uterus are described. The diagnosis is made to a woman after receiving the results of other tests and studies.
Consultation of narrow specialists
In case of infertility, a woman turns to a gynecologist, who prescribes the necessary tests and studies. Often, in the absence of pregnancy, 12 months after the start of planning, a married couple is recommended to contact a fertility specialist. This doctor specializes in conception and infertility.
A gynecologist or reproductive specialist can refer a woman or couple to specialists. It is advisable for a couple to visit a geneticist in the following cases:
- the age of the spouses is over 35 years;
- genetic diseases in the family;
- consanguinity between spouses.
Infertility in women is often caused by hormonal imbalances. It is necessary to visit an endocrinologist for the following pathologies and conditions:
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- overweight;
- acne;
- hirsutism.
For diseases of the genitourinary system, consultation with a urologist may be required. In some cases, infertility is psychosomatic in nature. Psychological infertility is spoken of in the absence of disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. In case of infertility of unknown origin, a woman needs to visit a psychologist or psychotherapist.
Ovulation confirmation
Adequate functioning of the ovaries ensures reproductive function in women. The ovaries contain eggs that are capable of fertilization. The processes occurring in the ovaries are controlled by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
The hormone FSH, produced in the pituitary gland, promotes the secretion of estrogens and the maturation of follicles in the first phase of the cycle. During each cycle, several follicles laid in the ovaries in the prenatal period begin to mature. Only one follicle goes through all stages of development, which after its maturation is called the Graafian vesicle.
When the egg inside the follicle becomes mature, its wall is destroyed under the influence of the hormone LH. The egg is released from the follicle for subsequent fertilization in the fallopian tube. In place of the follicle, a corpus luteum is formed that synthesizes the hormone progesterone. If fertilization occurs, high levels of the hormone progesterone ensure prolongation of pregnancy until the placenta forms. In the absence of pregnancy, the corpus luteum is destroyed before menstruation.
Ovulation in women divides the cycle into two phases, being a necessary condition for conception. An imbalance of hormones leads to a distortion of the ovulation mechanism due to disruption of the functioning of the ovaries.
Distortion of the ovulation mechanism and its absence is the most common cause of infertility.
Ovulation can be confirmed by both laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods. Ovulation is supported by changes in the level of sex hormones during the cycle, which is determined by the results of a blood test.
The fact of ovulation can be determined through rapid tests that determine fertile days using saliva and urine. The test strips are impregnated with special chemicals that react to the release of the LH hormone in the urine. A positive result indicates ovulation, which should occur within two days.
There are optical systems that detect ovulation using saliva. These devices resemble a microscope and are designed for reusable use.
Ovulation can be confirmed using folliculometry. This procedure is a series of ultrasound examinations performed to evaluate the growth of the follicle and confirm the fact of ovulation. Folliculometry is an informative method of examining women, allowing to identify anovulation and concomitant pathologies of the internal genital organs.
An increase in the level of the LH hormone leads to an increase in basal temperature, which is measured in the rectum, vagina or oral cavity with a mercury thermometer. The objectivity and reliability of the results is achieved by observing the following conditions:
- measurement in one area;
- determination of temperature after a continuous night's sleep at a strictly set time.
ARVI, consumption of alcoholic beverages, and physical activity affect the measurement results.
The release of the LH hormone is manifested by an increase in basal temperature by 0.4 degrees. Anovulation is indicated by the absence of a rise in temperature in the middle of the cycle.
Changes in hormone levels during ovulation are accompanied by the appearance of subjective symptoms and sensations:
- enlargement and engorgement of the mammary glands;
- cramping pain in the lower abdomen;
- feeling of fullness in the rectum.
Confirmation of ovulation is carried out using laboratory tests, tests and instrumental methods in women.
Tests for sexually transmitted infections
Infertility in women can be a consequence of a chronic inflammatory process occurring in the area of the appendages, uterine cavity, and cervix:
- adnexitis;
- endometritis;
- endocervicitis.
Chronic inflammation is caused by sexually transmitted infections of a specific and nonspecific nature. Some sexually transmitted infections have mild symptoms or occur latently.
Experts call the following infections leading to infertility:
- gonorrhea;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasma;
- cytomegalovirus;
- herpes simplex virus;
- trichomoniasis;
- some types of HPV;
- ureaplasma.
Somewhat less frequently, inflammation of the genital organs in women can be caused by:
- enteroviruses;
- streptococci;
- coli;
- Candida fungi.
In order to diagnose infections that can be sexually transmitted, microscopic examination of smears from the following areas is carried out:
- vagina;
- urethra;
- cervical canal.
To identify the RNA and DNA of pathogens, urine, blood, and mucus of the infectious agent are analyzed using the polymerase chain reaction method. This analysis is called PCR diagnostics.
Sowing for microflora and sensitivity to antibiotics increases the effectiveness of therapy.
Thyroid hormones
With a deficiency of thyroid hormones (hypothyroidism), the synthesis of testosterone and estradiol is hampered, which affects the production of germ cells. The normal course of all processes of the menstrual cycle is disrupted, pregnancy occurs with complications. Hypothyroidism is diagnosed in almost 30% of infertile women.
- TSH is a thyroid-stimulating hormone produced by the pituitary gland and regulates the production of all biologically active substances in the thyroid gland. Abnormal TSH levels and infertility are often diagnosed together. Its concentration is a universal indicator of the functional capacity of the thyroid gland.
- T3. A separate study for this hormone is not carried out; its concentration is determined in combination with TSH and T4. A normal amount of T3 in the blood is not reliable evidence of sufficient thyroid function.
- T4 is a hormone derived from T3; its precise balance with TSH is very important for the reproductive sphere.
- Antibodies to TSH detected during the analysis can confirm the autoimmune nature of hormonal disorders.
It does not matter on which days of the cycle to take tests for thyroid hormones in case of infertility. The main thing is to adhere to the general rules of preparation for hormonal examinations and stop taking hormonal medications for a 2-day period.
By identifying the hormonal nature of infertility and establishing its exact cause, it becomes possible to undergo appropriate treatment or maintenance therapy and improve the delicate functioning of the body. All hormonal medications for infertility are selected by the doctor individually for each person. Precise dosages and compliance with recommendations for taking them ensure the success of treatment and bring the desired pregnancy closer.
Read
Also:
- Female sex hormones: interpretation of tests, norm and deviations
- Immunological infertility: treatment and causes
- Is it possible to do colposcopy during pregnancy: the course of the study and its importance
- How to treat infertility in women with folk remedies
- Test to determine female infertility
- Infertility of 1st and 2nd degree in women, primary infertility
When do men undergo hormonal testing?
In cases where a couple cannot conceive a baby for more than 12 months, doctors recommend that the spouses undergo examinations. More often, women seek medical help, but it is important to understand that even the presence of an identified pathology in the wife does not exclude the possibility of problems in the husband, which means that both spouses must undergo examination.
The first test that a man who has long dreamed of fatherhood undergoes is a spermogram, which determines the quantity and quality of sperm. If the results of the first spermogram are unsatisfactory, another verification test is usually prescribed. If a repeated test again shows a reduced sperm count, this is a reason to check the man’s hormonal status.
Expert commentary
When there are no or very few sperm in two repeated spermograms, it is necessary to begin a comprehensive examination, which includes a hormonal study.
What hormones should be tested to determine a woman’s hormonal imbalance?
Analysis of hormonal levels in women is the most important study to determine the state of the patient’s reproductive system, identify the cause of the development of problems such as infertility, menstrual irregularities, hirsutism, severe acne, etc.
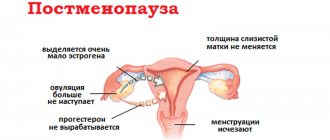
An analysis of female hormones during menopause is carried out in the event of the development of severe menopausal symptoms (severe emotional lability, nervousness or depression, heart rhythm disturbances, rapidly progressing osteoporosis, frequent “hot flashes”, insomnia, dryness and atrophy of the vaginal mucosa, etc.)
The hormonal profile is also examined when planning pregnancy and during pregnancy.
Hormone testing is prescribed by an endocrinologist or gynecologist. How to check a woman’s hormonal levels should be decided exclusively by a specialized specialist, since hormone tests are performed according to special schemes, depending on the day of the menstrual cycle.
All treatment is prescribed individually, based on a comprehensive examination.
Independent interpretation of tests and selection of treatment is strictly prohibited and can lead to serious health consequences.