Currently, cervical cancer is one of the most common types of oncology, which occurs not only in older women, but also in young women under 30 years of age. Testing for tumor markers allows not only to diagnose the formation of pathology in its early stages, but also to select the right treatment tactics. The first step is a general gynecological examination, which is the reason for prescribing additional examinations.
The cervix is the lower segment of the organ, consisting of connective and muscle tissue. In a smaller volume, the cervix consists of elastic fibers and smooth muscle cells.
Blood test for tumor marker SCC: interpretation and norm
SCC tumor marker is a tumor-associated antigen of squamous cell carcinomas with different localizations. SCC (SCCA, TA-4) tumor marker indicates squamous cell carcinoma that develops in the uterus, its cervix and in other organs: lungs, neck and head. When the level of SCC concentration increases, the development of cancer is suspected. If a negative result is obtained, pathology in the organs cannot be ruled out. The dynamics of SCC growth are examined at the first positive test. With the first negative SCC test, repeated tests will not be informative.
Content
An SCC tumor marker is a substance produced by malignant cells or the body in response to the presence of a tumor. The SCC tumor marker is a glycoprotein that inhibits serine proteases. Molecular weight - 45–55 kDa. Healthy epithelial tissues synthesize minimal amounts of SCC without entering the systemic circulation. Scientists have not yet figured out the biological role of SCC.
SCC tumor marker is synthesized by epithelial cells of the cervix, anus, skin, esophagus and bronchi
What does the SCC tumor marker determine?
If the concentration of tumor marker in the blood is high, squamous cell carcinoma is suspected in the nasopharynx, ears, vagina and uterine cervix, esophagus and other areas.
Some inflammatory diseases: respiratory organs, acute respiratory infections, chronic tuberculosis, renal and liver failure, skin diseases such as lichen planus, psoriasis, neurodermatitis can give a false positive result.
To diagnose skin melanoma, a tumor marker for the S100 protein is used, the explanation of which is given in the article on our portal.
Important. Slight increases in tumor marker levels will occur in the presence of benign and inflammatory diseases and physiological conditions. To confirm the diagnosis, the examination is continued.
Tumor marker indicators
The SCC has several physiological functions:
- regulation of differentiation of normal squamous epithelium;
- stimulating the growth of cancer cells by inhibiting the process of apoptosis.
Tumor marker for cervical cancer SCC: normal - not higher than 2.5 ng/ml. Tumor markers for uterine fibroids should also not exceed 2.5 ng/ml.
Note. Myoma occurs due to changes in hormonal levels with a delayed onset of the menstrual cycle, heavy discharge, after abortion and the appearance of inflammatory processes in the genitourinary organs of women.
What tumor markers are used for uterine cancer? The names of the main ones are SCC and CA 125. The uterine tumor marker CA 125, when deciphered, shows the presence of oncopathology or somatic pathology. The norm for CA 125 is 0–35 U/ml.
You should not ignore the analysis for the HE4 tumor marker. What it is and what forms of cancer it shows, you can find out in the article on our website.
A high level of tumor marker SCC and CA 125 also determines cancer that develops on the cervix, ovaries, mammary and pancreas, lungs, liver, intestines, including the rectum and colon.
Tumor markers and types of cancer
Tumor marker CA 125 also increases in the presence of somatic pathologies, such as:
- endometriosis;
- inflammatory process of the uterus and appendages;
- cystic formations of the ovaries;
- pleurisy and peritonitis;
- liver cirrhosis, chronic forms of hepatitis and pancreatitis;
- autoimmune pathology.
Therefore, it is incorrect to take only the tumor marker for uterine cancer SCC or in combination with CA 125 as a basis for diagnosis. It is necessary to conduct a complete examination of patients.
Deciphering a venous blood test can indicate, based on the concentration of markers, an incipient relapse, which makes it possible to select patients for radiation or surgery.
If you have taken a blood test for CEA tumor markers, a breakdown of these indicators can be found in the article on our website.
Early diagnosis of cervical cancer
Early diagnosis of cervical cancer can prevent the development of malignant neoplasms of the genital organs and identify pathological neoplasia of epithelial cells in the early stages. It is recommended to be examined by a gynecologist every year and determine tumor markers of the uterus. Simple rules can maintain a normal state and diagnose pathology before its aggressive manifestations.
Indications for use
Examinations must be carried out in the following cases:
- annual examination for preventive purposes;
- the appearance of pathological discharge from the vaginal cavity;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- menstrual irregularities;
- menopause;
- pain, burning, itching in the genital area and lower abdomen;
- cervical cancer in close relatives;
- detection of papilloma virus;
- benign formations;
- hyperplasia of the cervical mucosa.
The RUSSCO national program “Molecular genetic diagnosis of cancer” offers the necessary list of procedures for the early detection of cervical cancer.
Blood tests
When diagnosing pathology, blood tests are necessary to identify specific proteins and the level of red blood cells.
- Biochemical research. Indicates intoxication of the body with tumor metabolic products, which is manifested by hypoproteinemia, dysproteinemia, and increased C-reactive protein.
- General blood test for uterine cancer. Detects anemia in the form of a decrease in the number of red blood cells - erythrocytes and hemoglobin, a high level of ESR.
Pap test
This is the name of a cytological test for cervical cancer. It is mandatory for a gynecological examination.
After a bimanual examination, the doctor uses a special Wallach brush to scrape the epithelial cover from the cervical area. This is a painless diagnostic procedure that does not take much time.
Next, the material from the brush is fixed onto a glass slide, which is labeled and sent to the laboratory for examination.
Determination of tumor markers
These substances are specific proteins that are formed as a result of the metabolism of tumor tissues. The presence of metaplasia of squamous epithelium is reflected by their appearance in the blood, which is diagnosed in the laboratory. Tumor markers for uterine cancer include the following tests:
- tumor marker SCC;
- carcinoembryonic antigen;
- TPS—tissue-specific polypeptide;
- CYFRA 21—1.
If cervical cancer is suspected, the SCC tumor marker is identified, which is normally zero.
Tumor marker for cervical cancer type SCC is the most widely used in detecting oncology and monitoring the adequacy of therapy after diagnosis.
It changes with the appearance of atypical growth of surface cells of the epithelial cover. It is determined in venous blood. The name stands for Squamous cell carcinoma antigen - antigen of squamous carcinoma.
Normally, the tumor marker for cervical cancer SCC in the blood should be completely absent, that is, equal to 0.
Do you need to prepare?
The Pap test requires a special selection of the day for it. This is explained by the peculiarities of changes in the condition of the mucous membrane of the cervix on different days of the menstrual cycle.
To minimize the deviation of results from the true ones, it is better to carry out diagnosis no earlier than 5 days after menstruation, but no more than 10 days after the 1st day of the cycle.
The day before the study, it is recommended to refrain from sexual intercourse and not to use vaginal products.
Diagnosis of uterine tumor markers also requires preparation. In order to ensure the purity of the examination, it is necessary to adhere to several simple rules that increase the purity of the results:
- do not consume food or water at least 12 hours before the test;
- give up alcohol the day before the test;
- dinner before the day of analysis should be light and low-calorie;
- stop taking medications 24 hours before testing.
Preparation for the study cannot be ignored, as this can lead to a false result and difficulty in making a diagnosis.
Conducting research
Venous blood is examined in a special laboratory, where its immunohistochemical procedure is carried out.
Examinations for tumor markers SCC, CEA, TPS, CYFRA 21-1 are performed in the laboratory.
Using sterile devices, blood is taken from a vein, which is placed in a test tube and sent for immunohistochemical examination.
If the patient is taking medications that he cannot refuse, this must be indicated.
Cytological examination
The normal smear implies the same shape and size of epithelial cells. There are 5 classes of Pap test changes:
- 1 - there are no pathological abnormalities in the cervical smear.
- 2 - morphological disorders of mucosal tissue caused by an acute inflammatory disease.
- 3 - cell neoplasia is detected in isolated cases, which is interpreted as a suspicion of cancer, since deformation is detected only in the nuclei.
- 4 - atypical growth of a small part of the cells.
- 5 - the number of malignant cells exceeds normal, which is diagnosed as cervical cancer.
Tumor markers
If the tumor marker values exceed the permissible norm, then the patient may develop cirrhosis of the liver.
The study shows the concentration of pathological proteins in 1 ml of blood.
Normal values include those that do not exceed 2.5 ng in the corresponding volume. Results that are in the range of 2.5-10 indicate malignant degeneration of cervical epithelial cells.
But there are conditions that are not related to cancer, but are accompanied by high SCC. These include:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system;
- skin pathologies;
- liver failure;
- endometritis.
Therefore, if the SCC tumor marker produces such a result, it is imperative to use additional diagnostic methods and instrumental techniques to confirm or refute cervical cancer.
An antigen concentration of 10 ng/ml or higher indicates a malignant tumor and the aggressive effect of pathological tissues on the body.
Obtaining such an interpretation of the analysis requires immediate anticancer therapy.
Source: //InfoOnkolog.ru/obsledovanie/sposoby/rannyaya-diagnostika-raka-sheyki-matki.html
Indications for blood tests
The cervical tumor marker is determined to:
- Evaluate the treatment provided to patients whose diagnosis was established, as well as the initially elevated concentration.
- Determine the probability of spread of tumor metastases.
- To predict the survival of patients after complex oncology therapy.
- Monitor the course of the disease and prevent relapses.
An analysis for tumor markers of cervical cancer is examined before the start of complex therapy, in order to further compare and analyze the course of treatment and the course of the disease, and build new treatment regimens.
Important. After removal of the tumor, the control SCC tumor markers paired with CA 125 will be normal for the first 4 days. The next study is carried out after 2 months, then once every six months.
Clinical picture
The disease is characterized by an asymptomatic course. In such cases, detection of cervical cancer is possible through general and special tests, as well as smears. With cervical cancer, manifestations most often occur in advanced stages of the disease. That is why the timely determination of pathology, including the necessary examination, comes to the fore.
Symptoms of cervical cancer include:
- loss of strength and constant fatigue;
- low-grade fever;
- leucorrhoea with light inclusions;
- thin or bloody discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- contact discharge;
- intermenstrual bleeding;
- pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, sacrum;
- dysfunction of the intestines and bladder;
- fistula formation;
- swelling.
The appearance of a characteristic clinical picture is associated with the spread of the pathological process to surrounding organs and tissues. To determine violations of the internal organs, it is necessary to undergo an examination, including general tests and smears.
How to prepare for research
For a blood test to be reliable, it is necessary:
- donate venous blood on an empty stomach in the amount of 3-5 ml between 7-11 am, no earlier than 8-12 hours after the last meal;
- do not drink alcohol or alcohol-based medications three days before the test;
- do not smoke 1–3 days before the study;
- do not eat fatty, fried, spicy and exotic foods 3 days before the tumor marker study;
- do not exert yourself physically for 3 days before donating blood;
- 10–15 minutes before the procedure you should sit and calm your nervous system.
Important. If possible, you should stop taking any medications 3 days before the procedure. If the medicine was taken, then in both cases you need to warn the doctor about it. The attending physician should also be notified if examinations are carried out a week before blood donation for another reason or in connection with suspected cancer of another organ or metastasis: ultrasound, CT.
Given the narrow limits of testing standards for tumor markers and the availability of different equipment, all studies should be carried out in the same laboratory. A tumor marker can be determined by urine, saliva, sweat and sputum. Therefore, they should be excluded from entering the blood sample.
SCC and CA 125 values depend on tumor size, disease progression and metastasis. Based on the results obtained, the stage of the tumor can be determined. Tumor markers are not used during screening or for primary diagnosis.
When and why does a doctor refer a cervical scraping for analysis?
Many diseases of the cervix are practically asymptomatic for a long time. In order to identify them in time, it is necessary to examine a sample of biomaterial. Most often, a smear or a very small piece of tissue is taken for analysis. A referral for analysis can be given by an oncologist or gynecologist, in some cases a venereologist.
Analysis of cervical tissue makes it possible to identify oncological diseases; it is also prescribed if the presence of human papillomavirus or cervical erosion is suspected. Such studies can be not only diagnostic - the doctor can refer the patient for a cervical analysis in order to monitor changes during treatment of the disease, and, if necessary, adjust therapy.
Cytological analysis of cervical scraping
Such an analysis of the cervical smear (study of the structure, cell structures and comparison with normal ones) is the most accurate and at the same time simplest research method for the patient. It makes it possible to detect modified cells, including those affected by malignant processes; it is also used to diagnose dysplasia and detect the presence of human papillomavirus.
It is recommended to undergo this test regularly. At a young age - once every three years, and after 50 - once every five years, but better - annually.
There is no need to be afraid of this procedure - it is simple and painless. The material is collected during a gynecological examination. The analysis can be taken at any period of the cycle, except for menstruation and three days after its end. First, the doctor cleans the cervix of secretions with a cotton swab, and then uses a special brush to take a sample of the material and place it on a glass slide, which is sent to the laboratory.
There are several methods for studying the obtained material.
- The most common is the Papanicolaou cell staining method (PAP test), which allows you to detect cellular changes in the early stages. This is an inexpensive test that has been successfully used for a long time to detect pathological changes in cervical cells.
- A cytological examination of scrapings of the cervix and cervical canal with a description according to the Bethesda terminological system, which is based on the identification of pathological changes in the cell nucleus, provides maximum information and allows timely identification of dysplasia and cancer.
- NovaPrep fluid testing is one of the most advanced and accurate.
In order for the results of the cervical analysis to be accurate, you need to follow simple preparation rules:
- Avoid sexual intercourse for two days before the test.
- For the same period, you should stop taking any antibacterial and antiviral drugs.
- It is also not recommended to use intimate hygiene products, contraceptive and medicinal vaginal ointments, suppositories, balls, gels and sponges.
- You should not douche on the day of the study.
After taking a smear, doctors do not advise having sexual intercourse for another 1-2 weeks; it is also recommended not to use tampons and douching.
The result is designated as CIN 1, 2 or 3 - that is, dysplasia of the first, second or third severity. Carcinoma means detection of carcinoma. If the result of the analysis shows the designation CIN, this almost always means the presence of human papillomavirus, the most common culprit in the development of cervical dysplasia.
Histological analysis of biopsy tissues of the cervix
Sometimes the data obtained from a cervical smear test is not enough. Then a biopsy is prescribed. A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue from the cervix for microscopic examination. Like cytological analysis, this study can be therapeutic and diagnostic. Cervical biopsy is a more accurate method than cytology.
There are several ways to remove a piece of cervical tissue.
Most often, the low-traumatic pinching method is used, when the sample is pinched off with special forceps for biopsy.
- The radio wave method involves the use of a radio wave loop; its advantage is that it is bloodless, although sometimes vaginal discharge may be observed for several days after the procedure.
- Conization - cutting off a cone-shaped piece of tissue - is used both to collect material and to remove the affected area. The choice of method depends on the goals of the study.
The conditions and rules for preparing for a cervical biopsy differ little from the conditions for taking a smear. However, unlike taking a smear, this manipulation is performed under anesthesia. Therefore, you should go to the doctor on an empty stomach, the last meal should take place 10–12 hours before the test.
Sometimes after a biopsy, patients complain of nagging pain in the lower abdomen and spotting. In order for recovery to take place as quickly as possible and all discomfort to pass quickly, the following recommendations must be followed for 1.5–2 months after the biopsy:
- Do not visit the bathhouse or sauna, do not take a bath (only showers are allowed).
- Avoid significant physical activity.
- Do not use tampons, vaginal ointments and suppositories, and do not douche.
- Do not have sexual intercourse.
- Take blood thinning medications, including aspirin, with caution.
How often to conduct research
You should take blood samples and examine tumor markers after treatment:
- in the first year - monthly;
- in the second year - once every 2 months;
- in the third year - once;
- for 4-5 years - twice, then - annually.
Deviations in the direction of increasing the main tumor marker SCC and additional CA 125 will occur in 80-90% of sick women, but this does not always indicate tumor growth, since it is known that they increase in other diseases of the genitourinary organs. If necessary, additional research methods are carried out so as not to miss the development of secondary cancer.
Determination methods
The absence of specific symptoms can significantly complicate the definition of the disease. Doctors call the similarity of signs of cancer and other gynecological diseases one of the main factors in late diagnosis of the disease.
To identify pathology, the patient must undergo a full examination, including various tests.
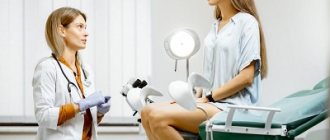
- General gynecological examination. For cervical cancer, determining the disease begins with a gynecological examination and medical history. During a bimanual examination and examination with a vaginal speculum, the doctor can visualize changes, including the structure and color of the mucous membrane. In addition, cancer processes are often accompanied by characteristic growths of epithelial tissue. A general examination is especially important for invasive cancer. With endophytic growth of cancerous elements, the neck has a denser consistency and may be larger in size. An exophytic type of cancer pathology during a gynecological examination looks like the formation of a tuberous structure.
- Lab tests. To determine cancerous structures, a screening test is used, called an oncocytology smear. Unlike a general smear, this analysis shows the presence of cancer cells, as well as the inflammatory process. It is advisable to perform a cytological examination or smear for oncocytology in the middle of the cycle. Before collecting biological material, suppositories and spermicides should not be used. A smear for oncocytology is taken with a special brush during a gynecological examination. To identify cancer cells, a cytology smear is examined under a microscope.
Many women are interested in whether it is possible to detect cervical cancer using a general blood test. In fact, cancer cells cause changes throughout the body that can be seen in a complete blood count. A general blood test in medicine is called a basic blood test. However, in order to determine the type of oncology, a general blood test is considered uninformative. In such cases, it is necessary to perform a biochemical blood test showing the presence of cancer cells in a specific organ.
A general blood test with the spread of cancer cells indicates an increase in ESR and the number of leukocytes, a decrease in hemoglobin levels and the appearance of myeloblasts.
Tumor markers are a specific type of protein that appears as cancer spreads. Normally, these proteins are absent in a blood test or are contained in small quantities. Each organ has its own tumor markers, diagnosed in a blood test. For example, a blood test to measure CA 125 and SCCA levels may be used to detect cervical cancer. Such blood tests are not always reliable and are used mainly to evaluate the therapy performed. They are not suitable for primary diagnosis, since cancer cells do not always produce specific proteins.
When determining cervical cancer, an HPV test is prescribed. Of particular importance is the identification of highly oncogenic strains of the virus that can contribute to the formation of cancer.
- Colposcopy. The study is necessary for oncological suspicion and is carried out according to the results of a diagnosis called a cytological smear. The procedure is a diagnosis carried out using a colposcope - a device with a magnifying and lighting system. Often, extended colposcopy is used using special reagents applied to the cervix to determine the clinical picture.
- Hysteroscopy. The manipulation is carried out using a device called a hysteroscope. This device is inserted into the vagina to detect diseases and treat them.
- Biopsy. The study is indicated if a cytology smear and colposcopy show conflicting results. Sometimes a cytological smear to determine cancer may not reveal pathology. The biopsy procedure involves removing tissue for further examination in the laboratory. Such an examination can be carried out in the following ways:
- colposcopic;
- wedge-shaped;
- curettage.
Wedge biopsy has several varieties:
- Ultrasound. The examination is carried out abdominally and transvaginally. With this type of examination, you can evaluate the appearance of the cervix and its structure. With cancer, the cervical part has an irregular shape and position, as well as a blurred outline.
The following instrumental types of research are used to detect metastases:
Timely diagnosis, including a cytological smear, ensures the prescription of adequate therapy and significantly increases the patient’s chances of a complete recovery.
Tumor markers for uterine cancer - interpretation of tests on Oncoforum
Cervical cancer is one of the most common types of malignant tumors in women. The cancer process develops at any age. Tumor markers for uterine cancer increase even at the preclinical stage of the disease. Early diagnosis of the tumor contributes to the woman’s complete recovery.
What tumor markers should be taken if uterine cancer is suspected?
Tumor markers are biologically active substances that are synthesized in a cancer cell from the moment of its metaplasia. Tumor markers consist of a protein molecule to which a carbohydrate and a lipid are attached. Cancer markers are produced in different quantities depending on the phase of the tumor process and the histological structure of the uterine cancer. Some of these markers enter the blood, where they can be detected using non-invasive methods.
Due to the effect of cancer cells on the body, some organs begin to produce excess amounts of hormones or enzymes that are physiological for them in normal concentrations. Also, when uterine cancer metastasizes to other organs, tumor markers characteristic of the cancer of the organ in which the metastases formed enter the blood.
To diagnose uterine cancer, a woman needs to check the level of tumor markers:
· squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA);
· beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (βhCG);
· carcinoma embryonic antigen, or cancer-embryonic antigen (CEA);
· tumor marker CA 27-29.
Since in ninety percent of cases cervical cancer is a squamous cell neoplasm, when the pathological process is localized in the cervix, the most informative tumor marker is squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA). It is used to monitor the course of the disease, assess the effectiveness of treatment, prognosis and preclinical detection of relapses.
Squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA, SCC) is a tumor associated antigen of squamous cell carcinomas localized in different organs: cervix, esophagus, vulva. The SCCA group of tumor markers belongs to the family of serine proteinase inhibitors. It consists of more than ten proteins. They are divided into two groups - acidic and neutral SCCA. The salivary glands produce SCCA.
Colposcopy
This technique is a diagnostic examination using a specialized device - a colposcope.
This is a fairly highly informative diagnostic procedure used in cases of suspected cervical cancer.
This research method allows for a more precise diagnosis. The best time to carry out such a diagnosis is after the end of menstruation and before the onset of ovulation.
Colposcopic diagnosis is considered completely safe and does not cause any consequences, however, it is not recommended to conduct examination with a colposcope:
- Within 2 postpartum methods;
- During the first month after an abortion;
- For several months after surgery on cervical tissues;
- For menstrual and other bleeding;
- With extensive inflammation, accompanied by discharge of purulent origin.
In other cases, colposcopic diagnosis has no contraindications.
Features of uterine cancer
Cancer can arise in endometrial cells of the uterus, which, due to various reasons, have undergone mutations, leading to metaplasia and tumors. Subsequently, the altered cells metastasize to various organs through the circulatory and lymphatic systems. Cervical carcinoma is divided into two histological types: adenocarcinoma (more details here) and squamous cell carcinoma. Timely analysis of tumor markers makes it possible to detect tumors at preclinical stages.
The causes of cervical cancer have not been fully established; it is only known that the risk group includes women with obesity, diabetes, and those who have not given birth. Manifestations of the disease include discharge and bleeding from the genitals, pain, including during sexual intercourse. It must be remembered that the cancer marker cannot be considered a final diagnosis, it only indicates the presence of such a pathology in the patient, and a biopsy (tissue histology) provides accurate data. Symptoms of uterine cancer in women include pain in the mammary glands and abdomen, and fatigue. With a significant size of the cancer tumor, it affects the pelvic organs and this is also considered a symptom of the disease. Unfortunately, these signs appear in the later stages and complete cure in this case is difficult. Diagnostics that detect cervical cancer at various stages include establishing the level of tumor markers.
Strokes
During the examination, the doctor takes smears for cytology. It allows you to determine the condition of the epithelium of the cervix and its canal. On the outside it is covered with multilayered squamous epithelium, and on the inside – cylindrical. The appearance of atypical cells allows one to suspect a precancerous condition or cancer.
The material is taken with a special cytobrush or spatula, separately from the cervical canal and its surface. The resulting mucus is applied to glass. The result is ready in 5-10 days.
The study cannot be carried out if there is inflammation in the cervix; this condition will give a false positive result, which can be regarded as a precancerous condition. On the eve of the study, do not engage in sexual intercourse, douche, place suppositories or tampons.
The result of a smear is a description of the structure, shape and structure of the cells.
A smear for oncocytology is performed even on pregnant women. This condition is accompanied by hormonal changes that can trigger the growth of carcinoma.
The status of endometrial cells can be determined using aspiration biopsy. It is performed with a special syringe through the cervical canal without preliminary dilatation.
For research, the resulting material is sent to the laboratory. The conclusion describes the state of the endometrial cells, their size, structure and shape, and the presence of atypically changed ones.
Is a positive prognosis possible for late-stage squamous cell carcinoma of the uterus? This article describes complications after surgery to remove uterine fibroids.
Follow the link https://stoprak.info/vidy/zhenskix-polovyx-organov/matka/mioma-vo-vremya-beremennosti.html photo of uterine fibroids during pregnancy.
What are tumor markers and their types
Tumor markers are special cells detected in the urine or blood of a cancer patient. The presence of such cells is detected by the results of their vital activity, which are released into the blood and make it possible to identify the disease in the initial stages.
Today, different methods for diagnosing cervical cancer are used, but this particular one not only allows one to identify malignant neoplasms even before their clinical manifestations become noticeable, but also shows how effectively the treatment used works.
Determining the level of tumor markers and the degree of their deviation from the norm also indicates the localization of the disease, but in order for the results of the study to be as accurate as possible, several diagnostic methods should be used.
The tumor marker SCC is a marker for squamous cell tumors of the neck, head, lungs and cervix. An increased content of it indicates the occurrence of malignant formations, but pathology cannot be excluded even with a negative result. Dynamic results are required if the first test was positive; if the initial result is negative, a repeat test is not informative.
- Determining the possibility of survival to establish subsequent treatment;
- Establishing the aggressiveness of tumor formation processes.
- Low specificity (changes in indications due to various factors), so a comprehensive analysis of the results is needed;
- Insufficient information content at the initial stages of the disease.
CA-125
Tumor marker for cervical cancer CA-125 is a glycoprotein found in serous membranes and tissues. The endometrium is responsible for its production in patients of reproductive age. This is why the level of tumor markers may change depending on the menstrual cycle. For example, during menstruation, the tumor marker CA-125 is synthesized in increased volumes; it is also present in the blood serum in the first trimester of pregnancy, as well as in the placenta and amniotic fluid during a certain period of pregnancy.
The hCG tumor marker molecule consists of two parts; it is secreted by the placenta during pregnancy. The course of pregnancy is assessed by the level of concentration of the β-subunit, and an increased level of hCG in the blood in the absence of pregnancy indicates the process of tumor formation.
Carcinoma caembryonic antigen (CEA) is used to diagnose cancer of various organs; it is also a good marker of cervical cancer. It is synthesized by the cells of the embryo; after the child is born, the production of the antigen stops. In adults without cancer, only traces of CEA are detected in the blood, and its presence indicates the appearance of a tumor, but without indicating its location.
CA 27-29
CA 27-29 is a unique tumor marker that has a clear localization - the mammary gland. It is expressed on the cell membranes of breast tumors, but is also synthesized in large quantities in uterine cancer and endometriosis.
Types of biopsy
Often, if cancer is suspected, a biopsy is performed, which is the removal of a suspicious tiny piece of tissue for examination. Depending on the method of taking biomaterial, the biopsy can be colposcopic, wedge-shaped or curettage.
Colposcopic
A targeted biopsy is performed during a routine gynecological examination. The patient is given a colposcope and then a manipulator to remove a piece of tissue. The procedure is absolutely painless and takes less than half a minute.
Curettage of the cervical canal
A similar diagnostic procedure is also called an endocervical biopsy and involves scraping tissue from a small area of the uterine cervix with a special gynecological instrument - a curette.
Wedge biopsy
Such a diagnostic procedure can be carried out in several ways:
- Loop excisional biopsy is considered a very traumatic technique and can lead to the formation of scars on the uterine cervix. The specialist inserts a loop-shaped manipulator into the neck, through which current flows. With this instrument he peels off the pathological tissue;
- Cryoconization. Instead of an electric loop, liquid nitrogen is used, otherwise the principle is similar to the previous method;
- Radio wave conization. A biopsy is taken using a radio wave knife.
The results of a biopsy examination are more accurate than those obtained with oncocytology or colposcopy.
Indications for window marker analysis
Cancer tumor markers for various organs, including the uterus, are necessary for timely diagnosis, when effective treatment is possible, guaranteeing maximum restoration of health. They help determine whether uterine cancer is completely removed during surgery, to predict the results and adjust the prescribed treatment. The normal level of tumor markers may be an indicator of the absence of oncology of the reproductive system, but if there are clinical symptoms of the disease, you should not reassure yourself about the level of tumor markers. It is necessary to take other tests to establish a clear diagnosis.
How to prepare
Recommendations for determining the level of any of the markers should be established exclusively by specialists, and to obtain the most accurate information, a number of recommendations are given, including:
- Food should be taken eight to ten hours before testing;
- Quitting alcohol and tobacco;
- Avoid psycho-emotional and physical stress;
- Maintaining sexual rest;
- If you are taking any medications, inform your doctor;
- Blood sampling is carried out in the morning.
Norms
Laboratories use different methods for determining the level of tumor markers. To eliminate errors in the perception of results, laboratories conducting analyzes provide information about the normal values and the analysis method used. It is recommended to interpret the test results in the clinic where the tests were performed, and when re-determining tumor markers (screening studies and follow-up over time), it is also recommended to contact the laboratory or clinic that performed the initial tests.
Sources:
https://moyakrov.ru/analizy/onkomarkery/rasshifrovka-onkomarkera-scc/ https://www.oncoforum.ru/o-rake/rasshifrovka-analizov/onkomarkery-raka-matki.html https://matkamed.ru /rak/onkomarker
conclusions
Modern medicine does not stand still and now there are a huge variety of tests for cancer. At the first manifestation of unpleasant symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. He will prescribe the necessary tests for uterine cancer that are right for you and will allow you to develop a plan for high-quality and effective treatment. Remember that a disease detected in time is easier to treat!
Sources:
https://www.kp.ru/guide/analizy-pri-zabolevanijakh-sheiki-matki.html https://ginekola.ru/ginekologiya/shejka-matki/rak/analizy-na-opredelenie-raka-shejki-matki .html https://orake.info/analiz-na-rak-matki/