How does this happen?
The initial stages of pregnancy are considered the most critical; it is at these stages that the chances of its termination are especially high, this is due to the fact that, in fact, the fertilized egg has a genetically foreign composition for the maternal body (after all, half of the genetic set there is paternal), and therefore it can be rejected by the body . Most spontaneous interruptions occur at this stage.
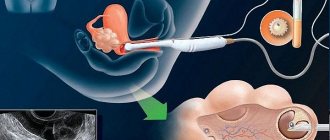
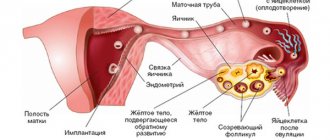
After the fusion of the paternal and maternal germ cells, an embryo is formed. It forms and develops over several days, during which it is in the uterine cavity in a free state, not associated with the maternal body. After its formation is completed, it penetrates into the mucous layer of the uterus - the endometrium, which by that time has sufficiently recovered (normal).
Attachment occurs thanks to the villi on the embryo, with which it clings to the mucous membrane, damaging it. Attachment occurs finally, and the embryo begins to develop. At this stage, the fetus is quite developed - it has inner and outer petals (the fetus develops from the inner one, and the placenta develops from the outer one). It is the outer petal that prevents the antibodies of the mother’s body from attacking the foreign organism of the embryo, which would lead to its rejection.
Required behavior
Among women planning a pregnancy, there is an opinion that it is necessary to limit physical activity as much as possible (even to the point of bed rest) in order for the fetus to become well established and continue to develop normally. However, this is not true.
At 1-2 weeks of pregnancy, genetic factors in the formation of the embryo and the preparedness of the endometrium to accept the embryo are important for its preservation. Therefore, a woman, preparing for conception, can continue her usual lifestyle without any fear. The only exceptions are those representatives of the fair sex whose fertilization was carried out using artificial methods.
What day after ovulation?
When does the embryo attach to the wall of the uterus, and on what day after ovulation does this occur? It is worth remembering that you can get pregnant not only during ovulation (although during it it is most likely that this will happen), therefore it is more correct to talk about how long after fertilization of the egg the fertilized egg is fixed on the endometrial lining of the uterus.
The duration of this process can vary significantly depending on the individual characteristics of the expectant mother’s body, the conditions in which she is located, the conditions in which conception occurred, etc. On average, the process from fertilization to the beginning of attachment takes from six to twelve days (but sometimes shorter and longer periods occur). If we assume that fertilization occurred during ovulation, then the first symptoms of attachment of the fertilized egg to the uterus will appear on days 20-28 of the menstrual cycle, right before the expected period.
All this time, from conception to implantation, the fertilized egg is completely autonomous from the mother’s body and is in no way connected with it. Therefore, it cannot be affected by negative processes that can occur in her body (therefore, there is nothing wrong if, without knowing about pregnancy, in the first days after fertilization a woman took alcohol, medications, junk food, etc.) .
It is important to note that doctors even distinguish two types of process depending on its duration. When the egg, or rather the fertilized egg, has implanted within 6-7 days after fertilization, we speak of early implantation. Late is diagnosed when the process occurs on the 10-12th day. The early form of leakage is extremely rare due to the fact that the fertilized egg has to travel quite a long way, and in addition, the endometrium may not be ready for attachment.
Late also does not occur very often and is most typical for women over 40 years of age. If we are talking about the procedure of in vitro fertilization, then this period is the most favorable, since the embryo manages to adapt better after replanting. But on average, most often, the embryo is attached at 8-9 days.
Attachment
First trip
Now it is no longer an egg, but an embryo that begins its journey to a place where it can develop over the next nine months. The journey takes from seven to ten days, if you count from ovulation. Soon enough, the embryo will attach to the uterus. On what day this will happen is unlikely to be answered unequivocally. It all depends on the woman’s cycle and the day on which sexual intercourse occurred. In addition, sperm carrying the Y chromosome are more mobile and can reach their goal faster, while its counterparts carrying the X chromosome (future girls) are slower, but can live longer and wait for the egg to be released.
Process Features
When the fertilized egg is implanted, some characteristic symptoms of this process appear (in some cases). Their appearance is connected precisely with the specific features of this process. These features are as follows: if implantation occurs, then glycogens, lipids and fluid accumulate in this area of the endometrium. This is what causes minor bleeding. This occurs because a small local microtrauma of the mucous membrane occurs, which also causes an increase in body temperature and mild malaise.
Onset of pregnancy
It takes approximately 2-3 days for the embryo to go through the implantation stage. After this, obvious signs of pregnancy begin to appear. This is a metallic taste in the mouth, as well as mild nausea. You may experience dizziness, increased irritability, and weakness. Some people note an extraordinary emotional uplift and a feeling of endless euphoria, others, on the contrary, depression and resentment towards others. These days it becomes obvious that the next menstruation is delayed. Plus, there is soreness in the mammary glands. All together - these are reliable signs that you will soon become a mother.
Why doesn't implantation occur?
The reasons for the embryo not attaching to the uterus are varied. Rejection of the fertilized egg by the body occurs in the following cases:
- Insufficiency of the hormone progesterone, the corpus luteum has not formed;
- Too thin or too thick, heterogeneous and/or altered endometrium, etc.;
- Frequent surgical abortions;
- Surgical interventions, the presence of scars and adhesions in the uterus;
- Infectious and inflammatory processes in the organs of the reproductive system;
- Processes associated with pathological tissue proliferation - hyperplasia, fibroids, tumors, polyps, etc.;
- Genetic defects of the fetus;
- Enhanced or pathological functioning of the body's immune system, as a result of which antibodies are produced in such a volume that they can cause death and rejection of the fetus no matter what.
When the embryo attaches to the uterus, in general, its tone plays an important role. But in the early stages, even hypertonicity cannot be the reason why the fertilized egg does not attach. Problems most often lie in the hormonal composition and condition of the endometrium.
What can be done to ensure that the embryo takes root?
The treatment performed (in order to increase the chances of attachment) is selected taking into account the morphological changes in the decidual tissue.
To improve the quality of the endometrium in case of deficiency of immune activity, it is recommended:
- local irritation of the mucosa using pipell biopsy (collection of endometrial cells with a disposable tube with a side hole and a piston inside) or hysteroscopy;
- moderate ovarian stimulation;
- support of the luteal phase with low doses of human chorionic gonadotropin;
- injection of seminal fluid after embryo transfer;
- intrauterine injection of peripheral mononuclear cells cultured with human chorionic gonadotropin.
With increased immune activity, a condition precedes inflammation occurs, and embryos do not engraft after IVF transfer.
HCG after IVF: normal concentration by day
Therefore, in this case it is recommended:
- avoid local irritation of the uterine mucosa;
- carry out standard ovarian stimulation;
- sufficient support for the luteal phase;
- use corticosteroids, intralipids, intravenous immunoglobulins;
- sexual rest after embryo transfer;
- intrauterine injection of follicular fluid.
Symptoms of ongoing attachment
Are there symptoms of embryo implantation in the uterus? Is it possible to somehow feel and suspect this process? Certain symptoms exist, but their appearance is by no means necessary. It is considered normal both when they are present and when they are absent. Approximately equal numbers of women experience them and are not affected by them. If symptoms do develop, they have the following character:
- Minor vaginal bleeding or brown or pinkish discharge, which can be either one-time or last less intensely for several hours;
- Tingling, pain and/or heaviness in the abdomen;
- When the fertilized egg attaches to the uterus, there is a slight increase in basal temperature - up to approximately 37.0-37.3 degrees.
After passing this stage, quite clear signs of pregnancy may be observed, which appear immediately after the end of the implantation stage. First, there is a delay in menstruation, then heaviness in the stomach and mood swings appear. Usually, around this stage, a woman consults a doctor and is diagnosed with pregnancy. This condition is often accompanied by nausea, metallic taste in the mouth, dizziness, and weakness.
First sensations
Is it possible to feel the attachment of the embryo to the uterus? The symptoms may not always be obvious, but if a woman is in harmony with her body, then she is able to recognize what is happening now. At first glance, only a tiny cell is introduced into the wall of the uterus, but, on the other hand, this dramatically changes the hormonal background. That is why it is quite natural that unusual sensations can be tracked.
Minor bleeding is the first and main symptom that accompanies the attachment of the embryo to the uterus. Symptoms can be obvious (for example, a blood stain appears on the underwear, which can be mistaken for the beginning of menstruation) and latent - in this case, the discharge becomes light brown or barely pink, so if you do not wear a daily planner, you may not notice it in the dark linen.
During the implantation period, you may experience abdominal pain, tingling and a feeling of heaviness. However, if a woman is expecting her main menstruation, then it is quite possible that these symptoms will be regarded as PMS. The main symptom can be considered an increase in body temperature to 37-37.3 o C. If you plot basal temperatures, you will probably notice this jump.
However, everything is very individual. Some people do not notice any changes, so the attachment of the embryo to the uterus is completely asymptomatic. The sensations may be vague, and if a woman does not count the days until pregnancy and does not look for signs of its onset every day, then they can be ignored. There is nothing wrong with this; soon nature itself will tell you that it is time to prepare for the arrival of the baby.
Symptoms of attachment after IVF
The signs of embryo implantation into the uterus after IVF (in vitro fertilization) are no different. However, later implantation is characteristic and favorable for such a procedure, therefore the main difference in symptoms is this: it begins to appear much later. Although such symptoms after this procedure have greater emotional significance, since, most often, failures with this procedure are due to the fact that the egg does not attach to the uterus. The characteristic symptoms indicate that the embryo has attached, which means that the likelihood of a successful pregnancy has increased significantly. However, the absence of symptoms cannot be a guarantee that the procedure was unsuccessful, since normally they may be absent.
Short description
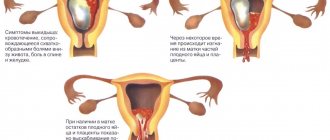
Now let's talk about what, in fact, is the attachment of the embryo to the uterus. On what day this will happen - you can find out exactly by drawing up an ovulation schedule. We'll talk about this later, but a little later. So, the fertilized egg descends into the uterus and chooses a place for final attachment. On this day, she sheds the zona pellucida to attach to the endometrium. It is called "trophoblast".
The expectant mother may not yet have any idea what is happening in her body. And at this time, the villi sink deeper into the mucous membrane and secrete special enzymes. They promote the growth of the mucous membrane, which allows the embryo to burrow deeper and deeper. Here he will receive everything he needs for development: protection, nutrition and oxygen.
The influence of morphological changes in the structure of the endometrium
A significant reason why embryos do not implant after IVF is controlled ovarian stimulation (COS). But it should immediately be noted that the exact cause and mechanism of changes in the uterus that occur under the influence of CBS are poorly understood. There is no possibility to histologically examine the endometrium on the eve of transfer, since if the integrity of the mucous membrane is damaged, embryo transfer cannot be performed (it will be ineffective). That is, obtaining material to study the issue is problematic.
Studies show that in stimulated cycles, a premature release of progesterone can be observed (even before follicle puncture), which negatively affects the implantation properties of the endometrium.
The level of preimplantation losses after stimulation of ovulation, compared with natural pregnancy, is significantly higher - this confirms the unfavorable effect of CBS on implantation.
The following have a negative effect on implantation:
- hyperplasia;
- polyps;
- thinned endometrium (less than 7 mm).
Hyperplasia and polyps have been well studied. For their treatment, a complex of surgical and therapeutic measures is used, which successfully allows the problem to be overcome and embryos to take root after IVF and in natural cycles (spontaneous pregnancies).
To treat thinned endometrium, hysteroscopy was previously used as a local irritation of the endometrium, prolonged stimulation with estrogen, a combination of pentoxifylline and vitamin E. But the effectiveness of therapy remained questionable.
Since 2012, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor preparations have been used intrauterinely for the treatment of resistant thin endometrium. The new technique gives more positive results regarding endometrial growth compared to standard treatment methods.
Which embryos take root better: fresh or cryo?
Analysis of fresh and “cryo” cycles (transfer is carried out in a natural cycle) showed a pattern that the pregnancy rate in cryoprotocols is higher than in fresh protocols. And the frequency of miscarriages in fresh protocols is higher than in “cryocycles”.
Cryo embryos take root better in the uterus. In addition, Italian scientists have confirmed that the frequency of clinical and progressive pregnancies in “cryo” cycles is higher, and the frequency of miscarriages is lower.
Therefore, it was concluded that freezing embryos and transferring them in a natural cycle (without stimulation) is a fairly effective technique and allows one to overcome unfavorable endometrial transformations that occur during stimulation.