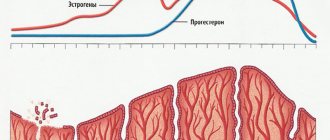
The endometrium is the inner lining that lines the uterine cavity. This is a unique tissue of the body that is subject to female hormones. The tissue undergoes monthly changes: under the influence of hormones it grows, reaches a certain thickness, and then is rejected and removed from the genital tract during menstruation.
The endometrium consists of numerous vessels, glands and connective tissue. Various diseases can develop in it: from inflammation, hypo- or hyperplasia, to benign tumors and cancer.
Early diagnosis using modern research methods helps to identify pathology at an early stage of development and preserve the reproductive function of a woman.
Endometrial biopsy - indications for performing
A biopsy can be performed on patients of any age and reproductive status, including women who have not given birth.
The procedure is prescribed in cases where a gynecological examination and other tests do not allow an accurate diagnosis and identification of the cause.
Indications for biopsy are:
- dysfunctional bleeding;
- scanty menstrual flow and menstrual irregularities - amenorrhea;
- suspicion of tumor development;
- endometriosis;
- suspicion of inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity;
- infertility for an unknown reason;
- upcoming IVF;
- spontaneous abortion;
- pathologies of early pregnancy.
Consequences
If the preparatory recommendations are not followed, as well as if there are violations during the manipulations, some complications may arise.
Perforation of the uterine fundus
This condition occurs if the procedure was performed by a doctor with little experience. In such a situation, severe blood loss will be observed, which is the basis for visiting a medical facility.
Bleeding
Minor discharge after a biopsy is considered normal. In addition, with this condition, the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen is often noted. If the bleeding is intense and does not stop for a long time, you should consult your doctor.
Infection of the uterine body
Penetration of infection into the uterine cavity is one of the most dangerous complications. The reason for this problem in most cases is non-compliance with recommendations during preparation and rules for performing a diagnostic study.
When infected, severe pain, intoxication of the body, and brown discharge with an unpleasant odor are noted.
Contraindications for biopsy
An absolute contraindication to a biopsy is the period of pregnancy, because The doctor's actions will lead to a miscarriage.
Other contraindications:
- inflammation of the genitourinary system;
- blood clotting disorder;
- severe anemia;
- allergic reaction to anesthetics;
- general unsatisfactory condition of the body;
- sexually transmitted diseases.
The reason for canceling the biopsy may be the anticoagulants the patient is taking, which increases the risk of bleeding. In such cases, their use is interrupted in advance or the endometrial examination itself is postponed.
How to prepare for the procedure?
Before taking a biopsy, the patient must undergo a preliminary examination by a gynecologist and undergo a number of tests:
- flora smear;
- cytology smear;
- blood tests - general, hCG, Rh factor, blood group;
- tests for hepatitis, syphilis and HIV;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- colposcopy.
During an interview with the patient, the attending physician clarifies information about taking medications and adjusts drug therapy. Avoid blood thinning medications 7-10 days before the biopsy.
The day of the examination is selected based on the phase of the patient’s menstrual cycle, if the woman has not entered menopause.
Aspiration research is carried out within the following time frames:
- 18–24 days to determine the current phase of the cycle;
- on the day of the discovery of pathological bleeding - to determine the cause;
- on the 10th day of the cycle - with pathologically heavy menstruation;
- on the 1st day of the cycle or one day before the start of menstruation - in case of infertility;
- once every 7 days in the absence of menstruation - if the possibility of pregnancy is excluded;
- on days 17–28 in case of treatment with hormonal drugs.
If there is a suspicion of the development of a cancerous tumor, an endometrial biopsy is performed without reference to the cycle.
Three days before taking a biopsy, a woman should follow the doctor’s recommendations:
- do not engage in intimate contacts;
- stop douching and refuse vaginal suppositories, creams, tampons;
- avoid eating foods that promote gas formation;
- On the eve of the biopsy, give an enema to cleanse the intestines.
In the morning before the examination, the woman takes a hygienic shower and removes hair in the external genital area. For patients with varicose veins, the use of elastic bandages is recommended to prevent thromboembolism.
The procedure does not require pain relief.
Local anesthesia is used only in cases where the patient has a high pain threshold. Then it should be established that there is no allergy to the painkiller.
On the topic of biopsy - How is a prostate biopsy done?
Biopsy techniques
Taking material for analysis can be carried out in different ways.
Today the following techniques are used in medicine:
- curettage of the uterine cavity;
- aspiration biopsy;
- pipel biopsy - a type of aspiration technique;
- CUG biopsy.
Scraping
The technique is radical and traumatic. The cervix is opened with medical dilators to provide access to the organ cavity.
When the cervix is secured with forceps, the doctor inserts a sharp curette and scrapes off part of the mucous membrane. Such an endometrial biopsy requires increased care from the specialist, since the risk of damage to the walls of the uterus is very high.
During curettage, the patient is under general anesthesia. Therefore, on the eve of the procedure, the woman should refuse to eat and drink.
Curettage can be carried out for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, if pathological tissue is removed along with the mucous membrane.
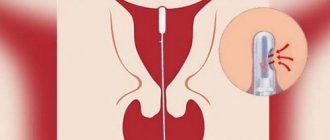
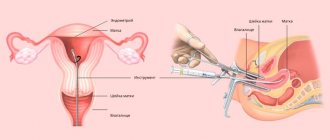
Aspiration biopsy
On the day of the planned study, the patient with a referral comes to the office where an aspiration biopsy will be performed. A vacuum is used to take a biopsy sample.
Cervical dilatation is not required, so the procedure does not cause pain, but only minimal discomfort when inserting medical instruments.
The woman sits on a gynecological chair. The specialist inserts a speculum and a special tip into the vaginal cavity, connected to an electric suction device.
In some cases, a syringe is used as an analogue of an electric vacuum apparatus.
Pipelle biopsy
The biopsy sample is removed by analogy with the aspiration technique. However, a thin tube approximately 3 mm in diameter is used to collect tissue.
A Pipel instrument is inserted into the uterus, after which the doctor pulls back the piston and creates negative pressure, thereby causing the separation of part of the endometrium.
The method is preferable for nulliparous patients, as it is the most gentle.
CUG biopsy
A CG biopsy is performed using a small curette, but does not require dilatation of the cervix.
The specialist scrapes out narrow parts of the mucous membrane in the form of small strips from different parts of the uterus, from the fundus to the pharynx.
The method is often used to monitor the effectiveness of hormonal treatment.
The most modern and informative method of endometrial biopsy is hysteroscopy. To carry it out, a hysteroscope is used. However, due to insufficient instrumental equipment of clinics, this technique is used very rarely.
What complications may arise after collecting an aspirate?
Rarely, but still sometimes injury to the uterus occurs. In this case, the patient experiences severe pain in the abdominal area. Sometimes the pain radiates upward, almost reaching the collarbone area.
In this case, the patient experiences nausea, dizziness, decreased blood pressure, pain in the abdominal area, and in some cases, bleeding may appear.
In rare cases, inflammatory processes may begin to develop in the uterus. This situation causes a woman to experience general weakness, abdominal pain and sometimes an increase in body temperature. Signs of this inflammation may occur several days later or immediately after aspirate collection.
According to numerous reviews from patients, aspiration is most often absolutely harmless. No special preparation is required for the procedure; hygienic actions are sufficient.
Many gynecologist patients hear about such manipulation as aspirate from the uterine cavity. Let's talk about what this procedure is, why it is performed on women at different ages, and what its advantages and disadvantages are.
The term “aspiration” literally means “to suck out.” In medicine, aspiration biopsy is widely used - that is, obtaining tissue fragments using “suction”, usually based on a pressure difference. The procedure is carried out with a syringe, special probes, vacuum electric aspirators, and so on.
Such aspirate can be taken from the lungs, bronchi, stomach, sinuses, and large fluid formations. In gynecology, aspiration biopsy from the uterine cavity is very common.
There are three main types of this procedure:
- Aspiration biopsy of the endometrium using a vacuum aspirator;
- Aspiration biopsy using a syringe or manual (manual) vacuum aspiration;
- Pipelle endometrial biopsy or aspirate using a special uterine probe.
Recently, these manipulations have become widespread for various indications:
- Approximate and initial diagnosis for suspected various diseases of the uterine body. This manipulation can be performed to diagnose conditions such as uterine cancer, endometrial hyperplasia, chronic endometritis, various variants of abnormal conditions of the uterine cavity - hematometer, serosometer.
- Routine examination before various gynecological procedures and operations. An endometrial biopsy is performed before IVF, insemination, and stimulation of ovulation in women with infertility.
In gynecological patients, this manipulation is performed as a primary stage before planned operations, for example, before removal of uterine fibroids, pelvic floor plastic surgery. Previously, separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity was used for these purposes, but in recent years in most cases there is no need for such a traumatic examination.
Diagnosis of the causes of infertility in women. In this case, endometrial tissue can be obtained for histological examination.
This is important for assessing the usefulness of the endometrium, its correspondence to the phase of the menstrual cycle, and the presence or absence of an inflammatory response. Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of treatment for a particular condition. An aspirate from the uterine cavity can give an answer as to whether prescribed medications help, for example, for endometrial hyperplasia, or whether chronic endometritis has been treated with antibiotics.
Now let's look at each type of aspiration biopsy separately.
Evaluation of results
After removal, the endometrial fragment is sent to the laboratory for microscopy and histological examination.
For a more accurate analysis, the pathologist must have information regarding the exact day of the patient’s menstrual cycle, age and current therapy regimen.
If deviations are not recognized during the study, the absence of atypical signs is indicated in the conclusion.
Among the pathological processes the following can be identified:
- diffuse hyperplasia of the mucous membrane - proliferation of the endometrium;
- complex hyperplasia of the mucous membrane - proliferation of the endometrium, complicated by the formation of glands inside hypertrophied tissues;
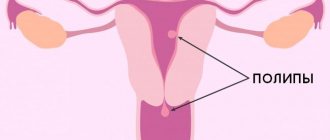
- local processes of hyperplasia - the formation of polyps in the uterine cavity;
- atypical hyperplasia - a mutation of overgrown endometrial tissue;
- malignant processes;
- endometrial atrophy;
- endometritis - inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane;
- discrepancy between the status of the endometrium and the current phase of the menstrual cycle.
Endometrial atrophy is not always a pathology. For elderly patients, atrophic processes may be a variant of age-related changes.
Post-procedure period
After the procedure, the patient can go home immediately. Hospitalization is not required after an endometrial biopsy. The next 1-2 days may cause mild pain, which can be relieved with antispasmodics.
Bloody vaginal discharge is observed for several days after the procedure and is considered normal. After bleeding has stopped, you can resume sexual activity.
The menstrual cycle may be disrupted with a delay of up to 10 days. If the delay exceeds this period, you must consult a doctor.
After a biopsy, patients often complain of discomfort during sexual intercourse. This symptom is temporary.
With a minimally invasive biopsy, pregnancy can occur in the current cycle, since the intervention does not affect the reproductive functions of the ovaries.
With a radical biopsy - curettage - the recovery process takes longer and is associated with heavy bleeding.
Recommendations after the biopsy for the first few days:
- avoid hot showers, baths, baths and saunas;
- do not use tampons;
- avoid physical activity;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- carefully observe genital hygiene.
On what day of the cycle is it done?
Eûø þÃÂýþòýðà÷ðôðÃÂð ÿÃÂþòõôà VALUE þÿÃÂøÃÂÃÂøà÷ðúûÃÂÃÂðõÃÂÃÂàò ÃÂþü, ÃÂÃÂþñàþÿÃÂõôõûøàÃÂÃÂþòõà½Ã Ã±ÃµÃÂÿûþôøÃÂ, ÃÂþ ðýðûø÷ ÃÂÃµÃºÃ¾à ¼ÃµÃ½Ã´ÃÂõÃÂÃÂàôõûðÃÂà÷ ð ôõýàôþ ýðÃÂÃÂÃÂÿûõýøàüõýÃÂà VALUE › ð.
ÃÂÃÂûø ôøðóýþÃÂÃÂøÃÂþòðýð ÿþûà¸Ã¼ÃµÃ½Ã¾ÃÂõÃÂ, ÃÂþ ôõûðÃÂàøÃÂÃÂûõôþà²Ã°Ã½Ã¸Ãµ ò 5 ø 10 ô õýÃÂ.
àÃÂûÃÂÃÂðõ úþóôð þÃÂüõÃÂðõÃÂÃÂàÿà VALUE òÃÂôõûõýøù, ñøþÿÃÂøàý à°Ã·Ã½Ã°ÃÂðõÃÂÃÂàýð 1-2 ôõýààüþüõýàð, úðú ýðÃÂðûðÃÂàüõýÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂðÃÂøÃÂ.
ÃÂþóôð ÃÂõû÷ðúûÃÂÃÂðõÃÂÃÂàò þÿà VALUE ¸Ã¹ ôþñÃÂþúðÃÂõÃÂÃÂòõýýþóþ øûภ÷ûþúðÃÂõÃÂÃÂòõýýþóþ ÃÂðÃÂðúÃÂàµÃÂð, ÃÂþ ðýðûø÷ ÿÃÂþòþôÃÂàòýõ ÷ ðòøÃÂøüþÃÂÃÂø þàÃÂøúûð.
ÃÂÃÂûø õÃÂÃÂàÿþôþ÷ÃÂõýøõ ýð ýðà VALUE °, ÿÃÂøüõýÃÂõÃÂÃÂàæãÃÂ-ñøþÿÃÂøÃÂ. áþñøÃÂðÃÂàñøþüðÃÂõÃÂøðû ýõþñ Chapter 7-8 1 -óþ üõýÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂðûÃÂýþóþ ÃÂøúûð.