10/24/2020 Alena Masheva Health
In the article we will consider such a pathology as an inverted uterus.
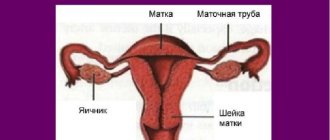
This is the main reproductive organ of a woman. It is located in the lower pelvis. When an inversion occurs, this indicates that some layer of the organ partially or completely protrudes beyond the pelvis. This disease is diagnosed quite rarely, but there are a number of signs by which pathology can be determined. And treatment should begin immediately and only with a trusted, qualified gynecologist.
Basic concept
Uterine inversion is a severe and life-threatening obstetric complication that occurs in one case per 400 thousand births. Inversion of the uterus is the pressing of the fundus of the uterus from the side of the abdomen and chest inward until the entire uterus is everted through the cervix with the mucous membrane outward. In this case, the uterus descends into the vagina, and a deep funnel is formed inside the abdominal cavity, which is lined with a serous layer. The fallopian tubes, uterine ligaments and ovaries are retracted into it.
An inverted uterus can occur when groups of tissues and muscles that support the pelvic organs weaken. If these organs sag, the upper part of the uterus prolapses. A woman may experience either a sagging of the uterus towards the upper part of the vagina (this is considered the first degree of the disease), or a prolapse of the uterus up to 10 cm, which will lead to its prolapse from the body.
Most often, uterine inversion is associated with abnormal labor; it is dangerous for the woman and requires immediate elimination.
Cause of the disease
The cause of an inverted uterus may be:
- atony, when there is no muscle tension of the organ after childbirth, which is especially evident during coughing, sneezing, or pressure on the abdomen;
- premature pulling on the umbilical cord when the placenta has not yet separated;
- rough management of labor by a doctor, when strong pressure is applied to the uterus to separate the placenta;
- removal of polyps or myomatous nodes using short knives.
- attachment of the placenta to the fundus of the uterus;
- the presence of a large myomatous node in the area of its bottom.
The factors of spontaneous eversion are also determined:
Symptoms
Symptoms of an inverted cervix appear:
These manifestations should not go unnoticed.
Forms
An inverted uterus can be caused by its relaxed state, with a simultaneous increase in pressure in the intra-abdominal area. This is called spontaneous eversion. Violent occurs in cases of early pulling of the umbilical cord and rough pressure on the uterus.
There are both complete and incomplete inversions:
Classification
Classification by degree:
- Full. In this case, inversion of the cervix, vagina and the uterus itself occurs, which is located outside with its mucous membrane.
- Incomplete. With this inversion, the uterus is located in the vagina.
- Partial. The fundus of the uterus has not yet descended beyond the internal opening of the cervix.
Types depending on the reason:
- Natural (spontaneous, spontaneous). This type of inversion occurs without the influence of obstetric aggression. It can occur with a pronounced decrease in the tone of the uterine muscles.
- Artificial (violent). It occurs when special techniques are used in obstetric practice. For example, when the umbilical cord is pulled when the placenta is truly fused with the muscular layer of the uterus or when the baby’s place has not yet separated. This inversion is also possible if the Credet-Lazarevich method for separating the placenta is performed incorrectly.
According to the nature of the flow:
- Acute inversion of the uterus during childbirth or immediately after is called acute.
- Chronic. Develops within a few days after birth.
Non-invasive cervical cancer - what is it? ⇐⇐⇐
Inverted uterus after childbirth
With a weak muscular system of the pelvic organs and birth injuries, uterine inversion occurs. Most often, ruptures occur because of this. This can also be provoked by thrush, since under the influence of this infection muscle tissue is eroded, which makes it thinner and weaker, so they themselves can tear during childbirth. Torn areas are sometimes difficult to stitch up, and scars heal very poorly and take a long time.
In some cases, obstetric forceps are used during childbirth, which can also easily injure weakened tissues.
To maintain them in an elastic form, the female body needs estrogens. With age, the level of the youth hormone decreases, which leads to a loss of former elasticity, tissues become thin, and it is at this time that women most often face the problem of uterine prolapse.
Is it possible to invert the uterus outside of labor?
Cervical inversion.
I finally found a doctor who explained to me what was wrong with my cervix. It turns out it's a twist. During pregnancy, I heard everything from doctors about my cervix. One said that I have the cervix of a woman who has given birth, the other - that it is erosion, the third - that the cervix is hanging, the fourth - that this is such an anatomical feature. At the same time, any doctor who looked at me in the chair incredulously asked several times whether I had had an abortion, whether this was definitely my first pregnancy and whether there had been any miscarriages. I was terribly furious that no one answered my specific questions: “What’s wrong? What do you have in mind? What do your words mean? - They just shrugged their shoulders.
And so my husband and I gathered for the second doll. For the first time, I didn’t bother with any tests and examinations, I got pregnant “without looking.” And everything seemed to go well. This time I decided to do everything right. I went to the doctor, she said that there was inflammation in the cervix, tests confirmed it (red blood cells). By the way, during pregnancy I also saw and then didn’t see this inflammation, but after giving birth it went away on its own. This time they prescribed me terzhinan vaginally and trichopolum to drink, I was treated and went for a second examination (the doctor ordered that after treatment I be tested for all infections and have a colposcopy). My doctor was on vacation, so I made an appointment with someone who was free so as not to procrastinate. I told the new doctor the whole story and - oh, miracle! — I finally got answers to all my questions! She said that I have an inversion, which is why my red blood cells will flash periodically, that the fact that I was treated is good, and also that an inversion is often mistaken for erosion. She also said that nothing needs to be done about it and that it does not affect the course of pregnancy and childbirth in any way. And that this is a consequence of the first birth. But I know that my reversal is not a consequence! It existed before, but for some reason no one told me about it.
For the first time, I didn’t bother with any tests and examinations, I got pregnant “without looking.” And everything seemed to go well. This time I decided to do everything right. I went to the doctor, she said that there was inflammation in the cervix, tests confirmed it (red blood cells). By the way, during pregnancy I also saw and then didn’t see this inflammation, but after giving birth it went away on its own. This time they prescribed me terzhinan vaginally and trichopolum to drink, I was treated and went for a second examination (the doctor ordered that after treatment I be tested for all infections and have a colposcopy). My doctor was on vacation, so I made an appointment with someone who was free so as not to procrastinate. I told the new doctor the whole story and - oh, miracle! — I finally got answers to all my questions! She said that I have an inversion, which is why my red blood cells will flash periodically, that the fact that I was treated is good, and also that an inversion is often mistaken for erosion. She also said that nothing needs to be done about it and that it does not affect the course of pregnancy and childbirth in any way. And that this is a consequence of the first birth. But I know that my reversal is not a consequence! It existed before, but for some reason no one told me about it.
They prescribed me tests and an ultrasound of the pelvic organs in connection with planning a second pregnancy and sent me, in fact, to get pregnant with encouraging words: “Such a woman! Such a gorgeous basin! Yes, you have to give birth and give birth!” ))) Of course, I was happy... and have already signed up for an ultrasound and tests, waiting for my period to end. But still, I went online to read about inversion and found out that this thing is not at all safe. It turns out that the risk of cervical cancer increases significantly and it is necessary to constantly monitor its condition so that, if anything happens, surgery is performed on time! You can give birth even after surgery, but most likely it will be a caesarean section.
At the moment, if the tests are normal, I will become pregnant and the issue of the cervix will no longer be raised before childbirth. But then what to do? Maybe someone has encountered such a problem and can tell me the contacts of a good doctor?
But first of all, I’m interested in how to monitor the situation in order to detect deterioration in time!? A simple examination or some specific tests? How often? And, of course, not in the residential complex. We need a doctor who is in the know.
Cause of illness outside of childbirth
Such an unpleasant situation can occur not only during childbirth. A woman who has a history of a number of gynecological problems may encounter a similar pathology. This can also happen after heavy physical exertion, which is extremely dangerous; she may experience severe bleeding and go into shock. She should be taken to hospital as soon as possible for emergency care.
In the presence of uterine tumors, inversion of the organ is also possible. In this case, the symptoms of this condition will gradually increase; the woman herself may not even notice what happened, and, most likely, she will seek medical help only after a few days.
In any case, the woman is hospitalized. Her treatment will depend on her age and how long the uterus has been inverted. If the organ falls out completely, it will be wrapped in a sterile bandage.
Uterine inversion not associated with childbirth
In a woman suffering from a gynecological disease and not in labor, uterine inversion can occur in non-hospital conditions. Most often this happens during physical activity. In this case, bleeding develops, the patient is in a state of shock.
Sometimes, with tumor damage to the uterus, uterine prolapse occurs gradually. Symptoms of the pathology increase over time. Several days pass from the onset of ectropion to seeking medical help. The condition can be detected by inspection in the mirrors.
The patient is immediately hospitalized. If the uterus is outside the vagina, then it is wrapped in sterile gauze bandages. Treatment tactics depend on the patient’s age, the cause of the uterine inversion, and the duration of its inversion.
Safe treatment of the uterus⇐
Diagnostics
Only a gynecologist can diagnose an inverted cervical mucosa. First of all, the patient is questioned: when and what kind of discharge appeared, what is its volume, whether there is pain in the lower abdomen, whether there have been surgical interventions or labor.
Next, obstetric and gynecological information is collected: possible gynecological diseases suffered early, pregnancies, what kind of births, the characteristics and outcome of childbirth, the course of the last pregnancy.
The attending physician also examines the woman, measures her blood pressure, pulse, and palpates her abdomen and uterus. During an external examination, the doctor determines the size of the organ, shape and tension. Next, an examination is carried out on a special chair. The doctor, inserting one hand into the vagina, palpates the uterus itself, its ligaments and ovaries, and holds the other hand on the patient’s stomach. Also, to determine the exact picture, the doctor examines the cervix in special medical mirrors.
Medical diagnosis and treatment
The gynecologist confirms the diagnosis by examining the inverted uterus using speculum and detecting a funnel-shaped depression at the site of the usual location of the uterus during a two-handed examination.
A person with such a complication needs urgent help; if it is not provided, then severe sepsis or death from shock and blood loss is possible. Cervical inversion after childbirth cannot be corrected on its own; the help of doctors is needed here. Reduction is carried out urgently in compliance with the rules of antisepsis and asepsis under general anesthesia on a gynecological chair with preliminary separation of the placenta.
In cases where it is not possible to reduce the uterus manually, a posterior colpohysterotomy is performed (Küstner Piccoli Duré operation).
Timely diagnosis and competent surgical treatment provide a favorable prognosis. If more than one day has passed since the inversion, the uterus is removed.
Treatment
There is a manual method for eliminating pathology, i.e. returning the organ to its place. The doctor presses on the fundus of the uterus with his hand, bringing it back. If this happens during childbirth, he first manually separates the placenta from its walls. Doctors consider this method dangerous due to the possibility of developing shock and infectious complications. The most commonly used conservative treatment for uterine inversion is:
During surgical treatment, a colpohysterotomy is performed, when an incision is made on the posterior wall of the vagina and uterus, it is set in place, and then the defect is sutured. This method is used if manual reduction is not possible. If more than 24 hours have passed since the uterus prolapsed, it is removed. After successful reduction of the uterus, tamponade is required, broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are prescribed, and the cavity is treated with an antiseptic solution. Afterwards, a cold and heavy heating pad is placed on the patient’s lower abdomen. The patient's movement should be limited in the first hours after the procedure, her position should be strictly horizontal, her legs should be slightly elevated.
Why is an inverted uterus dangerous in a woman?
Signs and symptoms
Uterine inversion is a clinical diagnosis and should be suspected when the fundal area cannot be palpated abdominally along with the sudden onset of rapid vaginal bleeding, resulting in hemodynamic instability in the mother. It has traditionally been thought to cause hemodynamic shock "out of proportion" to blood loss, possibly mediated by parasympathetic stimulation caused by tissue distension. However, the need for blood transfusion should be carefully assessed as blood loss is significant and greatly underestimated. Other symptoms are mainly severe pain in the lower abdomen with a strong sensation of pressure below, although most women may not complain due to severe shock. This can happen before or after placental abruption.
Possible complications and consequences
In medical practice, they encounter the following complications:
To prevent this, you need to take preventive measures.