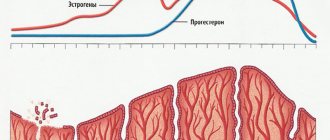
A biopsy makes it possible to identify any disorders and pathological conditions of the uterus, as well as their nature and cause. Using pipell diagnostics, you can detect thickening or proliferation of mucous membranes and determine the presence of oncologically suspicious areas (endometrial carcinoma). Also, a pipel biopsy of the endometrium may be required to monitor hormonal therapy, monitor pathologies of the luteal phase, as well as study the causes of uncharacteristic uterine bleeding and as part of a bacteriological examination.
Endometrial aspiration biopsy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed to examine the condition of the uterine cavity.
An endometrial biopsy is performed after a preliminary consultation between the patient and the doctor, at which the date for the procedure is determined. The manipulation is carried out under general or local anesthesia. The choice of anesthesia method is selected by the anesthesiologist at a preliminary consultation, taking into account the condition and individual characteristics of the patient’s body. After receiving the biopsy results, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis and develops effective therapeutic tactics.
Indications and contraindications for aspiration pipette biopsy
Pipelle endometrial biopsy is performed in the presence of the following pathological disorders and abnormalities:
- Endometrial hyperplasia;
- Uterine fibroids;
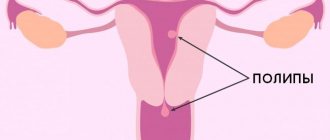
- Polyps;
- Endometriosis;
- Chronic endometritis;
- Suspicions of cancer pathology;
- Bleeding in women after 40-45 years;
- Menstrual irregularities.
Like any surgical intervention, endometrial examination has several contraindications. This manipulation is not performed during pregnancy, in the presence of inflammatory and infectious diseases in the acute stage, as well as in pathologies of the homeostasis system in the decompensation stage.
Indications
A biopsy is performed on patients in the following cases:
- With bloody discharge from the uterus.
- For the diagnosis of luteal phase deficiency.
- In case of preliminary identified deviations during the ultrasound examination:
- tissue remnants after abortions;
- polyps in the endometrium;
- malignant tumors;
- inflammatory processes in the surface layer of the endometrium;
- hyperplasia;
- uterine fibroids.
Endometrial aspiration biopsy is also prescribed to nulliparous women who have been unable to conceive a child for a long time, for dynamic diagnosis in the treatment of uterine diseases and hormonal therapy. The diagnosis of chronic endometritis can be confirmed only after histological and cytological analysis and examination of biological material.
Aspiration pipel biopsy of the endometrium: advantages of the method
In comparison with other surgical interventions in the uterine cavity, aspiration biopsy is characterized by the following undeniable advantages:
- Minimal invasiveness of the procedure;
- Virtual absence of pain;
- Possibility of obtaining a biological sample from any uterine section;
- There is no need to stay in a hospital, since the manipulation is carried out on an outpatient basis;
- Minimal risk of infectious and inflammatory processes. During the procedure, disposable sterile instruments are used. In addition, performing a biopsy does not require dilation of the cervical canal;
- Maintaining good health after endometrial examination, which allows you to return to your usual lifestyle without losing your ability to work.
What is uterine cavity aspirate?
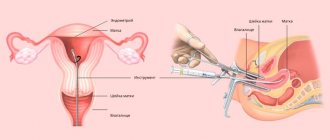
In gynecology, an aspirate is a sample of tissue from the inner layer of the uterus or endometrium obtained by aspiration, or “suction.” Material is taken from several parts of the organ: the bottom, corners and other parts. The research method itself is called “aspiration biopsy”.
Aspiration biopsy has become an alternative to the outdated mechanical method of obtaining material from the uterus or scraping, which is equivalent to a medical termination of pregnancy in terms of technique and traumatic effects. The sample collection in this case was performed with the same instruments as the final stage of the abortion.
Preparing for aspiration biopsy
Like any surgical intervention that involves the introduction of instruments into the uterine cavity, pipel endometrial biopsy requires a preliminary comprehensive diagnosis. To do this, the patient should undergo the following clinical studies and laboratory tests:
- Consultation with a gynecologist;
- Gynecological examination;
- Microflora smear;
- Extended colposcopy;
- Analysis for hidden infections;
- Bacteriological culture from the vaginal cavity;
- Blood tests (biochemical, general, coagulability, HIV, hepatitis);
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
After receiving the results of a comprehensive examination, the attending doctor decides on the advisability of performing a biopsy and determines the presence of possible contraindications. The specialist also refers the patient for a consultation with an anesthesiologist to select the most optimal method of anesthesia and sets a date for the pipell diagnostics.
How to take aspirate
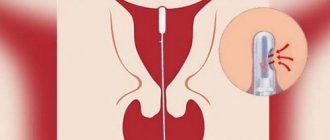
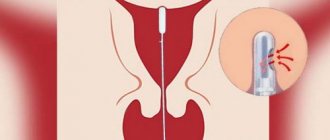
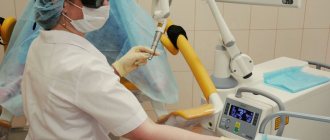
The material is collected in a antenatal clinic on a gynecological chair. Before taking the aspirate, prophylactic antimicrobial treatment of the vagina is performed. Using a speculum, the vagina is dilated, and a thin probe with a blunt metal tip is inserted into the cervical canal. Next, a vacuum is created in the uterus and the tissue sample is absorbed.
After the procedure, the probe and speculum are removed and the vagina is re-treated. The resulting material is treated with a preservative.
If the patient feels normal, she goes home immediately after the biopsy. In total, the manipulation lasts from 15 to 20 minutes.
Depending on the instruments used and the performance characteristics, there are two types of aspiration biopsy.
- Manual. A vacuum in the uterus is created using a special Brown syringe. The device is a cylinder with a piston and handles for fixation. A probe extends from the bottom of the syringe. After the probe is inserted into the uterus, the doctor lifts the piston and thereby creates a vacuum.
- Electric. The vacuum in the uterus is created using a miniature compressor powered by electricity.
Another type of aspiration biopsy is pipell biopsy. In this case, the aspirate is taken using a special device - a pipel - a thin probe with a built-in piston. The device is intended for one-time use. Pipelle biopsy takes less time and, if necessary, is performed during a standard gynecological examination.
Sometimes, to make the examination more reliable, a small volume of saline solution is injected into the uterus before the procedure. Afterwards, the saline solution containing fragments of endometrial tissue, together with the aspirate, is sent for histological and microscopic examination.
Women are often concerned about whether it will hurt or not during the collection of material. It depends on the characteristics of the organism. Typically, aspiration biopsy is painless. However, sometimes with increased sensitivity mild pain occurs. In this case, local anesthesia is used at the patient's request.
Pipelle endometrial biopsy: specifics of the procedure
To perform aspiration biopsy, a special instrument is used - a pipel. This is a flexible plastic tube with a piston, the diameter of which is about 3 mm. The doctor inserts the instrument into the uterine cavity, after which he creates negative pressure in the tube by pulling the piston from the tube. As a result of this, the tube absorbs endometrial tissue from different parts of the uterus. The instrument is then removed from the uterus, and the resulting biological sample is sent to the laboratory. An aspiration biopsy takes no more than five minutes.
It should be borne in mind that if the patient had a threat of miscarriage during a previous pregnancy, which was accompanied by early aging of the placenta, a biopsy is recommended to be performed in the second phase of the cycle. Thus, the doctor will be able to identify not only chronic endometritis, but also hormonal disorders of menstruation. Thanks to this, the doctor will be able to prescribe appropriate treatment, preventing undeveloped pregnancy, spontaneous miscarriage and pathologies of the placenta.
Contraindications
Some conditions sometimes become an obstacle to the diagnostic method. If aspiration is carried out against the background of their course, then the likelihood of complications increases sharply:
- In the first place are inflammatory diseases of the genital organs - both acute and chronic. Aspiration biopsy can lead to upward spread of infection, which is facilitated by trauma to the uterine mucosa. But the contraindication is temporary and is removed after adequate treatment.
- Pregnancy and suspicion of pregnancy also exclude the possibility of performing the procedure. Inserting a catheter into the uterine cavity and creating negative pressure will cause damage and rejection of the fertilized egg. The result will be a complete abortion or a non-developing pregnancy.
- The high risk of bleeding is a temporary limitation caused by the woman taking special medications - anticoagulants. Preliminary preparation, including temporary withdrawal of the medication, will allow the manipulation to be performed without consequences.
Aspiration biopsy, unlike surgical removal of a piece of tissue, is safe in terms of the development of early complications.
Features of the rehabilitation period after aspiration biopsy
After the Pipeline diagnosis, the patient needs a recovery period, which consists of following several recommendations:
- Refusal of intimacy for several days after the procedure
- Carrying out regular hygienic care of the genitals;
- Abstain from bathing in a hot bath, visiting a sauna or bathhouse, or drinking alcoholic beverages for 2-3 days after the biopsy.
The procedure may lead to the appearance of pathological symptoms such as bleeding, general malaise, nagging and aching pain in the lower abdomen. Such manifestations are considered normal and disappear on their own within a few days.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 2531 Date of publication: 10.20.2017
Gynecologists - search service and appointment with gynecologists in Moscow
After the procedure
Although modern procedures are not accompanied by gross manipulations in the uterine cavity, after them it is still necessary to follow some recommendations. Their implementation reduces the likelihood of developing infectious complications:
- Preventive measures should be carried out within three days after performing aspiration biopsy.
- General rules include limiting sexual activity during this period, as well as excluding swimming in pools and open water. In the cold season, a woman needs to prevent hypothermia.
- Hygiene measures consist of local toileting of the genitals. It is required to wash regularly and change underwear daily, and use vaginal antiseptics in various forms.
The question of the use of pads and tampons remains controversial - can they become a source of ascending infection? Since the procedure is carried out outside of menstruation, it is better to avoid using daily hygiene products.
When is it customary to prescribe the procedure?
Doctors prescribe taking an aspirate from the uterine cavity in the following cases:
- interruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- excessively heavy discharge during menstruation;
- if the duration of menstruation exceeds 8 days;
- when there is no menstruation for six months or more;
- there is uterine bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle;
- when menstrual flow has a non-standard consistency, color or volume;
- with endometriosis;
- for infertility;
- if a diagnosis of uterine fibroids is made;
- if you need to monitor the effectiveness of hormonal therapy;
- in the presence of endometrial hyperplasia or pathological proliferation of uterine tissue;
- if malignant neoplasms occur inside the uterus (or are suspected).
Taking an aspirate from the uterine cavity in case of fibroids
Contraindications for taking uterine aspirate are:
- acute and chronic diseases of the reproductive system;
- pregnancy (both confirmed and probable);
- taking anticoagulant drugs
How to prepare for taking an aspirate?
First of all, women are interested in: if an aspirate is taken from the uterine cavity, how to prepare?
The most suitable days for taking aspirate from the uterine cavity
There are a number of rules preceding this diagnostic procedure:
- manipulation is carried out on certain days of the cycle, usually 7-8 or from 25 to 26 days (but not during menstrual bleeding);
- it is necessary to exclude the possibility of pregnancy in advance;
- if the patient has sexually transmitted diseases, you should wait for recovery;
- a few days before the diagnostic procedure, stop taking blood thinning medications;
- You need to wash yourself an hour before aspiration.
How do you prepare for aspirate from the uterine cavity according to all the rules?
Blood test for HIV before endometrial tissue aspiration
The following preparations are recommended before performing diagnostic aspiration of endometrial tissue:
- take a clinical blood test;
- undergo a gynecological examination with your doctor;
- check for HIV, hepatitis, syphilis, herpes, chlamydia, cytomegalovirus and other infectious diseases;
- perform an ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- do a bacterial culture of a smear taken from the cervix.
Sequence of medical procedures
One of the most popular questions among women is: does aspirate from the uterine cavity hurt or not? Modern diagnostic methods do not cause severe pain and do not take much time. It feels like a “pinch” inside the uterus, which can be accompanied by mild discomfort and slight bleeding for half an hour, and then everything returns to normal.
Scheme for taking aspirate from the uterine cavity
The sequence of medical procedures is as follows:
- take a disposable sterile instrument - a thin and flexible catheter (called a pipel), which contains a piston inside;
- the cervix is visualized using gynecological mirrors;
- the doctor treats the cervix with antiseptic agents to prevent infection;
- the pipel is inserted through the cervical canal into the uterine cavity (since it is equipped with a soft tip, perforation of the uterine wall is excluded);
- the pipel is inserted until it reaches the uterine fundus;
- the final action is to slowly withdraw the piston, which creates negative pressure and the required aspirate enters the catheter.
Aspirate from the uterine cavity: what is it and how is the procedure performed?
If a woman fails to become pregnant for a long period, but is sexually active, it is necessary to conduct an examination and collect tests to determine the condition of the reproductive system. Of greatest importance for a successful pregnancy is the absence of pathologies of the ovaries, fallopian tubes and endometrium (the inner lining of the uterus to which the fertilized egg attaches, and subsequently the placenta develops).
Few women understand what is hidden under this or that medical procedure or analysis. Most people are afraid of pain, discomfort or negative consequences after medical procedures.
Therefore, those women who are prescribed an examination of the condition of the endometrium have to undergo the procedure of collecting aspirate from the uterine cavity. Many people ask before going to the gynecologist: how is aspirate made from the uterine cavity?
Aspirate is a scraping from the uterine cavity, which is performed in various ways. Several decades ago, this was precisely a scraping, that is, a surgical procedure similar to an abortion performed mechanically.
Modern methods of aspirate extraction are much safer and painless. For these purposes, gynecologists now use a special probe, which is inserted into the uterine cavity.
The endometrial tissue sample is "sucked in" either using a Brown syringe or vacuum aspiration, in which negative pressure is generated by an electric pump. Before aspirate is taken from the uterine cavity, a small amount of saline is injected into it. A tissue sample is taken from one area of the uterine surface (then the procedure is performed once) or from several.