Causes of cervical insufficiency
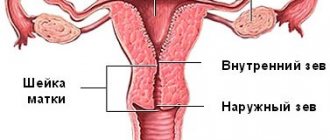
The uterus is an important organ of the woman’s body. Egg implantation and embryo development take place here. During pregnancy, the cervix normally begins to dilate slowly from the 36th week. But sometimes the opening begins at an earlier date. This leads to miscarriage or isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI), premature opening of the uterine pharynx. This occurs when the cervix is short. Its normal length is 40 mm, but in some it reaches only 20 mm. In a dangerous situation, in poor condition of the fetal bladder, doctors decide to suture the cervix. This could save the life of the unborn child.
Indications
For this type of surgical intervention during pregnancy there must be strict indications and clear recommendations from the attending physician. These factors include:
- high risk of miscarriage or premature birth due to the presence of similar cases in the anamnesis;
- recurrent miscarriage in the 1st and 2nd trimesters of pregnancy;
- miscarriage in the third trimester;
- earlier shortening and opening of the cervix, expansion of the internal or external pharynx;
- dubious scars left as “memories” from previous births in which cervical ruptures occurred;
- any destructive changes in the cervix during the process of bearing a child, which are prone to further development.
The doctor cannot make a decision that there is a need for such an extreme measure as suturing based on an examination on the gynecological chair alone. He needs comprehensive information about the condition of the lower segment of the uterus, which is the cervix. For this purpose, a full biometric examination , which includes colposcopy and ultrasound diagnostics, as well as laboratory smear testing.
Only after all risk factors have been identified, the length and width of the cervix have been measured, the condition of the cervical canal inside it has been assessed, as well as the patient’s personal history, can a decision be made about suturing the cervix.
Diagnostics
When examining a pregnant woman, the doctor cannot see that the cervix is shortened. Therefore, it is impossible to predict a miscarriage based only on examination.
The most informative method for diagnosing pathology is ultrasound. This research method allows you to determine the size of the cervix. Shortening of the cervical canal to 25 mm signals the danger of miscarriage and helps confirm the diagnosis with ultrasound. Sometimes the patient is asked to cough a little or lightly presses on the bottom of the uterine cavity. In this case, the lumen of the cervix increases, which is a sign of cervical insufficiency. A shortening of the cervix can be detected as early as 20 weeks, when the fetus begins to grow rapidly. It is during this period that miscarriages most often occur. For this reason, pregnant women are recommended to undergo an ultrasound examination.
Possible problems and complications
Like any surgical procedure, cerclage can also have its complications. The most dangerous are considered to be the addition of an infection, the development of an inflammatory process and an increase in the tone of the uterine muscles. Inflammation may develop due to an internal infection that could not be “defeated” in the preoperative period. Sometimes a woman has an individual allergic reaction to the suture material used by doctors.
Possible problems may be indicated by prolonged discharge after surgery, the appearance of a burning sensation, and mild pain . Moreover, inflammation can appear not only immediately after surgery, but also several weeks after suturing. This is why it is important to visit your doctor more often and monitor any changes.
Hypertonicity is also a reaction of the uterus to surgical intervention and suture material foreign to its structures. Some heaviness in the abdomen, slight tugging sensations may be quite normal in the first time after surgery, but subsequently they should disappear. If this does not happen, you should inform your doctor.
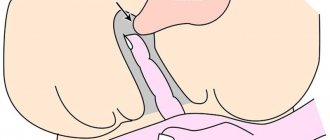
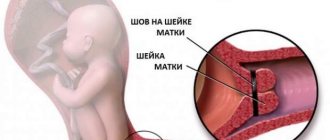
How is the suture applied?
The operation is performed at 14-21 weeks; suturing is not recommended later, as strong stretching of the tissue can lead to eruption and rupture.
The operation is performed in a hospital setting under general anesthesia. Depending on the condition of the uterus, a stitch is placed inside the cervix or outside with a strong thread. Sutures are placed in different ways. One surgeon “tightens” the cervix with special stitches to prevent dilatation of the uterus. Another does it using laparoscopy.
How is the operation performed?
- After admission to the hospital for two to three days, the doctor carries out preparatory measures before the operation: for this, tocolytic therapy is used to relieve the tone of the uterus, and the vagina is sanitized with the help of antibacterial drugs.
- In addition, before the operation, you will be asked to undergo general and biochemical blood tests, a general urine test, a smear to determine the sensitivity of microflora to antibiotics, and, if necessary, undergo an ultrasound examination.
- The actual suturing of the cervix is carried out in one of two ways:
- Suturing the external pharynx. The most widely used method is the Czendi method, which involves sewing the anterior and posterior lips of the cervix together with silk or kengut threads. However, suturing using this method can become an unfavorable factor for the development of pregnancy: during the operation, a closed space is created in the uterus, which can cause an exacerbation of a latent infection (if any). It is also ineffective in the presence of cervical erosion.
- Mechanical narrowing of the internal os of the cervix. This type of manipulation is more favorable, since such manipulations leave a hole for drainage in the cervical canal. The most common methods of suturing the internal pharynx according to MacDonald (circular purse-string suture), circular suture according to the Lyubimova method, sutures in the shape of the letter P according to the method of Lyubimova and Mamedalieva.
The operation lasts no more than 10-15 minutes, during which the woman is under anesthesia and does not feel pain. After the intervention, it is normal to experience nagging pain and scanty bleeding, which will go away on its own in a few days.
Recommendations
After the suturing operation, the woman remains in the hospital for some time to avoid complications. She is prescribed antispasmodics to reduce the muscle tone of the uterus, and medications to avoid infection. The vagina is also cleaned daily to prevent infection. On the fifth or sixth day, the patient is allowed to go home if her condition is normal.
Before discharge, the woman is given recommendations that she will have to follow before giving birth:
- Physical activity and long walking are unacceptable;
- lifting weights is also forbidden;
- you can only stand or sit for a short time;
- A few days before giving birth, go to the hospital.
Sex after stitches
Often women have questions about whether it is possible to have sex after surgery. The cervix becomes hyperactive after suturing. To “calm” her, special medications are prescribed. Sexual life excites the uterus. For this reason, sex with a stitch on the cervix can lead to miscarriage, and if the period is short, to premature birth or eruption of the uterus. Even with a calm pregnancy after a suture, sexual activity should be abandoned until the birth.
How does the water drain from the seams?
There is leakage of water after surgery that is not associated with labor. This phenomenon occurs when there is an infection in the vaginal cavity. Then you need to contact your treating gynecologist. He will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Usually, at the onset of labor, the amniotic sac bursts and contractions begin. The woman may feel a pop. But it happens that only cracks form on the bladder, and the water recedes before the contractions begin. When the neck is open, the water flows out in a stream, and the woman cannot do anything to stop the water. With sutures on the cervix, the waters may break earlier, and they are not as abundant.
If they begin to leave outside the medical facility and maternity hospital, you should call an ambulance. But first you should check whether it is water. After all, after installing the seams, there are often leaks. To do this, you can purchase an amniotest at the pharmacy to determine the nature of the fluid at home. The test is similar to a panty liner with two strips. How to use this test is described in the attached instructions. The result is 100 percent.
If you don’t have a test and it’s far from a pharmacy, you can check it yourself. To do this check, you need to wash yourself, lie on your back, placing a clean napkin on your panties. If the cloth gets wet quickly, it's water. The discharge will be stronger if you turn while lying from side to side.
Usually the sutures are removed before the water breaks and labor begins, but sometimes it happens that labor occurs earlier. If the pregnancy is already 36-37 weeks, the sutures are removed directly in the delivery room. This is done quickly and painlessly.
Amniotic fluid quality
Under whatever circumstances the water begins to break, you need to pay attention to it, this is important. The color of the water is especially important during cervical cerclage. It depends on how the birth proceeds:
- colorless - childbirth proceeds normally;
- Yellow-colored water also occurs during normal labor;
- a green tint indicates oligohydramnios and fetal hypoxia or that the baby has emptied his intestines;
- streaks of blood are always present when the water breaks, since this opens the cervix;
- there is a lot of blood in the waters, this is possible when the placenta has separated and you need to urgently call an ambulance.
Cork at seams
Often women who have or are about to have stitches are worried about the plug coming out, they are afraid that it will not come out in time. There is no need to be afraid of this. The plug comes off after cervical cerclage in the same way as during a normal pregnancy. If the sutures on the uterus were not removed before the plug came out, the doctor will remove them after contacting him.
Cutting seams
Stitches are usually removed at 37 weeks, although it happens that a pregnant woman comes to give birth with a stitch that has not yet been removed, and it does not cause her any inconvenience. Removal is painless.
A cut seam sometimes causes more than just discomfort. It hurts in the lower abdomen, inflammation begins. If the stitches on the cervix are cut, you should immediately consult a doctor. They will be removed and new ones installed if necessary.
Eruption occurs if:
- the surgical technique was violated;
- the doctor damaged the tissue of the cervix;
- vaginal hygiene was not maintained, which led to infection and fistulas;
- the tone of the uterus has greatly increased;
- inflammation has occurred inside the vagina or pharynx.
Sometimes the suture breaks through when it is installed during advanced pregnancy and during contractions, when the doctor did not have time to remove it. But all these complications rarely appear after surgery. It is enough for a woman to follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
If such a diagnosis is made and surgical cervical cerclage is proposed, do not be upset. The main thing is to set yourself up for a positive outcome, and the birth will be successful.
Video: suturing the cervix. Not an operation
Putting a suture on the cervix is not an operation!
What it is?
Putting sutures on the cervix is a necessary necessity, which gives a real chance to preserve and prolong pregnancy if the cervix for some reason cannot cope with its direct responsibilities. After conception has taken place, the cervix closes tightly. The cervical canal closes and fills with mucus. The task facing this part of the female reproductive organ is large and important - to keep the growing fetus in the uterine cavity and prevent it from leaving it prematurely.
In addition to retention, the cervix with a mucus plug prevents pathogenic bacteria, viruses, and other unpleasant uninvited “guests” from entering the uterine cavity from the vagina, which can cause intrauterine infection of the baby. This is dangerous, because infections suffered in the embryonic and later periods usually result in developmental defects and severe congenital pathologies, and intrauterine death of the baby.
If the cervix does not provide adequate protection to the growing baby, the likelihood of miscarriage and premature birth increases. If by this time the baby is not yet able to survive on his own in this world, then such a birth will end tragically. In order to strengthen a weak neck, doctors recommend in certain situations to sutured it so that the mechanical barrier in the form of sutures prevents it from opening prematurely.