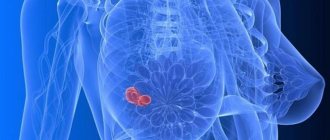
What is avascular formation in the mammary gland and what are its consequences? The female breast consists of glandular structures and subcutaneous tissue. In the absence of pathology, the mammary gland has a homogeneous structure and smooth, clear contours. However, on an ultrasound examination of the breast, a specialist can diagnose black shadows. These are hypoechoic formations. It is important to understand that avascular formations are just a description of the diagnosed picture. This is not a diagnosis of a disease or a symptom of it.
Vascularization of the breast
The medical term “vascularization” itself implies the formation of new blood vessels in organic tissue. Their growth is associated with a rapid increase in organ volume, various diseases, and hypertrophy. Vascularization of the mammary gland is often observed with malignant neoplasms.
Increased vascularization can be diagnosed with increased production or decrease of certain hormones, hormonal imbalance, hyperfunction. Doctors identify several neoplasms in the mammary gland:
- cyst
- fibroadenoma
- lipoma
- avascular formation
A cyst is a cavity filled with fluid. Fibroadenoma develops from the fibrous structures of the organ. Lipoma is a tumor that is localized in fatty deposits. Avascular formation is a tumor without blood vessels and, in fact, blood supply.
Main types
There are several types of anechoic formations in the mammary gland, which include the following:
- cystic;
- solid;
- mixed.
Cystic formations often have a round shape, with clear contours and homogeneous dark content. Multiple small cysts are a diagnostic sign of mastopathy.
Solid formations, which include abscesses and tumors, have a dense structure. They are round, oval or irregular in shape, and may also contain inclusions of varying densities. The mixed type is characterized by an unfavorable course and has various structural options.
For a more accurate and detailed diagnosis, ultrasound examination is carried out in several projections at once, as well as in color Doppler mapping mode. If necessary, elastography is prescribed. Sometimes the patient is prescribed additional imaging methods, in particular, such as tomography, x-rays and needle biopsy.
Hypoechoic avascular formation: characteristic features
Many organic tissue structures are hypoechogenic. These are low density fabrics. In the mammary gland, low tissue echogenicity is not always a specific symptom of the disease. From a medical point of view, hypoechoic structures are a deviation from the norm (ICD-10 code).
The pathology is most common among women. The presence of a hypoechoic avascular formation indicates the development of:
- cysts
- adenosis
- glandular carcinoma
- benign tumor
- fibrocystic mastopathy
- fibroadenomas
A hypoechoic avascular formation has no capillaries and is a benign tumor. It may resemble cancer; the formation has clear boundaries. If the contours of the spot are blurred during examination, doctors diagnose adenosis.
A distinctive feature of the tumor is the darkened structure of the mammary gland. During ultrasound examination, pathological cells slow down the passage of the wave. This is especially true for cysts with fluid. It is impossible to diagnose a cyst right away. After the ultrasound, a number of additional examinations and tests are required. Sometimes the lump may be a tumor or galactocele.
Since when the gland is avascular, there is no blood supply to the tumor, it cannot degenerate into malignant. There is also no risk of its rapid further development.
What is an avascular formation and where does it come from?
The appearance of avascular formations in the breast is a fairly common phenomenon. It is not considered a disease, but doctors prescribe additional examinations, because it is necessary to find out the cause of changes in the body.
It is extremely rare for women to notice a change on their own, because this type of formation is not a compaction. This is a certain area of the chest, the density of which is slightly lower. Ultrasound shows this part somewhat darkened.
The same thing happens when a cystic watery cavity is discovered.
Often, when patients hear about the occurrence of such changes in the structure of the breast, they immediately become worried.
Fear of cancer appears. However, the difference between cancer and avascular formation is significant. First, let's look at what this violation may indicate and what its causes are.
A short list of possible pathologies
- The appearance of a cyst . This is a hollow formation of a single or multiple nature. In most cases, the appearance of numerous small cysts is observed in the postpartum period. Larger and single cysts are found in breastfeeding women.
- Progressive cyst. This is a clearly visible compaction that forms a thickened capsule over time.
- The appearance of a benign tumor . This is one of the types of avascular formation, because the affected area is characterized by the absence of blood vessels.
- Fibrocystic mastopathy . Manifests itself as numerous avascular formations. The disease occurs due to hormonal changes.
- Breast carcinoma. A malignant formation that forms due to frequent reboots, stress, and early cessation of feeding a child.
- Fibroadenoma. In fact, it is a benign tumor that occurs between the ages of 25 and 45 years. If treatment was not provided in a timely manner, compaction may lead to pathology.
- Adenosis. This is one of the types of mastopathy when a glandular component appears in the breast. The list is wide, ranging from minor to serious illnesses. To accurately determine the type of pathology, ultrasound alone is not enough; you will need to undergo laboratory tests.
Causes of avascular formation
The number of reasons is quite extensive, but the source of the disease must be understood in order to accurately determine the course of treatment. It is worth saying that the basis for the appearance of the disease may be purely biological. Women suffer from such a lesion more often than the opposite sex.
Anechoic avascular formation: features
On the monitor during ultrasound examination, the anechoic formation looks like darkened roundness. These structures also do not allow ultrasound to pass through, so a specialist will quickly notice them during the examination. The formations are often benign in nature, but over time they can develop into malignant ones.
Focal pathology usually consists of soft, loose tissue. With the deposition of calcium salts, the echogenicity of the structures increases. The pathology is usually diagnosed as a cyst or galactocele.
Causes
There are certain factors that provoke changes in the structures of the mammary gland. Experts often associate the appearance of tumors with hormonal imbalances.
The outbreak occurs in the female breast for the following reasons:
- excess estrogen production
- long-term use of hormonal contraceptives
- hormone replacement treatment
- thyroid diseases
- inflammation in the fallopian tubes
- ovarian diseases and dysfunction
- operations
Stress and depression can be prerequisites for the development of a tumor. They cause hormonal imbalances and affect hormone levels in the body. Provoking factors are also obesity and poor nutrition.
Symptoms
A tumor in the mammary gland does not cause any discomfort to a woman for a long time. Pathology can only be detected using ultrasound and additional Doppler mapping of the color circulation. As the tumor progresses, some breast lumpiness appears. A lump inside the breast can be detected by palpation.
Symptoms of a tumor also include:
- hyperemia of the skin
- breast tenderness
- feeling of fullness of the mammary gland
- burning
- breast deformation
- the appearance of discharge from the nipple
Sometimes the severity of symptoms depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. When infected, the temperature rises, the lymph nodes become enlarged, and the pain intensifies.
Diagnostics
A qualified specialist will help diagnose focal formation. The doctor will palpate the chest and send you for the necessary examination. You will need to be tested for estrogens, thyroid-stimulating hormonal substances, and prolactin.
An ultrasound scan of the mammary glands and genital organs is mandatory. Mammography, MRI, and Doppler sonography are also prescribed. If a tumor is suspected of being malignant, a biopsy is performed. The biomaterial is collected and histologically examined in the laboratory.
When a pathology is detected, a test for the tumor marker CA-15-3 is sometimes prescribed. Additionally, differential diagnosis is carried out.
Prognosis for leaf-shaped tumor
A distinctive feature of leaf-shaped formations on the mammary glands is their intense tendency to relapse: as observations show, phyllodes fibroadenomas of a benign nature reappear in only 8.1% of cases, while more dangerous, borderline and malignant ones can occur in 25 and 20% percent of cases, respectively.
In the vast majority of cases, the occurrence of relapses is noticed within a period of several months to approximately two to four years. In addition, at this time there is a possibility of the tumor transitioning from benign to sarcomatous or intermediate.
By increasing the intensity of the intervention (that is, the use of mastectomy), the risk of recurrence of a leaf-shaped formation on the mammary gland is minimized.
In one case or another, with the prevention and treatment of the described illness, the main thing is not to hesitate in any case and, at the first suspicion, immediately contact a specialist.
With timely diagnosis and proper therapy, the prognosis for recovery is quite favorable. If you consult a doctor immediately after the first signs of the disease appear, this will allow you to get rid of the tumor at the initial stage.
It is worth remembering that not all tumors are pathological. This can only be determined by a qualified specialist.
How to treat
Therapy is prescribed only after a complete examination. For cysts and benign formations, comprehensive drug treatment is advisable. The following are used in therapy:
- anti-inflammatory drugs
- hormonal drugs
- herbal collections
To eliminate fibrocystic formation, the drugs Indinol and Fitonol are prescribed. They can be used for all types of tumors. Among hormonal drugs, medications containing gestagen and estrogen are prescribed - Duphaston, Estrogel, Utrozhestan.
To saturate the body with useful substances, various vitamin and mineral complexes are used. It is also important to provide adequate nutrition. It is recommended to eat a large amount of vegetables and fruits.
Effective homeopathic remedies are widely used as adjuvant therapy. Cyclodinone or Mastopol are taken for one month. Surgery is recommended when diagnosing a malignant tumor.
Traditional medicine can be used in complex treatment. Leaves of coltsfoot are applied to the lesion overnight. Then the chest is wiped with burdock oil in the morning.
You can prepare a healing mixture of honey, burdock rhizomes and castor oil. The compress with this homogeneous mass is left overnight. It is also recommended to make compresses on the chest with crushed pumpkin. To relieve pain and inflammation, a whole cabbage leaf is applied to the chest at night.
Why is a breast cyst dangerous?
The presence of a neoplasm in this area does not pose a threat to the patient; in most cases, its formation has virtually no effect on the quality of life (unlike, for example, a mediastinal cyst). The neoplasm begins to cause discomfort, discomfort and pain when it reaches a particularly large size, as a result of which the organ is deformed, its structure and functioning are disrupted.
Why is a cyst in the breast dangerous? The danger arises in the event of the development of an inflammatory process, when the liquid contents of the neoplasm cavity begin to fester.
The walls of the cystic capsule are composed of benign cells; cases of deterioration are rare. But such a possibility must be taken into account.
Cavity neoplasm in the mammary gland is one of the manifestations of fibrocystic mastopathy. The pathology is considered a pre-tumor condition and can potentially become a source of cancer.
The problem of neoplasms in the mammary gland can affect any woman at any age, regardless of her social status. In order to detect breast disease in time, it is very important to start diagnosis in a timely manner. A hypoechoic neoplasm means that its structure does not differ from the structure of the tissue. Typically, such an ultrasound conclusion indicates that additional research is needed to clarify the diagnosis.
Features of hypoechoic formation
In most cases, types of breast cancer are hypoechoic formations. The echostructure of the tumor varies and depends on many factors: the presence of areas of necrosis, fibrosis, calcifications, etc.
You need to know that this is not a final diagnosis, but only a description of the structure of the tumor.
It is detected only during an ultrasound examination. During this procedure, the ultrasonic sensor produces high-frequency sound vibrations. The device also picks up reflected signals.
Breast ultrasound procedure
Evaluation of the ultrasound waves emanating from the transducer is very subjective. It depends on many factors:
- wave frequencies;
- some anatomical features of a person;
- doctor's qualification level;
- completeness of information about the signs of a particular disease in a patient.
The hypoechogenicity of an object in the mammary gland depends on the acoustic density of its tissue. In the photo it will appear as an area with a dark color. In this area, high-frequency sound moves much slower than in any other space. These characteristics most often have an object filled with liquid.
What does it mean if a deviation is detected in the mammary gland?
fibroadenomas of the mammary glands
The presence of a hypoechoic formation on the image indicates such diseases.
- Breast carcinoma. It has unclear contours, as well as an acoustic shadow. In addition, it is uneven in its structure.
- Adenosis. This pathology has similar signs - unclear boundaries and hypoallergenicity.
- Typical cyst. She has reduced echogenicity. A typical cyst has regular and clear contours.
- An atypical cyst has very thick walls. There is noticeable growth inside it.
- Fibroadenoma is characterized by the presence of clear and even contours. It looks like a malignant object with slow growth.
Types of breast tumors
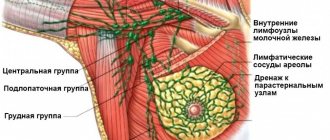
Diagnostics of the mammary glands also helps to detect changes in the lymph nodes. Using ultrasound, the presence of painful phenomena in the mammary gland, hypoechoic rims, etc. is determined.
What pathologies does this formation indicate?
The presence of a hypoechoic object in the mammary gland makes one think about the development of cancer . Tumors that give a stellate appearance of the pattern have a scirrhous type of structure. One or more areas of fibrous tissue are visualized in the center of the tumor. Along the periphery of such tissue there are areas of tumor cells formed from epithelial tissue. Ultrasound examination of the breast may reveal infiltrative ductal cancer.
Hypoechoic content is also characteristic of medullary and colloid cancer tumors. Medullary cancer has a round or lobular shape. The lobules are very clearly demarcated from each other and do not have a capsule inside. With the growth of such a tumor, dead areas with a lack of echogenicity are discovered.
Sometimes anechoic areas may indicate the presence of an area of active growth of a malignant tumor in the mammary gland. These types of cancer are rarely seen after menopause.
Colloid cancer grows very slowly. Its cells produce large amounts of mucous secretion. Colloid formation in the mammary gland is characterized by reduced echogenicity.
Intracavitary cancer is also quite rare. Cavity hypoechoic formation with thickened walls and growths often occurs in elderly patients. The difficulty of diagnosis is that they are not easy to differentiate from benign formations.
Hypoechoic structures in the mammary gland also indicate the development of an edematous-infiltrative form of malignant neoplasm. Clinically, this cancer is characterized by redness as well as thickening of the skin. In some cases, it becomes like a lemon peel. The image shows a thickening of the skin, an increase in the echogenic ability of fatty tissue, as well as the presence of hypoechoic tubular structures.
With metastases to the mammary gland, a hypoechoic formation with a heterogeneous structure is visualized. Its shape is round and has definable contours. Metastases can also be located in the area under the skin.
Echogenicity of benign tumors
Among all benign tumors, fibroadenoma is the most common. It is usually formed as a result of improper development of the gland. The size of fibroadenoma can vary. Occasionally - no more than 20 percent of cases, they are multiple.
Echographically, this is a formation with clear and smooth edges. Compressing a fibroadenoma with a sensor leads to a sliding effect, that is, the tumor moves in the surrounding tissues. If the size of the tumor is less than one centimeter in diameter, such a formation has the correct structure and shape. The larger the size of the fibroadenoma, the more often its hypoechoic rim is detected. In one out of four cases, microcalcifications are visualized.
A fibroadenoma more than 6 cm in diameter is gigantic. It is characterized by the severity of the acoustic shadow. Hypoechoic fibroadenoma is usually poorly defined if the mammary gland has a lot of fatty tissue.
Phylloid tumor is very rare. In one out of ten cases, it can degenerate into sarcoma. The benignity or malignancy of such a tumor can only be determined histologically.
The ultrasound picture of the lipoma is also hypoechoic and homogeneous. If there are hyperechoic inclusions in it, a rim sometimes stands out. Sometimes it can be quite difficult to determine on ultrasound due to the high content of adipose tissue in the mammary gland.
Further diagnostics of the breast
Dopplerography of the breast. Circumflex blood flow of fibroadenoma
As already mentioned, the presence of a hypoechoic formation in the mammary gland is an indication for further diagnostics in order to clarify the diagnosis. Thus, it detects newly formed tumor structures.
Doppler mapping, as well as power Doppler ultrasound, are highly informative types of research. Thanks to them, it is possible to detect a much larger number of tumor formations.
In addition, the following methods are used to diagnose the mammary gland:
Mammography breast cancer
Women should remember that after reaching the age of forty, all women should undergo regular mammograms. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging provide the most accurate diagnostic results.
Mammoscintigraphy is one of the newest types of breast examination. The doctor determines the nature of cancer in the gland using radioactive substances. Women do not need to be afraid of using such substances, as they are harmless.
And of course, every woman should pay special attention to self-examination of the mammary glands. In most cases, women go to the doctor after noticing a suspicious tumor.
Conclusion
Hypoechoic formation of the mammary glands does not yet indicate the malignancy of the process. However, it can be a sign of many diseases. Only a comprehensive diagnosis can accurately determine the disease. Women should not be afraid of further diagnostic measures after an ultrasound examination. In most cases, they help make the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Cause of breast cyst
The main cause of breast cysts is hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body. A woman of any age is not insured against the disease, but in most cases, patients after the age of 30 who have not given birth or breastfed are susceptible to pathology. Often this pathology is a consequence of repeated abortions.
A neoplasm can develop in one or two organs at once. Cavity formations in some cases can be associated with pathologies of the woman’s reproductive system: endometritis, polycystic disease, inflammatory processes in the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Mechanical damage to organ tissue can provoke the development of hollow formation.
The main types of neoplasms in the mammary glands
Several main types of neoplasms developing in this area have been identified. Any type of cavity growths must be carefully examined in order to avoid the negative consequences that each of them can provoke.
Atypical breast cyst
A normal or typical neoplasm is a cavity with a smooth, even internal surface, while an atypical breast cyst is a hollow formation, on the walls of which there are growths directed into the capsule, salt deposits (calcifications). The shape is a round or oval fibrous capsule. At a certain stage of development, the atypical formation becomes inflamed.
Solitary cyst of the mammary gland
A solitary cyst of the mammary gland is a single benign neoplasm. The shape is round, the consistency is soft-elastic. As it develops, the formation acquires a dense structure with clearly defined outlines. The development of this type of neoplasm provokes the development of pain, burning and itching during menstruation.
Fibrous cyst of the breast
The type of neoplasm manifests itself in the form of cluster-shaped cavity seals. Fibrous formations are easily palpable. An accompanying symptom is severe pain in the mammary glands that occurs before the onset of menstruation. The pain is intense, it is impossible to touch the chest.
Ductal cyst of the mammary gland
Neoplasms are hollow growths formed in the ducts of the organ. Women over 45 years of age are at risk. The pathology does not pose a serious threat to health and does not cause inconvenience if drug therapy is prescribed upon the onset of menopause.
Multilocular cystic formation in the breast
This type is formed as a result of the development of polycystic disease, when multiple internal growths combine and form multi-chamber formations. Multi-chamber neoplasms spread to most of the organ, deformation of the mammary gland occurs, and disruption of its functioning occurs.
Fat cyst
The neoplasm is formed as a result of blockage of the sebaceous duct, due to which a cavity filled with fatty content develops in it. This type of formation is easily inflamed.
Types of benign tumors
Anatomy of the mammary gland
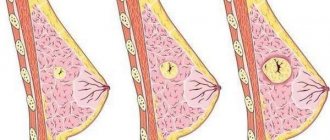
The mammary gland in women is the most vulnerable place in the body, as it is exposed to sex hormones. Due to their imbalance, an inadequate response of cells is possible, which mutate and cannot perform their functions. A benign process in breast tissue is capable of regression. The same can be said about the initial stages of cancer.
The common name for all benign tumors is mastopathy, but this is not an exact name, since mastopathy is a tumor that depends on the hormonal levels in the body. Among them there are those who are prone to malignancy without proper treatment. There are also tumors that are less likely to develop into cancer. In any case, it is necessary to carry out diagnostics, at least the simplest ones - using ultrasound, in order to exclude the presence of cancer and to calm down psychologically.
Breast cyst
Breast cyst
Cystic formation in the breast is the result of excess estrogen due to improper functioning of the ovaries. Along with lumpiness in the mammary gland, women experience irregular periods and enlarged lymph nodes in the armpit, in the center, under the collarbone. The cavity is filled with liquid. The neoplasm is painful on palpation. Cysts can develop into malignant tumors, so they need to be treated and controlled. If atypical cells are detected, it is recommended to remove the cyst before extensive metastasis begins.
Fibroadenoma and its types
Appears as a result of the proliferation of connective and glandular tissues. Symptoms of breast tumors in women are mild or absent altogether. You can feel a soft, painless growth in the chest. It can be found in both adult women and adolescents during puberty.
Among the types of fibroadenoma, the most dangerous is the leaf-shaped tumor of the breast. It is called a precancerous condition and treatment is prescribed. Tumors can reach large sizes, weighing up to 5 kg, then, due to poor circulation, decay occurs inside the fibroadenoma itself. In 10% of cases it degenerates into sarcoma - an extremely aggressive type of cancer.
Intracanalicular fibroma affects the lumens of the ducts, growing into them and clogging them. Pericanalicular is characterized by the growth of connective tissue near the ducts. In the mixed form, there are symptoms of both types.
Ductal papilloma
Intraductal papilloma
Lumps in the breast can cause papillomas to grow inside the ducts. This disease is common among women during menopause. The tumor is unstable and is easily damaged by mechanical stress. The nipple produces fluid that may be brown, red, yellow, or colorless. The diameter of the tumor is small - up to 1 cm. It can be painful. Treatment is usually surgical, as there is a risk of papilloma malignancy.
Atheroma
Atheromas occur anywhere hair grows, including on the breast. When the sebaceous gland that approaches the hair follicle is blocked, a cystic type compaction with thick contents is formed. With prolonged blockage, an abscess with pus of both small and large size with swelling and pain may occur. A predisposing factor is excess secretion of the sebaceous glands, which is characteristic of some diseases, poor metabolism, and lack of hygiene.
Lipoma
A lipoma or wen comes from the fatty tissue of the breast. Doesn't cause any trouble if it grows slowly. It rarely reaches large sizes; neoplasms up to 2 cm in diameter are more often found. The problem is eliminated surgically. This happens almost painlessly, since the lipoma is located in the subcutaneous layer.
The causes of lipomatosis are genetic, hormonal, metabolic. The ratio of cells may vary. Depending on the composition, fibrolipomas, angiolipomas, and myolipomas are diagnosed. After surgery, the lipoma does not recur.
Adenoma
Grows from glandular epithelial cells. It is believed that with a lack of progesterone and excess estrogen, the risk of adenoma is higher. The hormone prolactin stimulates tumor growth if the functions of the pituitary gland are impaired. There are also many cases of adenoma detection in women with dysfunction of the thyroid and pancreas. After 40 years, the glandular epithelium evolves into adipose and fibrous tissue, so the disease is rare.
The adenoma does not bother the woman and often occurs completely without symptoms. You can feel a smooth spherical formation, which increases in size before menstruation, then decreases again.
Diffuse and nodular mastopathy
The proliferation of breast tissue can occur diffusely or in single nodes.
Depending on the way the tumor grows, it is diagnosed as focal or general. These are hormone-dependent tumors that respond to estrogen with increased growth, especially if the woman’s body produces little progesterone.
The first signs of mastopathy are pain and enlarged lymph nodes in the armpit. There may be discharge from the nipple that is dirty gray in color or mixed with blood. In some cases, the pain may spread to the arm or back.
Avascular tumor
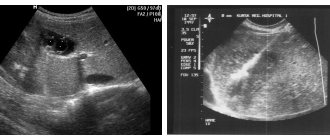
An avascular formation in the mammary gland is a benign tumor without blood vessels. Such neoplasms are not prone to malignancy and grow slowly due to lack of nutrition. On an ultrasound monitor, avascular tumors appear as a dark spot, that is, they have low echogenicity.
Symptoms of a breast cyst
In cases where the size of a cyst with fluid in the mammary gland does not exceed 10 mm, the pathology is asymptomatic and is detected by chance during an ultrasound examination.
Nonspecific manifestations include pulling sensations and roughening of the glands during menstruation.
The growth of the tumor is accompanied by the appearance of the following symptoms of a breast cyst:
- Increase in organ size;
- Deformation;
- The occurrence of edema;
- Burning sensation, pain in the affected area;
- Discharge of yellowish, brown, green color;
- Change in skin color: bluishness, redness appears;
- In the area of the armpits there is an increase in lymph nodes;
- When an inflammatory process occurs, an increase in temperature is observed.
In the early stages of tumor development, pain appears before menstruation or during menstruation. As the formation grows and increases in size, the pain syndrome is constantly present, then a burning sensation appears.
Hypoechoic formation: causes of formation and possible risks
Using ultrasound diagnostics, the presence of a hypoechoic or hyperechoic neoplasm can be determined. In the first case listed, the patient has nodes that have a reduced level of density. Such a diagnosis can be either normal or a disease.
Only a doctor can determine why a hypoechoic formation occurred. It is impossible to do this on your own. The presence of a disorder can only be determined using an ultrasound machine. All tissues and organs have a certain level of echogenicity. Hypoechogenicity is characterized by a reduced level of density.
This can be clearly seen on the monitor during an ultrasound.
Hypoechoic and hyperechoic formations can be clearly seen on ultrasound
What is a hypoechoic formation?
Hypoechoic formation is a formation localized in any organ and having echogenicity below the normal level. This area weakly reflects ultrasonic rays. The monitor is darker than other areas.
A hypoechogenic formation contains water or a cavity. On the monitor, the area is visualized as gray or black spots. With hyperechogenicity, the zones are light or even completely white.
To decipher the picture, a special scale with 6 categories of gray shade is used. The diagnosis is made by specialist doctors. Often hypoechoic formations are cysts. In this case, the patient is additionally referred for a biopsy.
You can decipher the image using a special scale
The root causes of hypoechogenicity
The formation can have any localization. Formations also have different underlying causes of development and symptoms.
The root causes of hypoechogenicity, depending on the location of the formation, are listed in the table below.
| Liver and gallbladder | The causes of hypoechogenicity include: • polyps; • lymphoma; • angiosarcomas. |
| Bladder | The following factors provoking the lesion are identified: • fibroids; • transitional cell malignant process. |
| Abdomen and pelvis | Among the root causes that contribute to the finding of hypoechogenicity on ultrasound are: • hernia; • abdominal hematomas; • phlegmon; • inflammatory process in the lymph nodes; • spread of metastases; • carcinoma of the cecum: • testicular cancer in men. |
| Subclavian zone | The violation is a consequence of: • benign neoplasms; • cysts; • thymomas of the thymus. |
With all of the above factors, an ultrasound examination will diagnose a neoplasm with a reduced level of echogenicity. The current disorder does not always require any specialized treatment.
Similar formations can be found in different organs
Locations of formation localization
The clinical picture and the main diagnosis depend on the localization of the formation with a low density index. Pathological changes may affect:
- thyroid gland;
- uterus;
- mammary gland;
- spleen;
- ovaries;
- kidneys;
- pancreas;
- liver.
Hypoechogenicity is not a diagnosis, but only the result of an examination. That is why in an area with low density you should not worry ahead of time.
If the pathological process has affected the thyroid gland, then the presence of cysts and nodules can be suspected. Cancer is diagnosed in only 5 patients out of 100. An altered structure of the uterus indicates an inflammatory process, fibroids or miscarriage. Often the symptom indicates neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature.
Hypoechogenicity in the mammary glands may indicate various pathologies
Most often, hypoechogenicity is observed in the mammary glands. The symptom indicates:
- cancer;
- adenosis;
- the presence of cystic formations.
In the kidneys, an area of low density indicates either cancer or cystic formations. With a malignant tumor, the boundaries of hypoechogenicity are erased and the structure is uneven. Additionally, the patient may be recommended a biopsy.
Changes in the pancreas may be explained by:
- metastases;
- cysts;
- pancreatitis.
Hypoechogenicity can manifest itself in absolutely any human internal organ. Some of the underlying causes require drug therapy or urgent surgery. Ignoring any doctor’s orders is strictly prohibited. First of all, it is important to exclude the possible presence of a cancer process.
Such formations may indicate cancer and are observed in different organs
In some cases, hypoechogenicity does not cause any discomfort and does not provoke the appearance of negative symptoms. The reduced density will be discovered completely by accident.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture varies depending on the underlying cause and location of the deviation. The main danger signs include:
- difficulty swallowing and eating;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- pain and discomfort at or near the site of hypoechogenicity;
- hoarseness and hoarseness in the voice;
- unreasonable decrease or increase in body weight;
- improper functioning of the digestive organs;
- constant drowsiness and feeling of fatigue;
- sudden mood swings;
- change in body temperature;
- dullness of hair;
- brittleness of the nail plate.
Patients often complain of drowsiness and fatigue
All symptoms are common. The patient may have several symptoms or all at once. It all depends on the factor that provoked the decrease in density.
In the presence of serious illnesses, the patient’s well-being rapidly decreases. Every day a person has less and less strength. Usual things become a real test. The skin becomes drier.
Signs of general intoxication of the body appear. Aggression may occur without obvious reasons. High risk of underweight.
Diagnostic methods
The only way to detect a hypoechoic area is to resort to ultrasound diagnostics. In this case, the examination is carried out with a special device that emits ultrasonic waves.
Ultrasound is a painless and completely safe procedure
In contact with internal organs, ultrasonic waves are reflected and returned. Thanks to this, everything that happens is displayed on the monitor. Subsequently, the doctor deciphers the results obtained.
Ultrasound is harmless regardless of the patient's age. The method can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The method does not require special preparation. An exception is abdominal ultrasound examination. In this case, sometimes you need to fill your bladder or follow a diet.
Before performing an ultrasound, an acoustic gel is applied to the area being examined. The product promotes better glide. Does not interfere with visualization and does not cause an allergic reaction.
After diagnosis, you need to remove the remaining gel. This can be done using dry wipes. The doctor will decipher the indicators and confirm or deny the likelihood of the presence of hypoechoic tissue.
From this video you can learn more about benign formations in the mammary gland:
Treatment measures
Treatment is selected by the doctor. Sometimes therapy is not necessary at all. Depending on the diagnosis, the patient may be recommended:
- vitamin therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- traditional therapy;
- homeopathic treatment;
- surgical intervention;
- taking medications.
There is no single treatment therapy. Self-medication is strictly contraindicated, since hypoechogenicity can be provoked by various provoking factors.
Possible risks
The most serious cause of hypoechogenicity is malignancy. Some tumors cannot be excised. The patient's condition is constantly deteriorating. Body weight rapidly decreases and appetite disappears.
Cancer is a serious disease, without treatment it always leads to death.
With cancer, the functioning of the body as a whole is disrupted. If left untreated, the patient may experience spontaneous death. Every day will begin with unbearable torment.
In order to avoid serious complications, preventive diagnosis is preferred. An ultrasound should be performed annually.
Did the article help? Rate it ( 4 votes, average: 4.00 5) Loading…
Source: https://infouzi.ru/ultrazvukovoe-issledovanie/o-procedure/gipojehogennoe-obrazovanie.html
Diagnostics
To identify tumors, the following studies are carried out:
- Ultrasound examination. The procedure allows you to identify the smallest neoplasms (up to 5 mm), evaluate their structural features, and allows you to differentiate a tumor-like neoplasm from a cystic one. A normal hollow growth is visible as a round formation with liquid contents and clear boundaries, an atypical neoplasm looks like a cavity with growths growing inside, a solitary formation is visible as a capsule with partitions. An ultrasound examination allows you to assess the condition and changes in all elements of the gland, determine the size of the ducts, and view nearby lymph nodes;
- Mammography. The procedure is the most informative and allows us to identify tumors located most deeply. During the procedure, photographs of the affected area are taken in several projections;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- In some cases, a biopsy is prescribed. The procedure is carried out under the control of an ultrasound machine. The biopsy specimen is examined for the nature of the contents of the capsule;
- Assessing the patient's hormonal levels.
Treatment of breast cyst
After conducting the necessary examination and confirming the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe treatment for the breast cyst.
In cases of detection of small tumors (size no more than 15 mm), conservative therapy and monitoring of the patient’s condition are carried out:
- Hormone therapy. This direction is aimed at equalizing hormonal levels. The main goal of therapy is to restore the normal menstrual cycle, consisting of 2 phases. In some cases, correction of the functioning of the endocrine system makes it possible to completely get rid of one or more neoplasms and allows for high-quality treatment of mammary cysts without surgery;
- Diet therapy. Women are recommended a specially designed diet containing a large amount of plant fiber and a minimum of animal fats. A specially designed diet will help normalize hormonal levels, speed up metabolism, and saturate the body with necessary substances and elements. Often, a special diet helps the patient not only improve her health, but also significantly reduce weight;
- Adequate physical activity. Physical activity allows you to improve the health of the body as a whole, speed up metabolic processes, and charge the body with the necessary energy. Patients need feasible physical activity: long walks, breathing exercises, yoga;
- A prerequisite for successful treatment for cysts on the breasts is the normalization of the psycho-emotional background. This organ is very sensitive to negative emotional states. Any stress, nervous breakdown, or overexertion can provoke processes that contribute to the development of tumors. At the same time, a stable positive state will significantly help in the fight against neoplasms. A positive attitude and an adequate attitude towards any events will speed up the healing process and make it more effective. In some cases, sedatives are prescribed;
- Puncture. If medium and large neoplasms are present and their growth is detected, puncture is performed. To do this, the tumor is pierced with a thin needle, and the internal contents are pumped out. A sclerosing substance (alcohol) is injected into the empty cavity, which helps glue the walls of the capsule and prevent relapse.
Removal of a breast cyst
In cases where abnormal cells are detected in the neoplasm, the cyst has a multi-chamber structure, the lesion is multiple in nature - the formation is removed regardless of its size.
The neoplasm is eliminated by sectoral resection. During surgery to remove a breast cyst, not only the tumor is excised, but also part of the tissue surrounding it. The edges of the wound are sutured with special cosmetic sutures to preserve the shape and aesthetic appeal of the breast.
The tissues excised during the operation are sent for histology (which takes no more than 30 minutes). If histological examination does not reveal atypical cells, the wound is sutured. In cases where cancer cells are detected, unilateral removal of the gland and nearby lymph nodes of the armpit is performed.
After a sectoral operation, a special tube is installed in the wound - drainage, through which fluid outflows. Manipulation prevents fluid from accumulating in the wound bed and causing complications.
Excision of a tumor is not a complicated operation and in most cases occurs without complications. To minimize the risk of negative consequences, you must carefully follow the doctor’s recommendations: take prescribed medications, adhere to a specially designed dietary table.
Contraindications for breast cysts and their removal include complete cessation of smoking and drinking alcohol. Meals should be frequent and portions should be small. It is recommended to wear special underwear - made from natural materials, properly cut, and does not cause discomfort or unpleasant sensations.
What is a hypoechoic breast formation?
If the woman’s health is normal, then both tissues will be endowed with a homogeneous structure. But sometimes you can notice the formation of areas that are characterized by high or low density. This phenomenon can cause different types of diseases - it is called hypoechoic avascular formation of the mammary gland.
When performing an ultrasound, they are clearly visible on the screen, since they will stand out strongly against the background of other tissues and also differ in shade. As a rule, healthy areas of tissue have a light gray tint, and hypoechoic formations have a dark gray tint. To make a correct diagnosis of the patient, in addition to ultrasound, a thorough examination is also carried out.
As a rule, a woman cannot independently identify a hypoechoic formation of the mammary gland, since it is not expressed by specific signs and symptoms.
Therefore, it is possible to accurately determine an avascular formation only with the help of modern examinations of the mammary glands.
Typically, formations in the mammary glands have a focal location, which means that they can be easily detected using ultrasound.
The shape of a benign tumor can be round or oval with clear or fuzzy contours. When making a diagnosis, the doctor must determine the shape of the tumor and also identify its size.
To avoid the development of such a pathology, all representatives of the fair sex should undergo regular breast examinations in order to promptly notice the development of diseases or pathological conditions.
Breast doctors advise women who have reached puberty to undergo such an examination every six months.
After all, early treatment of diseases, which will be carried out at the initial stage of their development, will help to avoid serious consequences for a woman’s health.
Symptoms of the presence of seals
A woman experiences severe pain when the nodular cysts have greatly increased in size - in this case, they can be felt independently, since only they will hurt during palpation, and not the entire breast.
Hypoechoic formations are felt most strongly during menstrual periods. In addition to pain in the right or left breast, a woman will also notice pathological discharge from the nipple part of the mammary glands.
Additional symptoms of tumor development include:
- Swelling of the lymph nodes.
- Increase in body temperature.
- The skin at the site of the tumor is thick and red.
- Pain while bending over or lying on the stomach, when the mammary glands undergo severe stress.
- The area around the chest is constantly hot.
If a woman notices such symptoms, she must consult a doctor and conduct an examination of the part of the breast where pathological changes are observed.
Causes of development and risk factors
There are many known factors for the appearance of hypoechoic formation in the chest. These include:
- Accumulation of fluid in the mammary glands.
- Mastitis.
- Complete refusal to breastfeed immediately after birth.
- First pregnancy, its medical termination or late conception.
- Lactostasis.
- Diabetes.
- Disorders at the mental and emotional level.
- Deterioration of the functioning of the endocrine system.
- Obesity.
- Mastopathy, which was inherited by a woman.
- Use of hormonal compounds.
By carefully reading this list, you can find out why a hypoechoic formation may appear. To prevent it, you should lead a correct lifestyle - this will help avoid the development of a benign tumor, as well as other health problems.
Reasons why a hypoechoic benign neoplasm may develop:
- Frequent mental stress.
- Stress that constantly overtakes a woman.
- Hormonal disorders that develop during pregnancy, menopause or diseases of the endocrine system.
- Long thermal procedures, for example, baths, saunas, hot baths and so on.
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the body (long exposure to the sun or solarium).
Depending on the cause of the disease, different forms of hypoechoic formation can be distinguished.
Conditions in which the occurrence of hypoechoic formation is observed
| Type of education | Characteristic |
| Common cyst | This is a homogeneous, regular formation of a round shape, which has smooth and clear edges. |
| Atypical cyst | This is a hypoechoic neoplasm with an irregular shape but clear contours. Such a cyst is endowed with a thick capsule and internal calcifications, the number of which increases as the disease progresses. |
| Adenosis | A neoplasm located in the breast, endowed with blurred contours and irregular shape. |
| Carcinoma | Education has unclear contours and a heterogeneous structure. There is also an acoustic shadow. |
| Fibroadenoma | A focal neoplasm in the mammary gland, which has clear boundaries. Sometimes fibroadenoma resembles a cancerous tumor, so women are sent for a full diagnosis to avoid misdiagnosis. |
| Benign type tumor | A mild form of the disease, the structure of which does not have a vascular network. |
It is important to note that natural formations that can develop in the breast are also endowed with a hypoechoic structure - these are the vascular network and the milk ducts.
Features of diagnosing hypoechoic compaction
The woman will also be prescribed a number of tests, namely:
- A blood test that can be used to determine the level of hormones in the body.
- Blood test to detect the tumor marker ca-15-3.
- A general analysis that will help identify inflammatory processes occurring in the body, as well as diagnose anemia.
- It would also be useful to carry out palpation, which can be done at home - with its help you can promptly detect compacted areas in the chest of an even or uneven contour.
- Diagnostic instrumental methods include:
- Judging by the test results, the doctor can make the correct diagnosis, which directly determines the treatment plan for the disease.
How is therapeutic therapy carried out?
The treatment regimen directly depends on the final diagnosis of the patient, which was established after a complete diagnosis. This takes into account the size, shape and location of the tumor, as well as additional characteristics.
Medications
Medicines based on herbal ingredients
Such drugs that are considered completely safe for health include:
- Indinol - you can take it for mastopathy, against the background of which cysts have appeared in the mammary glands. The drug dosage regimen is as follows: 1 tablet per day with meals. Depending on the health benefits of the medicine, the doctor may decide to extend Indinol therapy. Side effects of the drug include minor and quickly passing abdominal pain, which many people mistake for poisoning.
- Phytolon - prescribed for the development of tumors in the breast (benign and malignant). In this case, the medicine should be taken 1 tablet 3 times a day. Depending on the state of health and type of tumor, the number of capsules may be different. The course of treatment with Phytolon is 1-6 months. In some cases, the drug may cause allergies.
It is prohibited to drink herbal medicines without a doctor’s testimony, although they contain only natural ingredients.
Hormonal drugs
The most effective hormonal drugs that are often prescribed to patients are:
- Estrogel is an estrogen-type product used externally. The gel should be applied to the skin of the breast once a day to heal the hypoechoic formation.
- Utrozhestan is a modern gestagen that is prescribed for many diseases accompanied by hypoechoic neoplasms. The medicine should be taken at a dose of 200-300 mg. in a day. Utrozhestan can cause migraines and headaches or disrupt menstruation.
- Duphaston - this medicine is prescribed according to an individual regimen, which depends on the time and duration of the menstrual cycle. The drug can cause migraines, headaches and disruption of menstrual periods.