One of the safest, most accessible and popular research methods is breast ultrasound. For specialists, ultrasound gives a clear visual picture, but patients are frightened by the terminology used in the description. Today we will look into the phrase often used by doctors - anechoic formation of the mammary glands. Should you worry about this? Is treatment required?
Features of education
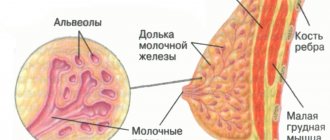
In a healthy woman of reproductive age, both mammary glands have a mixed regular structure, in which the smaller part is represented by adipose tissue, and the larger part by the glandular component. These include lobules consisting of glandular cells and milk ducts that open in the nipple area.
Adipose tissue has the appearance of a hypoechoic structure, which is located immediately under the skin and section of the pectoral muscles. Often during research it is visualized in the form of a polyhedral or ellipsoidal shape.
The mammary area consists entirely of tissue with greater echogenicity than fat and connective tissue septa. During ultrasound diagnostics, they are presented in the form of thin lines, the condition of which is assessed by the doctor.
An anechoic formation in the mammary gland is a cyst, which is diagnosed during an ultrasound examination. To determine whether it is malignant or not, a puncture and cytological analysis of its contents are required.
Often, middle-aged women are diagnosed with a hypoechoic formation, which can be a cyst or a benign tumor. They mainly occur due to hormonal changes and turn out to be an accumulation of fluid, especially if the size does not exceed 1 cm. If the formation increases in size, then a biopsy must be done for histological examination.
Types of anechoic formations in the chest
Cyst, fibroadenoma, galactocele, oleogranuloma, cancerous tumor - all these are types of formations in the gland that are noticeable during ultrasound examination.
- The cyst does not cause the patient any discomfort or pain. A cyst can be detected by ultrasound, so it is important to undergo regular examinations. In past years, doctors popularized self-examination at home, but current WHO recommendations indicate the need for palpation of the gland by a professional physician. In 99% of cases, a cyst is a benign neoplasm, but sometimes it acts as a precancerous condition.
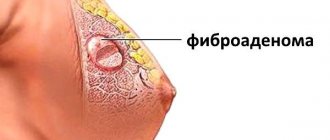
- Fibroadenoma is also a benign formation, which most often affects young women.
- A galactocele is a fatty cyst with milk inside, found in women during the lactation period.
- Oleogranuloma is a benign tumor that appears after a chest injury. Traumatic exposure contributes to tissue looseness and the development of gland necrosis. Necrotic areas are always contained within the oleogranuloma. The condition is accompanied by pain, changes in the shape of the gland and nipple, and bloody discharge.
- A cancerous tumor occurs in any part of the body, in the breast it is usually a large tumor or a diffuse structure. During an ultrasound, the specialist always looks at the shape, volume, density and level of tumor growth.
Standard cysts on ultrasound are described by the doctor as homogeneous structures. If there are other characteristics of the formation, the doctor records them as hyperechoic areas. None of these descriptions confirm or deny the presence of malignant cells; a biopsy must be performed to clarify. The doctor is especially wary of structures with uneven edges, additional inclusions and deformations.
A two-chamber formation is more prone than others to becoming cancerous. Cysts, consisting of many chambers, often contain tissue growths; they must be removed surgically. An avascular neoplasm in the gland is a structural element in which there is no vascular wall, so the likelihood of such a formation turning into cancer is negligible. Typically, cancerous tumors contain many vessels that feed the growing tumor. To accurately describe the tumor, ultrasound alone is not enough; a biopsy and histology will be required.
Main types
There are several types of anechoic formations in the mammary gland, which include the following:
- cystic;
- solid;
- mixed.
Cystic formations often have a round shape, with clear contours and homogeneous dark content. Multiple small cysts are a diagnostic sign of mastopathy.
Solid formations, which include abscesses and tumors, have a dense structure. They are round, oval or irregular in shape, and may also contain inclusions of varying densities. The mixed type is characterized by an unfavorable course and has various structural options.
For a more accurate and detailed diagnosis, ultrasound examination is carried out in several projections at once, as well as in color Doppler mapping mode. If necessary, elastography is prescribed. Sometimes the patient is prescribed additional imaging methods, in particular, such as tomography, x-rays and needle biopsy.
How is breast ultrasound performed?
The doctor can conduct an ultrasound examination when palpation reveals an oval or round lump in the mammary gland. In this case, instrumental research allows you to find out the diagnosis and further tactics.
The procedure does not require special preparation; doctors usually advise hygienic treatment of the skin of the mammary glands and armpits the day before. For women, ultrasound is recommended to be performed in the first half of the ovarian-menstrual cycle. In this case, it is possible to obtain the most accurate results.
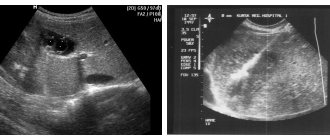
The procedure lasts 10–15 minutes. On the monitor of an ultrasound diagnostic device, a hypoechoic formation appears as a spot of uniform color. It can be different in shape - most often round or oval. The boundaries of the tumor can be of varying clarity - a smooth contour is characteristic of cysts and other benign neoplasms, uneven edges are an unfavorable prognostic sign.
Hypoechoic formation
A hypo-anechoic breast mass is an area of tissue that has a relatively low density compared to the rest of the breast tissue. This pathological condition is quite common among women. It is often diagnosed by age 45. However, if a woman’s pathology was not detected before menopause, then it is unlikely to occur after that.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of such formation, they include the following:
- ordinary or atypical cyst;
- fibroadenoma;
- glandular carcinoma;
- mastopathy;
- adenosis;
- benign tumor.
The cyst generally has a clear shape, and is also distinguished by the presence of many calcifications, which increase as the disease progresses. Glandular carcinoma has a heterogeneous structure and does not have an exact outline.
Fibroadenoma is a focal compaction with a clear shape. In some cases, it resembles a malignant tumor, so additional examination is required. Adenosis is a neoplasm with blurred edges and no definite shape.
Fibrocystic mastopathy is a multiple homogeneous lump that occurs due to hormonal changes in the body. A benign tumor is a formation without a vascular network. It is important to remember that hypoechogenicity is also present in the structures of the mammary gland itself.
Pathogenesis
The shape of the formation can be round, oval, or some other. The size can also vary: from a couple of millimeters to 6 or more centimeters in diameter. In addition, the formation can be located single or multiple (for example, if we are talking about polycystic disease).
In the vast majority of cases, the anechoic inclusion is benign. But it cannot be ruled out that over time, or under the influence of specific factors, it can degenerate structurally and acquire a malignant nature.
However, before making an accurate diagnosis, you should not be upset - the likelihood of degeneration of such an element is very low. In 90% of situations, the pathology is cured by prescribing adequate and competent treatment. Moreover, some types of anechoic inclusions tend to self-remove under the influence of certain favorable factors.
Therefore, you should never rush to conclusions after an ultrasound. Trust your doctor.
[3], [4], [5]
Causes
It is possible to determine the exact causes of the formation of an anechoic structure in the chest only after a diagnosis has been made. However, there are a number of common precipitating factors that can lead to its development. Among them it is necessary to highlight the following:
- hormonal changes as a result of dysfunction of the reproductive or endocrine system;
- menopause;
- pregnancy;
- excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- mechanical chest injuries;
- long-lasting thermal effect;
- metabolic disease;
- Frequent stress that provokes a hormonal surge.
In addition, the development of anechoic formation in the mammary gland may be due to genetic predisposition, surgery in the breast area, as well as uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives.
Main symptoms
A small-sized anechoic formation generally does not cause any discomfort at all and is detected completely by accident. However, in some cases certain signs may appear, among which the following should be highlighted:
- heaviness, pain and burning in the chest;
- nipple discharge;
- change in breast shape and skin color;
- enlarged axillary lymph nodes.
Soreness may occur periodically or be present constantly. Mostly, unpleasant sensations intensify before menstruation or in the second phase of the cycle. The symptoms of a cyst largely depend on its location and size. If the tumor is located near the milk ducts, there may be discharge from the nipple, and large tumors often change the shape or size of the breast.
To detect a hyperechoic formation with anechoic signs, women with the onset of puberty are recommended to undergo a breast examination at least once every six months in order to promptly detect the problem and begin treatment at the initial stages of the disease. In addition, it is advisable to periodically conduct self-examination of the breast using palpation.
In some cases, upon external examination, asymmetry of the mammary gland is noted. Upon palpation, a round, compacted formation is detected.
Carrying out diagnostics
Ultrasound of the breast will help detect an anechoic formation. Sometimes this method is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. In this case, a blood test for hormones, a general urine and blood test, as well as kidney and liver tests are prescribed.
To draw a conclusion about the causes and nature of the disease, during the study, an ultrasound specialist evaluates the structure of the tumor according to such parameters as:
- echogenicity;
- structure;
- localization and dimensions;
- mobility;
- borders and contours;
- absence or presence of vessels, their number.
Echogenicity is compared with the normal values of the organ being examined or nearby structures. The neoplasm can be homogeneous or heterogeneous. Its structure is mainly determined by the presence of inclusions of low or high density.
A simple anechoic avascular formation in the mammary gland is displayed on ultrasound as a rounded dark tumor with clear contours and homogeneous content. Their distinctive feature is the presence of a reinforcement effect along the rear wall. With an anechoic avascular formation, no vessels are found in the mammary gland.
A complex cyst can be multi-chambered, contain septa with vessels and large inclusions. They are not always benign, but are often asymptomatic.
Galactocele is a local expansion of the milk duct of the gland, which occurs as a result of excessive accumulation of secretions. This change looks like a protrusion of one of the walls of the duct. The neoplasm looks like a cyst with homogeneous contents. It is often found in women who have breastfed and poses absolutely no danger.
Fibroadenoma is an anechoic formation with clear contours. It has a regular shape, a uniform structure, a vascular rim and a thin capsule. Cancer is a formation of low or high density with vague, bumpy contours. Its dimensions may vary. Cancer is characterized by the presence of various inclusions, as well as central or mixed type of blood flow.
Instrumental research techniques include tomography and contrast-enhanced radiography. If all these methods do not help in diagnosing the tumor, then a biopsy of the anechoic cavity or laparoscopy is prescribed.
You should also remember about dynamic monitoring and repeat ultrasound of the anechoic formation once every few months.
Concept and symptoms of anechoicity
It is immediately necessary to clarify that the term “anechoicity” does not yet mean a final diagnosis; it is rather a preliminary description of the formation discovered by the doctor. The very concept of “anechoic” can be deciphered as “not reflecting sounds.” During the procedure, an ultrasonic sensor, transducer releases high-frequency sound waves and picks up return signals. Thus, the overall picture is built based on the frequency of the received waves. If there is no signal or it is very weak, this means that during the diagnosis the doctor discovered some kind of neoplasm in you. These can be various substances of a normal or malignant nature.
Features of treatment
Full treatment of an anechoic formation in the mammary gland is prescribed only after a comprehensive examination of the patient and diagnosis. Drug therapy is carried out when benign and cystic neoplasms are detected. Treatment includes anti-inflammatory drugs, herbal remedies, and hormonal drugs.
When the inflammatory process develops, Wobenzym and Ibuprofen are prescribed. The first is often prescribed for mastopathy. Herbal remedies include “Fitonol”, which is used for all types of breast tumors, as well as “Indinol”, which helps eliminate fibrocystic formations.
Among hormonal drugs, Utrozhestan, Estrogel and Duphaston are often prescribed. All medications should be selected only by the attending physician after conducting a full examination, studying the results obtained, and making a diagnosis.
In case of anechoic avascular formation, vitamin therapy is additionally required. It is recommended to include as many fresh vegetables and fruits in your menu. Vitamin A enhances cell growth, normalizes hormone production, and also helps the liver function properly. It is found in apricots, peaches, tomatoes, and carrots.
Vitamin C helps normalize redox reactions, removes toxic substances from the body, and also normalizes the energy-saving function. Ascorbic acid is found in almost all foods. Vitamin E performs a protective function, in particular, it protects cells from the effects of free radicals. It is found in products such as milk, eggs, vegetable oil.
After an accurate diagnosis, if there is an anechoic formation in the breast area, the doctor may prescribe physical therapy sessions. However, it is worth remembering that for some types of tumor such treatment is strictly contraindicated. In particular, it is not prescribed if there is a high probability of the tumor degenerating into cancer. In this case, physiotherapeutic techniques become a catalyst for the start of the process of malignancy.
In some cases, folk remedies and techniques can be used to treat anechoic avascular formation. However, you must first consult with your doctor regarding the presence of contraindications. It is worth noting that it is harmful to make hot compresses, use lotions and baths with alcohol, and also lubricate the affected area with warming ointments.
As folk remedies, you can use coltsfoot or burdock leaf, which should be applied to the affected area before going to bed. In the morning, wipe your chest with a damp cloth and apply a little burdock oil.
Prepare a mixture of burdock root, honey and castor oil. Make a compress from the prepared product and leave it overnight. For the same purposes, you can use chopped pumpkin pulp. Another good compress is cabbage leaf. Apply a little butter and lightly sprinkle with salt. After this, apply to the sore spot. In addition, folk remedies include various infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs.
Homeopathic medicines are used as auxiliary medicines. Among them it is necessary to highlight the following:
- "Mastodinon."
- "Cyclodinone".
- "Mastopol".
- "Mastiol-Edas".
A feature of such drugs is the absence of side effects. In some cases, an allergy to the components of the medicine may occur.
If the anechoic formation is large, surgery may be prescribed. For malignant neoplasms, additional treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation are used. There are certain contraindications to surgery, which include advanced age, the presence of cardiovascular diseases, as well as cancer in an advanced stage with the presence of metastases. It is recommended to carry out complex therapy, as this will allow you to achieve the best possible result of therapy.
Histological structure of the cervix
The cervix has a protective function as a barrier to foreign elements. The cervical canal has a covering in the form of glandular epithelium. This tissue produces characteristic mucus. During the ovulation period, the discharge becomes thinner, providing an open path for the man's sperm to travel. When the gland ducts are blocked, mucus retention occurs. In this scenario, a retention cyst is formed. This formation is often found in older women and rarely becomes malignant. The cervical canal also often receives pathology in the form of an increase in glandular epithelium with the presence of polyps. In 1% of such cases, the deviation becomes malignant.
The wall of the cervix has a structure of myometrial muscle fibers and durable epithelium prone to great stretching. The ectocervix is the external element of the cervix that can be examined using speculum. The area is covered with epithelium of several layers: intermediate, basal, superficial.
When the cervix begins to expand its walls, before labor contractions it is provoked by the destruction of collagen, which significantly softens the tissue of the organ.
The formation of pathologies in the cervix
Frequent infectious diseases in the cervical area can provoke the appearance of various neoplasms. The organ is built at the junction of various organs and consists of several layers of epithelium. Also, the cervix is called the “transformation zone.” Various types of injuries and microcracks caused by abortion or operations can also provoke the appearance of tumors.
Common factors for the onset of cervical tumors:
- oncogenic strains of human papillomavirus;
- mechanical damage to the organ epithelium;
- venereal disease of the reproductive system;
- chronic vaginitis, cervicitis, during frequent douching;
- organ damage by schistosomes;
- high levels of female hormones against the background of sexual problems; organs (ovary), hypothalamus. An imbalance may also develop; during hormonal therapy;
- bad habits, professional activity, radiation therapy.
Attention! A woman's body may be genetically predisposed to developing tumors. Also, pathologies often occur in workers of industrial enterprises.
Classification
There can be a benign and a dangerous malignant type of tumor on the cervix. Pre-tumor and background pathologies with a high chance of degeneration are noted.
If a tumor is present, other organs are also analyzed to determine the degree of penetration of the tumor - invasiveness.
| Endophytic tumor | Exophytic tumor | |
| Development of pathology deep into the internal organ | Extension beyond the organ | |
| non-invasive | germinating | |
Types of formations in the cervix
Neoplasms on the epithelial layer, squamous or glandular type. Histology defines such tumors as malignant. Benign neoplasms include papillomas and condylomas with symptoms of a viral infection.
- fibroids in the cervical area, in the muscle mass area;
- lymphoma, melanoma, teratoma and other neoplasms;
- stromal neoplasms: stromal sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, leiomyomas;
- neoplasms with a mixed type: stromal, epithelial elements;
- metastatic neoplasms.
What could be the consequences?
If appropriate measures are not taken in a timely manner to eliminate the round anechoic formation in the mammary gland, various complications may arise, which include degeneration into a malignant tumor.
The cyst does not pose a particular danger and does not affect a person’s life, unless it is too large. Complications often occur during inflammation or tumor suppuration.
This condition requires urgent antibiotic therapy and surgery. A very large cyst can put pressure on nearby vessels, muscles and nerves, causing the corresponding symptoms. In some cases, benign tumors can develop into a malignant stage and metastasize in the future. This significantly complicates the treatment process and worsens the prognosis for recovery.
Carrying out prevention
It is much easier to prevent any disease than to then carry out treatment for a long time. There are certain tips and tricks that will help significantly reduce the risk of developing a cyst in the breast. To do this, you need to minimize the consumption of strong tea and coffee. They have a negative effect on the nervous system, disturbances in the functioning of which can adversely affect the condition of the mammary gland.
It is also important to follow these rules:
- wear a comfortable bra that will not put pressure on your breasts;
- have a good rest, avoid stress;
- eliminate the consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- take hormonal medications only under the supervision of a doctor;
- avoid injury to the mammary gland.
You should also stop smoking, as this is one of the important factors that provoke breast diseases. It is important to ensure healthy and proper nutrition. Weight gain leads to changes in the hormonal system, which directly affects the appearance of formations in the mammary gland.
It is recommended to regularly visit a gynecologist and mammologist, since timely detected pathology is treated much faster and more effectively.