Why is human blood red?
Science knows that different living organisms on the planet have different blood colors.
However, in humans it is red. Why is blood red? This question is asked by both children and adults.
The answer is quite simple: the red color is due to hemoglobin, which contains iron atoms in its structure.
What makes blood red is hemoglobin, which consists of:
- From a protein called globin,
- The non-protein element heme, which contains the ferrous ion.
There are four hemes in hemoglobin molecules. Their number is 4 percent of the total mass of the molecule, and globin accounts for 96 percent.
The main effect in the activity of hemoglobin belongs to the iron ion.
Ferrous oxide makes blood red.
The metal that promotes the reproduction of red blood cells is continuously produced by the human body.
Nitric oxide, in turn, plays an important role in regulating blood pressure.
Types of blood
Arterial
| Venous |
| Rich in oxygen, comes from the heart. A bright scarlet hue distinguishes arterial blood from venous blood. | Gives oxygen to organs and returns to the heart. The dark red tint is a distinctive feature. What makes this blood dark is the carbon dioxide that fills it. |
What determines the color of blood?
The red color of blood can have different shades. Oxygen carriers, i.e. red blood cells (erythrocytes), are a shade of red depending on hemoglobin, an iron-containing protein found in them that can bind with oxygen and carbon dioxide to carry them to the desired location. The more oxygen molecules connected to hemoglobin, the brighter the red color the blood is. That’s why arterial blood, which has just been enriched with oxygen, is so bright red. After the release of oxygen to the cells of the body, the color of the blood changes to dark red (burgundy) - such blood is called venous.
Of course, the blood contains other cells besides red blood cells. These are also leukocytes (white blood cells) and platelets. But they are not in such significant quantities compared to red blood cells as to affect the color of the blood.
Blood color in anemia and cyanosis
With anemia (not enough hemoglobin or red blood cells), the blood can be said to be a paler red color, although this can only be seen by a specialist under a microscope. This is because when hemoglobin is not bound to oxygen, the red blood cells appear smaller and paler.
When the blood, due to health problems, does not carry enough oxygen and there is little oxygen in it, this is called cyanosis (cyanosis). That is, there is hemoglobin in the blood, but it is not associated with oxygen. A manifestation of cyanosis is the acquisition of a bluish tint by the skin and mucous membranes. The blood remains red, but even arterial blood has a color similar to the color of venous blood in a healthy person - with a blue tint. The skin, under which the vessels pass, which under normal conditions transport bright scarlet blood rich in oxygen, becomes blue in appearance.
But with anemia, the symptoms of cyanosis may not even be visible, because there is too little hemoglobin to affect the color of the skin and mucous membranes, and they are simply pale. In this case, external cyanosis will begin to appear only when the amount of reduced (without oxygen) hemoglobin becomes more than half of its total amount.
Compound
Blood is a rapidly renewing connective tissue that continuously circulates throughout the human body.
It was possible to find out what gives the red color, but its elements turn out to be no less interesting. What elements give it this color is an equally interesting aspect.
Blood contains:
- Plasma. The liquid is light yellow in color, with its help the cells in its composition can move. It is composed of 90 percent water, with the remaining 10 percent made up of organic and inorganic components. Plasma also contains vitamins and microelements. The light yellow liquid contains many beneficial substances.
- Formed elements of blood cells. There are three types of cells: white blood cells, platelets and red blood cells. Each type of cell has certain functions and characteristics.
Leukocytes
These are white cells that protect the human body. They protect it from internal diseases and foreign microorganisms penetrating from the outside.
This is a white element in color. Its white tint cannot be ignored during laboratory tests, so such cells are identified quite simply.
White blood cells recognize foreign cells that can cause harm and destroy them.
Platelets
These are very small colored plates whose main function is coagulation.
These cells are responsible for ensuring that the blood:
- It coagulated and did not flow out of the body,
- Coagulates quite quickly on the surface of the wound.
Red blood cells
More than 90 percent of these cells are in the blood. It is also red because red blood cells have this hue.
They carry oxygen from the lungs to peripheral tissues and are continuously produced in the bone marrow. They live for about four months, then are destroyed in the liver and spleen.
It is very important for red blood cells to carry oxygen to various tissues of the human body.
Few people know that immature red blood cells are blue, then acquire a gray tint and only then turn red.
There are quite a lot of human red blood cells, which is why oxygen reaches peripheral tissues so quickly.
It is difficult to say which element is more significant. Each of them has an important function that affects human health.
Main reasons
A person has problems with clotting due to the fact that the level of those substances that are responsible for this process decreases. Their main part is protein. With a deficiency of protein in plasma, disturbances occur in the process of blood clotting. Protein is a building material that “repairs” damaged areas of the vessel. When many diseases occur, protein levels may decrease. In rare cases, it may disappear from the blood completely.
As medical practice shows, these diseases are distinguished by genetic predisposition, that is, they are transmitted from generation to generation. A hereditary disease is not the only reason that can provoke this pathology. Among the main causes of thin blood are:
- Hemophilia.
- Vitamin K deficiency.
- Kidney diseases.
- Liver diseases.
- Long-term use of potent medications that have a destructive effect on blood clots.
- Low level of platelets in the blood.
- Anemia.
- Impaired functioning of internal organs.
Only a doctor can determine the exact cause that provoked the development of the pathology after a complete examination of the patient.
Explanation for the child
Children often ask questions regarding the components of the human body. Blood is one of the most popular topics of discussion.
Explanations for children should be extremely simple, but at the same time informative. Blood contains many substances that differ in function.
Consists of plasma and special cells:
- Plasma is a liquid that contains useful substances. It has a light yellow tint.
- The formed elements are erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets.
Liquid blood causes and treatment. Why is blood liquid?
Liquid blood, or in medical terminology - thrombocytopathy, is a special group of diseases, which includes about forty types of ailments associated with acquired or hereditary defects of platelets - white blood platelets.
The essence of the problem with this disease is that platelets in the blood do not perform their functions, causing it to liquefy, complicating the processes of its clotting.
In the presence of this type of disease, there are frequent cases of hemorrhage from the nasal cavity, oral mucosa, uterine bleeding, bleeding of the gums, and bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract.
Injuries in such diseases are accompanied by prolonged and heavy bleeding, which poses a serious danger not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient. For patients with thrombocytopathy, the question of how to make the blood thicker is vitally important, which is why modern medicine is doing everything possible to create the most effective drugs to solve these problems.
How to determine thrombocytopathy.
If a number of signs of poor blood clotting appear, measures need to be taken to make the blood thicker. The most common symptoms that indicate the development of the disease are frequent nosebleeds and heavy uterine bleeding.
If these symptoms appear, you should urgently seek help and advice from a hematologist, who will first of all suggest you do a blood test and a urine test. If necessary, you may also be asked to have a bone marrow sample taken from the sternum.
In cases where a blood test indicates a reduced number of platelets in the blood, the norm of which is about 150 - 400 thousand per 1 μl, we can talk about the presence of thrombocytopathy.
How to make your blood thicker yourself?
In order to thicken the blood and stop uterine bleeding,
Doctors may prescribe the use of a five percent solution of aminocaproic acid intravenously. In addition, to normalize platelet function, Androxon can be used intramuscularly.
In addition to these drugs, there are a number of others that also effectively cope with platelet problems, but it must be remembered that the unauthorized use of such drugs can cause the development of serious diseases, as well as various complications.
Also, in severe cases, doctors can transfuse platelet mass to the patient. In addition, the latest developments in the field of medicine are actively contributing to the solution of such problems, which make it possible to transplant stem cells, as well as bone marrow.
In order to effectively treat blood-related problems, you need to completely stop using drugs that affect platelet function and also reduce their number. So, in order to make the blood thicker, you need to avoid the use of penicillin antibiotics, papaverine, aspirin, antidepressants, and a number of other medications.
Proper, nutritious nutrition, which is rich in vitamins P, C and A, actively promote blood clotting and make the blood thicker. Among the products. Nuts that are richer in these substances than others include peanuts and almonds, as well as parsley and green tea.
Using a rich variety of medicinal plants can also increase blood clotting. The most effective natural remedy for thickening the blood is nettle. Grape and lingonberry leaves, oak bark, water pepper, cinquefoil and many other plants.
And against this background, chronic iron deficiency anemia may develop.
The fact is that with thrombocytopenia, the volume of platelets in the blood is much lower than normal, so the blood has increased fluidity. (if the platelet count is increased, this may already be thrombocytosis, in which case the blood is thickened).
Both thin and thick blood are bad for the body
If we consider liquid blood to be a normal state, then of course it’s bad. Such blood stops for a very long time in cases of cuts and wounds. There is a threat of dying from blood loss if severely wounded, although with normal blood the patient would have endured such a wound with less blood loss.
Liquid blood means poor blood clotting. I think it’s not difficult to guess what the threat of poor clotting is. A man cut his finger and that’s it, off to the next world. When it’s very thick it’s also bad. It's better to have a normal one.
Why liquid blood?
- nasal,
- menstrual of unknown origin,
- from the gums, prolonged bleeding after tooth extraction,
- due to cuts,
- during pregnancy.
Also on topic:
Please answer quickly, my pelemyanik has liquid blood, doctors said there is no treatment
Liquid fabric. What is blood and how to prevent its diseases
According to Chinese medicine, the blood is a separate organ that can feel good, or it can get sick and require treatment. According to Western medicine, blood is a fluid tissue that must have a certain composition and quality, otherwise the entire body will suffer due to its “wrong” state.
What does blood look like from a scientific point of view? This is plasma (the liquid part of the blood), in which the so-called “formed elements of blood” are suspended: red blood cells, leukocytes and platelets.
Plasma consists of 60% water, the remaining components of plasma are proteins (albumin, globulins, etc.) and some other organic compounds. For blood transfusions, blood plasma is taken from donors, because...
Whole blood (except in rare cases) is not transfused.
As for the formed elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets), they must be kept in balance in the blood. Any deviation may indicate a particular disease.
White blood cells: infection or cancer?
Leukocytes are guard cells whose task is to detect pathogenic agents in the body (for example, bacteria) and destroy them.
Accordingly, an increased level of leukocytes may signal that the body is fighting bacteria or viruses - that is, there is inflammation. In the case of a cold, it is easy to detect the source of inflammation (throat, nose, etc.).
), but there are times when there is inflammation somewhere, but it is asymptomatic. For example, pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys) can occur against the background of mild nagging pain in the lower back, to which the patient is accustomed and does not notice.
A reduced level of leukocytes may indicate a successful infection: in battles with bacteria or viruses, leukocytes won, but lost many “fighters”. In addition, a decrease in leukocytes is typical, for example, after poisoning.
However, a strong increase in the level of leukocytes, as well as a sharp decrease, may indicate a malignant process occurring in the body. Unfortunately, these processes can also be asymptomatic for several months, and preventive annual testing can save lives.
Platelets: a lot, a little, just right
The main function of platelets is to protect the body from blood loss. By binding to plasma proteins, platelets “seal” blood vessels in case of damage. It is thanks to platelets that our cuts and abrasions heal quickly enough.
Accordingly, a lack of platelets is dangerous to life and health: without them, a blood clot does not form and bleeding does not stop.
When platelet levels are low, there is a risk of internal bleeding, possible nosebleeds, and bleeding gums.
An excess of platelets is dangerous because blood particles can stick together inside the vessel and form a blood clot, which can clog the vessel. If the artery supplying the heart is blocked, myocardial infarction occurs.
You may have heard that the cause of a heart attack is cholesterol deposits on the walls of blood vessels, but, as a rule, cholesterol plaques alone are not enough: they narrow the lumen of the vessel, and the “last straw” is a blood clot that settles on the problem area and blocks blood flow.
Fluctuations in platelet counts can be caused by infectious diseases and exposure to toxic substances, as well as blood cancers. There are simpler reasons: taking antidepressants (removes fluid from the body, “thickening” the blood and increasing platelet levels) or regular use of aspirin (this drug thins the blood, worsening clotting rates).
Where is the hemoglobin?
Red blood cells are the most numerous part of the formed elements of blood. It is erythrocytes - red blood cells - that color the blood of all mammals on the planet red. Mature red blood cells store the iron-containing protein hemoglobin. Why do we need it?
Thanks to it, blood performs its main function: it carries oxygen throughout the body, nourishing tissues with it. In the pulmonary alveoli, hemoglobin binds oxygen coming from the external environment and turns into oxyhemoglobin - that is, hemoglobin enriched with oxygen.
This blood has a bright red hue, and it flows through the arteries. Venous blood is darker in color due to the fact that hemoglobin has already given up oxygen and the red blood cells have “faded.”
In addition, hemoglobin has the ability to bind a certain amount of carbon dioxide, take it from tissues and transport it to the lungs, from where a person can exhale it.
Source: https://netgusevu.ru/treatment/zhidkaya-krov-prichiny-i-lechenie-pochemu-zhidkaya-krov/
Why are veins blue
The veins carry burgundy blood. They are red, like the color of the blood that flows through them, but not blue. The veins only appear blue.
This can be explained by the law of physics about the reflection of light and perception:
When a ray of light hits the body, the skin reflects some of the waves and looks light. However, it transmits the blue spectrum much worse.
The blood itself absorbs light of all wavelengths. The skin gives a blue color for visibility, and the vein is red.
The human brain compares the color of the blood vessel against the warm tone of the skin, resulting in blue.
What color are blood and veins really?
There's so much you can't find on the net. Even the question about the color of blood and veins is often accompanied by assumptions and fiction, although most people actually know the answer.
Yes, everything is simple here - the blood is red, only in different shades, depending on the amount of hemoglobin in it and oxygen enrichment.
Everything is as taught in biology and BJD at school: arterial blood (rich in oxygen, coming from the heart) is bright scarlet , and venous blood (which has given oxygen to the organs, returning to the heart) is dark red (burgundy).
The veins that are visible under the skin are also red when blood flows through them inside. After all, the blood vessels themselves are quite transparent. But still, many people have questions such as “Why does blood come in different colors and what does this depend on?” and “Why are veins blue or cyan?”
What determines the color of blood?
The red color of blood can have different shades.
Oxygen carriers, i.e. red blood cells (erythrocytes), are a shade of red depending on hemoglobin, an iron-containing protein found in them that can bind with oxygen and carbon dioxide to carry them to the desired location.
The more oxygen molecules connected to hemoglobin, the brighter the red color the blood is. That’s why arterial blood, which has just been enriched with oxygen, is so bright red. After the release of oxygen to the cells of the body, the color of the blood changes to dark red (burgundy) - such blood is called venous.
Of course, the blood contains other cells besides red blood cells. These are also leukocytes (white blood cells) and platelets. But they are not in such significant quantities compared to red blood cells as to affect the color of the blood.
Blood color in anemia and cyanosis
With anemia (not enough hemoglobin or red blood cells), the blood can be said to be a paler red color, although this can only be seen by a specialist under a microscope. This is because when hemoglobin is not bound to oxygen, the red blood cells appear smaller and paler.
When the blood, due to health problems, does not carry enough oxygen and there is little oxygen in it, this is called cyanosis (cyanosis). That is, there is hemoglobin in the blood, but it is not associated with oxygen.
A manifestation of cyanosis is the acquisition of a bluish tint by the skin and mucous membranes. The blood remains red, but even arterial blood has a color similar to the color of venous blood in a healthy person - with a blue tint.
The skin, under which the vessels pass, which under normal conditions transport bright scarlet blood rich in oxygen, becomes blue in appearance.
But with anemia, the symptoms of cyanosis may not even be visible, because there is too little hemoglobin to affect the color of the skin and mucous membranes, and they are simply pale. In this case, external cyanosis will begin to appear only when the amount of reduced (without oxygen) hemoglobin becomes more than half of its total amount.
Why are veins blue and not red?
In fact, of course, although the veins carry dark burgundy blood, unlike the bright scarlet arterial blood, they are not at all blue in color. They are red, like the color of the blood that flows through them.
And you shouldn’t believe in the theory that you can find on the Internet that the blood actually runs through the vessels is blue, but when cut and in contact with air it instantly turns red - this is not so.
Blood is always red, and why is described above in the article.
The veins only appear blue to us. This is explained by the laws of physics about the reflection of light and our perception. When a beam of light hits the body, the skin reflects some of all the waves and therefore looks light, well, or different, depending on melanin. But it transmits the blue spectrum worse than red. But the vein itself, or rather the blood, absorbs light of all wavelengths (but less, in the red part of the spectrum).
That is, it turns out that the skin gives us a blue color for visibility, and the vein itself gives us red. But, interestingly, the vein actually reflects even a little more red than the skin in the blue spectrum of light.
But why then do we see veins blue or cyan? And the reason, in fact, lies in our perception - the brain compares the color of the blood vessel against the bright and warm tone of the skin, and in the end shows us blue.
Why don't we see other vessels through which blood flows?
If a blood vessel is located closer than 0.5 mm to the surface of the skin, then it generally absorbs almost all blue light, and reflects much more red light - the skin looks healthy pink (ruddy).
If the vessel is much deeper than 0.5 mm, then it is simply not visible, because the light does not reach it.
Therefore, it turns out that we see veins that are approximately located at a distance of 0.5 mm from the surface of the skin, and why they are blue has already been described above.
Why can't we see arteries from under the skin?
In fact, about two-thirds of the blood volume is permanently in the veins, which means they are larger than other vessels.
In addition, arteries have much thicker walls than veins, because they have to withstand greater pressure, which also prevents them from being sufficiently transparent.
But even if the arteries were visible from under the skin as well as some veins, it is assumed that they would have approximately the same color, despite the fact that the blood running through them is brighter.
What color are veins actually?
If you've ever cooked meat, you probably already know the answer to this question. Empty blood vessels are reddish-brown in color. There is not much difference in color between arteries and veins. They differ mainly when viewed in cross section. Arteries are thick-walled and muscular, while veins have thin walls.
Also learn about the main vein diseases worth knowing, as well as about varicose veins and their treatment.
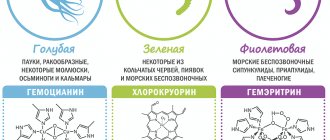
Blood of a different color in various living creatures
Not all living organisms have red blood.
The protein that gives this color in humans is hemoglobin, contained in hemoglobin. Other living beings have other fat-containing proteins instead of hemoglobin.
The most common shades besides red are:
- Blue. Crustaceans, spiders, mollusks, octopuses and squids boast this color. And blue blood is of great importance for these creatures, as it is filled with important elements. Instead of hemoglobin, it contains hemocyanin, which contains copper.
- Violet. This color is found in marine invertebrates and some mollusks. Typically, such blood is not only purple, but also slightly pink. The blood of young invertebrate organisms is pink. In this case, the protein is hemerythrin.
- Green. Found in annelids and leeches. The protein chlorocruorin is close to hemoglobin. However, iron in this case is not oxide, but ferrous.
The color of blood varies depending on the protein it contains. Whatever the color of blood, it contains a huge amount of useful substances necessary for a living organism. Pigment is important for every organism, despite its diversity.
Note to patients
Self-medication is prohibited, since this is a very serious pathology that directly affects the patient’s life expectancy. To avoid serious complications, it is important to immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment. A minor injury can lead to death (this is the whole danger of the disease). Traditional methods of therapy are not recommended to be used without consulting a doctor, as this can lead to the death of the patient. The cause of thin blood in a child will be determined by the pediatrician after a thorough examination of the patient.
Source: fb.ru
Diseases and conditions
Video Secrets and mysteries of our blood
Blood is a combination of many substances - plasma and formed elements. Each element has strictly defined functions and tasks; certain particles also have a pronounced pigment, which determines the blood color. Why is human blood red? The pigment is contained in red hemoglobin; it is part of the red blood cell. It is for this reason that there are organisms on Earth (scorpions, spiders, monkfish) whose blood color is blue or green. Their hemoglobin is dominated by copper or iron, which gives the characteristic color of the blood.
To understand all these elements, it is necessary to understand the composition of blood.
Compound
Plasma
As already noted, one of the components of blood is plasma. It takes up about half of the blood composition. Blood plasma turns blood into a liquid state, has a light yellow color and is slightly denser in properties than water. The density of plasma is ensured by substances dissolved in it: antibodies in the blood, salts, fats, carbohydrates and other elements.
Shaped elements
Another component of blood are formed elements (cells). They are represented by erythrocytes - red blood cells, blood leukocytes - white blood cells, platelets - blood platelets. It is red blood cells that answer the question why blood is red.
Red blood cells
At the same time, about 35 billion red blood cells move through the circulatory system. Appearing in the bone marrow, red blood cells form hemoglobin in the blood, which is a red pigment rich in protein and iron. The task of hemoglobin is to deliver oxygen to vital parts of the body and remove carbon dioxide. Red blood cells live on average 4 months, then they disintegrate in the spleen. The process of formation and breakdown of red blood cells is continuous.
Red blood cells give the blood a red color
Why liquid blood? Discussion on LiveInternet – Russian Online Diary Service
The causes of thin blood can be either hereditary or acquired, in both cases it is associated with dysfunction of the white blood platelets (platelets) contained in the plasma (this is the liquid part of the blood).
Their defects and, as a consequence, disruption (the main function of platelets is to prevent blood loss in the event of vascular injury) lead to blood thinning and disruption of its clotting process. For women during pregnancy, this poses a particular danger, since large blood loss can cause the most disastrous consequences for both the mother and the fetus, including death.
If the analysis revealed that a person’s blood is liquid, he is diagnosed with thrombocytopenia (a condition characterized by a decrease in the number of platelets and their qualitative inferiority, which leads to increased bleeding that is difficult to stop). Various types of bleeding appear, most often:
- nasal,
- menstrual of unknown origin,
- from the gums, prolonged bleeding after tooth extraction,
- due to cuts,
- during pregnancy.
The most dangerous bleedings are gastrointestinal, renal, retinal, brain and its membranes. This is often accompanied by symptoms such as an enlarged spleen and low blood pressure, and the causes of bleeding are usually completely unclear.
Against this background, chronic iron deficiency anemia can develop (a group of clinical syndromes caused by a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood), which is especially dangerous for women during pregnancy, so its treatment should be immediate.
People with thin blood should consult a doctor for any injury, even a seemingly minor one. But if you have such a problem, it is best to avoid injuries altogether, as well as enemas, rectal examinations and intramuscular injections.
When choosing a toothbrush, you should make sure that its bristles are not too hard. As for dental floss and straight razors, they should be completely eliminated from everyday use. You should not use medications that suppress platelet function.
For example, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Acetylsalicylic acid and other drugs based on it, which pose a particular danger to women during pregnancy.
Symptoms and causes.
Liquid blood may have hereditary causes. They lead in frequency, occupying 36% of the total number of patients. This may also be a consequence of decreased platelet production and their increased destruction in peripheral arteries and veins. The reasons may also lie in problems with the immune system, when platelets die under the influence of antibodies.
In other words, in the patient’s body, the patient’s own platelets are perceived as foreign, the body refuses to recognize them, and then the active immune system instantly produces antiplatelet antibodies against its unrecognized platelets, which is a disease that occurs in people who were previously completely healthy.
Blood thinning can be caused by:
- preeclampsia (a pathology that occurs during pregnancy, when blood pressure rises so high that there is a threat to life for the mother and child);
- severe form of nephropathy (a disease manifested in impaired kidney function);
- disorders of the blood clotting mechanism; bleeding during childbirth;
- antiphospholipid syndrome (a disease with many manifestations, characterized by a large number of produced antibodies to phospholipids - the elements that make up the parts of the cell);
- systemic lupus erythematosus (a connective tissue disease with vascular damage);
- folate deficiency (lack of folic acid in the blood serum);
- taking blood thinning medications; allergic reaction, viral infection.
Liquid blood in a patient manifests itself through symptoms in the form of minor hemorrhages and bruises. Hemorrhagic syndrome (bleeding due to changes in hemostasis) is much more pronounced in children, adolescents and women.
For the latter, the biggest problem is prolonged uterine bleeding, which results in the loss of a very large volume of blood (which is especially dangerous during pregnancy) and, as a consequence, severe anemia and hemorrhagic collapse (an acute drop in vascular tone and a decrease in circulating blood volume due to massive blood loss).
Liquid blood in pregnant women.
During pregnancy, a woman repeatedly has to donate blood for analysis, which reports the slightest problems in the body. If your health is not strong, you have to take it much more often, determining the level of red blood cells, platelets, leukocytes, etc., as well as their quality.
In the processes of blood coagulation, the main role is played by its formed elements, platelets, and they are also responsible for the reactions of nonspecific resistance of the body. Platelet formation occurs in the bone marrow, and they are determined by taking a general blood test.
Often during pregnancy, the level of platelets in a woman’s body changes ambiguously and is largely influenced by individual characteristics. In a healthy woman during pregnancy, the number of platelets may decrease slightly, which is caused by their low life expectancy and increased consumption in the peripheral circulation.
This is caused by the fact that during pregnancy the liquid part of the blood in the body increases in volume. A severe decrease in the number of platelets produced, their increased destruction or consumption cause blood thinning. Characteristic symptoms are bleeding and the appearance of small bruises.
Insufficient platelet production in a woman during pregnancy may be a consequence of her poor diet. In addition, low platelet levels can be caused by chronic bleeding or immune system disorders. In these cases, platelets are either produced in insufficient quantities or have a defective structure.
To identify bleeding disorders during pregnancy, the patient is prescribed a coagulogram (a test showing the effectiveness of the system responsible for blood clotting) and, if necessary, appropriate treatment is provided.
Low platelet levels during pregnancy increase the risk of bleeding during labor.
However, it should be mentioned that it only exists if the platelet count at the time of birth does not exceed 50,000. With spontaneous birth, the risk of internal bleeding in a child with immune thrombocytopenia increases sharply. Of particular concern is the risk of cerebral hemorrhage. In such cases, a caesarean section is performed to be on the safe side. But it also carries the risk of causing bleeding in the mother.
Treatment.
If the analysis shows liquid blood, such a patient is treated by a hematologist. He prescribes blood and urine tests, and, if necessary, a bone marrow puncture from the sternum. For heavy uterine bleeding, nosebleeds, etc., a five percent solution of aminocaproic acid is prescribed intravenously.
The drugs Adroxon and adenosine triphosphate are injected intramuscularly, normalizing platelets. Medicines such as Pamba, Emosint, Dicynon and tranexamic acid are also used. Treatment with glucocorticosteroids is one of the main methods. These hormones prevent the destruction of platelets by weakening the effect of antibodies on them.
In addition, glucocorticosteroids inhibit the destruction of platelets in the spleen, thereby increasing their number in the blood. After it has risen to the normal level, the prescribed dose is gradually reduced. The duration of the course of glucocorticosteroid therapy is from 4 to 6 weeks.
If treatment with hormones is ineffective, therapy with non-hormonal immunosuppressants is carried out. At the same time, the body’s production of antibodies hostile to its own platelets is inhibited, as a result of which the degree of platelet destruction decreases and their lifespan increases.
Drugs used: Azathioprine, Vincristine, Azathioprine and Cyclophosphamide. They are used for several weeks, accompanied by regular monitoring of blood tests. Treatment with Danazol is very effective when taken for a long time, gradually increasing the presence of platelets in the blood.
This treatment is most effective for patients over 45 years of age. Severe cases require platelet transfusion, as well as treatment using new modern technologies in the form of bone marrow and stem cell transplantation.
Treatment should not contain drugs that affect platelet activity and help reduce their number. The group of such medications includes: fibrinolytics, indirect anticoagulants and salicylates. These are: aspirin, Butadione, furosemide, antidepressants, Indomethacin, penicillin antibiotics.
Drug treatment must certainly be accompanied by proper nutrition, rich in vitamins C, A and P. To increase blood clotting, nuts (especially peanuts and almonds), parsley and green tea should be included in the daily diet.
Effective treatment can also be provided by medicinal plants, a wide range of which helps improve blood clotting. Nettle has proven itself best for this purpose.
No less effective treatment is provided by lingonberry and grape leaves, cinquefoil, linden blossom, horsetail, burnet root, oak bark, water pepper, shepherd's purse, etc.
Liquid blood is an alarming sign that requires mandatory treatment, especially in women during pregnancy, since in this case not one life, but two, are at risk. However, with a variety of therapy methods, a positive effect is guaranteed.
Quelle der Zitate: https://healthy2life.com/
https://www..com/
Series of messages “Anatomy. Anatomie.”:
Part 1 – Medical sensation. A new human organ has been discovered. Part 2 – How to hear what your body is saying….
Part 18 – Alzheimer's disease in myths and facts.
Part 19 – Hormones, cycle and mood. Part 20 – Why is blood thin?
Part 21 – Hemorrhagic stroke.
Part 22 – Classification of strokes….
Part 27 – Human Blood.
Part 28 – Diagnosis of uterine pathologies. Part 29 – Metabolic disorders: symptoms and treatment.
Series of messages “Diseases. Krankheiten.”:
Part 1 – Why is blood thin?
Part 2 – Cerebral hemorrhage.
Part 3 – Hemorrhagic stroke….
Part 15 – Human blood.
Part 16 – Diagnosis of uterine pathologies. Part 17 – Metabolic disorders: symptoms and treatment.
Source: https://www.liveinternet.ru/users/listra55/post421139117
Hemoglobin
The blood, enriched with oxygen in the lungs, disperses to the vital organs of the body. At this moment it has a bright scarlet color. This occurs due to the binding of hemoglobin in the blood with oxygen, resulting in oxyhemoglobin. As it passes through the body, it distributes oxygen and becomes hemoglobin again. Next, hemoglobin absorbs carbon dioxide from tissues and is transformed into carbohemoglobin. At this moment, the color of the blood changes to dark red. Immature red blood cells also have a bluish tint, and as they grow they turn gray and then turn red.
Symptoms and causes.
Liquid blood may have hereditary causes. They lead in frequency, occupying 36% of the total number of patients. This may also be a consequence of decreased platelet production and their increased destruction in peripheral arteries and veins. The reasons may also lie in problems with the immune system, when platelets die under the influence of antibodies. In other words, in the patient’s body, the patient’s own platelets are perceived as foreign, the body refuses to recognize them, and then the active immune system instantly produces antiplatelet antibodies against its unrecognized platelets, which is a disease that occurs in people who were previously completely healthy. Blood thinning can be caused by:
- preeclampsia (a pathology that occurs during pregnancy, when blood pressure rises so high that there is a threat to life for the mother and child);
- severe form of nephropathy (a disease manifested in impaired kidney function);
- disorders of the blood clotting mechanism; bleeding during childbirth;
- antiphospholipid syndrome (a disease with many manifestations, characterized by a large number of produced antibodies to phospholipids - the elements that make up the parts of the cell);
- systemic lupus erythematosus (a connective tissue disease with vascular damage);
- folate deficiency (lack of folic acid in the blood serum);
- taking blood thinning medications; allergic reaction, viral infection.
Liquid blood in a patient manifests itself through symptoms in the form of minor hemorrhages and bruises. Hemorrhagic syndrome (bleeding due to changes in hemostasis) is much more pronounced in children, adolescents and women. For the latter, the biggest problem is prolonged uterine bleeding, which results in the loss of a very large volume of blood (which is especially dangerous during pregnancy) and, as a consequence, severe anemia and hemorrhagic collapse (an acute drop in vascular tone and a decrease in circulating blood volume due to massive blood loss).
Shades of red
The color of the blood may vary. Answers to the questions why blood is dark red or bright red. A person’s blood takes on a different shade depending on whether it moves towards the heart or away from it.
Dark red and bright red blood
Very often people wonder why veins are blue and blood is red? The fact is that venous blood is the blood that flows through the veins to the heart. This blood is saturated with carbon dioxide and deprived of oxygen, has lower acidity, contains less glucose and significantly more final metabolic products. In addition to being dark red, venous blood also has a bluish, blue tint. However, the blue tint of blood is not so strong as to “stain” the veins blue.
Why is blood red? It's all about the process of passing light rays and the ability of bodies to reflect or absorb solar rays. In order to reach venous blood, the beam must pass through the skin, the fat layer, and the vein itself. The sun's ray consists of 7 colors, three of which the blood reflects (red, blue, yellow), the remaining colors are absorbed. Reflected rays pass through tissues a second time to enter the eye. At this point, red rays and low-frequency light will be absorbed by the body, and blue light will be transmitted. We hope that we have answered why a person has dark red and bright red blood.
Menstruation and the cycle reflect the state of the female body. Any violations require contacting a doctor. Light blood during menstruation is normal if menstruation has just begun. Gradually the color will become darker. If this does not happen, the course of the pathology should be suspected. In this case, you need to urgently seek help from a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination.
During menstruation, the discharge should not have an unnatural color
You need to pay attention not only to the color of the discharge, but also to other characteristics. Normally, there should be no extraneous manifestations. Many pathologies, if left untreated, can lead to complications, including death.
Patient Research
If one of the symptoms of the pathology is present, it is important to immediately consult a doctor and undergo a thorough medical examination. If you have had similar problems in your family, it is important to visit your doctor regularly. To diagnose blood clotting problems, it is necessary to study the complete clinical picture and overall health of the patient. The causes and treatment of thin blood is a topic that worries many, but not everyone knows that this is a purely individual process. Only after examining the patient does the doctor find out the cause and prescribe treatment.
First of all, you need to pass the following tests:
- thoroughly examine the blood;
- check the amount of blood loss due to mechanical damage;
- determine the level of white and red blood cells in plasma;
- study platelet aggregation;
- measure bleeding time.
Based on the results of the study, the doctor will prescribe the appropriate treatment.
When a symptom is normal
The blood itself should not have a light pink tint. Normal shades of menstruation include:
- scarlet;
- Dark red;
- brown.
In the first days of menstruation, the discharge is heavy. Gradually, the amount of blood decreases and its color becomes darker.
Menstruation should not be accompanied by burning and itching. Pain should be absent or moderate in severity. Blood should not be black. This symptom requires an urgent visit to the doctor.
Normally, periods come at regular intervals.
Normally, menstruation is regular and comes at the same time. The duration of critical days should not exceed 7 days. The volume of discharge is 150 ml for the entire period of menstruation.
Often, pink periods require a visit to the doctor, since they are a manifestation of an existing pathology. The physiological causes of this symptom are presented in the table.
| In teenagers | Another year after the onset of menarche, disruptions are observed. This is due to the fact that the hormonal balance is just being established. Light discharge should not be accompanied by a strong deterioration in health. |
| After 40 | Light menstruation after 40 years may indicate the onset of menopause. In this case, the symptom is accompanied by other signs: • increased body weight; • failures of menstruation; • long delays; • decreased libido; • the appearance of new wrinkles; • weakness; • drowsiness. Menopause is not a pathology and does not require treatment. Only if symptoms are severe will a woman be recommended hormone replacement therapy. |
Causes and treatment of thin blood
Summary of the article:
Thin blood is a bleeding disorder, a very serious abnormality. This disease means bad blockage of blood vessels if they are damaged. In a healthy person, the blood in the area of the defect begins to thicken, which forms a natural plug.
This saves a person from fatal blood loss. It happens that the blood does not clot as it should, which leads to heavy blood loss and large uncontrolled bleeding. Poor blood light quality does not always manifest itself in external bleeding.
The bleeding may occur under the skin, or even into the brain.
Causes of thin blood
Poor clotting is explained by the fact that the number of substances responsible for this process is reduced. Most of them are various proteins. The lack of protein in the plasma is what disrupts the normal coagulation process. Proteins are building materials that are used to repair damaged areas of blood vessels.
Some diseases lead to the fact that the amount of protein decreases or it completely disappears from the blood. Almost all of these diseases are genetic, that is, they are transmitted from ancestors to descendants. However, hereditary diseases are not the only cause.
So, the reasons for liquid blood:
- Hemophilia. The most common factor is a genetic disorder;
- Lack of vitamin K;
- Liver carcinoma, cancer;
- Hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver;
- Long-term use of strong antibiotics or drugs that destroy blood clots;
- Taking inhibitors;
- Reduction in platelet count to the point of dangerous;
- Anemia;
- Disruption of the functioning of certain organs.
The most common causes of blood incoagulability
As is already clear from the previous block, liquid blood is a consequence of a genetic disorder or an acquired disease. In certain cases, spontaneous bleeding occurs, often invisible to the eye, that is, inside the body, or the bleeding is caused by mechanical damage.
- The most common circumstance of this diagnosis is hemophilia A and B. In this case, there is a critical deficiency of proteins necessary for the plasma. Severe and unusual bleeding occurs;
- Lack of substances for coagulation of forms II, V, VII, X, XII. This is where clotting problems and abnormal bleeding occur;
- Von Willebrand syndrome. When observing this genetic deviation, there is a deficiency of established proteins that clump platelets and attach to the vessel wall.
A number of certain diseases may cause bleeding disorders, as well as inappropriate medical care. All this provokes the destruction of these or other proteins in the plasma.
Symptoms of liquid blood
The surest sign of this disorder is abnormal bleeding. Its anomaly is manifested in long-term bleeding and undiminished pressure. Even a small cut causes similar manifestations. Under normal conditions of injury, bleeding does not appear to be normal and has clear abnormal features.
Other symptoms:
- Bruises. Bruises periodically appear throughout the body, despite the fact that no damaging actions occurred in this place. Bruises can vary in color and size;
- Profuse bleeding during menstruation. Too much blood coming out is a sign that you should go to the doctor as soon as possible;
- Periodic nosebleeds. Blood pressure fluctuates for many, but too frequent bleeding already indicates a probable pathology of blood clotting;
- Prolonged bleeding after any injury. Even a small scratch bleeds like a big wound. If you see this, do not waste time and rush to a medical professional. People with thin blood live at constant risk to their lives, since any wound can provoke significant blood loss.
Diagnostics and necessary tests
If you have at least one point regarding symptoms, then you should urgently visit a specialist and conduct an examination. If you or someone close to you with this kind of problem has suffered mechanical damage to blood vessels, you should call an ambulance and provide first aid, based on the location of the damage and its nature.
Poor clotting can only be diagnosed by examining the patient’s complete medical record. The main questions that will form the initial picture:
- What accompanying symptoms have you noticed?
- How often does bleeding occur?
- How long does the bleeding last?
- What caused the bleeding?
Tests that will give an answer about the presence of poor clotting:
- Complete blood test. The amount of blood loss due to mechanical damage and the volume of white and red blood cells in the plasma are checked;
- Platelet aggregation study. It allows you to find out the strength of platelet attachment;
- Measuring bleeding time. After taking the test from the finger, the doctor tracks the time during which the vessel will be blocked.
Treatment of poor clotting and consequences
Based on what caused this deviation, a treatment plan is built, which is individual in each case. At the same time, the root cause of the disease is treated, if it is a disease such as liver dysfunction or an oncological tumor. However, there are general additions to each of the therapies:
- Administration of vitamin K through injections;
- Medicines are prescribed whose task is to improve the functioning of proteins for coagulation;
- In acute cases, blood transfusion or use of donor plasma;
- Drugs that have a good effect on the interaction of platelets and their attachment to the walls.
The consequences of this syndrome are treated in only two ways:
- Preparations with a significant iron content. Iron replenishes the volume of blood in the body that was lost during illness. If you do not take iron in the required amount, there is a risk of iron deficiency anemia, the symptoms of which are weakness, shortness of breath, and dizziness. Hematogen is the first assistant in this problem, because it contains a large amount of essential iron;
- Blood transfusion. If too much blood has been lost, donated plasma is indispensable. The main thing is to choose the right type of blood to be transfused, otherwise complications may occur. The procedure is performed exclusively in a hospital under the supervision of several doctors.
What pathologies may be
Most often, a light shade of blood indicates the need to visit a doctor. Often the symptom is pathological in nature. The disorder may occur when the intrauterine device grows in, if one is installed in the vagina.
Another probable reason is oncological processes. In this case, menstruation is watery and in volume exceeds the accepted norm. The discharge has an unpleasant odor.
It is also worth excluding the possibility of the presence of benign neoplasms.
The patient may be diagnosed with:
Benign formations are accompanied by copious discharge. There is obvious discomfort. There is pain during sex. After an abortion, light critical days indicate that particles of the fertilized egg still remain in the uterus. Gradually, the discharge may acquire a bright color.
For any deviations, you should visit a gynecologist
Any illness requires consulting a doctor. Ignoring any changes is strictly prohibited. Otherwise, complications will occur.
Could there be pregnancy?
If light blood comes instead of normal menstruation, the possibility of pregnancy should not be ruled out. Diagnostics needed to rule out:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- risk of miscarriage.
In an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg attaches outside the uterus. The condition requires urgent hospitalization. The woman is prescribed surgery. If the operation does not occur on time, the risk of death increases.
You can recognize the course of an ectopic pregnancy by the following symptoms:
- nausea;
- decreased performance;
- intense vomiting;
- sharp pain in the abdomen;
With an ectopic pregnancy, a girl may feel sharp pain in the abdomen
- bowel dysfunction;
- headache.
At first, there are no pathological symptoms. Then the condition worsens greatly. We urgently need to call an ambulance. An ectopic pregnancy, like a regular one, can be confirmed using a special test.
There is a possibility of miscarriage: light blood may indicate partial detachment of the endometrium.
When is it necessary to see a doctor?
It is necessary to carefully monitor women's health. Any alarming changes must be noticed and eliminated in a timely manner. Light menstruation requires consulting a doctor in the following cases:
- more than 35 or less than 20 days have passed between periods;
- menstruation is scanty or, on the contrary, abundant and lasts more than 7 days;
- a large number of clots are observed;
- failures in the cycle are regular;
- menstruation remains light until the end;
- the discharge smells like rotten fish;
- additionally there is itching and dryness.
The listed signs are pathological. Even one symptom is a good reason to see a doctor.
From this video you will learn what the color of blood during menstruation indicates:
Liquid blood: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, health hazards, treatment
Many people are interested in what causes thin blood.
If a person has thin blood, this is a serious deviation in the clotting process. Under such conditions, damaged vessels become poorly clogged. If a person does not have any health problems, then during an injury the blood thickens, resulting in the formation of a natural plug. Thanks to this phenomenon, a person is able to survive. If there are problems with blood clotting, this can lead to heavy bleeding and large blood loss. The danger of the pathology is that it is not always possible to determine blood clotting by external signs.
In frequent cases, hemorrhage occurs under the skin or even in the brain.
Main reasons
A person has problems with clotting due to the fact that the level of those substances that are responsible for this process decreases. Their main part is protein.
With a deficiency of protein in plasma, disturbances occur in the process of blood clotting. Protein is a building material that “repairs” damaged areas of the vessel.
When many diseases occur, protein levels may decrease. In rare cases, it may disappear from the blood completely.
As medical practice shows, these diseases are distinguished by genetic predisposition, that is, they are transmitted from generation to generation. A hereditary disease is not the only reason that can provoke this pathology. Among the main causes of thin blood are:
- Hemophilia.
- Vitamin K deficiency.
- Kidney diseases.
- Liver diseases.
- Long-term use of potent medications that have a destructive effect on blood clots.
- Low level of platelets in the blood.
- Anemia.
- Impaired functioning of internal organs.
Only a doctor can determine the exact cause that provoked the development of the pathology after a complete examination of the patient.
Common causes of pathology
Most often, liquid blood is a hereditary pathology. In rare cases, heavy bleeding occurs inside the body due to mechanical damage. In addition, severe and unusual bleeding can occur due to a critical deficiency of the protein required in the plasma.
von Willebrand syndrome
If a patient is diagnosed with this genetic disorder, then the body experiences a deficiency of the established protein, which “crumples” platelets and attaches them to the walls of blood vessels. Von Willebrand syndrome is a common cause of thin blood in humans.
Symptoms of pathology
Heavy bleeding is one of the most important and common signs of a bleeding disorder. Even small cuts can cause heavy blood loss.
The main symptoms include:
- The appearance of bruises. A person who has thin blood occasionally develops hematomas, provided there is no mechanical damage. A bruise can be of any color or size.
- Heavy menstruation. If during menstrual periods heavy bleeding occurs that exceeds the norm, then this should be a cause for concern and immediate consultation with a doctor. In this case, it is important to visit a gynecologist and therapist. Systematic discharge of blood from the nose often occurs due to high or low blood pressure. But if such a phenomenon happens systematically, then it is necessary to seek help from a specialist and carry out a medical examination. Since the presence of one of the signs may indicate that a serious pathology is developing in the body.
- Prolonged bleeding after minor injury. Even small scratches can bleed like wounds.
If there are problems with blood, it is important not to waste time and seek help from medical personnel. People who have liquid blood risk their lives every day, since any injury can cause death due to significant blood loss. The cause of liquid blood in a person will be determined by the doctor after a detailed examination of the patient.
Patient Research
If one of the symptoms of the pathology is present, it is important to immediately consult a doctor and undergo a thorough medical examination. If you have had similar problems in your family, it is important to visit your doctor regularly.
To diagnose blood clotting problems, it is necessary to study the complete clinical picture and overall health of the patient. The causes and treatment of thin blood is a topic that worries many, but not everyone knows that this is a purely individual process.
Only after examining the patient does the doctor find out the cause and prescribe treatment.
First of all, you need to pass the following tests:
- thoroughly examine the blood;
- check the amount of blood loss due to mechanical damage;
- determine the level of white and red blood cells in plasma;
- study platelet aggregation;
- measure bleeding time.
Based on the results of the study, the doctor will prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Treatment process
During the treatment process, it is necessary to build an individual scheme and find out the cause of very thin blood. It is equally important to examine the functioning of the liver and find out whether cancerous tumors are present.
During therapy, it is necessary to prescribe the patient injections with vitamin K. The doctor prescribes a medicine that improves the functioning of the protein. In case of significant blood loss, donor blood should be used.
It is imperative to include in the treatment process medications that restore platelet function.
Many patients are concerned about the question of why blood is liquid. There are several reasons. Only after examining the patient can this question be answered. The entire process of research and treatment of the patient must be supervised by a doctor. Medicines should be taken only as prescribed.
During treatment, it is important to take medications that contain iron. Thanks to this substance, you can replenish the volume of lost blood. If not treated promptly, anemia may occur.
As a result, the patient experiences lethargy, headaches and respiratory problems. Blood transfusions are performed in emergency situations.
To avoid complications, it is important to choose the right type of blood to be transfused.
Which medicine is effective?
The causes of thin blood in women and men can be very diverse - from genetic predisposition to a serious illness that provoked a decrease in protein in the blood. The doctor prescribes specific medications depending on the individual characteristics of each patient. It is important to take into account the general state of health, the presence of other pathologies and the person’s age.
Note to patients
Self-medication is prohibited, since this is a very serious pathology that directly affects the patient’s life expectancy. To avoid serious complications, it is important to immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment.
A minor injury can lead to death (this is the whole danger of the disease). Traditional methods of therapy are not recommended to be used without consulting a doctor, as this can lead to the death of the patient.
The cause of thin blood in a child will be determined by the pediatrician after a thorough examination of the patient.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/419354/jidkaya-krov-prichinyi-simptomyi-diagnostika-opasnost-dlya-zdorovya-lechenie
What diagnostics
The cause of the appearance of light blood during menstruation can only be determined through comprehensive diagnostics. The patient is referred to:
- Ultrasound for a general examination of the reproductive organs;
- blood test to assess hormonal levels;
- colposcopy to identify possible malignant processes;
- a vaginal smear to confirm or refute a probable infectious process;
- histology for scraping.
If necessary, other examinations may be prescribed, but only based on individual characteristics.
What treatment
Treatment is also chosen privately. Self-medication is prohibited. Depending on the main diagnosis, the girl may be recommended:
- hormonal medications;
- antibiotics;
- antifungal medicine;
- surgical intervention;
Treatment is often done with antibiotics
- radiation or chemical therapy.
Regardless of the reason, a girl should lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right. Any bad habits should be eliminated.
What kind of prevention
As a preventive measure it is recommended:
- maintain personal hygiene;
- use contraception when having sex with an untested partner;
- Healthy food;
- avoid severe stress and hypothermia, as well as excessive physical activity;
- give up bad habits;
- take any medications only in consultation with your doctor;
- Visit a gynecologist annually for preventative care.
The recommendations listed above help to avoid many problems that lead to disturbances in the cycle and nature of discharge.
>