The risk of complications after an abortion depends on:
- duration of pregnancy (the longer the period, the more likely complications are);
- from the professionalism of the doctor;
- from the patient’s initial condition;
- on the thoroughness of the examination before this manipulation;
- on the number of previous abortions;
- sometimes, from a trivial case, etc.
There are two types of complications: early , which develop during or immediately after surgery, and late , which can appear after some time, even after 2-3 years.
Abortion
Abortion is the artificial termination of pregnancy. Typically, such an interruption is performed no later than 22 weeks, but very rarely, for medical reasons, it can be performed later. Depending on the stage of pregnancy, different methods are used.
- Mini-abortion or vacuum. It is prescribed before 6 weeks and looks like removing the fetus using a special device - a vacuum suction.
- Medical abortion can be performed up to 7 weeks of gestation. In this case, the patient is prescribed medications such as Pencrofton, Mifepristone and others. They provoke miscarriage.
- Surgical abortion is performed from 4 to 22 weeks of pregnancy. And if there are medical conditions and later than this period, surgical removal of the fetus is performed. The doctor performs a curettage of the uterus, during which the fetus is removed.
All abortions, regardless of the chosen technique, have a significant impact on the female reproductive system and on the entire body as a whole. Only the influence varies. With vacuum and medical abortions, there is a risk of incomplete removal of the fertilized egg, which leads to the need for curettage.
Also, all types of abortions have a great impact on hormonal balance. After all, a woman’s body has already adjusted to bearing a child and makes the corresponding hormonal changes.
It should be noted that the most serious consequences can occur after a surgical abortion; vacuum and medicinal abortions are easier to tolerate in this regard. The fact is that when curettage, you can damage the uterus with surgical instruments.
But all the consequences of an abortion can be minimized if you select a method taking into account the timing.
Post-abortion endometritis
One of the common causes of infection entering the uterus is traumatic intervention to terminate a pregnancy.
Endometritis after abortion can become the basis for focal or diffuse damage to the uterine mucosa, which damages the deep layers of the endometrium.
The main negative factor of post-abortion complications is the uterine variant of infertility, so you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations for the treatment and prevention of uterine inflammation.
Termination of pregnancy: surgical options
Abortion is one of the most common surgical operations in gynecology. A woman can terminate an unwanted pregnancy in the 1st trimester (up to 12 weeks) in a medical facility in the following ways:
- medical “velvet” abortion, in which in the early stages (up to 5 weeks) you need to take hormonal pills according to a special regimen prescribed by your doctor;
- vacuum aspiration (use of suction to remove the embryo up to 6 weeks);
- curettage of the uterus to remove pregnancy, used in all cases of termination of pregnancy between 6 and 14 weeks (artificial or spontaneous abortion);
- late termination of pregnancy for medical reasons (congenital pathology of the fetus or diseases of the mother, in which, during pregnancy, a real threat to the woman’s life arises).
The lowest risk of post-abortion endometritis is after a velvet abortion. The highest danger is after complicated curettage of the uterine cavity, when as a result of the operation it was not possible to completely remove all structures and tissues associated with pregnancy.
Causal factors of post-abortion inflammation
An inflammatory process in the uterine cavity after an induced abortion almost always occurs, but in most cases, against the background of preventive treatment, the classic manifestations of the disease can be avoided. The main causative factors of endometritis are:
- traumatic damage to all layers of the endometrium during curettage;
- retention of parts of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity;
- accumulation of blood clots;
- penetration of microbes from the vagina and cervical canal.
The combination of all these factors leads to the formation of inflammation: for microorganisms, the remains of the fertilized egg and blood clots are an excellent nutrient medium on which dangerous microbes quickly grow and multiply, forming a rapidly progressing infectious process.
Contributing factors to post-abortion endometritis include:
- gynecological infections (vulvitis, bartholinitis, colpitis, cervicitis, bacterial vaginosis);
- weakened immune defense;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- blood loss during surgery;
- general diseases (anemia, chronic foci of infection, endocrine pathology).
An extremely negative type of post-abortion complication is the remains of fetal tissue, in which it is necessary to perform repeated curettage of the uterus. Double trauma is the main factor leading to damage to the basal layer of the endometrium and the formation of recurrent chronic endometritis.
Options for post-abortion inflammation
The inflammatory process in the uterus after termination of pregnancy can manifest itself as acute symptoms in the first days after surgery or cause a delayed reaction that occurs only a few days later. Depending on the time factor and severity of manifestations, the following are distinguished:
- classic version of post-abortion endometritis;
- abortive form;
- erased type of inflammation.
Vivid classic manifestations occur in cases where there are remnants of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. Most often, a low-symptomatic, erased variant occurs, in which the risk of developing chronic endometritis is maximum.
Typical symptoms of the disease
The classic form of post-abortion endometritis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- high temperature with wave-like chills;
- cardiopalmus;
- abdominal pain (from pressing to cramping);
- purulent-bloody vaginal discharge.
All symptoms occur 1–3 days after the abortion and last for at least 10 days. It is extremely important to consult a doctor promptly when typical symptoms appear in order to begin treatment and prevent the possibility of dangerous complications.
The abortive version of endometritis manifests itself with standard symptoms, but all symptoms subside by 4–5 days of the post-abortion period. This type of complication is rare, but may be a reason to refuse a full course of antibacterial treatment.
The erased form is characterized by the following features:
- the increase in body temperature does not exceed 38 °C;
- pain in the lower abdomen is insignificant;
- bloody-purulent vaginal discharge is scanty.
A woman may ignore scanty or minimal manifestations of the disease without consulting a doctor, which will be the main reason for the development of post-abortion endometritis.
Basic principles of diagnosis
During a gynecological examination, the doctor will immediately pay attention to the following signs of endometritis:
- increase in the size of the uterus;
- softness and shapelessness of the organ when manually palpated;
- pain on palpation;
- unpleasant-looking bloody-purulent discharge.
To confirm a preliminary diagnosis, the following studies must be performed:
- undergo general clinical tests (there will be signs of inflammation in the blood - high white blood cells, accelerated ESR);
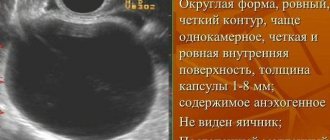
- do an ultrasound (during the scan, a specialist will see the remains of the fertilized egg, blood clots and signs of acute inflammation in the uterine cavity).
Having made an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will immediately prescribe effective treatment. If indicated, surgical intervention may be required.
Treatment tactics
Post-abortion endometritis should be treated in a hospital setting under the constant supervision of a doctor. The main therapeutic factor is antibacterial therapy using broad-spectrum drugs. But antimicrobial drugs will not help if there are remains of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. Indications for repeated surgery are:
- any amount of remnants of decidual tissue and parts of the embryo (incomplete abortion);
- pronounced accumulation of blood clots.
It is strictly unacceptable to perform repeated curettage without indications. Complete anesthesia (intravenous anesthesia) and all necessary therapeutic measures during the operation (intravenous administration of antibiotics and solutions to eliminate intoxication) are mandatory.
If there are no embryo remains in the uterus, in addition to antibiotics, the following types of treatment must be used:
- medicines to contract the uterine muscle;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- medicines to reduce fever;
- restorative and sedatives.
With the correct selection of antibacterial therapy, you can cope with the infection in 5–7 days. An important condition for successful treatment is the continuation of all therapeutic measures even after all symptoms disappear.
Prevention of post-abortion endometritis
It is optimal to avoid complications after curettage of the uterine cavity. To do this, you must follow the following recommendations:
- refusal of artificial termination of pregnancy;
- mandatory treatment of all infectious and inflammatory diseases in the body;
- local therapy of colpitis and cervicitis;
- mandatory use of post-abortion medications recommended by a doctor;
- selection of contraception to prevent unwanted pregnancies.
Post-abortion endometritis is one of the common complications after artificial or spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
When a woman has no opportunity to continue bearing the fetus, she should try to terminate the pregnancy as early as possible: there will be a minimum of complications after a medical abortion.
The highest risk of complications and endometritis occurs during surgery at 10–12 weeks. Optimal prevention of abortion is the use of effective methods of protection against unwanted pregnancy.
Source: https://gynecologyhelp.ru/endometrit/posle-aborta.html
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease in which the inner layer of the uterus grows beyond its normal location. The endometrium can grow both in the uterus itself, for example, in the muscular layer or cervix, and outside it (tubes, ovaries, and so on). Less common is endometriosis of organs that are not part of the reproductive system: intestines, kidneys, bladder.
For endometriosis to appear, several factors must coincide. Firstly, an imbalance of sex hormones, which will serve as an impetus for the pathological proliferation of endometrial cells. Secondly, insufficient functioning of the immune system, which normally should suppress such growth and prevent the endometrium from securing itself in places unusual for it. And, thirdly, the influence of various risk factors, such as heredity, inflammatory processes and various interventions in the integrity of the uterus, including abortions, is important.
Once the endometrial tissue has established itself in its new location, it begins to function in the same way as it did inside the uterus. That is, all phases of the menstrual cycle are observed, including endometrial rejection during the onset of menstruation. But since pathological foci of endometriosis often have nowhere to reject cells that have passed through the cycle, an inflammatory process can occur in this place.
Endometriosis is accompanied by symptoms such as pain in the lower abdomen, usually approximately where the source of the disease is located. These pains usually get worse during menstruation. Various menstrual irregularities may also be present. Usually the abundance and duration increase, the cyclicity changes and spotting appears in the middle of the cycle. But sometimes the disease may not manifest itself for a long time.
Abortion as a cause of endometriosis
Vacuum and medical abortions are not so often the cause of endometriosis, since they do not disrupt the integrity of all layers of the uterus so much. But if during these abortions the fetus was not completely removed and curettage is required, then the likelihood of developing endometriosis increases.
During a surgical abortion, the mucous layer that lines the inner surface of the uterus is removed. This is the endometrium. At the same time, during manipulations, the deeper layers of the uterus can be damaged, which will cause the appearance of scars and adhesions.
And if the surface of the uterus is heterogeneous due to such scars, then the subsequent growth of the endometrium will occur unevenly. Because of this, the nature of the menstrual cycle often changes, and prerequisites for the development of various diseases of the reproductive system appear.
Also, a strong hormonal imbalance, which is present after all methods of abortion, including after vacuum and medication, provokes disturbances in the functioning of the ovaries. Their dysfunction develops, which can cause endometriosis.
Quite often, abortion is the cause of the development of vaginal endometriosis. As a rule, pathological lesions are located on the posterior wall of the vagina. At the same time, the woman feels pain in the lower abdomen, which only progresses over time. Patients often come complaining of pain during sexual intercourse.
Abortion is also often caused by cervical endometriosis. In this case, the woman does not experience any pain symptoms, and the only sign by which this disease can be noticed is spotting 4–8 days before the onset of menstruation.
Condition of the cervix after abortion
In addition to the fact that termination of pregnancy is a severe psychological trauma for a woman, especially when the operation is performed in the later stages, damage to the cervix may also occur after an abortion, which leads to endocervicitis.
A healthy woman has a mucus plug in the cervical canal that protects the genitals from infection. During an abortion, the chemical composition of the vaginal environment is disrupted, due to which the mucous plug is destroyed, and the infection penetrates into the cervical canal, and then into the uterus itself.
Inflammation of the cervix after an abortion is the impetus for the development of infertility; it is accompanied by various symptoms, including aching and nagging pain in the abdomen, itching in the genital area, abundant or scanty mucous membranes, mucopurulent or purulent discharge.
Prevention of endometriosis
To prevent endometriosis from developing after an abortion, it is necessary to take some preventive measures.
The simplest thing you can do is ask your gynecologist to recommend medications to improve the functioning of the immune system. After all, if the immune system works as necessary, it simply will not allow the endometrial tissue to gain a foothold outside the inner layer of the uterus.
Also, to prevent many complications, including endometriosis, after an abortion, you can use hormone therapy. Most often, oral hormonal contraceptives are used for this. Some women believe that it is not necessary to see a doctor to prescribe these drugs and that they can buy them themselves. But in this case, you can harm yourself even more, because you cannot independently understand how the hormonal levels have changed after an abortion and which sex hormones predominate and which are lacking.
About modern drugs for the treatment of endometriosis >>
You should avoid having sex for some time after an abortion. Firstly, because the entire inner surface of the uterus is one large wound into which infection can easily occur. And inflammatory processes can trigger the appearance of endometriosis. Also, if the penis is large enough and reaches the cervix during penetration, then this part of the organ can be injured and also provoke the development of endometriosis.
It is very important to prevent another pregnancy during the first six months after an abortion. Since both carrying a child and repeated abortion are very dangerous for the female body and can provoke many complications.