Early miscarriage: is cleaning necessary?
Planning a pregnancy and the birth of a child does not always end favorably.
Sometimes a woman has to experience a miscarriage for various reasons. Cleaning after a miscarriage is an unpleasant but necessary procedure that can rarely be avoided. Some believe that the consequences of curettage will be more disastrous than the miscarriage itself, and are afraid of curettage (removal of the upper mucous layer). However, in most cases this cannot be avoided.
Treatment
Recovery after a frozen pregnancy also involves taking certain medications. They are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician. The list includes medications that relieve pain and antibiotics to reduce the likelihood of inflammation. To increase the muscle tone of the uterus and enhance its contractility, oxytocin is prescribed. Physiotherapy may also be prescribed to speed up the rehabilitation period.
Basically, the freezing of the development process occurs due to random genetic disorders in the fetus, so the risk of recurrence of a similar situation is low. But to confirm a woman’s ability to bear and give birth to a child after a frozen pregnancy and prescribed therapy, it is necessary to undergo an examination, including:
- Ultrasound;
- analysis for the presence of various infections;
- blood and urine tests.
But there is a risk of repeated death of the embryo in the mother’s womb. When a woman experiences a repeat miscarriage, the above list is expanded with the following points:
- hormonal balance study;
- conducting a spermogram of the partner;
- examination of the fetus for pathologies of histology and genetics;
- carrying out bacterioscopy;
- preparation of an immunogram, coagulogram;
- carrying out analysis for hidden infections.
Karyotyping of partners is also carried out. The listed studies will allow us to diagnose the causes of fetal development arrest and identify ways to eliminate them. With proper and timely treatment, a woman will be able to carry and give birth to a baby.
It is worth considering that such a complication as infertility occurs only in rare cases: when the operation is performed incorrectly, or the woman refuses to follow the doctor’s prescription.
With normal rehabilitation, pregnancy after cleaning can occur within 1 month. If a woman does not plan to become a mother in the near future, she should consult her doctor to select the optimal means of contraception.
My mother had her period for 8 days last month, this month for 2 days and heavy bleeding began. She said that they had done a cleansing, it was pregnancy and how long do they usually stay in bed after a cleansing?
Curettage procedure after miscarriage
The manipulation takes 15–20 minutes. A preliminary referral is given for a coagulogram and general blood tests, testing for infections. Cleaning after an early miscarriage (up to 12 weeks) is carried out if, according to ultrasound, fragments of the fertilized egg are detected in the uterus.
You should not take food or liquid 8–10 hours before surgery. The curettage procedure takes place on a gynecological chair: the genitals are disinfected with an antiseptic, the cervix is dilated and the mucous layer is scraped out with a vacuum or curette. These manipulations are quite painful and are performed under anesthesia - local or general. If possible, hysteroscopy (examination with a video camera) is performed simultaneously with curettage: curettage after a miscarriage is considered the least dangerous when the doctor sees the uterine cavity.
If there is an early miscarriage, the embryo may come out entirely (it looks like a gray round bubble), then cleaning is not required. In other cases, fragments of the fetus will begin to decompose, which will give rise to the spread of pathogenic microbes and damage to the lining of the uterus. Therefore, even if a miscarriage occurs outside a medical facility, and the woman is sure that the embryo has been released completely, you should not neglect a visit to the doctor.
Carrying out the procedure
Before carrying out cleansing during a frozen pregnancy, it is mandatory to undergo a general clinical examination, including tests and research:
- determination of blood group;
- diagnosis of syphilitic infection;
- general and biochemical blood and urine tests;
- Rh factor diagnosis;
- examination of the cervix, smear;
- urethral smear.
An electrocardiogram is also performed as part of the examination. Such a diagnosis is necessary to eliminate the risk of genital diseases and other contraindications to surgical intervention. Then the woman removes all hair from the intimate area and washes thoroughly.
Before performing curettage of the uterine cavity when the development of the fetus has stopped, it is necessary to avoid eating foods that contribute to the active formation of gases in the gastrointestinal tract. Also, the final consumption of food should be no later than 6 hours before surgery, since it is carried out on an empty stomach. If urgent curettage is indicated, gastric lavage is performed before the procedure.
Before surgery to remove the remaining fertilized egg, it is necessary to prepare the cervix. This is mandatory, especially for nulliparous women, and is necessary to dilate the cervix and reduce the likelihood of damage to it.
Preparation is carried out by introducing kelp into the cervical canal. Algae gradually absorb vaginal secretions, swell, and expand the canal. This is done on the eve of the operation. Also, before the procedure, you should consult an anesthesiologist or obstetrician-gynecologist.
After the preparatory stage is completed, an operation is scheduled, which is performed under general anesthesia. The woman sits on a gynecological chair. Before the procedure, the gynecologist must conduct an examination. It's necessary:
- to determine the location of the uterus;
- assessment of the size characteristics of the uterus;
- disinfection of genital organs.
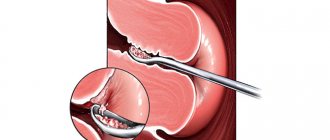
Then anesthesia is administered and the cervical canal is expanded using an expander. Curettage is performed using a curette. The gynecologist removes the contents of the reproductive organ, capturing the upper layer of the endometrium. During the operation, the doctor uses substances that cause contractions of the uterus.
The duration of the described procedure is 15 minutes.
Vacuum aspiration for a frozen pregnancy is considered a more modern method of curettage, so we recommend studying the information about its implementation in more detail.
Cleaning after early miscarriage
Pregnancy interrupted immediately - at 5-8 weeks - is not uncommon. The doctor must find out the cause and inspect the uterus so that the infection does not penetrate the genital tract. In the early stages, spontaneous miscarriage can occur without cleaning.
If, after an unexpected termination of pregnancy, the fertilized egg is expelled entirely, there is no need to curettage the uterus. The specialist makes a decision based on the results of tests and ultrasound. Inspection of the uterus is also carried out during a frozen pregnancy.
The mucous membrane is scraped out for the purpose of prevention in case of bleeding, accumulation of blood clots, so as not to leave pieces of the fertilized egg.
If necessary, curettage of the upper layer of the mucous membrane of the uterus and its cervix is performed. Samples are sent for histology to determine the cause of the miscarriage.
Consequences of cleaning after a miscarriage
Like any intervention, cleaning the uterus during a miscarriage is not always without complications. If there are problems with blood clotting, uterine bleeding may occur. To stop it, oxytocin injections are prescribed.
Abdominal pain and fever are signs of an ongoing inflammatory process. Due to spasms of the cervical canal during curettage, blood clots may accumulate in the uterus.
A circulation disorder is called a hematometra. Accumulating in the uterine cavity, blood cannot escape, causing painful attacks. If you ignore this diagnosis, you may subsequently lose your uterus and the possibility of childbearing.
A complication of hematometra is blood poisoning, which can be fatal. Doctors prescribe medication and special procedures to remove accumulated blood from the uterus as therapeutic methods.
After cleansing as a result of spontaneous abortion, complications may appear in the form of endometritis, in which the mucous membrane becomes inflamed. Therefore, a course of antibiotics is necessarily prescribed, which is important to complete according to the regimen.
Vacuum cleaning of the uterus after a miscarriage is the most effective and safest method of curettage. But in some cases problems may arise:
- Not completely removed embryo. The doctor often has to manipulate blindly, so there may be remains of the fetus in the uterus.
- Mechanical damage to the cervical canal with instruments, which occurs when the uterus dilates. Possible consequences are miscarriage of the next pregnancy.
- Bleeding caused by damage to existing fibroids or blood vessels. In some cases, the uterus has to be removed.
- Infection that occurs when hygiene recommendations are not followed due to the fault of a woman or a doctor. Leads to infertility and inflammation.
- Weakness of the cervix. During surgery, the cervical canal may weaken and subsequently lead to miscarriages.
Do not delay going to the hospital if the following signs appear:
- temperature;
- intense bleeding;
- absolute absence of discharge;
- stomach ache.
Why is curettage performed?
Curettage is carried out for two purposes: to obtain material
(scraping of the mucous membrane) for histological examination - this allows for a final diagnosis; the second goal is to remove the pathological formation in the uterine cavity or cervical canal.
Diagnostic purpose of curettage
- If a woman’s ultrasound shows changes in the mucous membrane, ultrasound does not always allow an accurate diagnosis; most often we see signs indicating the presence of a pathological process. Sometimes ultrasound is performed several times (before and after menstruation). This is necessary in order to be sure that the pathological formation actually exists and is not just a variant of the structure of the mucous membrane only in this cycle (an artifact). If the formation that was found remains after menstruation (that is, rejection of the mucous membrane), then it is a true pathological formation, it has not been rejected along with the endometrium, curettage should be performed.
- If a woman has heavy, prolonged menstruation with clots, intermenstrual bleeding, pregnancy and other, rarer conditions do not occur for a long time, and according to ultrasound and other research methods it is not possible to establish the cause
- If there are suspicious changes on the cervix, a diagnostic curettage of the cervical canal is performed
- Before a planned gynecological operation
or procedure for uterine fibroids, in which the uterus will be preserved.
Therapeutic purpose of curettage
- Mucosal polyps (polyp-like growths of the uterine mucosa) - there is no other type of treatment, they do not disappear with medication or on their own (there will be a separate article on the site)
- The hyperplastic process of the endometrium (hyperplasia) - excessive thickening of the uterine mucosa - is treated and diagnosed only by curettage, followed by drug therapy or instrumental methods (there will be a separate article on the site)
- Uterine bleeding – the cause may not be known. Curettage is performed to stop bleeding.
- Endometritis is an inflammation of the uterine mucosa. For complete treatment, the mucous membrane is first scraped off.
- Remains of membranes and embryonic tissues - treatment of complications after abortion
- Synechia - fusion of the walls of the uterine cavity - is performed using a hysteroscope and special manipulators. Under visual control, adhesions are dissected
How to prepare for curettage?
If curettage is not performed for emergency reasons (as, for example, during uterine bleeding), but as planned, the operation is performed before menstruation, a few days before its onset. This is necessary so that the curettage process itself practically coincides in terms of the physiological period of rejection of the uterine mucosa (endometrium). If you plan to undergo hysteroscopy with removal of a polyp, the operation, on the contrary, is performed immediately after menstruation so that the endometrium is thin and the location of the polyp can be accurately seen.
If curettage is carried out in the middle of the cycle or at the beginning, this can lead to prolonged bleeding in the postoperative period. This is due to the fact that the mucous membrane of the uterus grows synchronously with the growth of follicles in the ovaries - if the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity is removed significantly before the onset of menstruation, the hormonal background created by the ovaries will “come into conflict” with the absence of the mucous membrane and will not allow it to fully grow . This condition is normalized only after synchronization between the ovaries and the mucous membrane occurs again.
It would be logical to propose curettage during menstruation, so that the natural rejection of the mucous membrane coincides with the instrumental one. However, they do not do this, because the resulting scraping will not be informative, since the rejected mucous membrane has undergone necrotic changes.
Tests before curettage (basic set):
- General blood analysis
- Coagulogram (assessment of the blood coagulation system)
- ECG
- Tests for hepatitis B and C, RW (syphilis) and HIV
- Vaginal smear (there should be no signs of inflammation)
On the day of curettage, you need to come on an empty stomach, the hair in the perineum should be removed. You bring a robe, long T-shirt, socks, slippers and pads.
Menstruation after curettage
Menstruation after curettage of the uterine cavity usually begins on time, that is, after 26–29 days. To normalize the cycle and prevent pregnancy, the doctor may prescribe birth control pills on the day of cleansing or the next.
Discharge during menstruation is usually scant because the endometrium has not yet recovered.
If heavy bleeding occurs, it can be predicted that when eliminating hyperplasia, not all of the endometrium was removed. The results of an ultrasound examination help confirm the doctor’s guess. Secondary cleaning is not prescribed, but helps reduce blood loss.
A pathology is considered to be vaginal discharge that lasts too long (10 days or more) and has an unpleasant odor, which may indicate the onset of an infectious process. An abrupt cessation of discharge, which is a sign of the formation of blood clots in the uterus, should also alert you.
What is scraped out (a little anatomy)?
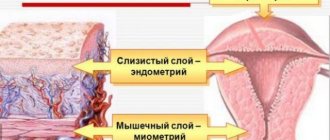
The uterus is a muscular organ shaped like a “pear”, in which there is a cavity that communicates with the external environment through the cervix, which is located in the vagina. The uterine cavity is the place where the fetus develops during pregnancy. The uterine cavity is lined with mucous membrane (endometrium). The endometrium differs from other mucous membranes (for example, in the oral cavity or in the stomach) in that it is capable of attaching a fertilized egg to itself and giving rise to the development of pregnancy.
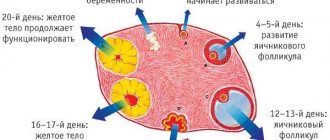
During the entire menstrual cycle, the lining of the uterus (endometrium) thickens, various changes occur in it, and if pregnancy does not occur, it is rejected in the form of menstruation and begins to grow again in the next cycle.
During curettage, it is the mucous membrane of the uterus - the endometrium - that is removed, but not the entire mucous membrane is removed, but only the superficial (functional layer). After curettage, a germinal layer of the endometrium remains in the uterine cavity, from which a new mucous membrane will grow.
For example, every autumn a rose bush is cut at the root and in the spring a new rose bush grows from this root. In fact, curettage is similar to regular menstruation, only performed with an instrument. Why this is done - read below.
During this operation, the cervical canal (the place where the entrance to the uterus is located) is also scraped. This is where the curettage procedure usually begins - the mucous membrane that lines this canal also down to the germ layer is scraped off. The resulting scraping is sent for examination separately.
Explanation of names
Scraping
- this is the main action during manipulation, but the manipulation itself can have different names.
Russian Far East
– separate diagnostic (sometimes an addition: therapeutic and diagnostic) curettage of the uterine cavity. The essence of this name: will be fulfilled
- separate
(first curettage of the cervical canal, then the uterine cavity) - treated-diagnostic
- the resulting scraping will be sent for histological examination, which will allow an accurate diagnosis to be made, “treated” - since in the process of curettage the formation (polyp, hyperplasia) for which it was prescribed is usually removed. - curettage
- description of the process.
RDV+ GS
– separate diagnostic curettage under hysteroscopy control is a modern modification of curettage. Conventional curettage is performed virtually blindly. When using hysteroscopy (“hystero” - uterus; scopia - “look”) - the doctor inserts a device into the uterine cavity with which he examines all the walls of the uterine cavity, detects the presence of pathological formations, then performs curettage and finally checks his work. Hysteroscopy allows you to evaluate how well the curettage was performed and whether there are any pathological formations left.
Subsequent pregnancy
Gynecologists advise abstaining from pregnancy after cleansing for at least six months. A body that has not recovered from surgery is not ready to bear a child. To prevent the development of complications, antibiotics and oral contraceptives are prescribed, medical supervision and testing are offered.
Sexual rest should continue for at least three weeks after cleaning to prevent infection and bleeding. It is necessary to limit physical activity, alcohol consumption, refuse to visit baths and saunas, and take a bath (shower only).
Physiotherapeutic procedures are recommended:
- EHF (for the prevention of endometritis);
- ultrasound (from adhesions);
- phototherapy (for anti-inflammatory purposes).
To speed up healing, doctors use sorption treatment: a composite solution is injected into the uterine cavity. The regeneration process is monitored by taking an aspiration biopsy.
Pain in the lower abdomen indicates the presence of disturbances as a result of curettage. If mild discomfort is observed, this is normal, do not worry; in a couple of days, in the absence of other negative signs, it will pass.
Severe pain should cause alarm, the causes of which are a tear in the cervix or a puncture of an organ, an inflammatory process, or accumulation of blood. After eliminating all negative factors, the doctor allows you to plan a new pregnancy.
Recovery after the procedure
The rehabilitation period depends on the reason for the surgery. May last for 6-12 months. All this time, it is recommended to pay increased attention to your health and the changes occurring in the body. The patient should be warned about bloody discharge that persists for 10 days and nagging pain in the lower abdomen, similar to menstruation. With a faster disappearance of these signs, a suspicion arises about adhesions in the cervix and the accumulation of blood clots in it. These symptoms are a reason to immediately consult a doctor. For 2 weeks prohibited:
p, blockquote 21,0,0,0,0 —>
- Having sex.
- Use of sanitary tampons, only regular pads are allowed.
- Taking medications containing acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin).
- Intense physical activity.
- Visiting the bathhouse, sauna, showers are allowed.
- Performing the douching procedure.
It is recommended to inform your doctor if you are concerned about:
p, blockquote 22,0,0,1,0 —>
- Pain in the abdomen that does not go away after taking analgesics.
- The cessation of discharge or the appearance of unpleasant-smelling vaginal secretions.
- Fever (from 38 °C).
- Heavy bleeding.
- Weakness, dizziness, loss of consciousness.
A week after cleaning, the patient receives histology results, based on which the doctor develops tactics for further action. At the end of the rehabilitation period, sexual activity resumes.
p, blockquote 23,0,0,0,0 —>
Recovery
In order to quickly return to normal after a harmless cleansing process, you should strictly follow the doctor’s instructions, adhere to a healthy lifestyle, maintain hygiene, do not overwork, get proper rest and eat right. In this case, recovery after curettage will be much easier.
After a miscarriage, some women become depressed. The right decision would be to see a psychotherapist.
To plan a new pregnancy, you need to fully restore your health after cleansing, make sure that all indicators (urine, blood) are normal and there are no infections. The uterus, ovaries and cervix must be ready for conception and gestation. Such conditions will guarantee the birth of a healthy baby.
Medical abortion: description of the procedure, consequences, recovery
Medical abortion is the termination of pregnancy using medications, without gynecological intervention. It is carried out at the request of the woman, for a fee, according to the accepted scheme and only in clinics licensed to carry out this procedure. There are quite a lot of these in Russia now.
When is the procedure possible?
The period until which a medical abortion is performed is described in official medical documents - this is 6 weeks in Russia. Moreover, the period is calculated from the first day of the last menstruation.
Recommendations after uterine curettage
The period after curettage of the uterine cavity requires a special approach on the part of the doctor and responsible implementation of all recommendations on the part of the patient. The reproductive and physical capabilities of the female body are not limitless, therefore, an important task of the gynecologist who has performed uterine cleansing is considered to be complete, careful observation and provision of a protective regime.
In the period after cleansing the uterus, experts identify three main areas of work for complete rehabilitation:
- Prevention of infections.
- Restoration of the endometrium and menstrual cycle.
- Restoring physical and mental health.
To achieve these goals, gynecologists give recommendations in terms of taking antibacterial drugs, oral contraceptives, limiting physical activity, maintaining sexual rest and performing general strengthening measures.
How you feel after cleaning
Not everyone is able to quickly get into the usual rhythm of life, resume sports and exercise. Recovery time largely depends on the individual characteristics of the body.
After curettage, moderate abdominal pain, mild anesthesia-related dizziness, and moderate bleeding are usually noted.
Restoration of the uterus after curettage, both therapeutic and diagnostic, lasts one menstrual cycle, the whole body - from 2 to 6 months.
General health after curettage:
- Body temperature up to 37.2-37.3 is considered normal in the first 2-3 days.
- Moderate abdominal pain lasts up to 7 days.
- Slight dizziness is acceptable.
Curettage of the uterine cavity: how long to stay in the hospital
Abortion according to indications or voluntary with the help of medications is a simple option for ridding the uterus of fertilized remains. A woman is initially given one tablet, and a day later another; the uterus independently pushes everything that is in it, along with the blood, out. A woman experiences her usual menstruation.
Depending on the stage of the frozen pregnancy at which the operation was performed, the condition of the uterus will differ. So, in the early stages (up to 6 weeks), the size of the uterus is not greatly increased, which means the recovery process does not take more than one month.
The lower part of the uterus is the cervix. This is a thin tube two to three centimeters long that connects the organ cavity and the vagina and in which the cervical canal is located.
However, it is always necessary to initially free the uterus from a frozen pregnancy and only then carry out restoration procedures.
The inconsistency of the topic with the chosen community (buying, selling, renting, looking for a vacation spot, family problems, non-gynecological diseases, politics, etc.) is unacceptable.
I did it in a paid clinic. They cleaned it up, after I recovered from the anesthesia, I went home. I was prescribed doxycycline for 5 days.
Curettage of the walls of the uterine cavity is performed in case of uterine bleeding, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, suspicion of a hyperplastic process or a malignant tumor of the endometrium, incomplete abortion, placental polyp after an abortion or childbirth.
If you have been prescribed a cleaning for diagnostic purposes, you should refuse the procedure if there are alternative ways to establish a diagnosis.
Now let’s take a closer look at how long they stay in the hospital after curettage. Depending on the type of cleaning, the length of stay in the hospital differs. If you agree to scraping for diagnosis, you can go home the same day. Intravenous anesthesia, which is used for this type of operation, lasts 30-40 minutes. For some time after the operation, weakness, nausea, dizziness and loss of coordination are observed. This goes away after 2-3 hours, and immediately after talking with your doctor, you can go home. How long they stay in the hospital after cleansing a missed pregnancy or removing pathological tumors in the uterine cavity is determined by the doctor. Such an intervention requires monitoring the patient’s condition, and she is allowed to go home only after 3–7 days. After curettage, bleeding and inflammation are possible, and you should not rush home until the doctor says that everything is fine. The attending physician should give recommendations on how best to recover after curettage of the uterine cavity. These recommendations are based on the patient's diagnosis. Rehabilitation after curettage takes from 2 months to a year, and during this time you should especially carefully monitor your health. Within two weeks after curettage you cannot:
- Have sex;
- Use tampons;
- Do douching;
- Hot shower/bath/sauna, etc. are contraindicated;
- Blood thinners (such as aspirin);
- Sports and heavy physical activity are prohibited.
It is undesirable to cleanse in parallel with the onset of menstruation due to the low information content of such research results.
But neither histology nor ultrasound can confirm such a diagnosis as chronic endometritis. The reference point is the level of leukocytes in the blood. Although only the immunohistochemistry method has high reliability.
For the first 5 days after the procedure, a woman may feel pain in the vagina and may be bothered by pain in the lower abdomen.
I started bleeding before the new year. She treated me with injections and pills. On January 10, they gave me another course of treatment, they said this was the last attempt, if it doesn’t help, curettage would be the only option. It didn't help, it got worse. But it’s not the placenta that remains, it’s just a hormonal imbalance and bleeding has started.
How dangerous is the period after the procedure?
The uterine cavity after cleaning is an extensive wound surface.
The lion's share of recommendations after curettage will be aimed at preventing microorganisms from entering the cavity of the operated organ. Gynecologists are aimed at preventing the development of inflammation of the reproductive organs and its chronicity. Experts identify two groups of risk factors for the development of infectious complications after uterine curettage:
- Main group. This category includes women with a history of endometritis, chronic recurrent chlamydia, urea and mycoplasmosis, candidiasis, human papillomavirus infection, and persistent vaginal dysbiosis. In such patients, the likelihood of developing purulent-inflammatory diseases in the gynecological area during curettage is most likely. Patients are subject to the closest attention from doctors. This also includes emergency cases of curettage.
- Additional group. Patients who had uterine cleansing due to bleeding (endometrial hyperplasia), miscarriage, curettage of placenta or ovum remnants have a lower risk of infectious complications compared to the main group.
Women who have undergone diagnostic curettage have the lowest risk of developing infectious complications. Typically, this type of study is carried out in cases of infertility of unknown origin, in preparation for IVF, suspected polyps and subserous fibroids, and menstrual irregularities.
Factors that indirectly influence the period after curettage:
The above diseases have an indirect effect on the course of the recovery period of curettage, but their presence significantly reduces physical strength, the body's resistance to infections and slows down the healing processes of the wound surface in the uterus after curettage.
The causative factor of the disease is the opportunistic vaginal flora (staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli), as well as representatives of the pathogenic flora, if the patient before the operation had untreated sexually transmitted infections - chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, gardnerellosis and others. That is why, in the period after therapeutic curettage, gynecologists recommend taking antibacterial drugs without fail, regardless of the infectious history. After diagnostic cleaning, you can limit yourself to taking sulfonamides.
According to statistics, the incidence of endometritis after uterine cleansing is 20%.
Purulent-inflammatory diseases of the genital area do not always appear after curettage due to non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations. Nosocomial infection is still relevant today. A woman should choose modern clinics with rich obstetric and gynecological experience.
Poor quality cleaning can result from the penetration of endometrial cells into the cervical tissue, which leads to endometriosis.
Complications
When curettage of fetal remains there is a possibility of complications. Such an operation can provoke the following consequences:
- Surgical manipulations can result in rupture of the uterine walls. The cause of this complication is mainly defects in the uterine cavity.
- After completion of the procedure or after a short period of time, there is a possibility of bleeding. This complication occurs against the background of weak uterine contractions. It is worth considering that excessive bleeding can cause anemia, so if such a problem occurs, you should urgently seek help from a doctor.
- Since the uterine mucosa after surgery is a wound, you can notice the appearance of an inflammatory process on it - endometritis. This pathology can be recognized by the following symptoms: pain in the lower abdomen, increased body temperature, weak uterine contractions, copious vaginal discharge, accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
- Since curettage is carried out blindly, remnants of the membranes may remain in the uterus. The problem can be recognized by bloody discharge, which is characterized by increased duration. In this case, the size of the uterus will not decrease to the levels observed before pregnancy. The presence of residues can be confirmed using ultrasound. If they are found, repeated cleaning will be required.
- Curettage involves removing the top layer of the endometrium along with the membranes. Because of this, there is a possibility of damage to the basal layer of the reproductive organ. This mainly happens when the procedure is carried out carelessly. The consequence of such an operation may be the occurrence of adhesions and fusion. These formations can subsequently interfere with the process of attachment of the fertilized egg to the uterine walls, which causes infertility.
Also, if the operation is carried out carelessly, scars may appear on the cervix, which complicates the process of pregnancy.
To minimize the risk of these complications, a woman needs to carefully prepare for the operation and follow all the recommendations of the attending physician. Also, if alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately contact a specialist to diagnose the causes of its occurrence.
Doctors' recommendations
- Sexual activity is excluded for 3 weeks after cleansing. The goal is to prevent infectious complications and bleeding. In addition to bacteria, semen contains prostaglandins that relax the uterus.
- It is recommended to use a condom for 6 months after curettage to prevent pregnancy.
- You should not take a bath or visit the pool for a month.
- It is not recommended to use tampons to absorb blood after curettage. This can provoke the development of inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity.
- After curettage, physical activity should be limited as much as possible.
Recommendations for taking antibiotics and other medications during curettage:
- Antibacterial medications must be taken strictly at regular intervals.
- Minimum duration of taking antimicrobial agents: 3 days for Azithromycin and 5 days for other drugs.
- The dosage of the drug should correspond to the patient’s weight.
- Drinking alcohol while taking antibiotics is not recommended.
- To relieve pain, you should take Ibuklin or Diclofenac.
- To prevent the formation of adhesions, enzyme preparations (Wobenzym, Longidaza) are usually prescribed.
If the recommendations of the gynecologist have not been announced, then the above advice must be followed.
Restoring menstrual function is an important part of the rehabilitation period after curettage. The cyclical work of the female body is very sensitive to various fluctuations and outside interference. “Artificial” getting rid of the endometrium sends incorrect signals to the main regulators of the menstrual cycle - the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. The ovaries, as performers, will also respond to this type of influence.
The drugs must be taken for 2 to 6 months, depending on the diagnosis that served as the reason for cleaning the uterus.
Oral contraceptives after the uterine cleansing procedure:
The first tablet is taken on the day of curettage. The selection of the drug is carried out only by a gynecologist and based on the results of a blood test for hormones.
After curettage, it is recommended to resume physical activity no earlier than after 2 months. Visiting the gym should be delayed, and heavy lifting (more than 3 kg) and running should be avoided. Any physical activity is stressful for the body, which undoubtedly reduces immune activity and will interfere with healing.
One of the important recommendations of a gynecologist after curettage is the implementation of physiotherapeutic measures. The most effective methods of physiotherapy in gynecology include:
- EHF therapy. The therapeutic effect is achieved through irradiation with electromagnetic waves in the EHF range, which increases the nonspecific resistance of the body, increasing resistance. It is recommended to use EHF therapy after cleansing to prevent endometritis.
- Ultrasound therapy. The method is recommended for preventing the formation of adhesions in the uterus and pelvis resulting from curettage.
- Phototherapy. Infrared rays have an anti-inflammatory effect.
After curettage manipulation, many experts recommend using sorption therapy as a preventative measure, the essence of which is the introduction into the uterine cavity of a special solution that has sorbent and antiseptic properties. Usually a mixture of Enterosgel and Dioxidin is used. The composite solution is injected into the uterus using a thin catheter. Due to its thick consistency, the mixture does not leak, so no special restrictive recommendations for physical activity are required. Aspiration biopsy is used to monitor healing. The aspirate is examined under a microscope and the condition of the resulting cells is assessed.
After the uterine cleansing procedure, doctors monitor the healing process using aspiration biopsy. It is carried out on days 23-25 of the cycle, 2 months after all types of curettage.
An equally important task facing the gynecologist is to provide comprehensive rehabilitation using means aimed at restoring psycho-vegetative disorders.
As a rule, after curettage, the patient is recommended the following therapeutic measures and medications:
- Acupuncture.
- Psychotherapy.
- Herbal soothing infusions for 2 weeks after cleansing (Phytosedan, soothing teas with lemon balm, sedative infusions).
- Antidepressants (Coaxil, Gelarium, Azafen) for 10-20 days.
What is curettage?
Curettage is a manipulation that comes down to removing the restored layer of the uterine mucosa using special instruments (curettes or vacuum aspirators).
The entire procedure sounds like “separate diagnostic curettage.” “Separate” - since tissues from the wall of the cervix and the uterus itself are examined separately.
During the intervention, it is preferable to use a hysteroscope, a system for a detailed examination of the uterus.
To better understand the essence of the procedure, some definitions should be revealed:
- Scraping as such is only an instrumental manipulation, i.e., a designation of the action itself. The operation has different names depending on the method and purpose of its implementation.
- Separate curettage involves the sequential removal of biomaterial, first from the cervical canal, then from the uterine mucosa. After the operation, the removed tissue will be sent to a histology laboratory, and at the same time the neoplasm for which the operation was scheduled will be excised.
- RDV + HS (hysteroscope) is an improved, more informative procedure. Previously, curettage was carried out mainly “blindly”. The instrument allows you to examine the uterine cavity in detail for pathological formations. Excision of tissue or neoplasm is carried out at the end of the manipulation. The final stage is the doctor’s assessment of the work done.
Spontaneous abortion
Spontaneous abortion is the spontaneous natural termination of pregnancy up to 22 weeks. This happens due to impaired development of the fetus or any pathologies in the mother. Spontaneous abortion is popularly called miscarriage. The difference between a miscarriage and a premature birth is that with a premature birth, which occurs at 22-37 weeks of pregnancy, a viable baby is born (weighing at least 500 g).
Symptoms of miscarriage depend on the stage of pregnancy. So, if spontaneous abortion occurs in the early stages, it begins with bleeding. And the pain is either insignificant or not at all.
With a late-term miscarriage, the first symptom is severe cramping pain, and bleeding begins later. Symptoms of spontaneous abortion may also include: pain in the sacral area, vomiting, rupture of amniotic fluid.
Abortion is the termination of pregnancy, resulting in the birth of an immature and non-viable fetus. Sometimes it is planned, more often it happens spontaneously, without the woman’s desire. According to statistics, 15-20% of pregnancies end in such spontaneous abortions. Although there is an opinion that a significant number of spontaneous abortions occur in very early stages and women do not notice them. Then the number of miscarriages increases to 50-78%. Moreover, 60% of them are caused by some kind of chromosomal abnormalities, so many doctors classify the majority of miscarriages that occur in the first trimester of pregnancy as a manifestation of natural selection. According to the stages of pregnancy, abortions are divided into:
- infraclinical abortion that occurred at a very early stage of pregnancy;
- abortion during the first trimester;
- abortion during the second trimester;
- repeat abortions.
Most often, spontaneous abortion occurs in the third month of pregnancy, in the second and fourth - much less often. And how many of them occur in the first month is very difficult to count. This can happen due to any past or current diseases (syphilis, toxoplasmosis, brucellosis, listeriosis), characteristics of the woman’s constitution and development (anomalies in the development of the genital organs, infantilism), pathologies of the ovum and diseases of the second parent. Also, the cause of spontaneous abortion can be previous abortions, a short interval between pregnancies, Rh conflict, hormonal disorders (excess male hormones, diabetes), smoking, alcohol and drug use, difficult or harmful working conditions and even the quality of nutrition.
There are several types of spontaneous abortion, depending on the degree of detachment of the ovum and emptying of the uterine cavity:
- threatened miscarriage;
- incipient miscarriage;
- abortion is in progress;
- incomplete abortion;
- complete abortion.
Now in more detail about each of them.
The threat of miscarriage occurs in 25% of pregnancies. About half of them end in miscarriage. In this case, detachment of the ovum does not occur, there may be no bleeding, cramping pain in the lower abdomen is disturbing, signs of pregnancy may decrease - swelling of the mammary glands, nausea, frequent urination ...
When a miscarriage begins, bleeding and cramping pain intensify, the uterus is painful on palpation. The fertilized egg is partially separated from the uterus.
During an abortion, fetal abruption intensifies; in addition to bleeding and cramping pain, there is also a feeling of compression of the rectum and the urge to defecate.
With an incomplete abortion, part of the fertilized egg is usually born. And the part remaining in the uterus interferes with its contraction and hemostasis. Bleeding continues and may lead to hemorrhagic shock. Even if the fertilized egg seems to have come out completely and the bleeding is insignificant, there is still a risk of renewed bleeding within 5-6 days due to remaining particles of the fertilized egg, the formation of a placental polyp and infection.
Complete abortion often occurs in later stages. The fertilized egg is expelled completely, which is accompanied by cramping pain and bleeding. After expulsion, the uterus contracts and bleeding stops. A failed abortion is also possible. In this case, the dead fetus is not expelled from the uterus.
If spontaneous abortion occurs for a long time, an infection from the vagina may enter the uterus. Moreover, if inflammation occurs only in the uterus, it is an uncomplicated infected abortion, and if the infection spreads to all pelvic organs, then it is a complicated infected abortion. It is also possible for the infection to spread throughout the body. This condition is called septic abortion.
Diagnostics
If a spontaneous abortion is suspected, a transvaginal ultrasound is required to find out how the pregnancy is progressing and whether the fetus has died, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood is determined, a general blood test and a general urine test are done. It is also necessary to determine the blood type and Rh factor of the mother and child. If this is not the woman’s first spontaneous abortion, the parents are examined for carriers of chromosomal abnormalities, infections, the presence of any systemic diseases and anatomical abnormalities of the woman that do not allow a normal pregnancy to be carried to term.
A morphological study of the placenta preparation is also carried out. In some cases, diagnostic curettage of the uterus and cervical canal is necessary.
As soon as a woman feels that there is “something wrong” with her, she should immediately contact a gynecologist. On the one hand, not every bleeding during pregnancy is a sign of spontaneous abortion. On the other hand, it’s better to play it safe. If there are no pathologies and the fetus is alive, if there is a threat of miscarriage, bed rest, vitamins, drugs to relax the myometrium, and diet are prescribed. Sex in this state is not recommended. In Russia, when there is a threat of miscarriage, a woman is usually admitted to a hospital; abroad, depending on her condition, she may be given an IV and sent home, having previously given the necessary recommendations, or she may even be admitted to a hospital. In many European countries, if there is a threat of miscarriage and miscarriage itself during pregnancy up to three to four months, nothing is done if it occurs in less than three pregnancies in a row.
In some cases, if there is a threat of miscarriage, hormonal and antibacterial agents are prescribed. Sometimes surgery is also required.
If the fetus is dead, it must be removed from the uterus. The procedure is carried out in a hospital and until the abortion is completed, and sometimes for several days after, the woman must be under the supervision of a doctor. She is given blood substitutes for severe blood loss, and the uterus is curetted. In some cases, such as cervical pregnancy, the uterus may also be removed.
If necessary, analgesics and anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin are prescribed.
Unfortunately, in the event of a miscarriage, complications are possible. When curettage occurs, there is perforation, infection of the uterus, and uterine bleeding. Depression often occurs after a spontaneous abortion.
Prevention
For most early abortions (before 12 weeks), there is no specific prevention. Only vitamins, proper nutrition, no stress, limited physical activity. Also, pregnant women should not lift weights, as this can also cause spontaneous abortion. Some doctors believe that hormone therapy is inappropriate before the 8th week of pregnancy, as it interferes with natural selection.
In general, therapeutic support for pregnancy is justified only if ultrasound has confirmed the viability of the fetus. It includes bed rest, antispasmodics and muscle relaxants (drugs that relax smooth muscles), and hormonal therapy.
If a woman has already had three miscarriages, she needs to do some research:
- genetic testing of both partners. It will help identify chromosomal abnormalities that may cause embryo death.
- hysterography. This study will help identify pathologies of uterine development, for example, adhesions, septa, and other developmental defects.
- hormonal examination.
- tests for infections.
- immunological analysis. Sometimes the cause of a miscarriage can be a weak or, conversely, too strong immune system.
Depending on the research results, the doctor will prescribe effective treatment to solve this problem.
How you feel depending on the trimester
In general, recovery after cleansing the uterus is quick, without any health-threatening complications. But after curettage of the embryo, unpredictable consequences may appear for the general condition of the woman and her reproductive system.
Most often they do not pose any danger, but are physiological in nature. Such consequences include the appearance of pain and bloody discharge from the vagina after curettage.
First trimester
When cleansing is carried out by an experienced doctor in the early stages, any complications rarely arise. In this case, the following side effects may occur:
- bleeding;
- the appearance of an inflammatory process;
- the occurrence of hormonal imbalance;
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- damage to the uterus;
- formation of scars on the internal uterine surface.
Also, as a result of removing an embryo that has stopped developing, an increase in temperature and painful sensations in the lower abdomen may occur. After surgery, therapy may be required to restore the cycle, but in most cases it normalizes on its own.
Second trimester
If the pregnancy is frozen and curettage is required in the second trimester, the risk of complications increases. Among them are:
- the occurrence of bleeding;
- damage to the inside of the uterus or its puncture by an instrument or fetal bone during the procedure;
- the appearance of bloody discharge without an unpleasant odor or a different color shade;
- formation of hormonal disorders;
- spread of abdominal pain after curettage;
- increase in body temperature.
Most often, as a result of cleaning in the second trimester, stabbing pain occurs. In case of any complications mentioned above, the woman should urgently consult a gynecologist.
If you start the prescribed therapy in a timely manner, the body will quickly recover and prepare for the next conception. In this case, planning a pregnancy after curettage is possible within six months.
Third trimester
Curettage during pregnancy fading in the third trimester requires the longest recovery period. In almost all cases, a woman needs long-term rehabilitation.
Before the operation, the doctor must evaluate the condition of the fetus. When it becomes dead, an abortion is performed. After such a procedure in the third month of pregnancy, a woman will have to stay in the hospital for at least 1 week.