The appearance of white plaque on the labia is a common occurrence and even healthy women are not immune from it. It occurs in girls in the first weeks after birth, and in teenage girls (11 to 14 years old) there is a light-colored discharge. Pregnant women also experience this stage of plaque due to hormonal changes in their bodies. In women who are sexually active, the body reacts with the appearance of a white coating in response to the flora of their sexual partners. But whether this is considered normal or a pathology remains to be sorted out, since the ability to distinguish one condition from another will help to avoid panic and various problems.
Causes of white plaque
There are several groups of factors influencing the appearance of discharge. Some of them are the body’s natural reaction to hormonal changes. These are harmless causes that go away on their own. Another group is associated with female diseases or diseases that are sexually transmitted.
Common natural causes include the following:
- Pregnancy - in the first time (especially in the 1st trimester), the volume of discharge in women significantly increases. This directly depends on hormonal changes, with a large release of progesterone. The body weakens the immune system so as not to reject the fetus. The unborn child is a foreign object in the uterine cavity, so it must be protected.
- Adolescence – during puberty, a girl’s body undergoes restructuring. This occurs from 11 to 18 years of age. At this time, the microflora of the vagina is disrupted, often a white coating forms between the labia and on them. After hormonal changes, the microflora becomes normal and the amount of whitish discharge returns to normal.
- Changes in microflora after sexual activity - when a girl begins sexual relations, at first the body undergoes changes. The fact is that the female microflora of the external organs comes into contact with foreign microflora. This leads to the appearance of a white coating. This condition goes away on its own, so there is no need to worry about it.
- The most common natural cause is the accumulation of smegma. This term refers to a mixture of secretion secreted by the sebaceous glands of the labia, dead epithelial cells of the mucous membrane and lubricant (it is necessary to moisturize the vagina). If smegma accumulates in large quantities, this indicates insufficient personal hygiene. With infrequent washing, the discharge may appear.
Smegma is a normal phenomenon; a white coating can be noticed even in girls of preschool age. In order to get rid of it, it is enough to wash your baby regularly. Twice a day will be enough.
Discharge in a newborn baby is a natural reaction of the body. The child adapts to unusual conditions. Discharge on the labia can be not only white, but also pink-brown. This symptom will subside 2 to 3 weeks after birth. The baby needs to be bathed 1-2 times a day, but you should not remove all the smegma from the child. It protects the genitals by preparing them for the environment.
White plaque on the labia may appear due to vitamin deficiency. With a lack of vitamins A, PP and E in women, the microflora in the vagina changes.
White clots in women's discharge: causes, how to identify the disease
All women secrete mucus from the vagina. This secretion is provoked by pathological and physiological processes occurring in the body.
In many ways, its volume and character depend on hormonal levels. White clots in women's discharge can appear under the influence of many factors.
The main thing is to promptly distinguish normal secretion from that which indicates the development of diseases.
Pathological causes
If the underwear is stained from the vagina, resembling cottage cheese in appearance, we are talking about
, or vaginal candidiasis. This disease most often affects the genitals, and its development is caused by the pathogenic fungus Candida.
The body of a healthy person can contain various fungi and bacteria, but they become more active as the immune system weakens.
Pathogens accumulate on the vaginal mucosa in so-called colonies and, in addition to producing new spores, release toxic substances.
These dangerous products of fungal activity do not just irritate the delicate mucous membrane of the vagina. They are capable of completely disrupting its integrity, just like the skin of the external genitalia. Thus, every day the symptoms of thrush are expressed more and more clearly.
Treatment for thrush is short-term. The doctor may prescribe tablets for one or two doses, or suppositories for insertion into the vagina.
In most cases, thrush goes away quickly, and only 5% of women experienced a recurrent or chronic form of the disease. Therapy in this case becomes more difficult, but over time the disease still recedes.
In order not to provoke the development of the disease or its repeated episodes, women must adhere to certain rules: • maintain personal hygiene, especially during menstruation; • combine antibiotics with drugs that prevent the development of dysbacteriosis; • wear comfortable underwear made of breathable fabrics.
Women who like to eat a lot of sweets should give up this habit, otherwise thrush will become, although unwanted, a permanent guest for them. Cases of frequent recurrence of the disease require a visit to an endocrinologist to rule out diabetes mellitus.
As for the nature of thrush, it is not an infectious or venereal disease. Its development is caused only by a violation of the vaginal microflora. It is better to refuse sexual activity during treatment, but if you cannot follow this recommendation, you must use a condom.
Uncharacteristic discharge may occur under the influence of pathological factors. Many of them are asymptomatic, and their presence is indicated only by a smearing brown secretion. As a rule, such clinical manifestations are observed in cases of damage to the reproductive organ. They can appear before the regulation, immediately after its completion, and sometimes during other periods of the cycle.
Erosion
Ulcerations on the cervix of the reproductive organ often do not cause any symptoms. Occasionally, scanty discharge may appear after intimacy. When the scale of the lesion increases and the pathology is in an advanced stage, the mucus acquires a sharp, purulent aroma.
Endometriosis
With the development of this pathology, an abnormal growth of the functional uterine layer is noted. Due to this, blood from the reproductive organ cannot escape and begins to accumulate in the uterine cavity and genital tract. As a consequence of this, a brown spot appears at the end of menstruation.
Polyps
An abundant dark secretion that appears some time after menstruation has ended is considered a clear sign of pathology.
This process can be triggered by polyps growing on the tissues of the cervix or the reproductive organ itself. In addition to scanty leucorrhea, there is often a delay in regulation.
When the growth grows, pain and pus in the secretion are also observed.
When plaque speaks of disease
In some cases, white discharge indicates diseases of the reproductive system. In these situations, a whitish coating is only an indirect sign of pathology; in addition to it, women will experience a number of other unpleasant and painful symptoms.
Among them: burning, severe itching of the genitals, pain when emptying the bladder or sex, and clitoris, redness and dryness of the mucous membrane.
Photos of reasons
Women need to seek help from a gynecologist. The doctor will examine the vaginal mucosa, collect anamnesis, and give directions for the necessary tests. After receiving the results, doctors will make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
The most common diseases of the reproductive system that cause white plaque on the inner lips include: thrush, genital herpes and vulvovaginitis.
Thrush
If leucorrhoea on the labia minora is accompanied by a sour smell, and the discharge itself is similar in consistency to cottage cheese, then we are talking about thrush or vaginal candidiasis. This disease is caused by Candida fungi. They are found in the microflora of every person, but with weakened immunity, fungi begin to multiply.
Other symptoms include:
- swelling of the genitals;
- severe itching;
- redness of the vulva;
- pain when urinating;
- severe pain during sexual intercourse.
Typically, vaginal candidiasis appears in women during pregnancy, after taking antibiotics or hormonal drugs; as a result of long-term chronic diseases that have weakened the immune system.
White plaque due to herpes
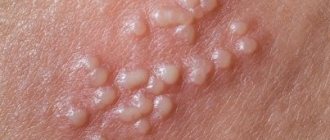
Genital herpes is one of the most common causes of plaque on the labia. Once in the body, the virus constantly circulates in the human blood. Treatment only alleviates the patient’s condition, the relapse rate is over 98%.
Herpes is transmitted through unprotected sex (and the type of sexual relationship is unimportant). Bubbles filled with transparent or appear on the genitals. Tingling and itching appears. The ulcers burst, and in their place cracks appear, which are covered with a white coating. Soon the wounds tighten and heal.
Usually herpes is mild, but sometimes the virus can affect the cervical canal, urethra, and anus.
Vulvovaginitis
This is a disease in which the vaginal mucosa and external genitalia become inflamed. The pathology is caused by staphylococci, streptococci, gonococci and other microorganisms. Representatives of the fair sex develop a white coating.
Leucorrhoea is foamy, with air bubbles and an unpleasant smell of rotten fish. Ladies experience pain when urinating or having sex. The disease is also accompanied by itching and hyperemia of the genital organs.
Usually the disease occurs against the background of sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, trichomoniasis). It also appears after taking antibiotics, after damage to the vaginal mucosa, as a result of disruption of the endocrine gland.
Diagnostics
It is not always possible to determine the disease visually, because white plaque and itching on the head in men may indicate various pathologies. First, the doctor collects anamnesis and analyzes what could have caused the discomfort. Then he decides to take several or all tests:
- blood for sugar content, biochemistry, Wasserman test, ELISA, RIT, RIF;
- urine for bacteriological culture;
- secret for sowing;
- urine for sugar content;
- microflora smear.
If necessary, instrumental studies may be prescribed. Most often this is an ultrasound of the prostate, MRI of the abdominal cavity. If diseases of the internal organs are suspected, parallel therapy for the underlying cause will be required.
Treatment of white plaque
If the discharge is caused by natural causes, then no therapy is required; the leucorrhoea goes away on its own. But it is necessary to maintain personal hygiene, wash twice a day. You should not use ordinary soap, it dries out the mucous membrane. Stores sell special intimate hygiene products.
Antiviral drugs (Acyclovir, Zovirax) are used to treat genital herpes. At the same time, you should take a course of immunomodulators and vitamins.
Treatment of vulvovaginitis depends on the pathogen. Antibiotics from the tetracycline class and douching with zinc or copper sulfate are usually prescribed.
Conclusion
When leucorrhoea, itching and other symptoms occur, many women begin to panic. They don’t know why the labia itch and a white coating appears on them. The causes of discharge can be natural, which do not require medical intervention. In the second case, the signs indicate the presence of gynecological diseases.
White plaque on the labia often indicates the presence of a pathological process. It all depends on the accompanying symptoms of the disease. Moreover, a whitish coating can be observed at any age and even in newborn girls. This condition is dangerous during pregnancy, as it often indicates the presence of a disease. A white coating between the labia that does not cause an unpleasant odor, itching or burning will be considered normal.
Prevention of misfortune
In order to prevent the occurrence of a misfortune, it is necessary to avoid errors in observing the rules of personal hygiene. Performing them is much easier than in the near future getting rid of the consequences of negligent treatment of them reflected in the intimate area. In order to prevent the accumulation of white matter under the foreskin, it is necessary to carry out a number of procedures included in preventive measures:
- the penis is washed with warm water and hypoallergenic soap (baby soap is best) twice a day;
- During the evening shower, the use of bactericidal agents is not advisable, as this can lead to the washing out of beneficial microflora and its replacement with pathogenic ones.
It is necessary to teach the rules of personal hygiene from early childhood. A boy who is accustomed to regularly using them in practice, as an adult, is more likely to avoid the occurrence of this scourge.
White plaque on the labia - causes
White plaque on the labia often appears as a result of the presence of genital candidiasis or thrush, as it is colloquially called. This is a fungal infection that causes a cheesy coating on a woman's genitals.
The main reasons for the development of this disease can be the following circumstances:
- Sexual contact with a sick person.
- Hormonal imbalance, often associated with age-related changes in teenage girls.
- Disturbance of the microflora of the external genitalia in connection with the onset of sexual relations.
Vaginitis
Vaginitis is an inflammation of the vaginal mucosa. With vulvovaginitis, the external genitalia also become inflamed in a similar way. The third type, vulvitis, affects the clitoris and labia. All 3 diseases are common in gynecological practice and are usually provoked by one of 10 reasons:
- STDs (chlamydia, gonorrhea, the aforementioned vaginal candidiasis, trichomoniasis and others).
- Weakened immunity as a result of an infection.
- Obesity, diabetes, menopause, various ovarian diseases. In each case, there is a decrease in the endocrine function of the secretory glands.
- Prolapse of the vaginal walls or gaping of the genital slit.
- Irritation of the vaginal mucosa or carrying out actions that injure the area of the vagina and uterus.
- Vascular disorders and senile atrophy.
- Allergy to condoms or medications inserted into the vagina.
- Long-term use of antibiotics.
- Lack of personal hygiene.
- Ignoring hygiene rules when engaging in sexual activity.
Where does plaque come from between the labia?
As mentioned above, a white formation on the labia can appear as a result of the physiology of the female body or as a result of illness.
Physiological reasons
Vaginal microflora can react to internal or external changes. During the period of hormonal changes in the body, girls aged 12 to 14 years may develop plaque on the genitals. Similar cases can be recorded during the period of bearing a child.
The beginning of a sexual relationship can also affect the condition of a woman’s genital organs. For example, in some cases, in this way, a woman’s organs are protected from foreign microflora of the sexual partner.
Other non-pathological factors can also cause white formations:
- lack of vitamins;
- tight underwear;
- errors in nutrition;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- Low quality body cosmetics.
If such factors are eliminated, the plaque will disappear on its own, without additional treatment. Such a plaque in infants is called a sexual crisis and is considered normal. Because this is how the body cleanses itself after childbirth. After 7-9 days, this condition usually goes away.
Plaque caused by natural causes should not be eliminated. It protects the normal microflora of the vagina and also fights pathogenic microorganisms. Smegma (the so-called white formations between the labia) is associated with the functioning of the sebaceous glands. Remove it with a cotton swab and vegetable oil. You can also moisten it with water. But you should not use various aromatic soaps and gels, so as not to irritate the delicate skin of the labia.
Pathogenic factors
If, along with plaque, additional signs appear - burning, itching, redness, pain, etc., then this may indicate the onset of a disease.
These include the following pathologies:
- infections associated with human genitalia;
- sexual diseases;
- fungus.
Among these pathologies, the following diseases are the most common:
- Thrush (candidiasis) and other fungal infections.
- Vulvovaginitis and vaginitis.
- Genital herpes.
- STDs such as syphilis, gonorrhea, etc.
There is no need to guess where the plaque on the genitals came from; it is better to immediately visit a gynecologist. Through examination and additional tests, he himself will understand the causes of this condition. To avoid catching candidiasis, you should use a condom if you are not sure about your sexual partner.
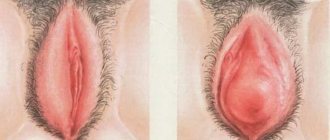
The appearance of a white coating on the labia is not uncommon, but whether it means that a woman has any disease or is a variant of the norm needs to be investigated. During the menstrual cycle, the color, consistency, smell and structure of vaginal discharge in the fair sex changes.
They may become more abundant, slimy, or creamy. The main thing is that the discharge does not have an unpleasant odor and does not cause discomfort in the form of burning and itching. The slightly sour smell of discharge from the genital tract may be the result of the work of conditional bacteria that normally live in an intimate place.
If, in addition to white plaque on the labia, you are bothered by pain in the lower abdomen, redness of the mucous membrane, pain after urination, as well as itching of the genitals and bad smell of discharge, immediately visit a gynecologist for examination and treatment.
White pellets in an intimate place
Leucorrhoea that has a uniform consistency is considered normal; it does not have an unpleasant aroma and does not cause discomfort.
In a healthy woman, parts of the epithelium are included in the leucorrhoea, due to which small clots may appear. This can be seen on linen as small yellowish smears. If the lumps are whitish and have the smell of sour milk, we can talk about the presence of thrush. The appearance of such discharge in the form of white lumps is not normal and requires treatment.
A woman can determine on her own whether the discharge is normal, knowing the number of days of the cycle and its beginning. Leucorrhoea may vary for each girl - for some it is abundant, for others it is scanty throughout the entire cycle.
The appearance of dark brown discharge with small clots before menstruation is normal. They mean that parts of the endometrium are rejected. In some cases, brownish leucorrhoea may appear after taking hormonal medications.
Perhaps such symptoms indicate the development of endometriosis, which also requires medical intervention.
Reasons that may result in the appearance of such leucorrhoea:
- Constant stress overexertion.
- Abortion.
- Age over forty years.
- Reduced hemoglobin level.
- Hormonal diseases.
- Use of contraceptives.
- Anorexia.
- Excessive physical activity.
As a preventive measure, it is recommended to maintain hygiene, get rid of bad habits, and avoid stress and viral diseases.
Mucus can appear for various reasons - this phenomenon can be a natural physiological process, they can occur during pregnancy, menopause or before sexual intercourse, when a woman is aroused. But in some situations they are a pathology - with a large number of leukocytes, inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs and other diseases.
The discharge of mucous snot after menstruation is acceptable; in such a situation, it should not have color, odor or large volume. The consistency should be homogeneous and without foreign inclusions.
Reasons why leucorrhoea appears normally:
- With hormonal fluctuations - puberty and menopause, as well as pregnancy.
- Taking contraceptive medications.
- Constant stress overexertion.
- Sexual arousal.
- An allergy that stops after the irritant is removed (underwear, soap, lubricant and condoms).
If the leucorrhoea changes color to yellowish or green, you should worry - this is one of the first signs of a pathological condition.
In the presence of diseases, the appearance of an unpleasant odor of mucus, an increase in their volume and the appearance of blood or pus are also noted.
Discharge can also be a signal that a woman has gynecological diseases, which can lead to infertility and even disability.
We suggest you read: Can thrush be caused by tampons?
White discharge in lumps can be caused by candidiasis (thrush). This is an infectious, fungal disease that manifests itself on both the external and internal surfaces of the vagina. It can spread over fairly large areas. With this disease, the discharge can have a different appearance.
The cause of the disease may be:
- hormonal disorders;
- antibiotics taken by the woman;
- vaginal douching;
- contraceptives;
- decreased immunity;
- infection from a sexual partner;
- violation of diet, unhealthy diet;
- excess weight;
- constipation
Those who, due to certain circumstances, have a permanently reduced immune system, are also more likely to develop thrush, for example, those who have diabetes or an HIV-infected person.
Discharge in the form of white lumps can be considered normal. But this is the case if the lumps themselves are small in size, their consistency is not too thick, the color is transparent or slightly white, but without a pungent odor and without itching.
In addition, if we talk about different phases of the menstrual cycle, then with normal discharge they will differ depending on the period. But the discharge characteristic of thrush will always be the same.
Characteristics of different secretions
As such, vaginal discharge is normal for any healthy woman. But changes in their color, smell and consistency may indicate the presence of various kinds of problems or simply changes in the body itself.
For example, when hormonal status changes, the intensity of discharge may change. This often happens during pregnancy and shortly before the start of menstruation. But a decrease in the intensity of discharge is a harbinger of menopause.
White plaque on the labia in women photo
If symptoms are detected, you should consult a doctor and get tested. Only after this the doctor prescribes treatment. These are often medications in the form of suppositories that need to be placed in the vagina for 5-10 days. This period is usually enough to eliminate the problem in both pregnant and non-pregnant women.
Antifungal drugs are used to treat thrush, which can neutralize and destroy the disease. It is most effective when both sexual partners undergo treatment, this helps to avoid re-infection. There are quite a lot of methods for treating candidiasis: in addition to vaginal suppositories, these can be ointments and tablets.
Genital herpes
The second type of virus affects the nerve cells of the body and manifests itself in the form of blistering rashes on the genitals. The infection has a high recurrence rate (up to 98%). You can catch it through vaginal, anal or even oral sex. The risk of infection increases if the partner and the woman herself have microdamages on the skin.
We suggest you read: A child has a white dot on his tonsil
https://www..com/watch?v=h-mKI9GLpKY
For some time, the pathogen does not manifest itself in any way, being in a dormant state. Then redness, tingling and itching occurs in the perineal area, and small watery blisters appear. Excessive dryness may cause cracks and white coating to appear on the skin. After opening the rash, painful ulcers form, which become covered with a crust and heal completely.
Usually the disease is mild. But in severe cases there is a risk of damage to the urethra, vagina, cervix, cervical canal, anus and rectum. Therefore, when the first symptoms of herpes appear, you should consult a gynecologist. The doctor will prescribe medications that stop the pathogen from multiplying.
Thrush
A white, cheesy coating on the labia with an unpleasant sour odor is a sign of candidiasis. Fungal infection is localized mainly in the vestibule and on the vaginal mucosa.
It can appear in both a little girl and an adult woman. Yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida live on the skin and mucous membranes of a healthy person, being part of the normal microflora.
Their growth is provoked by the following factors:
- weakened immunity;
- long-term use of antibiotics and hormonal drugs;
- unprotected and promiscuous sex;
- insufficient or excessive hygiene of intimate organs;
- microtrauma of the vagina and labia;
- diabetes;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- pregnancy;
- lactation.
The first symptoms of thrush are itching and burning associated with the reaction of the mucous membrane to a fungal infection. There is redness, rashes and swelling of the labia majora. Thick, white or gray cheesy discharge with inclusions of flakes and lumps also occurs. When they dry, they leave yellowish marks on the laundry.
When white plaque is not accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, it is a normal variant and does not require therapy. It is enough to keep the intimate area clean and change your underwear daily. But if you experience itching, burning during urination, cracks or rashes, pain and pain in the lower abdomen, redness, bloody, curdled or purulent discharge, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Thrush is a fungus that develops on the mucous membranes of the genital organ, the main symptom of the development of which is the appearance of white smelling discharge with lumps.
The causes of this disease:
- Presence of diabetes mellitus.
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics.
- Taking hormonal drugs.
- Diseases associated with hormonal disorders.
- Weak immune system.
- Acclimatization.
- Stress overvoltage.
- Lack of personal hygiene.
- Wearing low-quality underwear that is tight or made of synthetic materials.
- Use as a product for intimate hygiene, a soap with an antibacterial effect. It reduces the local protection of the mucous membranes.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Removing plantar warts with varnish
Microorganisms that can cause this disease are found in every woman’s vagina, but in very small quantities. Their uncontrolled spread leads to the development of candidiasis, or thrush.
The main symptoms of candidiasis are lumpy leucorrhoea that smells like sour milk, as well as itching and burning in the intimate area. In the absence of timely treatment, fungi can spread over the entire surface of the genitals, then therapy will be the most lengthy and complex.
To prevent the disease, it is recommended to avoid frequent changes of sexual partners and promptly treat emerging STDs, such as gonorrhea, genital herpes, chlamydia, etc.
Smelling leucorrhoea with foreign color and inclusions indicate a pathological condition. The smell of rotten meat may indicate the presence of inflammatory processes and the occurrence of sexually transmitted diseases. Such pathologies can lead to serious complications; the risk of infertility is high if treatment is not started on time.
A sour smell often indicates the development of thrush. This fungus, if not properly treated, can affect the entire surface of the vaginal mucosa. This disease not only reduces the patient’s quality of life, but can also be transmitted to a sexual partner.
Discharge during pregnancy
Candidiasis can often occur during pregnancy. Reasons for its occurrence during pregnancy:
- Decreased immune defense.
- Avitaminosis.
- Lack of hygiene.
Usually, after diagnosing thrush during pregnancy, the doctor advises you to stabilize your diet and eat foods rich in vitamins, as well as remedies to get rid of the unpleasant pathology.
White discharge in the form of lumps often appears during pregnancy. As practice shows, 95 percent of pregnant women suffer from heavy discharge. Although the discharge may sometimes be thin and sparse, it is often thick, white, and copious. And if lumps appear, there is a possibility that the disease has some advanced form.
That is why many pregnant women are forced to undergo treatment in order not to harm their child during childbirth, since, passing through the birth canal, the child can become infected. Therefore, during such an important event as pregnancy, it is impossible to ignore the doctor’s advice regarding treatment.
How to treat
If you experience symptoms such as pain, amenorrhea, pain when urinating, discomfort and itching, lethargy, swelling and the appearance of ulcers on the vagina, you should consult a doctor.
As a diagnosis, a doctor can use anamnesis, a routine examination and/or with the help of special equipment, ultrasound, results of blood and urine tests, etc.
After this, the gynecologist prescribes treatment strictly individually, based on the disease, its severity, characteristics of the body and other factors.
Source: https://tvoiapapiloma.site/belye-katyshki-intimnom-meste/
Treatment
Depending on the identified disease, therapy is selected. It involves the use of external and internal products (vaginal tablets, ointments, creams, suppositories). The most popular medicines:
White plaque on the labia, not accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms (itching, burning, vaginal discharge), is not a sign of a dangerous disease. In other cases, you should immediately contact a gynecologist and undergo the necessary tests to identify the disease and subsequent therapy.