Hyperplasia - features of pathology
Cervical hyperplasia is a pathological process, the essence of which is the increased division of its elements. In many cases, gynecological disease develops against the background of benign neoplasms in the pelvic cavity, which can become malignant at any time. In order to avoid this, great importance is given to competent diagnosis and treatment of pathology.
The disease is closely related to the production of hormones and some other biologically active components, which can not only accelerate, but also stop the pathological division of normal endometrial cells.
Hyperplasia of the glandular epithelium has the most severe consequences for the female body, including the development of such a dangerous disease as cancer. It is for this reason that when a pathological process is identified, you should immediately contact a specialist and begin treatment.
Reviews
Statistics show that 30% of women at an appointment with a gynecologist are diagnosed with endometrial hyperplasia. This is a rather disappointing statistic, because many beautiful women do not pay proper and timely attention to their health. As a result, many curable (with timely treatment) ailments become chronic, sometimes preventing a woman from fulfilling her calling - to become a mother.
But, with timely diagnosis and properly selected treatment, you can recover from the disease, especially if you listen to the recommendations of the gynecologist and act comprehensively.
According to patients who have tried folk recipes, the tactics are quite effective.
Olga, 45 years old
I learned about my diagnosis at the age of 43. I was very afraid that without surgical treatment I would not achieve a full recovery. But the doctor convinced me that the disease was diagnosed on time, so it’s worth trying to get rid of it without surgery. Therapeutic measures were based on taking herbal decoctions, tinctures of nettle and boron uterus. The duration of therapy was 4 months, after which the diagnosis could not be confirmed by ultrasound.
Galina, 38 years old
Hyperplasia was diagnosed accidentally during a medical examination. After the examination, the gynecologist prescribed curettage and hormones, since it would not have been possible to recover using less radical methods. After a successfully completed procedure, I consumed flaxseed oil for 4 months in a row. The treatment was also supplemented with carrot juice and douching with celandine. In the end, my health improved, and the hyperplasia began to subside. There have been no relapses for more than a year.
Causes of the disease
In order for the treatment of glandular epithelial hyperplasia to be as effective as possible, the cause of the pathological process must be accurately established. Most often, the cervix is affected under the influence of the following factors:
- hormonal imbalance in the body;
- diabetes mellitus, obesity and other pathologies of the endocrine system;
- abortions, diagnostic curettages;
- various gynecological diseases - polyp, pseudo-erosion and erosion;
- inflammatory processes in the pelvis;
- long-term use of certain hormonal medications;
- the onset of menopause after 50 years of age;
- too early start of sexual life.
If a woman uses intrauterine contraceptives, this can also lead to intensive proliferation of epithelial cells. In some cases, the development of hyperplasia of the glandular epithelium can be provoked by a decrease in the level of immunity, as well as bad habits such as smoking or frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Types of glandular epithelial hyperplasia
The mucous tissue of the uterine cervix is lined with epithelium of several forms - glandular squamous and multilayered. That is why the pathological uterine process has several varieties.
- Glandular;
- Squamous;
- Cystic;
- Glandular-cystic;
- Microglandular;
- Atypical.
Glandular formation develops against the background of hormonal changes in the female body. In most cases, the reproductive organ is affected in young girls, which is associated with the formation of the hormonal system. Polyps or cysts appear on the surface of the deformed mucosa, affecting the cervical canal. Hyperplasia can also be characterized by the formation of pseudo-erosion of the epithelium.
Squamous cell type of the disease - the squamous layer of the epithelium changes, the basal cell area expands and thickens. The most common causes of squamous cell hyperplasia are viral or inflammatory processes in the pelvis.
The cystic type of pathology is a focal process in which the surface of the epithelium is covered with multiple or single cysts.
Glandular-cystic form - accompanied by rapid proliferation of glandular-type cells. In this case, the cell grows simultaneously with the formation of small cysts.
Microglandular cellular process is the rapid growth of cervical cells as a result of rapid cell division.
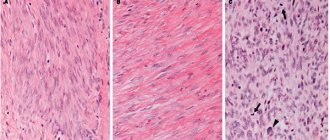
An atypical process is a precancerous form of the disease, which involves a noticeable thickening of the epithelial layer located in the cavity of the cervical canal.
Some experts identify a moderate pathological process - this is a form that is considered average between a simple and complex type of gynecological disease.
Symptoms of the disease
In most cases, damage to a reproductive organ such as the uterus is completely asymptomatic and does not manifest itself in any way. The doctor discovers the pathology during an examination or histological examination.
But sometimes a woman can independently detect the presence of hyperplasia. Characteristic symptom of the disease:
- changes in the menstrual cycle – periods may become more intense and longer, or occur once every 4-6 months;
- vaginal discharge between periods, which is so strong that the woman has to wear a sanitary pad or change her underwear regularly;
- bleeding that occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle is a characteristic sign of hyperplasia;
- pain, discomfort and discharge after sexual intercourse.
Since hyperplasia of the glandular epithelium is accompanied by a lack of ovulation, women suffering from this disease experience infertility. Therefore, as soon as the patient is diagnosed with this, it is necessary to immediately begin a course of treatment.
Diagnosis of the disease
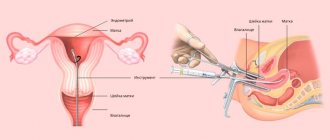
Most often, hyperplasia of the glandular epithelium of the cervix is diagnosed during a regular gynecological examination - when using special mirrors, the doctor has the opportunity to see the overgrown epithelial cells.
In order to obtain the most accurate and informative result, the following diagnostic measures are used:
- Biopsy is the removal and laboratory examination of several cells of the affected tissue, which helps determine the benign or malignant nature of the neoplasm;
- Colposcopy – is a determination of the condition of the uterine cervix using special coloring pigments and optical instruments;
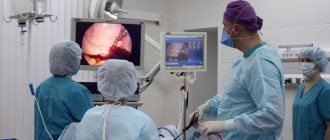
- Hysteroscopy is a diagnostic procedure during which a visual examination of the pelvic organs is carried out using an optical probe;
- Tests to determine the level of hormones in the female body;
- Ultrasound examination of the reproductive organs - as a result, the specialist is able to thoroughly determine the form of hyperplasia, the degree of endometrial thickness, as well as the presence of concomitant acute and chronic diseases.
Also, to clarify the diagnosis, the patient must undergo a general clinical urine and blood test.
The doctor carefully examines all the woman’s complaints, finds out whether she has any vaginal discharge and what nature it is, and whether she feels pain and discomfort after sexual intercourse. An important point is the duration and frequency of the menstrual cycle, as well as possible problems with conception.
For the final diagnosis of a gynecological disease, a computed tomography scan of the pelvic organs may be prescribed, which allows one to examine the condition of the mucous surface of the cervix in great detail.
How is atypical endometrial hyperplasia treated:
The main thing is the timely detection of this disease or the initial stages of cancer, when atypical cells have just appeared in the basal layer of the endometrium. Therefore, all menstrual irregularities should be immediately examined. To do this, women first undergo an ultrasound examination of the uterus, and then, if changes are detected, endoscopic (hysteroscopy) and RDV.
Hysteroscopy can be diagnostic and therapeutic. Most often, diagnostic hysteroscopy, when the doctor examines the endometrium enlarged with optical equipment, turns into a therapeutic one, that is, the endometrium is removed. But this is not always done. In childbearing age, today they try to use mainly hormonal therapy: suppression of estrogen secretion using drugs with antiestrogenic properties, progestogens (synthetic analogues of progesterone) or analogues of Riesling hormones of the hypothalamus (they suppress the secretion of pituitary hormones).
If it is not necessary to preserve reproductive function, then ablation of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity is performed - its complete destruction in various ways along with the basal layer, after which the endometrium is no longer restored. Subsequent hormonal correction is also carried out.
To prevent endometrial cancer, any irregularities in a woman’s menstrual cycle should be promptly identified and treated.
Treatment of cervical hyperplasia
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, treatment of the disease brings quick positive results. Drug therapy for glandular epithelial hyperplasia involves the use of hormonal medications that normalize hormonal levels in the female body.
In the most complex and severe cases, surgical intervention is used. The type of surgical treatment is selected by the doctor individually, depending on the patient’s age, form and severity of the pathological process.
Main types of surgical intervention:
- curettage – the focus of the disease and the pathologically altered columnar epithelium are removed;
- laser cauterization – exposure of the affected area of the mucous membrane to a laser beam;
- cryodestruction – elimination of pathologically changed tissues through exposure to low temperatures;
- hysterectomy is a radical surgical intervention, which is the removal of a pathologically changed uterus, most often performed in elderly women.
After surgical treatment, women are recommended to take hormonal contraceptives, which include a special combination of gestagens and estrogens, which allows them to completely restore progesterone deficiency.
Prognosis for hyperplasia
The prognosis for a gynecological disease depends on what cause provoked the development of hyperplasia of the glandular epithelium and in what form the pathological process occurs.
Many women are interested in the question of whether it is possible to become pregnant in the presence of pathology. There is no clear answer to this question - most often, hyperplasia is accompanied by a lack of ovulation, which makes ovulation itself impossible. As a result, pregnancy does not occur.
If pregnancy does occur, the likelihood of premature birth or the development of intrauterine pathologies of the fetus increases significantly.
After curing the disease, doctors recommend planning pregnancy no earlier than 12-36 months later. As a rule, in such cases, conception is successful, the woman can fully carry and give birth to a healthy child.
Video: endometrial hyperplasia using PDT
Endometrial hyperplasia using PDT
Video: fragment of uterine hyperplasia surgery using PDT
Fragment of surgery for uterine hyperplasia using PDT
Folk remedies for uterine bleeding:
1.1. Stinging nettle leaf - 2 tbsp. Make an infusion. Take 1/2-1/4 cup before meals 3-5 times a day for uterine bleeding.
1.2. Liquid alcoholic nettle extract (70%): Take 25-30 drops 3 times a day before meals for bleeding, menorrhagia and metrorrhagia.
2. Shepherd's purse.
2.1. Shepherd's purse herb - 2 tbsp. Make an infusion. Take 1 tablespoon 4-5 times a day after meals for uterine bleeding.
2.2. Liquid extract of shepherd's purse (70%): Take 20 drops 3 times a day for spotting and uterine bleeding.
3.1. Rhizomes and roots of burnet - 2 tbsp. Make a decoction. Take 1 tablespoon 5-6 times a day after meals for uterine bleeding.
3.2. Burnet extract, liquid alcohol (70%): Take 30-40 drops 3-4 times a day as a hemostatic agent.
4. Amur barberry.
Alcohol tincture (extract) from the leaves of Amur barberry (40%): 30-40 drops 2-3 times a day for 2-3 weeks for spotting and uterine bleeding.
5.Water pepper (Pepper Knotweed).
Peppermint for endometrial hyperplasia
5.1. Water pepper herb – 2 tbsp. l. Make an infusion. Take 1/3 cup 3-4 times a day before meals as a hemostatic and uterine tonic.
5.2. Water pepper extract liquid. Take 30-40 drops 3-4 times a day for bleeding, heavy menstruation and uterine bleeding.
Vitamin teas for endometrial hyperplasia
Vitamin tea is taken as a general strengthening, immunostimulating, adaptogenic agent, as well as for maintenance therapy for anemia due to endometrial hyperplasia.