The diagnosis of uterine fibroids (fibroma, fibromyoma) is made quite often, and just as often the disease raises questions among patients: what is it, how dangerous is it, how and what to treat, what will happen if left untreated, etc.
You can get answers to all these questions, as well as diagnose the presence of the disease, only at an appointment with a gynecologist
. You can sign up for a consultation and undergo examination at a medical center at a time convenient for you.
How are fibroids different from uterine fibroids?
Benign tumors of the uterus are often diagnosed in women, especially those of reproductive age. There are certain differences in the structure of these neoplasms. As a rule, we are talking about tumors of smooth muscle tissue.
Myoma, fibromyoma and uterine fibroid occur in more than 80% of representatives of the reproductively active age group, which indicates the prevalence of the pathological process.
In most cases, these diagnoses are combined into one term “fibroids”.
When it comes to fibroids and myomas, what is the difference between these two diagnoses? Many women are also interested in the difference between fibroids and fibroids.
Using ultrasound, you can not only detect the neoplasm itself, but also attribute it to a specific type. Each form of uterine tumor has its own characteristics and differs in its structure and composition.
Doctors distinguish several types of uterine formations depending on the ratio of connective and smooth muscle tissue.
- Uterine leiomyoma contains predominantly smooth muscle cells, while the amount of connective tissue is small.
- Uterine fibroids are distinguished by a significant percentage of connective tissue rather than smooth muscle cells.
- Uterine fibroids consist entirely of connective tissue.
Clinically and in terms of disease prognosis, there is no significant difference between fibroids, fibroids and fibroids.
Myoma differs from fibroma and fibromyoma only in histological characteristics. There are no significant differences in the choice of treatment tactics.
Fibroids, like fibroids or fibromyomas, contain blood vessels that feed the uterine formations. The peculiarity of these vessels is that they are not only a source of nutrition, but also possible uterine bleeding.
There is a difference between exophytic and endophytic growth of tumors. Exophytic progression is characterized by the growth of fibroids, fibromyomas and fibroids into the pelvic area. With such developmental features, signs of compression of neighboring organs usually appear.
- 1 Diagnostic features
- 2 Treatment
Diagnostic features
There is no difference in the diagnostic method. Any examination begins with an examination by a doctor.
Typically, fibroids, myomas and fibroids are distinguished by their progression in the form of nodules. Tumor-like formations go through several stages in development from a tiny nodule to the size of a full-term pregnancy (rare).
The size of the nodes is determined in weeks of pregnancy.
As the nodule reaches a significant size, a characteristic clinical picture appears. While small tumors often progress hidden.
In order to distinguish myoma, fibroid and fibromyoma, it is necessary to conduct instrumental diagnostics.
- Ultrasound. Modern gynecology considers this technique one of the most valuable types of diagnostics. Ultrasound examination allows us to evaluate the location, size, composition of the tissue, as well as the nature and intensity of the blood supply.
An ultrasound machine detects the difference between the tissue composition of uterine fibroids and other formations consisting of smooth muscle tissue.
There is also a difference between the number of vessels supplying the nodes, which can vary significantly.
- Histological examination. Since there is a difference in the histological structure of different tumors, this method makes it possible to accurately determine their type. However, the study can be carried out after direct removal of fibroids, fibroids or fibroids. With submucosal growth of neoplasms, it seems possible to perform aspiration or other types of biopsy from the uterine cavity. At the discretion of the doctor, it is possible to perform diagnostic laparoscopy for the purpose of biopsy and more detailed examination of fibroids.
Gynecologists also widely use other methods as part of the examination. In particular, MRI, CT, and Doppler sonography are performed. Before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to perform a blood test for the content of sex hormones due to the hormone-dependence of the pathology.
Treatment
Despite the possibility of determining the type of formation, there is no difference in their treatment. First of all, the size and location of the tumor matters.
Myomas, fibroids and fibroids differ in the following sizes:
- small – up to 3 cm;
- medium – up to 8 cm;
- large and gigantic over 8 cm.
The difference is also observed in the localization of tumors:
There is a difference in the location of fibroids, fibroids and fibroids in relation to the uterus:
- intramural;
- submucosal;
- subserous;
- intraligamentary;
- retroperitoneal.
Submucosal as well as intramural neoplasms are characterized by the appearance of uterine bleeding or heavy discharge that accompanies menstrual periods.
Many patients are interested in whether there is any difference regarding the treatment of fibroids, fibroids and fibroids. There is no difference in the treatment of these pathologies, despite the fact that they differ histologically.
However, each species has its own growth characteristics. Uterine leiomyoma is characterized by fairly rapid progression. The difference also lies in the fact that uterine leiomyoma is more susceptible to hormonal influences.
Myomatous nodes are more often treated surgically, in particular, myomectomy, hysterectomy and uterine artery embolization. In the absence of certain features of the course, for example, a pronounced clinical picture, the pathology can be treated medicinally through hormone therapy.
The difference between fibroids and uterine fibroids is their slow progression. Observation and wait-and-see tactics are often used for these nodes.
The histological difference may be the slow destruction of pathological cells. Fibromatous nodes are not characterized by rapid degeneration into normal tissue.
Accordingly, conservative therapy is not always successful for this type of disease.
Gynecologists say that histological differences may be the basis for choosing surgical tactics.
In particular, the difference plays a role when taking into account postoperative complications.
Source: https://proctologys.ru/zhenskoe-zdorove/chem-mioma-otlichaetsya-ot-fibromy-matki/
The difference between uterine fibroids and fibroids
Uterine fibroids are one of the most common diseases that force a woman to seek medical help.
After the age of 40, fibroids become a reason to visit a gynecologist in 20% of cases. From different doctors you can hear names of pathologies that are similar to each other, but still different.
For example, fibroids and uterine fibroids - what is the difference between them? Or can these words be considered synonyms?
Histological structure of the uterus
The wall of the uterus is formed by three layers:
- Internal mucosa - endometrium;
- Middle, muscular – myometrium;
- The outer layer is the serous membrane.
The thickest part is the myometrium. It is formed by three layers of smooth muscle cells mixed with connective tissue and elastic fibers.
Histological structure of normal myometrium.
The direction of muscle fibers in different layers of the myometrium is different:
- The outer layer is tightly fused with the serous membrane. The fibers are arranged mainly longitudinally, but a small part of them are arranged in a circular manner;
- Middle layer - the fibers are arranged in a circle (they are especially well expressed in the cervix area). A large number of vessels pass through here, primarily veins, which is why it is also called vascular;
- The inner layer is the thinnest, the fibers in it are located longitudinally.
During pregnancy, the growth of the uterus occurs due to an increase in the number and size of muscle cells (as a result of the processes of hyperplasia and hypertrophy). At the same time, collagen synthesis increases, which makes the uterus more elastic. After birth, some myocytes die, others return to their original size. Collagen is also destroyed under the action of special enzymes.
Based on the histological structure of the uterus, tumors of various types often arise in it. These can be benign and malignant pathologies. Benign tumors of the uterus are described in more detail in the article: “Uterine fibroids and its treatment.”
Microscopic structure of fibroids
To unify the calculations, the size of the uterus with a tumor is compared with the week of pregnancy. The longer the period, the larger the size. This can be seen in the photo below.
Various sizes of myomatous nodes.
The general name for benign myometrial tumors is the term “fibromyoma”.
This tumor is caused by primary damage to a single cell, and therefore is monoclonal - all myocytes in it are the result of the division of this damaged cell.
Myoma is considered a hormone-sensitive tumor; it responds to changes in the concentration of estrogen and progesterone and, under the influence of the latter, is capable of increasing its growth.
The ratio of muscle and connective tissue elements in a tumor can be different, so all synonymous names do not mean the same thing. The predominance of myocytes allows the tumor to be called a fibroid.
If there are more fibrous connective tissue elements in the node, then they speak of fibroma. If the vast majority of cells are muscle cells, this is a leiomyoma. But this condition is very rare.
Uterine leiomyoma: a tumor composed of smooth muscle cells that form randomly arranged bundles of varying thickness (1).
It is noticed that first the first muscle cell appears in the lesion, which differs from its neighbors. She begins to multiply. The primary lesion is located diffusely and does not form a capsule delimiting it from other tissues.
The muscles of the neoplasm are initially arranged in the form of a ball, later vessels and connective tissue structures grow into it.
It is also useful to read: Removal of fibroids using conservative myomectomy
There is also a difference in the arrangement of muscle fibers from that in the normal structure of the uterus. They form a looser structure, which is confirmed by the nature of the staining of histological preparations. The shape of the nuclei in cells is variable, it can be from spindle-shaped to oval.
Then the fibroids begin to gradually form layers of connective tissue. From now on it can be called fibromyoma. At this stage of tumor development, smooth muscle cells (myocytes) contain many myofibrils. Collagen and elastic fibers are located in large quantities between the myocytes.
On the left is the histological structure of fibroids, on the right is normal myometrium.
Tumor growth occurs concentrically. In this case, the fabrics are layered on top of each other. A capsule is formed from an area with a predominance of connective tissue elements. There are very few vessels in the nodes, and those that feed it are located in the thickness of the capsule. There are no lymphatic vessels in the tumor.
The biochemical composition of substances isolated from fibroids resembles those during pregnancy. The cells contain a lot of ATP - the main energy material, glycogen, electrolytes in the form of potassium and calcium ions, which are necessary for uterine contractions.
On a note
Considering the mechanism of formation of the node, some researchers believe that fibroids are leiomyomas that have undergone the development of fibrosis.
Classifications of fibroids
There are several approaches to determining the type of tumor. Some of them base the stage of development of the pathological focus, or three stages of morphogenesis:
- Formation of an active rudiment with impaired metabolism;
- Tumor without signs of differentiation;
- Differentiation and maturation of the node.
Based on tissue composition, there are broader classifications:
- Leiomyoma;
- Fibroids;
- Angiomyoma;
- Adenomyoma.
Myometrial histology: (A) normal myometrium, (B) fibroids, (C) leiomyosarcoma.
Additionally, there are three morphogenetic types of fibroids:
- Simple - develops as benign muscular hyperplasia, there are no atypical cell mitoses;
- Proliferating – morphological criteria for a benign myometrial process are present, 25% of mitoses are observed;
- Presarcoma - occupies an intermediate position between sarcoma and a benign tumor, but does not necessarily become malignant. The number of atypical mitoses can reach 75%.
They also say that the growth of fibroids can be true or false. True growth is characterized by proliferation of myometrial smooth muscle. False growth occurs due to increased fibril formation by muscle cells, degenerative changes in the nodes and edema.
Degenerative processes in nodes
Given the initially poor blood supply to fibroids, it should be noted that it tends to worsen.
During pregnancy, this deterioration can reach a critical level, then red degeneration develops.
In the photo of the macroscopic specimen, you can see in detail how a sudden disruption of blood flow occurs in the node. Sometimes the symptom goes away on its own, but is accompanied by severe pain.
Malnutrition in a myomatous node (macropreparation).
With the rapid growth of the node and insufficient tissue trophism, hyaline degeneration develops, which is characterized by the deposition of a protein substance (hyalin) in the fibroid. Sometimes impaired blood flow leads to the appearance of foci of necrosis.
In its place, cavities form and cystic degeneration occurs. With a long course of the pathological process, calcium salts accumulate in the foci and calcifications appear.
They are sometimes found in histological preparations of women who have been “growing” fibroids for a long time.
It is also useful to read: Causes of uterine fibroids
Features of the disease
Despite the difference in histological structure, most doctors do not distinguish between the concepts of fibroids and fibrous node. The basis of tumor pathogenesis is the same processes, which are not fully understood.
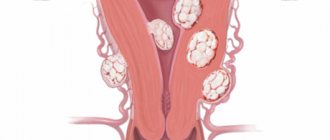
Clinical manifestations also do not allow differentiation of the histological structure of the node. What matters most is the type of growth:
- Subserous;
- Interstitial;
- Submucosal.
Types of myomatous nodes depending on location.
This affects the clinical picture of the tumor process and the characteristics of treatment tactics. For example, with a submucosal location, it is possible to remove nodes through vaginal access. In other cases this cannot be done.
But in the presence of interstitially located neoplasms, as well as other types of fibroids, they are increasingly resorting to new technologies - uterine artery embolization or FUS ablation.
These treatments help get rid of the tumor without penetrating the abdominal cavity.
The predominance of muscle elements leads to their necrosis.
In large tumors, the reduction in size also occurs due to muscle tissue, but there are much more fibrous elements there, so it is impossible to completely get rid of large fibroids using UAE or FUS ablation.
Dynamics of uterine fibroid reduction after FUS ablation.
Drug treatment in the early stages can be effective if combined drugs are used. Pure progesterone in this case, as numerous studies show, is harmful to a woman’s health. Under the influence of the hormone, fibroids begin to grow more actively, so instead of treatment, the opposite effect is observed.
Hormonal drugs that block the production of estrogen and lead to temporary artificial menopause are not effective in the long-term treatment of fibroids.
If you turn off the ovaries, the tumor without estrogen support will begin to decrease in size, regardless of the histological type.
But when you stop using the drug, it will resume its growth, sometimes even with greater force.
Hormonal drugs can only temporarily stop the growth of the tumor or reduce it in size.
Thus, for a specialist, different terms denoting a benign tumor of the uterus reflect the difference in the structure of the tumor, its histological features, stage of development and some other nuances. And for ordinary female gynecologist patients, the names fibromyoma, myoma, leiomyoma should sound like synonyms for one pathological process.
Differences between fibroids and fibroids
Source: https://mioma911.ru/opuxolevye-zabolevaniya-matki/mioma/fibroma-i-mioma-matki-v-chem-otlichie.html
Classifications of fibroids
There are several approaches to determining the type of tumor. Some of them base the stage of development of the pathological focus, or three stages of morphogenesis:
- Formation of an active rudiment with impaired metabolism;
- Tumor without signs of differentiation;
- Differentiation and maturation of the node.
Based on tissue composition, there are broader classifications:
Myometrial histology: (A) normal myometrium, (B) fibroids, (C) leiomyosarcoma.
Additionally, there are three morphogenetic types of fibroids:
- Simple - develops as benign muscular hyperplasia, there are no atypical cell mitoses;
- Proliferating – morphological criteria for a benign myometrial process are present, 25% of mitoses are observed;
- Presarcoma - occupies an intermediate position between sarcoma and a benign tumor, but does not necessarily become malignant. The number of atypical mitoses can reach 75%.
The difference between fibroids and fibroids
Fibroids and fibroids: what's the difference? This question worries many women who do not have a medical education. Often the doctor simply voices the diagnosis and does not bother with explanations. How serious is this disease and what to expect in the future?
The female body is a complex mechanism. It is constantly subject to changes and hormonal changes. What are the costs of pregnancy and childbirth! At the same time, the woman manages to look beautiful, attractive, and desirable. But women’s health often fails.
Decoding medical terms
Myoma, fibroma, fibromyoma are the names of benign tumors of the uterus. The difference lies in the structure of the neoplasm.
Myoma translated from Greek means “muscle”. In simple words, it is a benign tumor that contains more muscle tissue. The nodes are laid in the fibers, take root, grow in the uterine wall, grow towards the abdominal cavity or throughout the entire uterine mucosa.
Uterine fibroid is a benign tumor composed of connective tissue.
If the neoplasm contains 50/50 muscle and connective fibers, then the tumor is usually called fibromyoma. The process of occurrence and development of uterine fibroids begins in the same way as the previous type. Comes from muscle fibers. Then the connective tissue grows. The structure becomes mixed.
This tumor has the shape of a circle and varies in size. A barely noticeable formation can be detected during an x-ray examination of the uterus. A large tumor is easy to notice with the naked eye or by palpating the organ. Sometimes the weight of the tumor is 1 kg. Since the location is completely different, experts distinguish several types of fibroids based on these criteria:
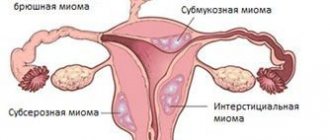
- Submucous fibroid of the uterus - grows under the mucous membrane and moves towards the location of the uterus.
- Interstitial (intermuscular) fibroma - located in the walls of the uterus. At the beginning, there is no pain. As the tumor grows, it changes the size and appearance of the uterus and puts pressure on nearby organs. Pain and discomfort occurs.
- Subserous fibroids - the location is the upper part of the uterus, closer to the abdominal cavity.
So, the difference between fibroids and uterine fibroids becomes theoretically clear. How to distinguish it in practice, and what sensations arise in the presence of a benign tumor?
Symptoms of a tumor
Among all gynecological diseases, myoma and fibromyoma make up 12%. In 95%, the body of the uterus is affected, in 5% - the cervix. Women who reach 30 years of age are at risk.
However, according to experts, fibroids can appear after puberty. Very often, a benign tumor does not reveal itself until it significantly increases in size.
The developing formation begins to put pressure on other nearby organs, causing a feeling of discomfort and pain.
Numerous uterine fibroids and fibroids begin growing in the core of the uterus and grow in different directions. They give themselves away by bleeding, painful sensations, irregular menstruation, and anemia. Or they can occur without any symptoms.
Neoplasms arise mainly due to an imbalance of hormones and can disappear on their own at the onset of menopause. The so-called “shrinking” myomas and fibroids do not cause much trouble.
Fibroids respond well to drug treatment. The patient simply must be under the supervision of a gynecologist.
Uterine fibroids and fibroids have the ability to grow rapidly. The process can only be stopped surgically.
Clinically, the neoplasm manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- heavy periods;
- prolonged absence of menstruation;
- cycle disruption;
- frequent urination;
- constipation;
- anemia;
- painful sensations during intimacy;
- pain in the lower abdomen, lower back;
- discomfort in the intestines and bladder;
- increase in abdominal volume.
Asymptomatic neoplasms can be detected by a gynecologist during a regular examination or during an ultrasound. The woman will have to constantly visit the doctor to monitor the growth of fibroids and undergo treatment.
The main differences between the neoplasms:
- Myomas consist of muscle tissue, fibroids – connective tissue, fibroids – 50/50.
- Myoma undergoes a medical treatment process. Fibroids are eliminated conservatively.
- Over time, fibroids may shrink in size on their own. Fibroids are quite unpredictable.
Thus, it is quite difficult to distinguish one disease from another. Apart from pronounced differences in structure, there are no other significant differences. The disease is classified into one class. It is almost impossible to determine myoma and fibromyoma based on the patient’s symptoms and sensations.
Source: https://dolojparazitov.ru/medicina/otlichie-miomy-ot-fibromiomy.html
Causes of uterine fibroids
The reasons for the development of uterine fibroids have not been reliably established to date. However, experts note a connection between the growth of this benign tumor and the level of estrogen in the female body. In addition, the occurrence of the disease can be triggered by the following negative factors:
- hereditary predisposition to the development of neoplasms in the uterus;
- uncontrolled long-term hormonal contraception;
- violation of the hormone-producing function of the ovaries;
- long-term insolation;
- absence of pregnancy and childbirth in a woman over 30 years of age;
- hemodynamic disturbances in the pelvis;
- inflammatory processes in the uterus and its appendages;
- the presence of cysts in the ovaries;
- abortions and diagnostic curettages.
Fibroids and uterine fibroids: what is the difference?
04.08.2017
A woman’s body is a rather complex mechanism, so it is more often subject to various changes and hormonal changes.
The most common female diseases are myoma and fibromyoma. What is the difference between these two diseases?
Myoma and fibroma
Myoma and fibroma are two benign neoplasms that are localized in the uterus. They have one difference from each other - the structure and structure of the tumor. Myoma is translated from Greek as “muscle”.
That is, the structure of fibroids includes muscle tissue. Myoma nodules are initially localized in the fibers and then grow to the uterine walls. After this, they spread into the abdominal cavity or along the inner uterine lining.
Uterine fibroids are a benign neoplasm consisting of connective tissue.
Fibroids form and develop in the same way as regular fibroids. Initially, the neoplasm is formed from muscle tissue, and then grows with connective tissue. Thus, the structure of fibroids is mixed.
The formation is round in shape and can be of different sizes. When the tumor is small, it can only be diagnosed by x-ray examination of the uterus.
If the neoplasm is large enough, then it can be diagnosed by palpation. It is not uncommon for a tumor to grow to weigh one kilogram. Since the neoplasm can be localized in various areas of the uterus, doctors divided them into several types:
- Submucous uterine fibroids. It begins its development from the inner shell and moves towards the uterus itself;
- interstitial fibroma. The neoplasm is localized in the uterine walls. As soon as it begins to develop, the woman does not experience much discomfort. Pain syndrome can only begin when the tumor begins to grow to a large size and put pressure on nearby organs;
- subserous myoma. Localized in the upper part of the uterus near the peritoneal cavity.
We looked at the internal differences between the two neoplasms, but is it possible to distinguish them from each other based on their symptoms?
Symptoms
Fibroids and fibroids account for 13% of all pathological processes in gynecology. In 93% of women, such neoplasms lead to damage to the uterine body, and 7% to damage to the cervix. Most often, such diseases are diagnosed in women aged 30 years and older.
But doctors do not rule out the fact that the formation of fibroids can be triggered by puberty. Most often, at the initial stage of development, the pathological process is asymptomatic.
But as soon as the tumor reaches a large size, the woman experiences discomfort and acute pain in the lower abdomen.
As a rule, myoma and fibroids begin their development in the uterine nucleus, and then spread in different directions. As a result, bleeding may begin, developing into anemia; pain syndrome and disruption of the menstrual cycle. Such symptoms are a result of hormonal imbalance, but with the onset of menopause, all symptoms subside.
Myoma is easily treatable with medication. The main thing is to diagnose it in time. Therefore, doctors recommend being checked by a gynecologist once a year.
Compared to fibroids, fibroids develop more rapidly. It is possible to rid a woman of such a tumor only through surgical intervention. These tumor processes are characterized by the following external manifestations:
- heavy bleeding during the menstrual cycle;
- prolonged absence of menstruation;
- menstrual irregularities;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- constipation;
- anemia;
- pain during sex;
- increased gas formation;
- abdominal enlargement.
If there are no symptoms, but a tumor develops, then it can only be detected by ultrasound.
What is the difference between fibroids and fibroids?
- The structure of fibroids includes muscle tissue, and the structure of fibroids includes connective tissue;
- Myoma can be cured with drug therapy, but fibroids can only be cured with surgery;
- Over time, fibroids may shrink, which cannot be said about fibroids;
Sometimes it is very difficult to distinguish fibroids from myomas, since they are no longer distinguished by differences in structure.
Reasons for development
There are a number of factors that provoke the tumor process. The development of fibroids and myomas begins as a result of:
- two or more instrumental abortions;
- surgical intervention in the uterine cavity;
- obesity;
- various gynecological diseases;
- disturbed hormonal balance;
- bearing a child and the birth process after 35 years;;
- genetics;
- sexual intercourse with more than one partner;
- cardiovascular pathologies.
Basically, fibroid nodules develop as a result of ovarian dysfunction caused by hormonal imbalance.
If estrogens predominate over all hormones in a woman’s body, then this is the first step towards the development of a tumor process.
Also, the development of benign tumors is influenced by a woman’s weak immune system. If treatment is not started in time, there is a risk that a benign tumor will become malignant.
Diagnostics
A gynecologist can notice the formation during an examination. The course of tumor processes is characterized by changes in the structure and shape of the uterus. As a rule, it increases in size, and the walls lose their smoothness.
Lumps and irregularities begin to form on them. The final diagnosis can be confirmed using ultrasound. Also, ultrasound can determine the exact size of the tumor, its location, and in which direction the growth is directed.
Also, the size and number of nodules are determined.
In 1/4 of women, the pathology is diagnosed as a result of the appearance of unpleasant symptoms; in other cases, tumors are diagnosed during various studies.
As soon as the doctor makes a final diagnosis, appropriate treatment begins. As we said above, fibroids can be treated with drug therapy, but fibroids must be removed surgically.
Every woman should be attentive to her health.
Pain in the lumbar and lower abdomen or discomfort during intimacy, unusual discharge or disrupted menstrual cycle - all this indicates that you need to visit a gynecologist.
Fibroids, if detected at an early stage of development, are easily treated with medications. And when the tumor process is advanced, surgical intervention is generally indicated. Especially if it is fibroids.
Timely diagnosis and treatment of tumor formations prevents their further development.
Source: https://wmedik.ru/zabolevaniya/onkologiya/fibroma-i-mioma-matki-v-chem-otlichie.html
What is the difference between fibroids and fibroids?
Benign tumors of the uterus are often diagnosed in women, especially those of reproductive age. There are certain differences in the structure of these neoplasms. As a rule, we are talking about tumors of smooth muscle tissue.
Myoma, fibromyoma and uterine fibroid occur in more than 80% of representatives of the reproductively active age group, which indicates the prevalence of the pathological process.
In most cases, these diagnoses are combined into one term “fibroids”.
When it comes to fibroids and myomas, what is the difference between these two diagnoses? Many women are also interested in the difference between fibroids and fibroids.
Using ultrasound, you can not only detect the neoplasm itself, but also attribute it to a specific type. Each form of uterine tumor has its own characteristics and differs in its structure and composition.
Doctors distinguish several types of uterine formations depending on the ratio of connective and smooth muscle tissue.
- Uterine leiomyoma contains predominantly smooth muscle cells, while the amount of connective tissue is small.
- Uterine fibroids are distinguished by a significant percentage of connective tissue rather than smooth muscle cells.
- Uterine fibroids consist entirely of connective tissue.
Clinically and in terms of disease prognosis, there is no significant difference between fibroids, fibroids and fibroids.
Myoma differs from fibroma and fibromyoma only in histological characteristics. There are no significant differences in the choice of treatment tactics.
Fibroids, like fibroids or fibromyomas, contain blood vessels that feed the uterine formations. The peculiarity of these vessels is that they are not only a source of nutrition, but also possible uterine bleeding.
There is a difference between exophytic and endophytic growth of tumors. Exophytic progression is characterized by the growth of fibroids, fibromyomas and fibroids into the pelvic area. With such developmental features, signs of compression of neighboring organs usually appear.
Conclusions TheDifference.ru
- Myoma is a benign formation consisting primarily of muscle tissue. Fibromyoma is a tumor that grows from muscle tissue, but subsequently acquires a fibrous structure due to the proliferation of connective tissue.
- In fibroids, muscle fibers predominate; in fibroids, connective tissue predominates.
- In most cases, fibroids do not require surgical intervention and can resolve on their own by the time of menopause. Fibroids are capable of rapid growth, so their treatment often requires surgical intervention.