The main reasons why the ovary is not located on ultrasound
Thanks to the pelvic organs, the most important event in the life of every girl occurs - the onset of pregnancy, which the majority of the female population dreams of. Therefore, after undergoing an ultrasound examination, some are shocked and puzzled by its results: what does “the ovary is not visualized” mean, what is it and is there any threat? The main task facing a woman in such a situation is not to lose heart. There are many reasons why the ovaries are not detected. They require more detailed consideration.
Why is ultrasound performed?
Typically, a woman should register before 12 weeks of pregnancy, this will allow qualitative observation of the development of the fetus and the condition of the mother.
Despite the serious diagnostics that healthcare offers today, ultrasound remains the only sure way to obtain objective information about the baby’s condition. Although in some cases, poor visualization on an ultrasound examination may be observed, and the doctor will definitely notify the mother about this.
Thanks to this technique, the doctor receives the following information:
- the degree of provision of the baby with oxygen and nutritional compounds;
- functional features of organs.
And in this, great importance is attached to the second screening, which is carried out at 20 weeks of pregnancy. The specialist first of all examines the baby’s internal organs, the structure of his body, he also determines the gender of the child, and this is the most desired information for many.
Ultrasound also evaluates the condition of the mother's birth canal. The second ultrasound also evaluates the condition of the placenta. It must be said that at this time pregnancy may experience various disturbances.
Anatomical location of the pelvic organs
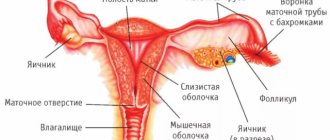
Before considering the reasons why the ovaries are able to hide from view, it is necessary to understand the structure of the pelvic organs. It contains the following organs:
- the rectum, through which processed food comes out;
- the bladder in contact with the walls of the vagina and the uterus;
- the vagina, which is adjacent to the cervix and passes through the urogenital diaphragm;
- the uterus, which is pear-shaped and consists of muscles; performs reproductive function;
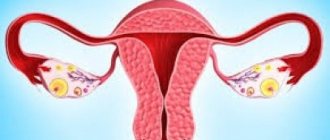
- two ovaries, which produce hormones and are responsible for the maturation of eggs;
- fallopian tubes that connect to the ovaries on either side of the uterus.
The ovary is not visualized, what does this mean, reasons for poor visualization of the right or left ovary
Thanks to the pelvic organs, the most important event in the life of every girl occurs - the onset of pregnancy, which the majority of the female population dreams of.
Therefore, after undergoing an ultrasound examination, some are shocked and puzzled by its results: what does “the ovary is not visualized” mean, what is it and is there any threat? The task facing a woman in such a situation is not to lose heart.
There are many reasons why the ovaries are not detected. They require more detailed consideration.
Localization of the ovaries
The ovaries are paired glands of the female reproductive system, located in the pelvis, on both sides of the uterus. Normally, the glands are located to the right and left of the midline of the abdomen in the groin area.
They are connected to the uterus and the walls of the small pelvis using connective tissue cords - ligaments in which the blood vessels and nerve fibers that feed them pass. The upper part of the glands is in contact with the fallopian tubes.
The collection of ovaries and fallopian tubes is called the appendages.
Although the gonads do not directly contact the abdominal cavity, loops of the large intestine are located above them. This localization feature often leads to the fact that the ovaries are not located during ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs due to shielding by the large intestine.
Under the influence of various factors, the location of the gonads can change significantly.
For example, during pregnancy they are shifted to the sides by the growing uterus; with a sharp decrease in body weight and a decrease in the volume of fatty tissue, the ovaries can move inside the pelvic cavity.
Adhesive processes often lead to the fact that the glands are located above the normal location or lie very close to the walls of the uterus.
Features of structure and functioning
The ovaries are covered with a connective tissue membrane, under which the cortex and parenchyma of the organ are located. As the follicle matures, it moves to the edge of the ovary and during ovulation, the egg is released into the abdominal cavity where it is captured by the fallopian tubes.
The female gonads perform two main functions.
- Reproductive function . The ovaries contain eggs that mature during the monthly cycle. Unlike the male body, in which the formation of sperm occurs throughout life, the number of eggs in a woman is limited (about 1 million) and is laid during the period of intrauterine development. This is the so-called follicular reserve, which will be used up during the reproductive period of a woman’s life (from 13 to 55 years).
- Endocrine function . The gonads synthesize substances that determine the female hormonal profile: estrogens, progesterone, and also a small amount of androgens. The work of the ovaries is under the control of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, which produces luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones.
Normal parameters of the ovaries according to ultrasound
In the absence of pathological processes, the ovaries have a shape close to oval with smooth, clear contours. Their sizes average 19–40 mm in length and 16–30 mm in width. Changes in the boundaries of the gland are considered normal only at the time of ovulation and the release of the egg.
In addition to the size of the organ, the doctor evaluates the volume of the parenchyma and its structure. Normally, it has a uniform consistency and makes up approximately 2/3 of the total volume of the gland. The number of small follicles in the early stages of development is also counted.
For a successful pregnancy, their number must be at least 20. A decrease in their number is one of the evidence of depletion of the follicular reserve and the imminent onset of menopause.
To avoid errors, the procedure should be performed like this
- the patient should present for examination with a full bladder
- you need to take a side position on the couch
- the researcher begins work by carefully adjusting the sensitivity of the device (if the parameter is set at high frequencies, there is a chance that the right ovary will not be visible.
The left ovary is often not visible due to poor filling of the bladder: the organ is hidden behind the fundus of the uterus, not visualized during the study. If this happens, you should drink more water and repeat the procedure after half an hour.
But in some cases, the amount of liquid you drink and the settings of the device do not matter much. The organ does not appear in the doctor’s field of vision. This can happen due to excessive filling of the intestines with gases.
Why are the ovaries not visible on ultrasound?
Ultrasound examination is the main way to quickly and effectively visualize the organs of the female reproductive system.
Using ultrasound, you can determine the size, shape, location of the glands, estimate the approximate number of follicles and the stage of the monthly cycle, and also identify the leading ovary.
For example, if the left ovary is not located, this means that the main functional load is borne by the right gland.
As a rule, ultrasound of the pelvic organs is performed in two ways: transabdominal and transvaginal.
During a transabdominal examination, the doctor places the device’s sensor on the anterior abdominal wall in the area where the uterus and appendages are projected onto it.
In some cases, to obtain a clearer picture, the study must be performed with a full bladder. To do this, an hour before the diagnosis you need to drink about a liter of liquid and after that do not visit the toilet.
During a transvaginal examination, the probe is inserted directly into the vagina. This method allows you to clearly visualize the appendages, uterus, and assess the condition of the endometrium. If there are contraindications for transvaginal examination, diagnostics can be performed by inserting a sensor into the rectum.
Possible reasons why the ovaries are not visualized on ultrasound
In rare cases, the ovary is not visible on ultrasound. As a rule, a repeat ultrasound examination (both transabdominal and transvaginal) is prescribed on another day of the cycle.
Let's consider the main reasons why the gonads are not visualized during diagnosis.
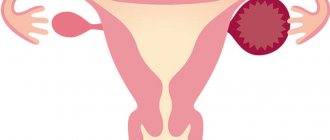
- Congenital malformations . The absence of one or both ovaries as a result of a genetic failure and underdevelopment of the glands. Pathology is detected in adolescence. The reason for visiting a gynecologist is the absence of menstruation.
- Ovariectomy . Surgical removal of glands if necessary to treat endometriosis, cysts, tumors, etc. The patient is usually aware of the situation and can inform the doctor about it.
- Significant reduction in the size of the glands . It is observed during menopause, when the process of involution (reverse development) and fatty degeneration of organs predominate in the female reproductive system. If a similar picture is observed in women of reproductive age, then this may indicate exhaustion of the reproductive system and early menopause.
- Abnormal location of organs . Most often, this situation is associated with some pathological process in the pelvis. Thus, with adhesive disease, one of the ovaries may be located behind the uterus or move upward, attracted by adhesions.
- Pregnancy . The increase in the size of the uterus, especially in late gestation, greatly complicates the visualization of the gonads.
- Screening with loops of the large intestine . The air environment is impenetrable to ultrasonic waves. A gas-inflated cecum is one of the possible reasons why the right ovary is not visualized during diagnosis.
What are gallstones?
Gallstones are a sign of cholelithiasis.
It is usually detected by ultrasound and can come as a surprise to the patient, because small stones do not cause severe attacks of pain, and a person may not be aware of their existence.
Of course, if a large stone closes the duct, it causes an attack similar to hepatic colic, and the patient will already learn about it on the surgical table. Let’s find out in detail how stones appear and what their varieties are.
Why are the ovaries not located on ultrasound?
The specialist may say that the ovaries are not located. What does it mean? Why is this happening? In simple words, if the ovary is not visible on an ultrasound, this means that the monitor shows the absence of an organ, i.e. it is not defined. With its presence, on the ultrasound picture in the conclusion they write that they are determined. In frequent cases, organs may not be located due to the incompetence of the gynecologist, who, due to his incompetence, simply could not see the organs on the monitor or adjust the sensors.
Normally, the contours of the ovaries in a healthy woman are uneven and clear. Fuzzy contours may indicate inflammation, cystic formations, or the presence of a corpus luteum. Blurred - they speak of a disease such as salpingoophoritis - inflammation of the uterine appendages. With a fuzzy outline and reduced size of the ovaries, the ultrasound picture indicates the probable onset of menopause.
Visualization also depends on the correctness of the ultrasound examination and the operation of the instruments. During transabdominal ultrasound, the patient should drink a lot of water to fill the bladder, since if there is a lack of fluid, the left ovary may disappear behind the uterus. Before a transvaginal ultrasound, you should empty yourself, because the sensor is inserted into the vagina and its location to the organs becomes close, and the liquid during this study makes it difficult to see what is happening inside.
Is it possible to do ultrasound diagnostics during menstruation? Read the article Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and menstruation
Intestinal disorders
The first most popular organic reason for not seeing the left or right ovary is a large accumulation of intestinal gases, flatulence, and fullness of the intestines after eating. As a rule, in the next study the organ appears in the field of view.
Previous surgical interventions
After gynecological operations, the organ is not located, because the stress suffered by the body can disrupt its functioning for a certain time, as a result of which the organ may shrink, down to the size of a pea.
Taking birth control pills
OK drugs are used to treat hormonal disorders and contraception. They suppress the hormones produced by the ovaries in order to prevent the eggs from maturing, thereby eliminating the possibility of ovulation for fertilization.
The embryo is not visualized: what does this mean, why is the embryo not visible at 5–6 weeks of pregnancy?
Most women find out they are pregnant 5-6 weeks after conception. During this period, the embryo is already actively developing. The formation of vital organs occurs.
Gynecologists often prescribe their patients the first ultrasound examination at this time. Ultrasound is designed to assess the diameter of the fertilized egg and the site of its implantation. There are situations when the embryo is not visualized during this procedure.
Why is the embryo not visible at 5–6 weeks of gestation? What to do if it is not located in the mother's womb?
At what stage is the embryo visible during ultrasound?
For each woman, the process of bearing a child is individual, so it is quite difficult to say definitely at what stage of gestation the embryo is visible. Despite this, there are certain standards for its initial visualization.
At 5–6 weeks of pregnancy, the diameter of the ovum is about 7 mm.
If a woman has a regular menstrual cycle before conception, an ultrasound examination at this stage in most cases results in relatively clear visualization of the embryo.
Ultrasound at 5–6 weeks of pregnancy: what should a specialist see?
The main purpose of performing an ultrasound during this period is to confirm the fact of fertilization of the egg. This issue is especially relevant when conceiving using IVF. The sonologist during this diagnostic procedure at 5–6 weeks of gestation:
- confirms embryo implantation and its location;
- excludes the presence of neoplasms in the uterus, which can be mistaken for pregnancy;
- assesses the viability of the embryo;
- checks to see if there are other embryos in the uterine cavity;
- excludes ectopic pregnancy;
- specifies the gestational age.
Why is the embryo not visualized?
Sometimes during an ultrasound at 5–6 weeks of pregnancy, there is no visualization of the embryo. There are many reasons for this phenomenon. The sonologist may not be able to see the embryo due to the presence of objective (pathological and physiological) and subjective factors. Urgent treatment measures are not always required.
Error in determining the gestational age, errors in the operation of equipment and sonologist
If the fetus is not visualized during the examination, the reason most often lies in incorrect determination of the gestational age. When an ultrasound is done at 3 or 4 weeks of gestation, the ultrasound machine is not able to detect the presence of an embryo in the uterine cavity. Until 5 weeks, the size of the fertilized egg does not exceed 2 mm, which makes its visualization impossible.
The embryo is often not located in the uterus due to the characteristics of the ultrasound scanner. To “see” the embryo, the device must have a certain sensitivity. In addition, its malfunction can also distort the image on the monitor, as a result of which the diagnostician will not be able to confirm the fact of pregnancy.
A functional diagnostics specialist must have sufficient practical experience and qualifications. Lack of knowledge and work experience is the likely reason that the embryo is not visualized during ultrasound examination in the early stages of gestation.
Absence of embryo in fertilized egg
There are many reasons for this problem, and it is not always possible to determine why this happened. Among the most common factors that provoke the occurrence of anembryonia are:
- infectious processes, including those transmitted during sexual contact;
- genetic abnormalities;
- intoxication of the expectant mother’s body with medications and household chemicals;
- exposure to radioactive radiation.
This pathology does not make itself felt in any way in the early stages of gestation.
Since the risk of an erroneous diagnosis cannot be excluded, a few days after the ultrasound, during which the absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg was revealed, it is recommended to do a repeat examination, preferably on a different device. To avoid this problem, doctors advise patients to plan their pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancy
The likely reason that during an ultrasound examination of a pregnant woman the embryo is not visible on the monitor of the ultrasound scanner is an ectopic or ectopic pregnancy.
In this case, the consolidation and development of the fertilized egg occurs outside the uterus. As a rule, in such a situation it is found in the fallopian tubes.
However, the possibility of its implantation in the abdominal cavity, cervix, and ovaries cannot be ruled out.
In addition to the cessation of menstruation and an increase in the concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin, the presence of this pathological process is indicated by the absence of a fertilized egg in the uterine cavity.
During an ultrasound, it is detected in the area of the appendages or cervix in the form of a space-occupying formation.
If during the study the visualization of the fetal egg is hampered by its small size and poor audibility of the heart, at the 7th week the increasing size of the membranes provokes deformation of the surrounding tissues, which is clearly visible during the diagnostic procedure.
Frozen pregnancy or completed spontaneous abortion
If the development of the embryo stops before the 5-week gestation period, detection of the embryo is impossible, just as in the case of spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
Many women who have a miscarriage in the early stages of pregnancy do not even notice it.
This is explained by the fact that the bleeding that accompanies this pathological process can easily be mistaken for another menstruation.
What to do if ultrasound does not detect a fetus?
If during an ultrasound examination the sonologist cannot see the embryo, it is recommended to undergo a second examination, preferably in another medical institution and using equipment with higher resolution. In addition, it is necessary to donate blood for analysis to determine the level of human chorionic gonadotropin. In this case, the woman should be prepared for the fact that she will have to be examined several times.
Source: https://www.OldLekar.ru/beremennost/analyzi/embrion-ne-vizualiziruetsya.html
Ovaries are not located: what does this mean?
If, as a result of the diagnosis, the doctor made a note: “The ovaries are not located” or “Not visualized” - this means that they are not visible. The cause may be not only developing pathology, but also poor-quality equipment, flatulence that interferes with visualization of the gland, and inaccuracies in the actions of the doctor. Finding it is not so easy due to the location of the pelvic organs.
The glands may not be visible because they are located behind the uterus and bladder. Often they are blocked by the intestines. It is especially difficult to examine the ovaries during menopause, when the size of the organs decreases naturally and they are not visualized.
Why is the left ovary not detected on ultrasound?
The left ovary is not detected on ultrasound when the bladder is not full. Patients underestimate the importance of following the doctor's recommendations in preparing for the examination. The reason is a lack of understanding of the essence of the process.
During an ultrasound scan, the glands, like other pelvic organs, may not be visible. They are covered by intestinal loops. Filled with air, they reflect ultrasound waves, interfering with image transmission, which is why the glands are not visualized. There is a need to create an “acoustic window” - a zone through which the examination could be carried out unhindered. A full bladder becomes just such a zone. If it is not full enough, you need to drink water, take a diuretic and return to the examination in half an hour. The diagnostician will have the opportunity to evaluate the structure of glands that were previously invisible.
Why is the right ovary not visualized on ultrasound?
During ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs, the sensitivity of the sensor must be adjusted. If the sensitivity level is exceeded, the device readings may be unreliable and the ovary is not visualized. Often the right ovary is not detected on ultrasound, access to which is blocked by parametrium tissue (peri-uterine tissue) and bone structures.
Ovaries are not located on ultrasound during menopause
The approach of menopause causes a number of changes in a woman’s body:
- the number of follicles in the glands decreases;
- the production of the hormone estrogen decreases;
- Connective tissue develops, gradually replacing the cortex with numerous follicles.
As a result of the changes, the size of the organs decreases; they are not visualized during the examination.
Ovarian volume depending on age
In a woman of reproductive age, the volume of the ovary is on average 8 cm 3, however, during the premenopausal period, an enlarged organ is a deviation from the norm. Its volume should not be more than 5 cm 3, this condition is regarded as pathological, and the difference between paired organs should not exceed 1.5 cm 3.
During menopause, scanning must be done with a transvaginal probe, otherwise the ovaries will not be visible. By choosing a transabdominal approach, the risk of the glands not being imaged on the monitor increases by 30-50%; the gland is not visualized.
The pancreas is visualized, not located, shielded
Clinical indications for the procedure:
- Abdominal pain in the left hypochondrium, in the pit of the stomach, in the left side.
- Dyspeptic symptoms, frequent bloating.
- Stool disorders (constipation, diarrhea), detection of undigested food residues in stool tests.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Blunt abdominal trauma.
- Diabetes mellitus of any type.
- Yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Suspicion of a tumor.
The manipulation itself takes 10-15 minutes. The patient lies down on a hard, flat surface, usually a couch, first on his back, then on his side (right and left). A special gel is applied to the abdomen, allowing the sensor to glide and enhancing ultrasonic permeability. The specialist moves the sensor over the abdomen in the projection of the pancreas. At this time, a series of images appears on the screen of the ultrasound machine.
Since functional disorders of the pancreas are accompanied by a “bouquet” of recognizable symptoms, an experienced doctor will immediately issue a referral for an ultrasound scan after hearing specific complaints from the patient:
- pain in the left hypochondrium;
- girdle pain in the middle part of the abdomen;
- digestive disorders - loose stools, diarrhea of unknown origin, constipation (may alternate or occur systematically, but irregularly);
- nausea, vomiting, often with increased body temperature;
- bloating, flatulence;
- an increase in the organ or a change in its shape revealed by palpation;
- yellowness of the skin;
- increased blood sugar levels.
Indications for ultrasound examination of the pancreas include:
- pain localized in the left hypochondrium or radiating to this area, which lasts for several weeks;
- discomfort, heaviness or heartburn that occurs even after eating a small amount of food;
- the appearance of a yellow tint to the skin and mucous membranes;
- dysfunction of the digestive system, accompanied by constipation or diarrhea.
Ultrasound of the pancreas
If any of the above symptoms appear, the patient needs a comprehensive diagnosis of all organs involved in the digestive process, including the pancreas.
Shape of the main duct [ edit | edit code]
The shape of the duct can be arcuate, knee-shaped or S-shaped and basically follows the shape of the pancreas. In most cases, the main bend of the main duct is located in the region of the head of the pancreas, and the part of the duct located in the body of the pancreas is more or less straight.
As it passes along the gland, the duct receives smaller ducts, gradually increasing in diameter. All elements of the ductal system are highly variable. Two types of its structure can be distinguished: main and loose.
With the main type, the number of smaller ducts flowing into the main duct is from 18 to 34, and the distance between them ranges from 0.5 to 1.5 cm.
With the scattered type, the number of small flowing channels reaches 60, and the gaps between them are reduced to 0.8-2 mm. [1]
What is the drug treatment for this pathology?
When performing an ultrasound, the doctor examines the pancreas with a special sensor, and an image appears on the screen, from which one can judge its condition. There are several indicators that allow you to determine the norms and pathologies in the structure of the organ.
Wirsung duct on ultrasound
- In a healthy person, the body of the pancreas has a homogeneous structure (minor inclusions no larger than 3 mm are allowed), clear and even contours, and is located in the center relative to the spinal column, exactly under the stomach.
- The brightness and intensity of the image on the monitor depends on the echogenicity of the organ, that is, the ability of its tissues to reflect sound waves - normally the echogenicity of the pancreas is the same as that of the spleen and liver.
- An organ should be clearly visualized on an ultrasound so that the doctor can determine the size of all its parts. The width of the body in the absence of pathologies is 21-25 mm, the head – 32-35 mm, the tail – 30-35 mm.
To assess the large vessels that are located next to the pancreas and supply it with blood, an additional duplex scan of the organ is performed. Interpretation of diagnostic results is carried out taking into account all indicators and is carried out exclusively by the attending physician.
Anatomical variability of the Wirsung duct
With pancreatitis, tumor processes and other diseases of the pancreas, the contours of the organ become blurred, uneven, it increases in size, and echogenicity significantly increases or, conversely, decreases. Sometimes changes are observed in the entire organ, and sometimes in its individual segments.
The causes of the pathology coincide mainly with the causes of the development of pancreatitis and other pancreatic lesions. Since it is possible to determine the causes of the inflammatory process of this organ only in seventy percent of all clinical cases, sometimes the nature of the pathological change remains a mystery. The reasons for the dilation of the Wirsung duct should be determined by a doctor.
Factors that provoke abnormal expansion of the channel are:
- Carrying out surgical operations on the bile ducts and stomach.
- Intestinal diseases along with traumatic injury to the abdominal cavity.
- Regular consumption of alcohol by a person.
- The effect of some medications in the form of antibiotics, as well as estrogens.
- Impact of infectious diseases.
- The appearance of hormonal imbalances.
In some situations, an abnormal expansion of the diameter of the ducts is explained by a genetic predisposition, namely the development of hereditary pancreatitis, leading to changes in the accompanying tissue and organs.
The main symptom of the development of pathology is a violation of the digestive processes. Pancreatitis can cause dilation as well as narrowing of areas of the Wirsung duct. Experts call this pattern the chain of lakes syndrome. The contours of the canal become uneven, and solid inclusions, which are calcifications or stones, are found in their lumen. Additional symptoms of the disease are:
- The appearance of severe pain in the hypochondrium area (the fact is that pain, as a rule, is not relieved by antispasmodics and analgesics).
- The occurrence of diarrhea and pasty stools.
- The appearance of nausea, vomiting and weight loss.
- Decreased appetite along with specific signs indicating persistent dilation of the gland canal.
Source: https://gb4miass74.ru/zabolevaniya/rashirnie-virsungova-protoka-na-uzi.html
What to do if the ovary is not visible on ultrasound
If the appendages are not detected, this means either a more serious change in hormonal levels, which occurs when taking contraceptives during menopause, or a peculiarity of the current state of the internal organs.
When re-examining with an abdominal sensor, you must:
- 3 days before the manipulations, give up carbonated drinks, as well as foods that cause flatulence (legumes, black bread, cabbage, fresh baked goods, sweets);
- a few hours before the examination, take the sorbent;
- in the evening take a laxative or cleanse the intestines with an enema.
Assessing the condition of the glands using a vaginal sensor does not require special preparation.
The only obstacle to obtaining a clear picture may be gases in the intestines, due to which the ovaries are not visible, so it is recommended to take the drug “Espumizan” a day before the examination (2 tablets three times a day, and 2 tablets an hour before the procedure) .
Why and how to do an ultrasound of the fallopian tubes
However, with a transvaginal examination, in a small percentage of patients, doctors are able to remove the organ against the background of peritoneal fluid that has leaked during ovulation. Thus, if the study protocol states that the fallopian tubes are not detected on ultrasound, this means that they were not subject to pathological changes.
Indications for echohysterosalpingography (EchoGSS), or hydrosonography (ultrasound examination of the uterine appendages):
- menstrual irregularities (irregularity, painful menstruation, changes in their duration);
- frequent inflammatory processes of the internal genital organs;
- suspected infertility (unsuccessful attempts to conceive a child within 12 months);
- pain in the lower lateral abdomen, suprapubic region;
- a history of sexually transmitted diseases;
- preparation for in vitro (artificial) fertilization.
If a transabdominal ultrasound , then the woman should exclude foods that increase gas formation in the intestines 2-3 before the procedure. On the day of the study, 1-1.5 hours before the procedure, you need to drink 800-1000 ml of liquid to fill the bladder. With the transvaginal technique, the bladder must be empty, that is, you need to urinate before the examination.
How is hydrosonography performed:
- The woman takes a comfortable position in a special gynecological chair.
- The doctor inserts a thin catheter into the uterine cavity through the cervix. After which, a sterile saline solution at a temperature of 37 degrees (or Echovist) is supplied to the organ.
- Under ultrasound control, the doctor monitors the process of filling the uterus and fallopian tubes with the solution.
- At the end of the study, the sensor is removed from the vagina, and the catheter is removed from the uterus.
With a regular scan, without the use of a contrast agent, this organ is not described in any way - this means that the fallopian tubes are not visualized. According to official statistics, complete or partial organ obstruction occurs in 42-80% of infertile women.
Anatomy of the pelvic organs
The following female organs are located in the pelvis:
- the bladder, which, due to anatomy, is located in contact with the uterus and vagina;
- the vagina adjacent to the uterus and passing through the urogenital diaphragm;
- rectum;
- the uterus, which is shaped like a pear;
- fallopian tubes;
- ovaries, which produce female hormones and are responsible for the production of eggs.
All these organs, functioning without abnormalities, provide a woman with the opportunity to bear children.
Indications for ultrasound
Ultrasound examination is rarely performed as an independent procedure; it is usually prescribed in conjunction with an examination of organs. But sometimes it can be prescribed to check the functionality of the ovaries. More often, this procedure is prescribed to find out the reason for the inability to conceive.
The main indications for ultrasound examination of the reproductive organs are the following diseases and symptoms:
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- changes in the regularity of the menstrual cycle or its absence;
- constant pain in the lower abdomen;
- pregnancy;
- heavy or scanty periods, with severe pain;
- suspicion of infertility;
- inflammatory process of the appendage;
- preparation for IVF and standard pregnancy;
- prevention.
Causes of disorders in the reproductive system
The main reasons that can provoke genital dysfunction include:
- termination of ectopic pregnancy
- development of inflammatory processes in the appendages: salpingoophoritis, adnexitis, oophoritis
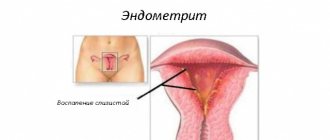
- progression of endometritis - an inflammatory process that affects the inner lining of the uterus and occurs as a complication of abortion, curettage
- formation of adhesions caused by surgical interventions, peritonitis
- abnormal development of internal genital organs (bicornuate uterus)
To confirm the diagnosis, a comprehensive examination by a gynecologist and a number of diagnostic procedures are required: both instrumental (ultrasound) and laboratory. In order to fully examine the uterus and its appendages, the administration of contract drugs is required. The procedure is carried out only in case of objective indications; this is not a routine study recommended for all categories of women.
Bicornuate, vestigial uterus
A bicornuate uterus is a pathology of organ development, which is accompanied by the formation of two separate parts with cavities. In the lower part of the uterus, such “horns” unite, and a common canal opens into the vaginal area. Such a disorder occurs as a result of hereditary predisposition and exposure to external provoking factors. These can be toxic substances, viral infections, heavy metals, pathogenic microorganisms of bacterial origin.
There are no specific symptoms for this disorder. In some cases, menstrual irregularities, uterine bleeding, miscarriage, and difficulty conceiving may occur. In most cases, a bicornuate uterus is discovered by chance, during a routine examination by a gynecologist. In most cases, specific therapy is not required. Surgical correction is performed only if there are difficulties with conception.
Oophoritis
Oophoritis is an inflammatory process that affects the ovaries. Develops under the influence of infectious and inflammatory processes: endometritis, vulvovaginitis, adnexitis, sexually transmitted infections. Among the predisposing factors that can provoke pathology are impaired functioning of the immune system, regular hypothermia, a history of multiple abortions, surgical interventions, the use of an intrauterine device, and disruption of the natural microflora.
The disease is accompanied by intense pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the sacrum or lower back, and intense purulent or mucous discharge. The pain intensifies when urinating. There are also complaints about deterioration in general health, the presence of intermenstrual bleeding. Therapy begins with treatment of the cause that provoked the oophoritis. They use medications with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial effects, as well as general tonic and immunomodulatory agents. During treatment it is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse.
Salpingo-oophoritis
Salpingo-oophoritis is a pathological process in which the fallopian tubes and ovaries become inflamed. One of the main reasons that leads to infertility. Develops under the influence of infectious pathogens: chlamydia, gonococci, mycoplasma, staphylococcus, Escherichia coli, streptococci. It is observed in women who are subject to regular hypothermia, overwork, stress, abortion, and multiple births.
The disease is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, which persists both during physical activity and at rest. Vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor and green color is observed, and body temperature rises. A woman complains of nausea, general weakness, libido and menstrual cycle disorders. During therapy, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and physiotherapy are used.
Adnexit
Adnexitis is an inflammatory process that affects the uterine appendages. Leads to simultaneous inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries, provokes adhesions. The causative agent of the disease is pathogenic microorganisms (chlamydia, gonococcus, streptococcus, staphylococcus). The disease is accompanied by pain, discomfort during menstruation, increased body temperature, weakness, and increased fatigue. For purulent forms of the disease, surgical intervention is indicated. In other cases, therapy is carried out in a hospital setting with antibiotics and painkillers.
Alternative Research
If ultrasound cannot detect certain pathologies, then alternative studies can come to the rescue, including the following:
- Laparoscopy with smear taking.
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging.
- Puncture of the pouch of Douglas with further cytological analysis of the washout.
The undeniable advantages include the following:
- painlessness;
- non-invasive;
- availability;
- when using it there is no ionizing radiation;
- soft tissue imaging;
- the ability to see processes occurring in the body in real time.
In addition, this technique is the most convenient for monitoring the intrauterine development of a child, allowing you to visualize all the processes and changes in the female body during the period of bearing a child.
An important characteristic of ultrasound examination is its affordability, which allows you to monitor the condition of the body at any necessary time, especially since it is completely safe.
Why are the ovaries not visualized on ultrasound?
This terminology does not imply the fact that this organ does not exist, but that it is not defined, that is, the structure and contour cannot be determined. Often this can happen due to the incompetence of the doctor who was unable to properly adjust the sensors.
This situation may arise when the examination was carried out on old equipment; here the situation can be corrected by doing another examination in another clinic.
But before a transvaginal ultrasound examination, it is necessary to empty yourself, otherwise the liquid during the movement of the sensor inside the vagina will interfere with seeing the organs.
Normally, the ovaries have an uneven and clear contour. If the woman has prepared properly for the procedure and the equipment is appropriate, then there should be no problems with visualization.
If there are pathologies, then the contours lose clarity. This is what an ovary with a cyst or inflammation will look like. If the ovary has shrunk, then menopause has begun. When the right or left ovary is not determined, this may indicate problems with the endocrine system or simply characteristics of the body.
Intestinal disorders
The main and most common reason that the ovary is not visible is the accumulation of gases in the intestines or a full stomach. If these factors occur, then the organ should be visible on the next ultrasound.
Anovulatory cycle
It happens that the ovary is not visualized due to the fact that there is no ovulation, but this can happen for the following reasons:
- temporary hormonal imbalance, when the normal state returns in a further cycle;
- serious pathologies in the pelvis or hormonal disorders.
When both cycles in a row give an abnormal result in ultrasound diagnostics, there is no ovulation, then it is necessary to examine the endocrine system.
Hormonal disorders
If all other reasons are absent, and the ovary is still not visualized on ultrasound, then you need to take tests for hormones, which include the following:
If there is an insufficient or excessive amount of the hormones listed above, it is necessary to check all the organs of the female body that are responsible for their production.
Imaging during pregnancy is difficult, what is it?
Good day, my readers!
I remember how impatiently I waited for the ultrasound examination, when the doctor would tell how the child was developing and its gender. But things don't always go as we plan. Visualization during pregnancy is difficult, what is it and how to respond to this specialist’s remark? An issue that we will examine today and remove it from the agenda.
What does visualization mean?
Visualization refers to the ability to visually observe an object. In our case, the object is a baby, and a special technique allows us to observe it, it is known to everyone - this is ultrasound. The focus is on the uterus.
In fact, the outcome of the study depends on the professionalism of the doctor and the quality of the hardware. Therefore, I strongly recommend that you carefully choose both the clinic for examination and the specialist. During the entire period of bearing a child, a woman should undergo an ultrasound scan 3-4 times.
If on your first visit to an uzologist he says that the visualization is unsatisfactory, then you should not be upset. You still have a second study, which, I’m sure, everything will be fine. Well, you need to understand that at 12 weeks there is little that can be seen on the monitor.
And if the doctor has any doubts about the condition of the fetus, then they need to be taken into account, but not to panic. During this period, all diagnoses are quite conditional. By the way, abdominal ultrasound is also based on data visualization. This method of research has been known for more than 50 years.
It is clear that at first the quality of diagnostics left much to be desired, but today this technique is reliable, the probability of error is almost zero. But if a specialist discovers a violation, the doctor is obliged to conduct additional research.
Why is ultrasound performed?
Typically, a woman should register before 12 weeks of pregnancy, this will allow qualitative observation of the development of the fetus and the condition of the mother.
Despite the serious diagnostics that healthcare offers today, ultrasound remains the only sure way to obtain objective information about the baby’s condition. Although in some cases, poor visualization on an ultrasound examination may be observed, and the doctor will definitely notify the mother about this.
Thanks to this technique, the doctor receives the following information:
- the degree of provision of the baby with oxygen and nutritional compounds;
- functional features of organs.
And in this, great importance is attached to the second screening, which is carried out at 20 weeks of pregnancy. The specialist first of all examines the baby’s internal organs, the structure of his body, he also determines the gender of the child, and this is the most desired information for many.
Ultrasound also evaluates the condition of the mother's birth canal. The second ultrasound also evaluates the condition of the placenta. It must be said that at this time pregnancy may experience various disturbances.
AmniSure test for determining leakage of amniotic fluid allows you to determine whether rupture of the membranes is present or whether there is such a possibility. To do this, there is no need to visit a doctor; just read the instructions carefully and use the test at home.
Why is it not visible
If the second study may not show the sex of the child and some other parameters, then you need to wait for 3 screenings. At this time, the child is already big enough for the doctor to be able to determine the pathology, and even more so the sex of the baby. Usually the third study is scheduled at 32 weeks.
If you are over 35 years of age, additional examination may be prescribed. Whether visualization is satisfactory or unsatisfactory depends not only on the quality of the device and the qualifications of the doctor, but also on the woman herself.
There are essentially two reasons why review is extremely difficult:
- the presence of a subcutaneous fat layer;
- features of the baby's location.
What does it mean? Let's start with the second one. Have you heard that it is impossible to determine the sex of a child due to the unusual position of the fetus? Usually the doctor says that the child is shy and hides, so it is impossible to find out the gender. But it’s worth talking about the presence of the subcutaneous fat layer in more detail.
Excess weight requires control
If visualization of the fetus is difficult, this is most often due to the woman being obese. Here are some statistics for you: in the 2nd trimester, overweight women experience poor visualization much more often than those who keep themselves within limits. And there are 25% more of them.
This is why doctors recommend monitoring your weight from the first days of pregnancy. What does it mean for a woman that visualization is difficult due to the PVC? On the abdominal wall of the mother there is a layer of fat, which is highly dense.
Ultrasonic waves cannot overcome it completely; a certain error is created, which necessarily affects the results of the study. By the way, it is possible to determine whether such a pathology is present in a simple way.
You can check how large the subcutaneous fatty tissue is and how it relates to the total body weight:
- take a layer of skin from the navel in your hand;
- managed to do this, then everything is fine with you;
- If you couldn't get a crease, you are overweight.
By the way, due to PFA, some pathologies in fetal development can also be observed.
What do we have to do?
Now do you understand why visualization is difficult? It remains only to answer the question of what to do in this case. The main thing is not to panic or get upset. Pull yourself together. You've probably heard about your excess weight before from your doctor, but you didn't attach much importance to this fact.
Apparently, it's time to think about it. Moreover, in this case, it is the heart that suffers first. How do you know if you are overweight? Every time at an appointment, the doctor asks mommy to step on the scale; if he is not satisfied with your kilograms, he recommends going on a diet.
On average, during the entire period of pregnancy, a woman gains from 9 to 14 kg. If in the first trimester the weight changes slightly, then in the second its rapid increase is noticeable - up to 1 kg per month. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, your pregnancy will definitely end with the birth of a healthy baby.
And then you will be faced with the difficult task of raising him. Particular attention should be paid to a baby from one year old. At this time, he begins to speak, repeating words after adults. The course “Secrets of folk pedagogy - beautiful speech without a speech therapist” will help you in the process of teaching your child.
It will be useful to parents whose child speaks incoherently, in his own language, which is incomprehensible to others. By the way, the course suggests that a mother can prepare for classes with her baby even during pregnancy, for which certain techniques are used. The course is very interesting for young parents, but experienced mothers will also find a lot of useful things in it.
Girls!
Don’t worry that the doctor couldn’t determine the sex of the baby during the ultrasound, the main thing is that he is healthy. Visualization is such a thing that today it is not there, but tomorrow it is, so be patient and repeat the study after a while.
Tell your friends about the article on social networks; by subscribing to the blog, you will receive regular updates. Until new topics!
Sincerely, Tatyana Chudutova, mother of three wonderful children!
Source: https://vladimir-sport.ru/vse-o-detyah/beremennost-i-rody/vizualizaciya-zatrudnena.html
Reasons for failure to visualize the ovary
In addition to the listed pathologies and factors, problems with organ visibility can arise for the following reasons:
- the presence of adhesions in the peritoneum or in the reproductive organs themselves;
- after surgery on the ovaries or fallopian tubes;
- congenital absence;
- high density of the peritoneum;
- developmental abnormalities;
- due to deformation of the uterus, which arose due to the presence of myomatous nodes;
- menopause;
- presence of scars on the anterior abdominal wall;
- the period before the onset of menopause;
- during severe polyetiological pathology of the uterus;
- due to an enlarged uterus;
- the presence of too dense fat layer;
- organic displacements.
The patient should take into account that ultrasound examination will be less informative if the woman is taking contraceptives.
Sources:
https://oyaichnikah.ru/diagnostika/ne-vizualiziruetsya.html https://ginekola.ru/ginekologiya/yaichniki/pochemu-na-uzi-ne-vidno-yaichnika.html https://boleznikrovi.com/uzi/ taza/ne-vidno-yaichnika.html
Excess weight requires control
If visualization of the fetus is difficult, this is most often due to the woman being obese. Here are some statistics for you: in the 2nd trimester, overweight women experience poor visualization much more often than those who keep themselves within limits. And there are 25% more of them.
This is why doctors recommend monitoring your weight from the first days of pregnancy. What does it mean for a woman that visualization is difficult due to the PVC? On the abdominal wall of the mother there is a layer of fat, which is highly dense.
Ultrasonic waves cannot overcome it completely; a certain error is created, which necessarily affects the results of the study. By the way, it is possible to determine whether such a pathology is present in a simple way.
You can check how large the subcutaneous fatty tissue is and how it relates to the total body weight:
- take a layer of skin from the navel in your hand;
- managed to do this, then everything is fine with you;
- If you couldn't get a crease, you are overweight.
By the way, due to PFA, some pathologies in fetal development can also be observed.