Heavy bleeding with blood clots
Uterine bleeding with clots, heavy menstruation - how to evaluate these phenomena, can they threaten life and health?
Many women believe that “good” menstruation, during which a lot of blood is lost, is good for the body. In this way it seems to be cleansed. And then they remember about “slags”. Doctors consider this phenomenon to be pathological, leading to a deterioration in the quality of life and anemia. Most often, dysfunctional uterine bleeding with clots is diagnosed in girls 12-15 years old and in women before menopause. In the former, the hormonal system is still unstable, while in the latter it is fading away.
Let us remember that menstruation is a monthly detachment of the endometrium as a result of a failed pregnancy. In the first half of the menstrual cycle, under the influence of estrogen, the endometrium becomes thicker. Afterwards, ovulation occurs (or does not occur during the anovulatory cycle), and progesterone begins to rise. If there is no pregnancy, its level begins to decrease a few days before menstruation. And as a result, the uterus “cries tears of blood” over a failed pregnancy.
Normally, the total blood loss during menstruation is 40-50 mg. Only about 3 tablespoons. It can be problematic to calculate your blood loss by eye, but if there are large blood clots during uterine bleeding, then it is probably more than normal. Blood loss of more than 80 grams, which occurs periodically, leads to iron deficiency anemia.
In addition, pathology is indicated by prolonged discharge, lasting more than 7 days, and occurring more often than once every 21 days. Absolutely always speaks of pathology and is never a normal variant of uterine bleeding with clots during menopause, that is, when blood appears in women during menopause. This should not happen, since the endometrium does not grow after menopause, the hormonal levels are calm.
Heavy periods with clots or uterine bleeding, how can you tell the difference? A few signs of trouble:
- the sanitary pad gets completely wet within an hour and this is repeated more than 2 times;
- it is impossible to carry out everyday activities for fear of “leakage” or pain;
- you have to get up at night to change the gasket;
- anemia in test results;
- pallor, weakness.
The causes of bleeding with blood clots in many cases remain unclear. Then doctors blame everything on hormonal imbalance. Sometimes, due to an excess of estrogen, the endometrium grows excessively and begins to peel off unevenly and earlier than during menstruation. This may be a consequence of taking and stopping medications with estrogen. In this case, hemostatic drugs help well with uterine bleeding.
There are so-called breakthrough bleedings. They occur when there are errors in taking hormonal contraceptives, the first three cycles of their use as an addiction to the body, as a side effect of using an intrauterine device. How to stop severe uterine bleeding with clots in this case? Hormonal treatment may be suggested. If the bleeding is profuse, the doctor prescribes taking certain hormonal medications in large dosages and gradually switching to planned hormonal contraception. Sometimes women bleed between periods due to a small dose of estrogen in the contraceptive drug. Then it needs to be replaced with one that has a slightly higher concentration of the hormone.
How to stop uterine bleeding with clots using folk remedies at home if there is no way to visit a doctor yet? For this, tincture of water pepper and nettle decoction are usually used. But the remedies are not very effective. And if the cause of the appearance of blood is pathological neoplasms in the uterus, herbs definitely cannot be saved. Surgery is required.
How to treat
After diagnostic procedures, the doctor selects the most appropriate method of eliminating clots: medication or mechanical.
If the release of clots is delayed, drug treatment is prescribed, which includes drugs for:
- increasing contractile function of the uterus;
- eliminating bacterial infections;
- relieving spasm of the uterine muscles.
If, despite preventive measures, a clot still forms after childbirth, continuing treatment at home is prohibited. Yes, you will have to seek help from a doctor to find the cause of the ailment. If the cause of delayed recovery is inflammation of the appendages, antibiotics, vitamins, and immunomodulators are prescribed.
If the tone of the appendages is reduced, hormonal drugs are prescribed: “Oxytocin” or “Pituitrin”, which stimulate contraction and, as a result, the removal of unnecessary tissues from the body.
After diagnostic procedures, the doctor selects the most appropriate method of eliminating clots: medication or mechanical.
Discharge and blood clots from the uterus
One of the most reliable ways to judge the condition of the patient’s reproductive system is to observe vaginal discharge. Cervical fluid changes depending on the phase of the cycle, the use or installation of a contraceptive, and hormonal changes. Gynecologists know the limits of the norm for the appearance of clots, the peculiarities of fluctuations when external and internal factors change. On their own, women cannot always confidently say whether their uterine discharge is normal. If you feel unpleasant changes or the appearance of blood, you should see a specialist to rule out pathology.
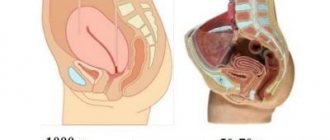
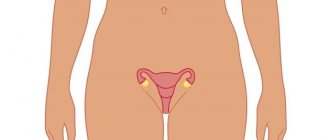
Structure of the uterus
The uterus consists of three layers, each of which has a specific function:
- the inner lining – the endometrium – is subject to hormonal changes. The functional part of the layer is rejected during menstruation, forming uterine clots. During pregnancy, it participates in the implantation process;
- the middle one - the myometrium - carries out uterine contractions, which is especially important during childbirth;
- external – perimeter – plays a protective role.
The organ is visually divided into the fundus, body, neck and isthmus. Tubes containing the ovaries approach the uterus on both sides.
Causes of discharge and clot formation
Discharge from the genital tract in women is constantly present. The appearance of a whitish-transparent liquid, which becomes viscous as ovulation approaches, is considered normal. There are no unpleasant sensations during the formation and discharge of mucous clots.
Various factors are known that lead to changes in the nature of vaginal fluid:
- sexual contact and arousal;
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- intrauterine or oral contraception;
- sexual infections;
- disruption of hormone levels;
- tumor;
- adenomyosis.
Serous uterine discharge from the cervix serves as protection and is absolutely normal. Their occurrence is due to varying degrees of activity of the cervical glands under the influence of hormones. Depending on the day of the cycle, hormonal imbalances, the nature and consistency of vaginal fluid changes.
Clots form less frequently. The occurrence of clots in the uterus during menstruation, after surgery, and childbirth is considered normal. A potential danger is the presence of blood, especially scarlet blood.
Prevention of clot stagnation
The blood in the tract should not stagnate, and at the same time it should not flow continuously, so it is very important for a woman to know what to do so that she gets out and stops in time.
- To prevent the vessels from being destroyed, ice is placed on the mother’s stomach (but only if the placenta is completely removed).
- To stimulate uterine contractions, so that clots in the uterus do not linger for a long time after childbirth, hormonal drugs are taken, in particular Oxytocin, and other medications containing it.
- A little physical activity will help prevent the formation of large lumps and relieve swelling. You can start with a banal daily warm-up. Lying on your stomach also prevents large formations.
- Do not lift heavy objects under any circumstances. A good prevention would be to wear a bandage or tight strip of fabric. This facilitates movement, and also helps the organs take their original place and supports the stomach. If surgery has been performed, the bandage will prevent the seams from coming apart.
- Breastfeed your baby. This stimulates the production of hormones necessary for uterine contractions. In addition, feeding itself provokes compression of the reproductive organs, due to which they are quickly freed from lochia.
- Empty your bladder and bowels often. Avoid constipation. Otherwise, problems with the gastrointestinal tract will increase internal pressure on the reproductive system and the vessels inside it, which can cause blood stagnation.
By examining a woman, the doctor is able to detect the location of the formations. This happens by palpation. If a lump of mucus is found, a massage is performed, the purpose of which is to increase the tone of the appendages. By pressing on the lower abdomen, the doctor pushes the lumps towards the “exit”. This procedure is carried out every 2-3 hours. This is quite painful and unpleasant, but, unfortunately, you cannot do without it.
A woman can stimulate the release of clots in the absence of pathologies on her own. To do this, you should follow simple advice that maternity hospital doctors give to their patients.
- Trigger the release of natural oxytocin. To do this, you need to give your baby breastfeeding more often. Sucking movements stimulate contraction of the uterus, which is especially noticeable in the first days after childbirth.
Frequently putting a baby to the breast provokes the natural production of oxytocin
Types of discharge
To understand the condition of uterine discharge, you need to evaluate it by:
- color;
- character;
- consistency;
- smell;
- the presence of related complaints.
For diagnosis, it is extremely important to know the patient's cycle. Dark clots outside of menstruation indicate pathology; they require additional diagnostics and identification of the cause.
It is equally important to monitor the nature of the discharge after surgery: abortion, curettage or after childbirth. In these cases, significant damage to the uterine wall occurs and large blood clots occur. The patient should discuss with the doctor the acceptable limits: how many days such discharge will continue and when to worry.
Mucous
The uterus is subject to hormonal changes depending on the day of menstruation. A change in cervical mucus should inform a woman about approaching ovulation, as the most favorable period for conception. Often, patients report at an appointment about the appearance of white fluid from the uterus, asking what it is and why such a phenomenon is dangerous. In fact, this is how the release of the egg manifests itself. Transparent mucous discharge is observed for another 2 days - the entire period of life of the female cell. Then the ductility gradually decreases.
White
A moderate amount of clear, white fluid from the uterus can be considered normal in the absence of unpleasant symptoms. Thick and white discharge is characteristic of pregnancy. The formation of thicker, drier, cottage cheese-like clots indicates a fungal infection. Additional attention is paid to the presence of odor. Normally, there is no specific aroma.
Brown
Dark discharge from the genital tract usually occurs with the onset of menstruation. These days, under the influence of hormones, the functional part of the inner layer of the uterus is rejected. Brown color indicates oxidation of iron in clotted blood. In this case, ongoing massive bleeding does not occur. On the days of menstruation, the appearance of blood clots in the uterus is considered acceptable.
Dropper for contraction of the uterus after childbirth: the drug Oxytocin
Oxytocin is not just a drug prescribed to women after childbirth. In fact, it is a female hormone that is produced by the hypothalamus and accumulates in the pituitary gland.
What is its important role:
- Contraction of the uterus. Oxytocin directly affects the contraction of the uterus and its return to its previous state. If the uterus does not contract, inflammation or subsequent prolapse may occur, which in the future can lead to prolapse.
- Beginning of lactation. Although colostrum appears in the first hours after birth, oxytocin is necessary for the normal functioning of the mammary glands.
- Antidepressant. An integral part of normal feeding and the absence of interruptions in lactation is psychological calm. According to reviews, the drug increases the mother’s resistance to irritants, increases the feeling of confidence, trust and security.
If the mother’s natural production of this hormone is not enough, then doctors introduce its analogue. This helps a woman avoid future problems with reproductive function, and also helps to establish the process of breastfeeding.
Oxytocin is also used to induce labor if a woman is pregnant or if labor suddenly stops. Oxytocin is not prescribed if the drug is intolerant, if the baby is lying incorrectly or the mother has an immature cervix.
Symptoms and possible consequences
Undesirable symptoms indicate the presence of diseases. Changes in vaginal secretions may be beneficial:
- the addition of a microbial or fungal infection;
- reduction of local immunity when taking antibiotics, cytostatics;
- endocrine regulation disorders (thyroid disease, diabetes);
- oncological process;
- endometriosis;
- uterine, ectopic pregnancy;
- endometritis.
Disturbances in the functioning of the reproductive system are indicated by:
- itching, unpleasant odor, pain in the lower abdomen, the presence of purulent, yellow-green fluid;
- the appearance of brown discharge from the uterus, streaked with blood, not associated with menstruation;
- delayed menstruation and minor blood clots instead;
- discharge after sexual intercourse with blood.
Endometriosis
The most common disease after childbirth is endometriosis. More and more women are seeking treatment for this pathology.
The disease means that during childbirth, parts of the endometrium or blood clots do not come out, but remain inside the uterus and grow to its walls. The disease does not make itself felt at first, but may appear six months after birth.
Factors that cause pathology to appear:
- long labor;
- vaginal rupture;
- perineal rupture;
- tight placenta previa;
- use of obstetric scissors;
- large fruit.
All this can cause pieces of tissue to begin to take root on the walls of the uterus without coming out.
The main symptom of the disease is pain similar to menstruation pain. But even after childbirth, the stomach still hurts with a contracting uterus. For this, you need to visit a doctor a month after being discharged from the hospital. Only through examination can pathology be identified.
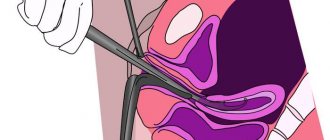
Diagnostics
To establish an accurate diagnosis, the doctor talks with the woman and performs a standard examination on a chair. If deviations from the norm are suspected, additional examinations are prescribed.
- Establishing the nature of the menstrual cycle by measuring basal temperature and ovulation test.
- Ultrasound.
- Fluid tests from the vagina and cervix.
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Tests for sexually transmitted infections.
- Cytological examination.
- Colposcopy.
- Hysteroscopy.
- Laparoscopy.
Treatment
The patient's treatment depends on the diagnosis.
- Infectious agents are eliminated with antibiotics and antifungal agents. To avoid the development of complications, an additional course is prescribed to restore the composition of the vaginal biocenosis.
- The threat of miscarriage is adjusted according to appropriate protocols depending on the gestational age and the phase of development of the process.
- If the ovum is located ectopically, it must be removed.
- After childbirth, it is allowed to wash the uterus to remove clots. If necessary, vacuum aspiration is performed to prevent endometritis.
- When a tumor occurs, the question of the possibility of conservative therapy or the need for radical intervention is decided.
- Hormonal changes are corrected together with an endocrinologist.
Uterine discharge is an important indicator of the patient’s health status. A whitish liquid almost always accompanies a woman and is the norm. The mucus changes slightly depending on the phase of the cycle. It becomes thicker under the influence of progesterone in the second half of the cycle. The appearance of blood and clots is typical for menstruation, the postpartum, and postoperative recovery period.
It is important to understand that in addition to the norm, there are also pathological signs. Large clots and blood outside the cycle signal the presence of a dangerous condition. To prevent complications, at the first sign of deviation from the norm, you must contact a specialist.
Consequences of pathology for the female body
- If the symptoms are ignored, as well as in the absence of proper comprehensive treatment, hematometra can lead to the development of serious infectious diseases such as endometritis.
- When an infection enters the uterine cavity, pyometra may develop, which is accompanied by the formation of pus in blood collections. Ultimately, this can be the beginning of the development of sepsis and necrosis, which often leads to surgery and amputation of both the uterus and other organs of the reproductive system.
- If the infection spreads throughout the abdominal cavity, there is a risk of developing peritonitis.
- Chronic infection can lead to infertility.
Why is bleeding from the uterus with clots dangerous?
Gynecological diseases bring quite a lot of unpleasant sensations to women, but uterine bleeding with clots truly causes fear in them. The intensity of the discharge may vary, but a pathological impurity in the form of coagulated blood is always alarming. If you promptly seek medical help when this symptom first appears, the diseases that could cause this manifestation can be quickly and completely cured. Recognizing problems with your body in the early stages of pathology allows you to use traditional therapy methods with the least number of side effects.
Pathological aspects
Pathological clots in bloody discharge from a woman’s genital tract are nothing more than areas of the mucous membrane. A woman cannot help but notice them, and they are indeed the cause of some life-threatening conditions and even deaths.
Uterine bleeding occurs in women of the fair sex every month due to physiological cyclic changes in the uterus and its appendages. If this happens outside the menstrual cycle, there is some kind of malfunction in the female body. Non-cyclical uterine bleeding is usually more profuse. A woman may also experience longer periods, the intensity of which does not decrease.
For most beautiful ladies, menstruation is almost painless, with minimal discomfort and pulling sensations in the lower abdomen. Afunctional uterine bleeding with clots is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- A sharp pain appears in the lower abdomen, often women characterize it as a dagger pain. The intensity of the symptom does not change when the patient's body position changes.
- Patients may have a pronounced pale skin tone, they feel dizzy from sudden movements and walking up the stairs.
- A woman may notice a gradual deterioration of her condition, an increase in weakness, and symptoms of malaise.
Most often, breakthrough bleeding from the uterus occurs on days 12-15 of the menstrual cycle. This pattern is determined by changes in hormonal levels due to the release of an egg preparing for fertilization. At this time, the uterus is actively preparing for its implantation if the process of conception takes place. At the same time, vessels actively grow into the mucous membrane of the reproductive organ, and their vascular permeability changes. This determines the likely release of a small amount of blood, which women almost never notice. If this symptom does come into view, it should last no more than 3 days, which otherwise indicates the presence of pathology in the female genital area.
Abnormal mucous may be noticed by a woman if conception does occur. Bloody discharge of uncharacteristic consistency appears in the discharge due to the fact that the fertilized egg penetrates the wall of the uterus for its subsequent life activity and somewhat destroys it with various enzymatic media. Minor bleeding should also stop within 2-3 days.
Blood clots in the uterus can also form due to the influence of infectious agents. Inflammation within the reproductive organ mediates various physicochemical reactions that can provide a substrate for clots. They are mixed with menstrual blood, and can independently form the causes of uterine bleeding and other malfunctions in the female body.
The need for medical help
If, despite all the measures taken, lumps of blood in the uterus continue after childbirth, home remedies are ineffective, there is a need to consult a doctor and find out the reasons for the delay in recovery. In case of inflammation of the mucous membrane, which is indicated by an abundance of discharge and the appearance of an unpleasant odor, conservative therapeutic treatment with antibiotics, vitamins, and immunostimulants prescribed by a doctor can help. If decreased uterine tone is diagnosed, hormonal therapy is performed to stimulate it.
More serious problems arise when a polyp forms from the remains of the placenta on the wall of the reproductive organ, which is very dangerous. This complication can only be cured surgically using a procedure called vacuum aspiration or cleaning, which often worries women. They are concerned not only about the pain, but also about possible complications after surgery. However, a more serious threat to health may be refusal of treatment, which will lead to advanced female diseases, for example, advanced endometritis and the spread of the inflammatory process to adjacent organs. The attending physician must choose the method of treatment - conservative or surgical - so as not to start the problem and not to aggravate it when it is necessary to resort to more radical intervention.
To avoid suffering from the consequences of clot discharge, it is best to take preventive measures. To do this, you should limit the load, but not completely abandon it, do not abuse heavy lifting, regularly perform hygiene procedures, and most importantly, monitor the doctor, inform him about emerging problems and doubts. Then it will be possible to maintain full female health for a long time.
Author of the article Ksenia Denisova
Ksenia is a regular expert on the PupsFull portal. She writes articles about pregnancy and the health of mother and child.
Pathological bleeding
Gynecologists consider uterine bleeding pathological if it continues for more than 1 week with an interval of less than 21 days. Such copious discharge with clots can be the root cause of various somatic diseases and conditions:
- Congenital anomalies in the development of the uterus and its appendages. The non-functional structure of the genital organs contributes to stagnation of blood, its coagulation and subsequent release in the form of clots. These etiological causes of bleeding with pathological impurities are extremely rare.
- The picture of uterine bleeding with clots occurs when hormonal levels change. The inner lining of the uterine mucosa is hormonally dependent. If an excessive level of biologically active substances is produced, the endometrium divides at a high rate and increases in volume. At the same time, this contributes to its early rejection, detachment and discharge from the uterus in the form of pathological mucus-like clots.
- Hormonal levels can also change due to processes occurring in the higher parts of nervous activity. Thus, the pituitary gland controls the production of estrogen, which increases the growth rate of the uterine mucosa. In this case, ovulation occurs earlier, as does menstrual bleeding with areas of the rejected uterine wall. The volume of menstrual blood also increases.
- Abnormal clotting of the blood itself can also cause bleeding with clots. Thus, with thrombocytopenia, there are not enough blood cells to carry out active hemostasis, which is why variously localized and extensive bleeding occurs. Clots arise as inflammatory elements or structures of a different nature.
- Endometriosis is a rather malignant disease that also threatens the formation of bleeding. The spread of the uterine lining beyond the organ increases the amount of expected blood in emergency pathology. It is necessary to identify the disease as quickly as possible and compensate for it with minimal losses for the physiological health of the woman and her reproductive function.
- Uterine bleeding with clots may be the first symptom of a cancerous tumor. The oncological focus can independently supply the substrate for clots, and also directs all organs and tissues to pathological work. Most often, gynecological tumors are benign, which allows for their complete eradication.
Causes of hematometers
Taking into account possible etiological factors, the following forms of pathology are distinguished:
- hematometra, which developed in the postpartum period
- hematometra, developed as a result of intrauterine interventions
- hematometra, which developed as a result of obstruction of the genital tract
- hematometra, developed due to stenosis of the cervical canal
The causes of hematometra can be congenital, as well as acquired (organic or functional). Congenital anomalies of the development of the genital organs can be represented by cervical canal atresia, intrauterine synechiae, intrauterine septum, and vaginal atresia. If this pathology was not diagnosed and corrected in childhood, then with the onset of menstrual function, blood may accumulate in the uterine cavity, i.e., a hematometra may form.