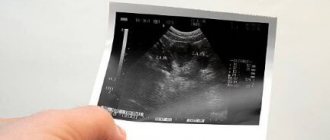
Fading pregnancy, or stopping the development of the fetus, occurs most often in the first trimester. The embryo dies in the womb, but it is not rejected immediately, so the pathology is usually diagnosed earlier than a miscarriage occurs. The level of hCG during a frozen pregnancy (FG) falls, and sometimes abnormal changes in its values are observed. Monitoring the content of gonadotropin in urine and blood allows for timely detection of pathology.
Anembryonia - what is it?
When, during an ultrasound about pregnancy, the doctor says that the fertilized egg is empty, what does this mean, the woman may not fully understand. Many expectant mothers have doubts at first, wondering: could the fertilized egg be empty or is this a medical error? A similar pathology occurs. It is characterized by the absence of an embryo inside the formed shells. At the same time, the rudiments of the future baby are very small.
Anembryonia is often considered a type of frozen or undeveloped pregnancy. A similar diagnosis is made before the 6th week of gestation. Anembryonia is common during IVF, when after fertilization the egg does not develop further. It is worth noting that with this type of pathology, diagnostic errors are often possible.
When the timing of pregnancy is not accurately determined, at the time of examination the embryo may be of insufficient size, so it is undetectable using standard ultrasound sensors. The doctor mistakenly diagnoses anembryonia. To exclude errors, if pathology is suspected, the examination is repeated after a few weeks.
The embryo is hard to see on an ultrasound: should I worry?
The mere absence of an embryo on ultrasound imaging does not mean anembryonia, even if the study was performed at 6 weeks or later. The equipment may not detect the embryo for the following reasons:
- Imperfection of ultrasound. Ultrasound diagnostics has long been firmly established in medical practice, but this method has its limitations. The resolution of some devices (even modern ones) is too low to detect a fetus, which in the early stages of pregnancy is only a few millimeters in size. Therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, a repeat examination is carried out after 6-8 days, which will confirm or refute the initial result.
- Excess weight. During ultrasound, an image of the organs being examined is formed using reflected high-frequency signals passing through the tissue. Some of the sound waves are absorbed, which distorts the data. Since during abdominal ultrasound the sensor is located on the surface of the patient’s abdomen, if she has a thick sound layer, the weakened signal may simply not detect the embryo. To increase the accuracy of this method, a transvaginal examination is used, in which a sensor is inserted into the patient's vagina - this reduces distortions caused by the tissues surrounding the embryo.
- Too early. Often, during natural conception, a woman cannot determine exactly when it occurred. In such cases, routine ultrasound can be performed earlier than the time when the embryo reaches a size sufficient for its visualization. To accurately determine the presence or absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg, you need to undergo the examination again using more sensitive equipment.
If, when diagnosing pregnancy, ultrasound “does not see” the embryo, doctors combine it with other examination methods - in particular:
- Dopplerography is a type of ultrasound that records dynamic processes in the body of the mother and fetus (for example, blood flow, fetal heartbeat);
- With cardiotocography - the essence of this method is to record electrical impulses accompanying the heart contractions of the embryo.
In addition to these methods, a gynecological examination, blood tests for progesterone or hCG are also used. In general, at 6-8 weeks of pregnancy, doctors can already confidently state the normal or abnormal development of the embryo.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Empty fertilized egg or absence of embryo - reasons
Why anembryonia occurs, doctors still cannot name the reasons for this disorder. Most doctors are inclined to the theory of genetic disorders. Chromosomal abnormalities in the genetic material of one of the parents often cause fetal death: at one stage the embryo stops growing and developing.
When a woman is diagnosed with an empty fertilized egg, doctors associate the causes of this phenomenon with the following factors:
- Acute viral or bacterial infections in the early stages of pregnancy. Under their influence, the fetal development process is disrupted.
- The effect of radiation or toxic substances on the mother's body.
- Hormonal imbalances in the body of the expectant mother (lack of progesterone).
- Bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
- Taking a certain number of medications with a pronounced embryotoxic effect.
- Excessive physical activity, stressful situations, worries.
Why is the embryo not visible on ultrasound?
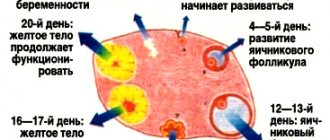
It is impossible to examine even a normally developing fetus immediately after conception - it is too small for an ultrasound scanner to distinguish it from the background of surrounding tissues and organs. Therefore, the first ultrasound to confirm pregnancy is usually done 6-7 weeks after conception. Until this point, the fact that a woman will be a mother can only be judged by the level of human chorionic gonadotropin, which begins to be secreted by the chorion (fetal membrane of the embryo) 6-7 days after conception. Normally, with the successful development of pregnancy, the concentration of hCG in the body increases along with the development of the fetus.
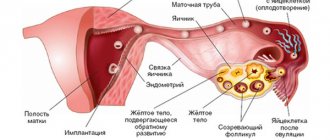
To understand the mechanism of anembryony, it is necessary to understand the structure of the embryo itself and its early development. It happens in several stages:
- A zygote is essentially a fertilized egg formed at the moment of conception;
- Morula is the next stage, characterized by the division of the zygote into several cells of the same type;
- Blastula is an embryo in which the cells are already divided into an inner cell mass (embryoblast) and an outer layer (trophoblast);
It is at the blastula stage that the future body of the embryo and the protective membranes surrounding it are formed. When the embryo leaves the fallopian tube and descends into the uterine cavity, enzymes secreted by the outer cells partially dissolve the endometrium, and its implantation occurs. Next, the embryo and amniotic membranes develop in parallel, gradually forming a mature fetus and placenta.
With anembryonia, this process is disrupted - the outer membrane (fertilized egg) continues to grow, releasing hCG, while the embryo either does not form at all or its development stops at an early stage. Because of this, for some time the tests give false results, showing a normal pregnancy. Only after some time the chorion stops secreting hCG, the level of which gradually begins to decrease.
The reasons for embryonic growth arrest, leading to an empty fertilized sac, are not fully understood. Today these include:
- Genetic abnormalities. In most cases, anembryony is caused by pathological chromosomal mutations, either originally characteristic of the parents, or appearing as a result of unsuccessful recombination of genes in their body. Genetic disorders in the embryo itself are also possible, occurring in the early stages of its development.
- Infections. Among them, the most dangerous for embryogenesis are the diseases included in the TORCH complex - rubella, herpes, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, hepatitis B and C, etc. Infectious pathogens can affect the maternal body, disrupting its reproductive function (for example, causing chronic endometritis) , or the embryo itself, leading to disruptions in its development.
- External factors. This primarily applies to ionizing radiation (radiation) and toxic chemicals (poisons, some medications). They cause functional disorders of the mother's reproductive system or genetic mutations in the embryo, stopping its normal development.
- Endocrine disorders. Disorders of a woman's endocrine glands can also lead to anembryonia. The appearance of a fertilized egg without an embryo is especially likely if there is a deficiency or disturbance in the metabolism of progesterone, a sex hormone that plays an important role in the decidualization (morphological change) of the endometrium at the point of implantation of the embryo.
- Immune disorders. Quite often, the cause of improper development of the embryo is damage to it by the protective system of the mother's body. This can happen indirectly - for example, when the embryo gets caught in the “crossfire” of immune cells attacking the infection. Sometimes the embryo itself is regarded by the woman’s immune system as a foreign object, because its genetic code is half composed of the genome of another person (the father).
Anembryonia can be caused by either one of these factors or their complex effects. It is impossible to predict the development of this pathology - it is observed even in absolutely healthy women who have already had experience of successful pregnancy.
This anomaly should be separated from a frozen pregnancy. With anembryony, the embryo does not form at all, and in the second case, its development stops at an early stage. Moreover, in terms of external manifestations and ultrasound, these pathologies may look the same.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Anembryonia - symptoms
Signs of anembryonia in the early stages are not specific. This explains the frequent accidental detection of pathology during a routine ultrasound scan during pregnancy. The signs that appear during pathology have a continuous connection with the process of implantation or the threat of miscarriage.
Among the symptoms that require examination, doctors identify the following possible signs of anembryonia:
- cramping pain in the lower abdomen;
- bloody discharge from the vaginal cavity;
- symptoms of toxicosis (nausea, increased fatigue, headache, fainting);
- increase in the size of the uterus;
- absence of regular periods;
- increase in body temperature to 37–37.5 degrees.
HCG for anembryonia
In order to determine the possible presence of pathology and consult a doctor in a timely manner, women often ask their gynecologist whether hCG increases with anembryonia. Human chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone that is synthesized by the chorion - the membranes that form at the beginning of gestation.
HCG for fetal freezing
After the formation of the zygote in the fallopian tube, its fragmentation begins. Then the chorion - the embryonic membrane - is formed. This structure produces a special protein hormone - human chorionic gonadotropin. One of the functions of hCG is to maintain the life of the corpus luteum. It produces large amounts of progesterone until the placenta can handle this task on its own.
The chorion develops quickly. The initial stages of pregnancy are characterized by a doubling of the hCG content in the blood every two days. If the fetus freezes, the embryonic membrane does not grow and loses its functions and stops producing gonadotropin.
Both genetic abnormalities and other factors that disrupt the normal course of pregnancy can provoke arrest of embryonic development. The pathology has characteristic external manifestations, but an accurate diagnosis can only be made after laboratory tests.
Causes of fading
Among the main factors causing fetal freezing, it is worth highlighting the following:
- The influence of hormones is a lack of progesterone, increased secretion of androgens.
- Mutations in the genome. With some chromosomal rearrangements, inheritance of a mutant parental gene, the embryo becomes nonviable.
- Infections in the mother - STIs (chlamydia, ureaplasmosis), herpes, rubella, toxoplasmosis, influenza.
- Antiphospholipid syndrome. This is an autoimmune condition caused by antibodies to blood phospholipids. Blood clots form in the uterus, and the embryo loses access to nutrition and oxygen.
- Abortion. After numerous curettages, the endometrium becomes defective, does not provide the embryonic egg with normal conditions for development, and pregnancy cannot be maintained
- Harmful addictions - alcoholism, smoking, drug addiction. Metabolites of alcohol and drugs have a teratogenic effect on the fetus, causing its death or developmental abnormalities.
Pregnancy miscarriage often occurs after IVF (in vitro fertilization).
This is usually due to the same reasons why artificial insemination was needed. If a pathology is detected in the first months of pregnancy, a medicinal termination of a frozen pregnancy is sometimes performed. At later stages, the undeveloped fetus is removed from the uterus by scraping (cleaning). This operation does not pose a threat to the woman’s health. Reproductive function is soon restored, and a new pregnancy can be planned within six months. Sometimes complications arise after an interruption - placental polyp, adhesions in the uterus, endometrial hyperplasia. The sooner you pay attention to alarming symptoms and visit a gynecologist, the less likely there are dangerous consequences.
Signs of fetal freezing
You can suspect fading pregnancy based on the following symptoms:
- nagging or cramping pain in the abdomen,
- bloody vaginal discharge of varying abundance,
- persistent increase in body temperature,
- disappearance of toxicosis,
- reduction in breast size.
The second line on the pharmacy test will be slightly colored or not appear at all. This is due to a decrease in hCG secretion. In the second trimester, when fetal movements are already noticeable, the main sign of freezing is the cessation of movement.
Anembryonia - what to do?
An empty ovum can only be detected using an ultrasound, so if there is a suspicion of pathology, it is necessary to undergo an examination. An accurate diagnosis is possible only after the 8th week of gestation - at this time an ultrasound is performed. In the case when the study for pathology was carried out earlier than the specified period, ultrasound is repeated every 5–7 days.
To completely exclude possible pathology, a pregnant woman needs to:
- visit a gynecologist.
- undergo an ultrasound.
Anembryonia – ultrasound
The diagnosis of anembryonia can be made only on the basis of data obtained during ultrasound. This method is the most reliable for such pathology. The timing of the procedure is important. The embryo reaches diagnostic parameters only by the 8th week of gestation, so conducting research to exclude anembryonia before this period is pointless.
It is worth noting that not only the absence of the embryo itself in the fertilized egg may indicate the development of pathology. Additional signs of violation include:
- irregular shape of the fertilized egg;
- small dynamics of increase in the diameter of the fertilized egg;
- insufficient severity of the decidual reaction;
- absence of heartbeats in the 7th week of gestation and later.
Cleaning for anembryonia
When a woman is diagnosed with anembryonic pregnancy, the only treatment method is artificial termination of gestation. In this case, the doctor takes into account the timing, severity of the clinical picture, and the woman’s condition. The procedure for termination of gestation is carried out in a hospital setting. For some time (from several hours to several days), the patient is under the supervision of specialists. The length of stay in a medical institution is determined by the condition and method of cleaning the uterine cavity. It is carried out by:
- Medical abortion
- expulsion of the embryo from the uterine cavity by taking hormonal drugs that provoke endometrial rejection and increase uterine contractility. - Vacuum aspiration
- carried out using a device operating on the principle of a vacuum cleaner. - Curettage
– removal of the implanted fertilized egg along with the endometrial layer using a carriage.
Two fertilized eggs, one empty - what to do?
In the case when a woman is diagnosed with two fertilized eggs, one empty, doctors take a wait-and-see approach. This kind of multiple pregnancy is often recorded after an IVF protocol. Of several fertilized eggs, only one takes root; the rest develop anembryony. The development of a healthy fertilized egg is assessed over time. In the case of normal viability indicators, it is left, and the rest are removed by vacuum cleaning.
Diagnosis of anembryonia
The main way to detect this pathology is ultrasound examination. It is with its help that the presence of an embryo in the fertilized egg and its normal development can be established. In a normal pregnancy, the embryo is not visible on average until 6-7 weeks after conception, so at this stage, indirect signs of pathology can be a drop in the level of hCG in the blood or a deficiency of progesterone.
To make a diagnosis of anembryonia, the following conditions must be met:
- absence of a yolk sac in a fertilized egg with a diameter of 8-25 mm;
- absence of an embryo in a fertilized egg larger than 25 mm.
There are also additional signs of anembryonia, in particular deformation of the ovum, an abnormally low increase in its size, mild decidualization of the endometrium at the point of implantation, and unregistered heartbeat at 6-7 weeks of pregnancy. Such a diagnosis may also be supported by signs of fetal rejection - changes in uterine tone, the appearance of areas of chorionic detachment with the formation of subchorionic hematomas.
Depending on the clinical picture of the pathology revealed during ultrasound examination, 3 types of pathology are distinguished:
- Anembryonia type I - the embryo is not detected on imaging, the size of the fertilized egg is usually no more than 2.5 mm, and the uterus is enlarged only until 5-7 weeks of pregnancy;
- Anembryonia type II - there is no embryo, but the size of the fertilized egg and uterus corresponds to the gestational age.
Separately, it is worth highlighting the resorption of embryos during multiple pregnancies. Most often, this condition occurs after in vitro fertilization, when several embryos are implanted into the patient at once to increase the chances of successful conception. Usually only one of them takes root, but in rare cases 2 or more embryos are successfully implanted. In this case, some of them freeze in their development, after which they resolve or are removed from the body naturally.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Pregnancy after anembryony
In most cases, the pathology does not affect reproductive function. Women who have experienced anembryonia once subsequently successfully carry and give birth to healthy children. At the same time, it is important to have a clear idea of when you can become pregnant after anembryonia. Each case is individual, so after suffering a pathology, before planning your next pregnancy, you must consult a doctor. At the same time, gynecologists do not recommend attempting to conceive again 3–6 months after diagnosing anembryonia.
Why is the fertilized egg empty after conception?
In a normally developing pregnancy, by 5-6 weeks the fertilized egg consists of several elements: (we recommend reading: what happens to the embryo at 5-6 weeks of pregnancy?)
- embryo;
- aqueous membrane (amnion);
- villous membrane (chorion);
- fetal membranes.
Sometimes an ultrasound shows that there is no embryo among the membranes. The monitor shows only an empty yolk sac without a fetus. This pathology is called anembryonia. It can develop for various reasons. Most often, anembryonic pregnancy is based on genetic and chromosomal defects that are formed when genes are incorrectly distributed during cell division.
In some cases, genetic abnormalities are present in the sperm or egg even before they fuse. In both cases, a blastocyst is formed containing incorrect genetic material that prevents normal cell differentiation. The result of this is a complete stop in the development of the embryo in the uterus and the formation of a false yolk sac in it.
In addition, anembryonic pregnancy can occur due to the following reasons:
- chronic inflammation of the uterine mucosa (endometriosis);
- papilloma virus infection;
- bleeding disorder (thrombophilia);
- decreased immunity;
- disruption of the formation of some embryos implanted in the uterus during IVF;
- infections of the genitourinary system (vaginitis, colpitis, cystitis, etc.);
- diseases transmitted through sexual contact (chlamydia, ureaplasma).
Analysis for hCG, norms in humans
During normal gestation, the amount of the hormone should double every two days, and by the tenth to eleventh week of pregnancy it reaches its maximum. After this period, the concentration gradually decreases.
USEFUL INFORMATION: IVF for HIV positive patients at ICLINIC
Normal concentrations in non-pregnant women and men are zero to five. In pregnant women, the dynamics of hCG begins to increase rapidly and then gradually decrease:
- During the first trimester, the level of the substance increases rapidly - from 26 mU / ml to 300,000, which helps prevent miscarriage;
- The second trimester is characterized by a slow drop in hCG levels from 300,000 to 3,000.
- The third trimester allows the body to produce relatively small amounts of the hormonal substance - the concentration can range from 2500 to 78000 mU/ml.
The table for the growth of hormone concentrations in pregnant women is as follows:
| Weeks of pregnancy | HCG norms, honey/ml |
| 3-4 | 25 – 160 |
| 4-5 | 100 – 4800 |
| 5-6 | 1100 – 31000 |
| 6-7 | 2600 – 82000 |
| 7-8 | 23000 – 150000 |
| 8-9 | 27000 – 233000 |
| 9-13 | 21000 – 290000 |
| 13-18 | 6000 – 103000 |
| 18-23 | 4700 – 80000 |
| 23-41 | 2700 – 78000 |
Symptoms of anembryonia
The development of an empty egg is often asymptomatic. With anembryonia, a woman experiences all the signs of pregnancy: cessation of menstruation, an increase in the size of the mammary glands, tension in the lower abdomen, morning sickness and other signs of early toxicosis. The reason for this is the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the body. With anembryonia, its level usually corresponds to the lower limits of normal. The level and dynamics of hCG can be viewed in the table.
There are two types of anembryonia:
- with the first type of non-developing pregnancy, not only the absence of an embryo is observed, but also a delay in the growth of the fertilized egg itself;
- in the second type, the yolk sac does not contain an embryo, but continues to grow due to the presence of fluid in its cavity, and its size corresponds to the gestational age.
In both cases, after some time, the fertilized egg dies and is rejected. Why is this happening? Normally, the embryo influences the maintenance of the level of progesterone necessary for the normal continuation of pregnancy and the normal functioning of all the elements that make up the fertilized egg.
The absence of an embryo leads to a disruption in the supply of necessary substances to the fertilized egg. Ultimately, this ends in his death, rejection from the uterine mucosa and spontaneous abortion in the early stages of gestation.
Diagnostic methods
The absence of an embryo can be detected using ultrasound. An ultrasound shows the presence in the uterus of an empty fertilized egg that does not contain an embryo. Due to the fact that the ultrasound method is not 100% accurate, errors are possible. Sometimes there is an embryo, but its size is too small and is not recognized during examination.
In order to avoid an erroneous diagnosis, the woman undergoes a repeat ultrasound after 7 or 10 days. During a normal pregnancy, the grown embryo is already visible in the uterine cavity. If it is not there, then the diagnosis of anembryonia is made. Further tactics largely depend on the woman’s condition, stage of pregnancy and the presence of complaints.
How to take hCG
An hCG test is always taken from a vein. You can take it at a antenatal clinic where a young mother is being monitored, or you can go to a paid clinic, where you won’t have to wait in line for several hours, and no one will require a referral. In order for the results to be more reliable, it is necessary to adhere to some recommendations, namely:
- Blood is donated only on an empty stomach. When prescribing a repeat study to track dynamics, it is advisable to donate blood at the same time.
- Physical activity is not recommended the day before the analysis.
- Don't be nervous the day before. Avoid stress.
- Warn your doctor about taking medications or hormonal medications, the course of treatment of which has not yet been completed.
- If the test does not take place in the morning, you will have to fast for half a day so that the analysis data is more truthful.
What is done during anembryonic pregnancy?
A pregnant woman who has been diagnosed with a fertilized sac without an embryo should continue to be monitored by a doctor. She is prescribed additional examinations and tests. This helps to assess the condition of the body and choose the most appropriate method for removing a defective fetus from the uterus in a particular case.
When an anembryonic pregnancy is detected in the early stages, most doctors adhere to expectant management, since there is a high probability that the body will get rid of the egg on its own. The absence of spontaneous rejection indicates that the membranes are attached too tightly. This means that special medications or surgical methods must be used to separate them. The exception is conception by IVF, in which you cannot resort to artificial rejection of the false sac, since this will result in the death of the remaining viable embryos.
Medical abortion
In the early stages (up to 8 weeks), you can use a method such as medical abortion. The procedure consists of two stages. First, the pregnant woman is offered to drink a hormonal drug that blocks the production of progesterone, which accelerates the death of the empty egg in the uterus. At the second stage, the woman is given a drug containing prostaglandins. It can be taken orally or inserted directly into the vagina. Prostaglandins cause the uterus to contract, while the mucous layer is rejected, and the defective rudiment comes out along with the blood.
Surgical intervention
Surgical intervention means removing the fertilized egg using vacuum suction or scraping the uterine cavity from the inside using instruments. This method is forced to resort to in the following situations:
- unsuccessful attempt at medical abortion;
- gestational age over 8 weeks;
- contraindication to the use of abortifacients.
Abortion is carried out in a day or regular hospital. Like any surgical intervention, this procedure requires sterility and high-quality anesthesia. It is preferable to use the hysteroscopy method, which allows you to remove the false fertilized egg with all the membranes under visual control, after which the doctor monitors the bleeding and rinses the uterine cavity with drugs to prevent the development of infection and inflammation.
How does it grow during pregnancy?
HCG has its own dynamics of growth.
After reaching the wall of the uterus, it begins to be actively produced, and its growth obeys the law: “ every 2 days, 2 times
.”
The period of doubling of concentration can be reduced to one and a half days, which is also the norm.
So it grows until 10-11 weeks
and by this time reaches its maximum concentration. After 10-11 weeks, the fetal membrane gradually degenerates into the placenta and continues to produce this hormone, but in reduced quantities.
This is due to the fact that in addition to hCG, the placenta completely takes over the synthesis of progesterone
which was previously carried out.
HCG was primarily needed to activate this process
, therefore, when the placenta itself became able to produce progesterone, the need for excessively active growth of gonadotropin disappeared.
In the second trimester, you can notice a short-term decrease in gonadotropin, which is due to the formation of the placenta. Then the concentration begins to increase again, until the very end of pregnancy. After childbirth, it decreases gradually and is comfortable for the female body.
Recovery period
After the uterus has emptied, the female body needs some time to recover. The standard duration of the recovery period is usually from 7 to 10 days, during which time the woman has the right to take sick leave. Recommendations for the regime are as follows:
- it is advisable to observe bed rest;
- Do not lift weights or play sports;
- it is forbidden to have sex;
- you cannot take a bath or go to the pool;
- carefully observe intimate hygiene.
At what time periods are ST risks high?
The threat of miscarriage exists at any stage. The most dangerous is the first trimester. According to statistics, fetal freezing most often occurs before the 8th week. This is due to the fact that a woman, not yet knowing about her condition, continues to lead her usual lifestyle, take medications, smoke, lift weights, etc. In the early stages of development, when the formation of the nervous system and internal organs occurs, the embryo is especially vulnerable.
Indications for the determination of human chorionic gonadotropin
The hCG test is part of the first perinatal screening complex, which also includes ultrasound. This examination is not mandatory, but is recommended for all expectant mothers. You need to take a gonadotropin test if there are signs of pregnancy fading, and also when a heartbeat is not detected during an ultrasound examination. An hCG test is recommended if there is a history of abortion, miscarriage, frozen or ectopic pregnancy. The risk of fetal pathologies is increased in patients over 35 years of age. They need to pass the full range of laboratory tests.
Possible consequences
Women who have suffered anembryonics are concerned about an important question: does this disorder affect the ability to subsequent conceptions and how long after this can one not become pregnant? A history of abnormal pregnancy is considered a risk factor and requires increased attention from doctors. Obstetricians and gynecologists recommend that such women use contraception for 6 months. During this time, the body has time to recover and prepare for a new conception.
During this period, the woman is recommended to undergo a full medical examination and treat all disorders that are risk factors for the development of anembryonia. If there is a possibility that the cause of the anomaly was a disorder in the man, then the partner also needs to undergo an examination and have a semen analysis and spermogram. Statistics show that with the right approach and following doctor’s recommendations, about more than 85% of women become pregnant safely and give birth to healthy children.