Coccyx cyst
A coccyx cyst is a serious disease characterized by a pathological change in the fiber in the coccyx area, due to which an epithelial-coccygeal tract is formed. The violation belongs to the field of proctological diseases. If the cyst is located close to the anus, then there is a serious threat of developing sepsis due to the penetration of bacteria from the stool into the affected area. The treatment method is selected depending on the degree of damage. The doctor will determine what to do to eliminate the disease. For this reason, it is unacceptable to use folk remedies to treat pain in the tailbone.
The formation of a coccyx cyst can be triggered by many factors, the main ones being:
- sacral injury;
- lack of physical activity;
- excessive sweating in the gluteal fold area;
- a sharp drop in immunity;
- insufficient hygiene.
The symptoms of the disease are clear and allow you to determine the cause of pain in the tailbone quickly and accurately, which is why treatment begins immediately. The fact that a cyst has occurred is indicated by pain in the coccyx (perhaps the pain will be stronger to the left or right of the coccyx) and the area of the buttocks, swelling of the problem area, ingrowth of hairs into the skin at the site of the cyst, pronounced compaction in the gluteal fold and severe general intoxication of the body. The pain in the tailbone is intense and intensifies with movement and changes in posture.
Treatment of the disease is predominantly surgical . The cyst needs to be removed. The manipulations are carried out under local anesthesia and do not cause severe discomfort to the patient. Complications after surgery develop extremely rarely. The disease is often mistakenly considered not dangerous, but in reality, if it is not treated, complications easily develop that pose a threat to life.
What is the coccyx?
The tailbone is the final part of our spine. It is attached to the sacrum by a semi-movable joint and is, in fact, a rudiment. That is, in animals this is the bone responsible for the movements of the tail. The person does not have a tail, but the tailbone remains.
This bone consists of several caudal vertebrae, which anatomists do not separate, considering the coccyx to be a single whole. With its shape it follows the sacrum, forming the bowl of the human pelvis. There are 4 types of coccygeal configuration, differing in direction and angle between the coccyx and the sacrum. It is believed that most cases of idiopathic (i.e., occurring for no apparent reason) pain are type 4.
Despite its vestigial origins, the coccyx performs a number of important functions. Attached to it are many of the muscles, ligaments and tendons that form the pelvic floor and support our internal organs. In addition, in a sitting position, a person’s weight is distributed precisely on the tailbone and sit bones.
Coccyx configuration - 4 types
Pain in the coccyx (coccydynia) usually occurs after 40 years, and women complain of it much more often than men. This syndrome has characteristic symptoms:
- The pain is localized in a specific place: between the buttocks, just above the anus, or directly in it.
- Touching the tailbone area is noticeable or painful
- The pain intensifies when sitting for long periods of time on hard surfaces or immediately upon standing up.
- In a sitting position, relief occurs if you lean forward
- Defecation may be difficult
- Women experience discomfort during sexual intercourse
Bruised tailbone
A bruised tailbone is one of the most common causes of pain, diagnosed in people of any age. Violation of the skin rarely occurs, and therefore it is not always possible to identify a bruise externally. Injury occurs when a person falls on the gluteal region. The pain develops severely and can sometimes even lead to stupor and inability to move for several minutes. When a bruise occurs, the tissue is first subjected to a compressive effect, which occurs due to the impact of the traumatic object on the tissue. Further, the pain persists due to pressure on the tissue of the hematoma, which is formed due to damage to small vessels.
The main symptoms of the disease are:
- pain of varying strength radiating to the spine (the back in the tailbone area hurts);
- swelling in the area of injury;
- bruise;
- difficulty moving;
- pronounced increase in pain when sitting;
- pain that radiates to the legs after standing for a long time;
- pain in the injured area during sex, which occurs in women and men;
- pain during bowel movements.
Treatment is carried out by a doctor. The patient is required to rest in bed with a position on his side. You need to turn from side to side regularly and very carefully. As the tissue recovers, bed rest is discontinued. Physiotherapy and medications are required for therapy.
When to see a doctor and which one?
Pain before and during menstruation can occur for a number of reasons and be of a different nature. You should contact a gynecologist if you have not experienced such unpleasant sensations before and the pain is severe.
The doctor needs to be informed about the factors that caused the tailbone to hurt or that preceded the onset of discomfort. Describe in what position the pain is felt more acutely: lying down, sitting, standing, or while moving. Particular attention should be paid to the duration and regularity of pain in the sacrum.
Source of the article: https://www.oldlekar.ru/plan-beremennosti/mesyachnie/pri-mesyachnyh-bolit-kopchik.html
Coccyx fracture
A fracture is diagnosed somewhat less frequently than a bruise and is a serious disease. The pain develops acutely and, depending on the location of the fracture, can persist for a long time or disappear several days after the injury. In such a situation, the victim may not seek medical help in a timely manner, and because of this, the disease will only progress, resulting in a serious complication that may even cause disability. It hurts in the tailbone area then constantly.
The main symptoms that appear with a fracture of the coccyx are particularly severe pain, swelling, redness in the affected area , as well as difficulty walking. In many ways, the symptoms of a fracture are similar to a bruise, and therefore an x-ray is mandatory to diagnose it.
Coccyx dislocation
Most often, the problem is of traumatic origin and occurs in women after a difficult birth with a large fetus. Pain in women in the coccyx area, minor, after childbirth, can occur without damage. In men, the problem most often appears in an accident when a general pelvic injury occurs. It is not possible to diagnose the disease on your own and you need to consult a doctor. The pain of a sprain is mild to moderate, and only in rare cases is it severe. It can radiate to the lower back or legs, significantly impairing mobility. In some cases, due to severe restriction of movement, a person finds himself practically immobilized.
In many patients, during defecation, the pain increases significantly, since at the time of cleansing the rectum, the coccyx moves. Because of this, when treating pathology, it is necessary to use cleansing enemas at least for the first time , which will provide maximum rest to the injured tailbone. Depending on how severe the injury is, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis or in a hospital. During the recovery period, a course of physical therapy is mandatory.
Osteochondrosis of the coccyx
Osteochondrosis of the coccyx is a spinal problem. If damaged, intervertebral discs and vertebral tissues are damaged. Like any type of osteochondrosis that affects the coccyx, it has its own striking manifestations and is easily diagnosed by a doctor. The disease must be treated urgently, and be sure to consult a doctor. On your own, you can only seriously worsen the patient’s condition. If the disorder is not treated, then as it progresses, the quality of life rapidly decreases.
The problem most often occurs due to injuries and lack of physical activity. Quite often, women who have had a natural birth with a large fetus face this problem. Pain in the tailbone appears almost immediately after the birth of the child and can be very intense.
The main symptoms of the disease are:
- pain that is constantly present or occurs in attacks (the back in the tailbone area hurts as with any form of chondrosis);
- increased pain during physical activity and sudden transition from a sitting to a standing or lying position;
- discomfort in the tailbone.
Exacerbations of the disease occur with varying intensity. Osteochondrosis of the coccyx can remind itself once every few years, or maybe several times a year. Treatment of the disease is aimed at relieving acute symptoms and prolonging periods of remission. The main provocateurs for the appearance of symptoms of osteochondrosis are strong physical exertion, hypothermia, severe stress and unsuccessful movements, which place unnatural pressure on the tailbone. The problem especially often manifests itself in winter during periods of heavy ice, when movements become very tense and constrained. Regular performance of physical therapy exercises at this time helps to avoid exacerbation of the pathology.
Why does the sacrum hurt during menstruation?
Pain in the sacrum during menstruation worries most women. The cause of this unpleasant phenomenon is the natural processes of the menstrual cycle. However, if the pain is severe and does not go away for a long time, it is time to consult a doctor.
Physiological reasons
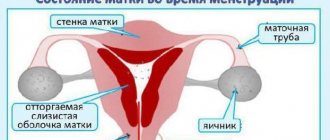
Before menstruation, the uterus begins to intensively prepare for the rejection of the endometrium. Contracts the muscles, causing pain. All this happens under the influence of hormones. A slight imbalance provokes unpleasant sensations. Taken together, all these transformations cause pain in the sacrum. Now in more detail about each process.
- When the uterus contracts, sedentary muscles are involved. Tension increases in the genital area. It is transmitted to the lower back, in particular the sacrum begins to hurt.
- On the eve of menstruation, the uterus increases in size. Presses on the nerve endings of nearby tissues of the sacrum. Aching pain appears. If the genital organ is abnormally positioned, for example, if the uterus is bent, the pressure on the nerve endings increases. The woman feels severe pain in the sacrum, throughout the lower back, and back.
- The sacrum may hurt due to hormonal changes. Shortly before menstruation, the level of progesterone decreases, and even earlier the amount of estrogen decreases. These hormones are able to calm nerve endings and control pain. On the eve of menstruation, the level of prostaglandins increases. Hormones stimulate uterine contractions. Estrogen and progesterone can restrain their growth. Due to their small number, the pain is more pronounced.
- Before menstruation, there is stagnation of fluid in a woman’s body. Hormones are also responsible for this process. Their quantity is regulated by the endocrine system. And it, in turn, is interconnected with the central nervous system. A slight disruption in the functions of these 2 systems leads to a delay in menstruation and stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs. The nerve endings suffer again, and the sacrum begins to hurt.
Lower back pain is part of premenstrual syndrome, the cause of natural processes in a woman’s body. The sacrum will hurt periodically every month. The only question is the intensity of the pain.
There are situations when a woman suffers severe pain only due to the individual characteristics of her body. This predisposition is inherited. A woman knows well how the body behaves before menstruation and during menstruation.
If the sacrum begins to hurt abnormally, there is cause for concern. A gynecologist will help you understand the cause of the unpleasant phenomenon. There is no need to delay your visit.
Pathological causes of pain in the sacrum
During menstruation, all hidden processes intensify. Diseases appear that had never shown themselves before. If your sacrum begins to hurt severely for the first time, you should visit a gynecologist. There may be several causes of pain.
- Inflammatory processes. Inflammation of the genital organs occurs due to infection or in the presence of intrauterine contraception. Infection leads to the formation of adhesions. The uterus is trying in every possible way to get rid of them. Contractile muscle movements are activated. The sacrum begins to ache, the whole lower back begins to ache, and the stomach ache. An intrauterine device is a foreign object inside the genital organ. Inflammation may occur at the beginning of its use, with prolonged use for more than a year. Inflammatory processes manifest themselves as a delay in menstruation, changes in discharge, and a burning sensation in the external genital area. The sacrum and the entire lower back begin to hurt constantly. Osteochondrosis increases pain.
- Neoplasms . The presence of additional tissue increases the size of the uterus, reduces blood flow, and puts pressure on nerve receptors. The sacrum begins to hurt due to uterine fibroids, cysts, or cancerous tumors.
- Failure of the endocrine system . Thyroid dysfunction leads to hormonal imbalance. A doctor can determine the cause of the pathology. You will have to undergo examination and tests. The menstrual cycle is disrupted, changes in behavior and health are observed.
- Pregnancy. After conception, new mechanisms are launched in a woman’s body. Hormonal levels change, the uterus increases in size. Painful sensations appear in the lower back and sacrum of an aching nature. Severe lower back pain is a cause for concern. Because it indicates a not entirely successful pregnancy. A miscarriage may occur or an ectopic pregnancy may be present. The presence of bleeding is a signal to urgently consult a doctor. Regardless of whether pregnancy is desired or not.
It is impossible to independently understand the cause of pathological discomfort in the lower back. There is no need to postpone a visit to the gynecologist. But the usual pain on the eve of menstruation can be reduced with your own efforts.
How to relieve pain
You can get rid of pain with simple exercises and massage. The main thing is not to overdo it. Because strong physical activity on the lower back will only worsen the situation.
- Turn the torso to the sides in a standing position.
- In a lying position, press your knees to your chest and clasp your arms. Perform rolls towards the head and buttocks.
- Massage your shins well. This area of the body is directly connected to the sacrum. Impact on the shins will improve the position of the lower back.
You should avoid physical activity and nervous tension a week before your expected period. Monitor your feelings and visit a gynecologist in a timely manner. Simple exercise every day will save you from unpleasant painful sensations in your back.
Source: https://moimesyachnye.ru/boli-v-kresttse-pri-mesyachnyh.html
Pelvic bone cancer
Cancerous lesions of the pelvic bones also lead to a dull pain in the tailbone, and sometimes pain near the tailbone. It is most often secondary and develops due to metastasis of the main tumor formation. In most cases, cancer spreads to the pelvic bones from the pelvic organs, abdominal cavity and soft tissues of the lower body .
In rare cases, pelvic cancer can appear as an independent disease, in which malignant cells develop directly in the bone tissue. The patient may be diagnosed with the following types of disease: osteogenic sarcoma, osteoblastoclestoma and parosteal sarcoma. Among all cancer lesions, primary bone cancer accounts for no more than 1%, and the pelvis itself accounts for even less. At the same time, this form of the disease is extremely severe and dangerous due to the complete secrecy of the pathology in the initial stages and especially rapid development.
The main symptoms of a dangerous disease, which, unfortunately, appear only at stages 3 and sometimes 4, are:
- pain in the area of the coccyx of an aching nature, which is constantly present and regularly intensifies in paroxysms and has a clear radiation to the coccyx;
- a sharp decrease in the mobility of the lower extremities;
- abdominal pain of unknown nature;
- causeless nausea;
- severe weakness;
- sudden weight loss;
- persistent increase in temperature.
With the disease, the prognosis for the patient is unfavorable. Most often, the disease is detected in a form where it is possible to provide only polyactive care to facilitate the last period of the patient’s life. Effective therapy is noted only if the disease is diagnosed at the very beginning of its development, which is extremely rare, since the tumor is discovered by chance during an examination for another reason.
Hormonal changes and lower back pain
Most often, the sacrum hurts before the onset of menstruation. Discomfort occurs due to the fact that the uterus, located in the pelvis, contracts under the influence of hormones. Most of the time she is at rest. During the process of intensive separation of the endometrium, the contracting walls of the uterus affect the nerve endings, which causes pain.
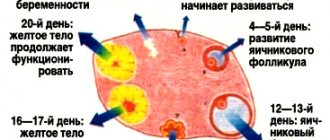
The menstrual cycle is divided into several stages. First, the female body produces estrogen. After ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum, progesterone production increases. If pregnancy does not occur, its level decreases.
Inflammation of the coccyx
Inflammation of the coccyx occurs when an infection enters the area of the organ. This can happen with an open injury or with blood flow from a source of inflammation in the body. Less commonly, the infection penetrates into the tissues of the coccyx in diseases of nearby organs. Coccyx pathology appears in people of any age and gender equally . Additionally, a sedentary lifestyle, wearing very tight underwear or clothes, which impairs blood flow in the pelvic area, and previous injuries to the tailbone, increase the likelihood of the problem occurring. During pregnancy, there is also a higher risk of experiencing inflammation of the tailbone.
If it is violated, a dull aching pain occurs in the area of the coccyx, which noticeably intensifies when sitting and palpating the problem area. Also, if the inflammation progresses, redness of the skin above the tailbone and a local increase in temperature are observed. If therapeutic measures are not started at this stage, the pain becomes sharp and jerking, and general intoxication of the body develops. It leads to loss of performance and requires urgent medical attention.
Of particular danger is rapid purulent inflammation of the coccyx, which begins with acute intense pain . A person has pain in the anus and tailbone. With it, if you do not consult a doctor immediately, sepsis develops in a short time, causing the death of the patient. If the inflammation turns out to be chronic, then without treatment it eventually leads to the development of a cancerous tumor.
Treatment of inflammation is carried out in the initial stage with medication , and in advanced conditions or acute purulent process - surgically. What kind of therapy is required will be determined only by a doctor. When treating with medications, antibiotics are mandatory.
Why do you feel pain in the sacrum when your period approaches?
Every third woman complains to her gynecologist that her sacrum hurts before her period. If this pain accompanies life and is expressed tolerably, subsides when you choose a comfortable position, you should not worry.
When at the beginning of your period you suddenly experience severe pain in the sacral area, pulling your leg and lower abdomen, you should definitely consult a doctor. This may be a signal of the occurrence of various pathologies.
Why does the menstrual cycle announce its approach with pain in the sacrum?
The sacrum contains many nerve endings, and premenstrual hypertrophy of the uterus irritates these nerve endings.
What are periods?
Rejection of the inner layer of the epithelium. To do this, the myometrial muscles are used, which are at rest between cycles. By contracting to reject the mucous membrane, they indirectly affect the sacrum.
Hormonal changes occur in the body before menstruation. The production of progesterone and estrogen, which directly influence a woman’s mood, decreases.
Only they are able to neutralize the painful effect of prostaglandins - hormones responsible for contraction of the muscles of the uterus. Therefore, a woman begins to feel the pain from contractions during menstruation to the fullest - the sacrum hurts and the lower abdomen pulls, the pain radiates to the leg - often to the thigh.
- Before menstruation begins, the body accumulates fluid. Internal swelling primarily affects the connective tissues, increasing pressure on the nerves of the genitals. The joints begin to ache - a slightly larger amount of fluid accumulates in them than is necessary for normal functioning, and the load on the musculoskeletal system increases.
- With osteochondrosis, the pain intensifies even more, especially if the pathologically altered discs are located in the lumbosacral spine.
- Sometimes the sacrum hurts, and the pain radiates to the leg before menstruation due to the individual characteristics of a woman’s structure. The uterus in the abdominal cavity may deviate backwards - gynecologists call this condition a “bent” uterus. This condition is not considered a pathology - unless the bend is at an obtuse angle. During menstruation, as the uterus enlarges, pressure on the sacrum increases and muscle pain appears.
In this case, the pain can spread not only to the upper thigh, but also to the back - even to the lower back - “twists” in the calves, and nausea may be felt. There is also pressure on the intestines: it is “propped up” from below, and it, in turn, exerts slight pressure on the stomach.
If you haven’t felt any pain all your life, or they were insignificant, and then from a painful attack you want to “climb the wall” or cry, then you should definitely consult a doctor. The body always signals the occurrence of problems in it by changing the nature of the menstrual cycle.
- Any infection in the genitourinary system results in swelling of the tissues surrounding the organs. The blood supply is disrupted, the uterus, when trying to push out the epithelium, encounters resistance, contractions intensify, and this process causes pain.
- The adhesions process affects the course of the cycle - adhesions prevent the uterus from functioning normally.
- Benign formations in the reproductive organs - fibroids and cysts - slow down the process of outflow of secretions. Due to the obstacles that have arisen, they accumulate, then are suddenly pushed out, causing blood vessels to burst. There are nerve endings in the wall of each vessel, which is why pain occurs. Sharp contractions put pressure on the sacrum.
- When the endocrine system is disrupted, the pain intensifies. The woman is not even sure that it is the sacrum that hurts - aches occur throughout the body, additional irritability appears, and sleep is disturbed.
When unusual pain in the cross coincides and your periods differ from typical ones, you need to go to the doctor before they end. This may indicate a termination of pregnancy - sometimes ectopic, or normal, in which the outflow is blocked, but the bleeding has not stopped.
If the sacrum suddenly begins to hurt, you can do something specific only after contacting a gynecologist.
In the event that the doctor does not find any abnormalities in the state of health, you can consult with him what to do to reduce discomfort.
Painkillers that relieve premenstrual or menstrual pain:
- non-steroidal drugs: “Ibuprofen”, “Nise” and the like;
- analgesics – “Analgin”, “Aspirin”, “Paracetomol”;
- antispasmodics – “Baralgin”, “Spazmalgon”, “No-shpa”...
Women often complain that the sacrum hurts more intensely when sitting. In this case, you should optimize the workplace - equip it with a special lining - it is inexpensive - the kind that is used for hemorrhoids or problems with the coccyx to relieve the load on the sacral area.
Such chair pads are similar to a lifebuoy or a toilet seat; they relieve stress from a problem area when sitting, prevent pinching of blood vessels and ease tension in the muscles of the pelvic organs.
The sacral area should be exposed to dry heat. You should not rub the sore spot - just tie a warm scarf around your lower back.
There is special gymnastics that helps strengthen the back and abdominal muscles and teaches them how to control them, which further helps reduce pain.
Physical exercises help relieve pain:
- Starting position – lying on your back. The hands rest on the stomach. The legs rise very slowly, to the “birch” position, and also slowly lower. You should breathe with your stomach;
- The starting position is the same. Exercise – slow scissors: raise your legs and begin to slowly spread them apart and bring them together. After 3 repetitions - tuck - the knees are tucked towards the chest.
- Lying on your back, you should relax. With your right hand, find a point on the stomach located 4 fingers below the navel. They step back from it to the right and left by 2 fingers, and determine the points of influence - when pressing on them, slight pain should occur. These points are massaged for about 3-5 minutes.
With the onset of menstruation, massage must be abandoned, and exercises can be performed. Only if 5-6 repetitions are done during the prestrual period - during the cycle 2-3 are enough. Massage of the lower leg also alleviates the condition - it can be used when the sacrum begins to hurt during pregnancy.
Gymnastics, massage treatments and elimination of diseases that affect the course of menstruation will help make them more painless.
Menstruation is a natural process that occurs in the female body, and you should try to make it comfortable for yourself.
The materials posted on this page are informational in nature and intended for educational purposes. Site visitors should not use them as medical advice. Determining the diagnosis and choosing a treatment method remains the exclusive prerogative of your attending physician.
Source: https://allergology.ru/zhenskoe/pri-mesyachnyx-boli-v-krestce
Osteomyelitis of the coccyx
Osteomyelitis is a purulent inflammation of the bone. Most often, the disease develops after purulent inflammation of the skin in the tailbone area has not been properly treated. Typically, primary suppuration appears due to blockage of the sebaceous gland, after which the inflammation spreads deeper. The main causative agent of osteomyelitis is staphylococcus.
With pathology, bursting pain occurs when palpating the coccyx, as well as when sharply bending forward and actively walking. If purulent masses extend beyond the bone area, they melt the tissue, forming external and internal fistulas. From them it is easy to notice the discharge of pus and ichor. Fistulas in the rectum are especially dangerous, as sepsis can quickly occur because of this. Home treatment for a disease of this kind is unacceptable.
Haemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are a common proctological problem in which pain is also felt in the tailbone. The disease affects men and women. Diagnosis is easy, and the doctor can determine the disorder with a simple visual examination. Pain in the tailbone most often occurs with internal hemorrhoids.
The main symptoms of the disease are pain during bowel movements or prolonged sitting and bleeding from minor to intense, dangerous . It is impossible to independently understand whether hemorrhoids or a rectal tumor are present. Pain in the coccyx appears at the time of exacerbation of the disease, when an active inflammatory process begins to develop (pain in the rectum in the coccyx area). The tailbone hurts especially severely at the time of defecation, when strong pressure is applied to the area of the hemorrhoidal lump.
Treatment of the disease can be carried out with medications or, in severe cases, surgery. Surgery is usually necessary only if the lumps are large and drug therapy does not bring results.
Physiological reasons
Hormones have a huge influence on the condition of the genital organs and the reproductive system as a whole. They play a decisive role in women's health. When the hormonal background is ideal, most often a woman does not experience pain during her period.
The functioning of the nervous system is of certain importance. The uterus is an organ made entirely of muscles. They contract intensively to peel off the unnecessary inner layer every month.
In order for functioning to occur normally, the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the nervous system work. The first goes into the uterus, which provokes nagging pain in the lower abdomen and cramps. The second section begins in the sacrum and continues to the cervix.
The sacrum hurts before menstruation precisely due to the work of the parasympathetic area. Its movements are controlled by the hypothalamus, so the intensity of sensations for a particular girl depends on many additional factors. These are stress, strong emotions, excitement, fatigue, etc. The stronger the emotional excitement, the more the sacral area will hurt.
Rare causes of tailbone pain
Rare triggers of pain in the coccyx should also be taken into account. I call doctors the main ones :
- abrasion of the gluteal fold;
- parasitic lesions of the large intestine;
- insect bites in the area of the gluteal fold;
- eczema - symptoms of pain in the tailbone are combined with itching;
- dermatoses;
- crack in the gluteal fold - pain radiates to the tailbone;
- prolonged sitting on a hard surface (the tailbone hurts for no reason and goes away on its own).
Treatment for such causes of pain in the tailbone is simpler.
conclusions
If you experience severe pain in your tailbone that persists for more than a day, you should definitely seek medical help. You cannot self-medicate, as it is important to accurately understand the cause of the unpleasant phenomenon, which can sometimes be very dangerous, and then wasting time due to home treatment can cost your life. The causes of pain in the tailbone are varied and are treated by specialists in several areas.
Found an error? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter.
Often the menstrual cycle is accompanied by unusual phenomena - for example, the tailbone before menstruation begins to give aching or pulling painful sensations. As a rule, such signs appear 5-7 days before the cycle and can intensify when bending forward. Find out why this happens and how to quickly relieve the symptoms right now.
How to get rid of pain in the sacrum?
If the gynecologist did not find any anomalies, but the pain in the sacrum continues, you need to do home treatment: take antispasmodics, apply a heating pad, etc. In addition, you can ease the sensations with the help of small exercises, which should be done a few days before menses.
- Lie on your back with your legs together. Place your hands on your stomach. Slowly raise your legs straight up, gradually finding yourself in the “birch tree” pose. Try, breathing with your stomach, to hold in this position for some time. Then lower your legs slowly. Repeat the exercise several times.
- Lie on your back, knees slightly bent, place your open palms under your sacrum. Slowly spread and bring your legs together. Repeat these movements for two minutes, moving your palms lower, pulling your knees towards your chest. Freeze for a few moments, then return to your starting position.
- It is comfortable to lie on your back and breathe deeply. Find a point four fingers below the navel, move away from it to the left and right by the width of two fingers and press on these points.
- Massage your shins, thus relieving pain.
- As a preventive measure, it is useful to strengthen the abdominal and back muscles.
About a week before their period, a large number of women complain of pain. But the location and severity of pain manifests itself differently in each woman; this is due to the physiological factors of each woman, and they serve as a signal that the menstrual phase is approaching. Most people experience lower back pain, and most often their source is located in the tailbone area. The pain in this place is often very severe, and can intensify with various movements: bending forward, standing up suddenly, lifting heavy objects. Doctors talk about pain in the sacrum using the term Sacrodynia.
Causes of pain
The fact that the tailbone hurts during or before menstruation does not mean that this particular part of the spine is wrong, except in obvious cases of injury to the tailbone from a fall or blow (more about this here). In fact, such a phenomenon can be caused by very different, completely unrelated reasons, or a combination of them.
Conventionally, they can be divided into 2 large groups:
- Associated with uterine pathologies.
- Having other root causes.
Pain associated with the uterus
All reasons from this group are explained by an increase in the volume of the uterus or strong muscle contractions of this organ. These phenomena can be generated both by processes occurring in the uterus itself and by other factors.
- During menstruation, the tailbone hurts because all the dead epithelium that lines the mucous membrane is excreted by the uterus, which causes it to contract strongly, and as a result, muscle pain radiates to the tailbone.
- If the pain is combined with strong pulling sensations in the lower abdomen, it is very likely that these are anatomical features of the location of the uterus - it can lie extremely close to the sacrum, as if leaning back. Since the muscles of the uterus are toned and enlarged during the monthly cycle, extraneous sensations arise. The situation is aggravated when using a spiral, which further enlarges the uterus.
- In some cases, such phenomena may be associated with hereditary characteristics - it is genes that lead to certain deviations in the location of the uterus or affect hormonal processes.
- Changes in hormone metabolism give rise to more intense contractions of the uterus - this is the physiological effect of the hormone prostaglandin.
- Endometriosis is a pathological growth of the so-called endometrium, a layer of cells in the tissue of the uterus.
- Posterior parametritis is an inflammation of the so-called parametrium - the layer of connective tissue that covers the cervix.
Pain not related to the uterus
This includes pathogenic processes that occur in other organs and parts of the body, but nevertheless, they also give rise to painful sensations in the tailbone.
- In some cases, the tailbone hurts with the development of osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region. Inflammatory processes increase the volume of intercellular fluid in the connective tissue, which seems to swell and put pressure on the uterus, causing nagging pain.
- Hemorrhoids are one of the most common causes. In this case, the pathology leads to an increase in veins and pressure on the pelvic area, which explains the symptoms that appear.
- Infectious diseases of the sacral region (tuberculosis, lesions of staphylococcus and other bacteria) provoke nagging and sharp pain, which can coincide with menstruation.
- Similar sensations can be caused by various infections that progress in the genitourinary system, since as a result of the activity of certain bacteria, adhesions are formed in the tissues of the uterus, due to which the discharge stagnates and puts pressure on the cell walls.
- In rare cases, such sensations are explained by thrombophlebitis of the pelvic veins - due to the accumulation of blood clots, the pressure on the walls of blood vessels increases greatly, which is why pain occurs.
- If, along with extraneous sensations, insomnia, anxiety, irritability, and fatigue are observed, there is a possibility that the cause is related to a hormonal disorder of the thyroid gland.
- The development of benign or cancerous tumors that press on the walls of the organ and cause pain.
- An ovarian cyst is accompanied not only by pain in the sacrum, but also by extraneous, pulling sensations in the groin area from the affected ovary.
- Coccyx cyst - in most cases, this is a congenital disease, and it occurs mainly in men. The essence of the pathology is that in the intergluteal fold under the skin a whole cavity is formed from overgrown epithelium (skin tissue), which leads to extraneous sensations.
Coccyx pain and pregnancy
Finally, cases of the appearance of these sensations during pregnancy can be classified as a separate group. In fact, such symptoms are normal and have been sufficiently studied. The reason is that due to hormonal changes and the growth of fetal mass, pressure on the pelvic area increases, which is accompanied by corresponding symptoms.
If a woman has already given birth and another pregnancy occurs, extraneous sensations are often explained by birth injuries, namely damage to the sacral ligaments. The corresponding pathology is called coccydynia. It can completely disappear after the first birth and make itself felt only in the last stage of the second pregnancy. In such cases, the doctor often prescribes wearing a bandage, which can completely eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Causes
With injuries to the coccyx, pain may occur, but it is constant and not associated with any specific time period. All pain in the coccyx that is not associated with the spine is conditionally divided into two groups. The first group includes pain in the coccyx associated with changes in the uterus.
Pain in the tailbone may appear due to contraction of the muscles of this organ. The same pain occurs in a woman whose uterus has increased in size. During menstruation, the uterus is forced to contract strongly, as it needs to remove the rejected layer of mucous membrane from its cavity.
Because of these muscle contractions, the tailbone hurts. It’s not the tailbone itself that hurts, the uterus hurts, and the pain radiates to the tailbone. Some women may experience pain in the coccyx due to the anatomical structure of the body. In such women, the uterus is a little closer to the tailbone than it should be, so any changes in the uterus cause pain in the area where the tailbone is located.
Pain in the tailbone is caused by the uterus tilting too far back. Such anomalies of location are programmed at the genetic level, and can sometimes be inherited from mother to daughter.
During menstruation, the tone of the uterine muscles increases, so a woman experiences sensations that are not present during the rest of the month. Such pain can intensify significantly if a woman has a coil installed.
The uterus may increase in size due to the presence of a spiral in it. Hormonal changes in the body can also cause pain in the tailbone. A large release of hormones into the blood can lead to increased contractions of the uterus, which are accompanied by pain in the tailbone.
The hormone prostaglandin can cause strong contractions of the uterus. There is a simpler explanation for pain in the tailbone during menstruation, which is not related to abnormalities in the location of the uterus. Most women have a high pain threshold, so many pains, including those associated with the onset of menstruation, go unnoticed. And only in a small part of women who have a low pain threshold, these unpleasant sensations result in pain in the tailbone before menstruation.
Diagnosis and treatment
It is very important to understand that independently determining a diagnosis based on your feelings in most cases leads to incorrect conclusions. Therefore, the patient often begins to be treated for the wrong disease, which causes even greater harm - on the one hand, the true disease progresses, and on the other, the body receives medicinal substances that it does not need at all.
Thus, contacting a gynecologist is a mandatory measure in this case. In this case, you should try to describe your feelings as accurately as possible, since the correct diagnosis largely depends on this.
It is necessary to pay attention to the following features:
- In what positions is there an increase in extraneous sensations or their occurrence - sitting, standing, when rising, after a long sitting.
- How long such signs are observed, and how regular they are - before each cycle or not, for how many months.
- Pain is always combined with menstruation (at the beginning of the cycle or before) or it occurs at other times.
- Is there a connection between the appearance/intensification of extraneous sensations and the act of urination, defecation, as well as sexual intercourse.
- Finally, are there any extraneous symptoms - increased fatigue, unexplained insomnia or drowsiness, fever, malaise and pressure surges.
Often, diagnosis does not end with the examination and interview of the patient.
To confirm the preliminary diagnosis, additional examination is necessary:
- Ultrasound;
- blood test for the concentration of certain hormones;
- tests to check for infection.
The course of treatment is prescribed depending on the specific case, and almost always involves conservative therapy (without surgical intervention).
Abnormal pain before menstruation
Every woman has studied her body over many years and knows how it reacts to the onset of menstruation. If the pain in the lower back, in the sacral area is stronger than usual, it makes you think seriously about the causes of the discomfort. In fact, there are enough of them to get confused and not make the correct diagnosis on your own. The best option is to seek help from a specialist. What could it be?
All painful symptoms are associated with the activity of the uterus. First of all, you should pay attention to the reproductive system. It is necessary to visit a gynecologist. If diseases are excluded, undergo examination by other specialists. Painful sensations in the lumbar region arise due to problems with the gastrointestinal tract, with intestinal dysbiosis. The roots of the problem may be hidden in pathologies of the endocrine system and pancreas. In any case, the problem should not be ignored.
Back pain often bothers people of different ages. Pain in the sacrum is expressed as an unpleasant pulling sensation, possibly with spasms, appearing on both sides of the spine below the lumbar region. A slight pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation can be considered normal, but when the sacrum hurts before menstruation, you should be wary.
Exercises to relieve pain
If the symptoms intensify, and it is not possible to seek professional medical help at the moment, you can do a few simple exercises that will not take much time, but are guaranteed to make you feel better:
- While lying on the floor (on your back), your legs are joined together and your hands are placed under your buttocks, palms down. The legs are raised slowly, held in the raised position for half a minute and lowered smoothly. You can repeat 8-10 times.
- Continuing to lie down, your legs need to be bent at the knees, and your hands should be placed under your buttocks, now with your palms facing up. Bring your legs together and spread them, touching your knees. The movements are smooth, repeat for 2 minutes.
- Next, you need to take several deep breaths and exhalations, and then press on the point below the navel 2-3 cm.
- And the last effective remedy is massage of the legs with circular, longitudinal movements and pinching.
Treatment
After establishing an accurate diagnosis, the necessary treatment is prescribed. The treatment regimen depends on the existing symptoms and is most often carried out conservatively. Pain in the tailbone caused by the approach of menstruation can be significantly reduced or completely eliminated with the help of a small set of exercises.
They take very little time to complete. The woman should lie on the floor on her back and place her hands, palms down, under her buttocks. In this case, you need to slowly raise your legs and then lower them just as smoothly. During menstruation, when the tailbone hurts, ten repetitions of the exercise are usually enough to eliminate the discomfort. An effective remedy for pain may be massage.
If the pain is very severe and creates significant discomfort, the doctor may recommend painkillers and antispasmodics to the woman. Such drugs help relieve symptoms, but do not eliminate the cause of the pain.
Malaise, pain in the lower abdomen and lower back are often unpleasant accompaniments of premenstrual syndrome in women. Painful sensations in the coccyx area, which occur during or shortly before the onset of menstruation, most often are not directly related to the lower parts of the spine, and are only a consequence of spasms of smooth muscles or mechanical compression of an enlarged uterus.
Causes of pain in the tailbone during menstruation
The causes of pain in the coccyx in women during menstruation and shortly before their onset can be both natural processes occurring in the uterus and pathologies of the pelvic organs.
Pain associated with the organs of the reproductive system
The most common cause of pain in the tailbone area during menstruation is natural contractions of the uterus. Every month, the epithelial layer of the endometrium lining the inside of the uterus is renewed, and its dead cells are washed out during menstruation. In order to push dead tissue out of its cavity, the uterus contracts strongly, and these spasms of smooth muscles become the cause of pain, including radiating to the tailbone area.
The second most likely cause of tailbone pain before and during menstruation is the special genetically determined structure and location of the uterus. In this case, it is displaced and tilted back and is very close to the lower spine. During menstruation, it increases in size and acquires increased tone, creating pressure on the ligaments and coccygeal bone, which can also cause discomfort, especially when bending, squatting, or lifting heavy objects. Often, such sensations are intensified if a woman has a contraceptive device installed.
Another possible cause of pain may be internal tissue swelling. Hormonal changes that occur in a woman’s body during the premenstrual period cause fluid retention. The increased volume of edematous connective tissue creates pressure on the nerve endings, causing pain.
Pain may also be caused by excess production of prostaglandins - hormones necessary to stimulate uterine contractions and also increase sensitivity to pain, especially in women with a low pain threshold.
The cause of pain can be not only physiological, but also pathological processes occurring in the organs of the reproductive system of women. Severe, persistent pain in the coccyx area before, during and after menstruation can be a sign of endometriosis - inflammation of the endometrium lining the uterus from the inside, or parametritis - a purulent-inflammatory process in the parametrium - the connective tissue surrounding the cervix.
The tailbone can also hurt with an ovarian cyst. In the presence of benign neoplasms, pulling sensations occur in the lower abdomen, in the area of the coccyx, lower back, mainly on the side of the affected ovary.
Separately, it is worth mentioning those cases when the tailbone hurts and at the same time there is a delay in menstruation. Such a symptom, especially if it is also accompanied by pain in the abdominal area, may indicate an ectopic pregnancy. This condition is very life-threatening, so you should consult a doctor even if a home pregnancy test shows a negative result.
Other causes of pain
Pain in the coccyx area in women may have causes that are not related to menstruation:
- Osteochondrosis of the sacrolumbar spine. Inflammation accompanied by swelling creates additional pressure on the tissue.
- Varicose veins of the small pelvis and hemorrhoids. Vascular problems associated with an increase in the lumen of blood vessels and circulatory disorders in the pelvis also create preconditions for the development of pain.
- Infections of the genitourinary system often provoke referred pain to the sacrum and coccyx.
- Pressure on the tailbone can be exerted by benign and malignant neoplasms that form in the pelvis.
- An acute purulent-inflammatory process - osteomyelitis - in the tissues of the coccygeal bone can cause severe pain in this area.
- Adhesions in the tissues and organs of the pelvis as a result of chronic inflammation of the genitourinary system are another possible cause of pain in the coccygeal area.
Separately, it is worth mentioning thyroid dysfunction. Hormonal imbalances can lead to sleep disturbances, fatigue, irritability and apathy and manifest as pain, including in the sacrococcygeal spine.
Spine
Many women make the same mistake. They make a diagnosis for themselves, guided only by their feelings. Meanwhile, pain in the coccyx may be associated with reasons that are far from related to the reproductive system. Their appearance in the period preceding menstruation or during menstruation may be a simple coincidence in time.
A coccyx cyst may be to blame for the appearance of pain in the sacral area. This pathology is congenital and can be detected in adulthood. This pathology predominates in men, but in rare cases, a coccyx cyst can also develop in a woman.
The essence of the changes taking place is that between the buttocks at the level of the coccyx, a small cavity is created from epithelial cells under the skin. This cavity is the source of pain in the coccyx area. Since this pathology is quite rare for women, it is not detected immediately. And all pain in the coccyx area is associated with close periods.
Another reason for pain in the sacral area may be mistakenly associated with the uterus and its changes. Infectious processes in the sacrum are always associated with pain very similar to pain arising from the uterus.
Such diseases include tuberculosis of the sacral spine. A staphylococcal infection of the spine will also be accompanied by pain in the coccyx area. The pain in this case will be severe.
Inflammation affecting the genitourinary system can also be diagnosed by pain in the coccyx area. Inflammation of the uterine tissue may be accompanied by adhesive disease. These adhesions cause pain in the sacrum area. Even less commonly, pain in the coccyx not associated with the uterus occurs due to thrombophlebitis of the pelvic veins. In this case, the source of pain is numerous blood clots that press on the walls of blood vessels.
Oddly enough, pain in the tailbone can be associated with disorders of the thyroid gland. Hormonal disorders associated with this gland are accompanied, in addition to pain in the sacrum, by general disorders associated with insomnia, anxiety, irritability, and fatigue. In this case, finding the cause of periodically appearing pain in the tailbone is no longer so difficult.
Diagnostics
If pain in the coccygeal area is associated specifically with the menstrual cycle, the first specialist you should contact is a gynecologist. After the examination, he can refer you for a consultation to a proctologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, vascular surgeon, oncologist and other specialists.
To clarify the diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental tests may be prescribed:
- radiography of the pelvic bones and lower spine,
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs,
- blood test to detect infection or clarify hormone levels.
Even minor pain sensations deserve attention, as they can be an early signal of the development of many dangerous diseases, and early diagnosis is one of the main conditions for their successful treatment.
Bad signal
You need to contact a gynecologist if the pain in the sacrum is severe or occurs for the first time, to find out what anomalies in the body can activate these pains.
After all, hormonal changes can “wake up” old pathologies. They block the path of blood to the exit from the uterus, as a result of which the flow of menstruation is disrupted. And this can be explained by such deviations:
- An infectious inflammatory process occurs in the genitourinary system, which causes adhesions that disrupt the outflow of secretions from the uterus. The muscles of this organ, contracting, try to push the blood out, but cannot. Therefore, the sacrum begins to hurt.
- It is possible that a tumor, cyst, or fibroid has formed that interferes with the release of secretions.
- Diseases of the endocrine system caused by hormonal imbalance. If the problem is the thyroid gland, then this can be determined by accompanying symptoms: weight loss, irritability, insomnia.
- An ectopic or abnormal pregnancy may block the flow of secretions.
Therapy methods
If the examination confirms the presence of any disease, treatment of pain in the coccygeal area begins with eliminating its root cause. Methods are selected individually depending on the nature and degree of pathology.
If it turns out that the pain is associated only with functional changes in the body during the menstrual cycle, the following remedies will help alleviate the condition:
- A week before the expected start of menstruation, you need to ensure that excess fluid does not accumulate in the body: limit the consumption of sweet and especially salty foods, smoked foods, and preserves. In some cases, you can use mild herbal diuretics.
- Dry heat helps relieve pain and reduce spasms - a woolen scarf or belt tied on the lower back, a heating pad, ointments and gels with a warming effect.
- For severe pain, a one-time dose of analgesics or anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs is allowed.
- A light massage relieves muscle spasms and creates a distracting effect, reducing the severity of pain.
Another way to eliminate discomfort is to perform a set of exercises that improve blood flow in the pelvic vessels and strengthen muscles and ligaments: raising straight legs together and alternately from a supine position, spreading and bringing together legs bent at the knees, “bicycle” and “scissors.”
Despite the fact that most women experience pain during menstruation, you should not perceive this signal from the body as something completely natural; you should consult a specialist to identify possible causes.
Pain as a sign of disease
When the situation arises once and does not cause significant concern, it is enough to start worrying less, avoiding stress, and resting more. But if pain has occurred more than once, it may be a sign of some serious illness.
Possible complications:
- edema;
- bend of the uterus;
- inflammatory process;
- infectious diseases;
- tumor;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- disorders in the endocrine system, etc.
Internal swelling
Unpleasant nagging pain in the sacral area often occurs due to excessive accumulation of fluid inside the body. It stagnates in the tissues, which leads to the formation of edema of the internal organs or the uterus itself.
The uterus increases in size, its walls become thicker, and begin to compress the nerve endings. The pain is localized not only in the lower back, but also in the tailbone area.
It's easy to check whether this problem exists. Gynecologists recommend reducing fluid intake 7 days before the expected start of menstruation. Water will not accumulate in the body, which will help avoid swelling. If the problem continues to bother you, your doctor may recommend using laxatives a few days before your period begins.
With internal edema, not only organs, but also joints are affected. Due to the fact that excess water affects the hip joint, discomfort often occurs in the legs. They go numb, the skin becomes cold.
When the sacrum hurts during menstruation, this may be due to the individual structure of the female body. When the uterus is abnormally curved and displaced back, the term "relapse" is used.
Despite the fact that such a structure is not considered a disease, doctors treat this feature with concern. This can affect, for example, pregnancy and childbirth. When the uterus is bent at an angle of more than 90 degrees, painful sensations in the lower abdomen and back bother the woman every day.
The sacral area begins to hurt the moment the endometrial cells separate.
The uterus increases significantly in size, and the nerve endings are under great pressure. Unpleasant sensations are most often not localized in one place. They are distributed along the back of the thighs and calves. Sometimes unexplained nausea occurs. This is also a sign of a bent uterus. Increased in size, it puts pressure on the intestines.
Infectious and inflammatory processes
Such diseases are not asymptomatic. Pain in the sacral region during menstruation is one of them.
Other signs of the inflammatory process:
- severe cramps;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- constant pain even after the end of menstruation;
- elevated temperature.
Particular attention should be paid to the last point. A high temperature in the absence of cold and flu symptoms always indicates the presence of inflammation in the body. In most cases, we have to deal with infectious diseases of the genital and urinary tract.
Pain in the sacrum may indicate an infection, because in such diseases there is inflammation, which is accompanied by swelling and impairs blood supply to the tissues. Thus, it is difficult for endometrial cells trying to detach from the inner surface of the uterus to make their way through. The passage becomes too narrow due to the increased size of the walls, as a result of which the muscles, trying to push through the secretions, begin to contract intensively. This causes spasms and pain.
If a woman observes all of the listed symptoms, it is necessary to contact a gynecologist and undergo all the necessary tests and do an ultrasound.
A woman can live with a small benign tumor in her reproductive system and not know it. Most often these are cysts of different sizes, less often - fibroids. Peculiar growths of various shapes and sizes can block the blood flow, obstruct discharge, causing its accumulation in the uterine cavity.
Signs of neoplasm:
- pain in the tailbone;
- delay of menstruation;
- palpable pain in the lower abdomen.
When menstrual flow moves forward, under pressure it damages small blood vessels and disturbs nerve endings. All this, combined with strong contractions of the reproductive organ, leads to pain in the sacrum.
The gynecologist may decide to remove the cyst if it can interfere with the outflow of blood during menstruation. This is especially true for large formations. The surgical method is not always used; sometimes medication is sufficient.
Other reasons
During an ectopic pregnancy, pain in the sacral area is common. However, in such a situation, a woman, as a rule, must guess about the possibility of such a condition.
Other signs are present:
- delayed menstruation;
- pain in the lower abdomen, localized on one side;
- malaise;
- drowsiness, mood swings, etc.
It is impossible to continue an ectopic pregnancy; there may be a danger to the health and life of the mother. Urgent medical help is needed.
If, along with pain in the sacrum, the lower back bothers you, insomnia, irritability, and weight loss are observed, you can suspect a problem with the endocrine system. It is responsible for many functions of the female body, including the release of hormones and immunity. In this case, it is advisable that the endocrinologist refer the woman for a full examination, including the necessary blood tests.
If a woman experiences pain in the sacrum before her period, endometriosis (an abnormal increase in the endometrial layer) can be suspected. Other symptoms should be present, such as abdominal pain, spotting before and after menstruation, and general malaise.
If you have severe back pain that is not dependent on your cycle, you should see a surgeon. This could be vertebral displacement or spondylolisthesis. The sensations intensify when lifting weights, not only the sacrum aches, but the entire back. The doctor must exclude other pathologies, such as osteoporosis, osteomalacia.