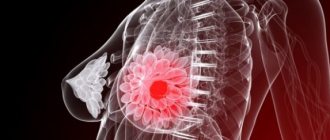
Every year, diseases of the mammary glands in women are only becoming more frequent. This could be a cyst, lipoma, fibroadenoma or other pathological lesion. Regardless of the size, any focal formation of the mammary gland must be diagnosed promptly, before the disease causes dangerous complications in the patient.
Focal formation of the mammary gland: what is it?
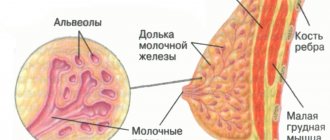
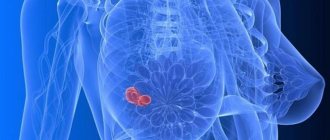
Focal formations of the mammary glands on ultrasound represent a local monotumor, which can be single or multiple. It can have both clear and blurred contours.
Most often, such lumps in the breast are benign and do not pose an oncological risk, however, if they are large in size, they can compress the tissue, thereby impairing blood circulation. That is why it is important to treat them promptly.
This formation can occur in any woman, regardless of age. Despite this, doctors note that stress, hormonal changes and bad habits significantly increase the risk of breast tumors.
Types of shading
The location of the dark spots, their size and shape depend on the developed pathological lesion of the lung. There are several types of dark spots in the lungs:
- Focal
- Focus
- Segmental
- Shading of an indeterminate shape
- Share
- Darkening with liquid
Total blackout syndrome
Total darkening of the lung on an x-ray is a complete or partial darkening (at least 2/3 of the lung field). In this case, gaps are possible in the upper or lower part of the lung. The main physiological reasons for the manifestation of this syndrome are the lack of air in the lung cavity, an increase in the density of the tissue of the entire surface of the lung, the content of fluid or any pathological content in the pleural cavity.
Diseases that can cause such a syndrome include:
- Bronchoscope in the bronchiWhat is bronchoscopy?
- atelectasis;
- cirrhosis;
- exudative pleurisy;
- pneumonia.
To carry out differential diagnosis of diseases, it is necessary to rely on two main signs. The first sign is to assess the location of the mediastinal organs. It can be regular or offset, usually in the direction opposite to the darkening focus. The main landmark in identifying the displacement axis is the shadow of the heart, located mostly to the left of the midline of the chest, and less to the right, and the stomach, the most informative part of which is the air bubble, always clearly visible on the images.
The second sign that makes it possible to identify a pathological condition is an assessment of the uniformity of darkening. Thus, with uniform darkening, atelectasis can be diagnosed with a high degree of probability, and with heterogeneous darkening, cirrhosis can be diagnosed. Interpretation of the results obtained using the radiographic method consists of a comprehensive assessment of all visually detected pathological elements in comparison with the anatomical features of each individual patient.
Limited dimming syndrome
To identify the causes of limited darkening of the pulmonary field, it is necessary to take an image in two directions - in direct projection and lateral. Based on the results of the obtained images, it is important to assess the localization of the darkening focus. If the shadow in all photographs is located inside the pulmonary field and is similar in size to its contours or has a smaller volume, it is logical to assume a lung lesion.
If there is darkening adjacent to the diaphragm or mediastinal organs with a wide base, extrapulmonary pathologies (fluid inclusions in the pleural cavity) can be diagnosed. Another criterion for evaluating limited shades is size. In this case, two possible options should be considered:
The size of the darkening clearly follows the contours of the affected part of the lung, which may indicate an inflammatory process;
The size of the darkening is smaller than the normal size of the affected segment of the lung, which indicates cirrhosis of the lung tissue or blockage of the bronchus.
Particular attention should be paid to cases in which there is a darkening of normal dimensions, in the structure of which light foci (cavities) can be traced. First of all, in this case, it is necessary to clarify whether the cavity contains liquid. To do this, a series of photographs are taken in different positions of the patient (standing, lying down or bending over) and changes in the level of the estimated upper limit of the liquid contents are assessed. If fluid is present, a lung abscess is diagnosed, and if it is not present, then the likely diagnosis is tuberculosis.
Important! The detection of several cavities with limited darkening of the lung is characteristic of pneumonia caused by staphylococcus. Such a lesion has an unfavorable prognosis, and often treatment is only possible through surgery.
Round shadow syndrome
I identify round shadow syndrome when the spot on the lungs has a round or oval shape on two photographs taken perpendicular to each other, that is, from the front and the side. To decipher the results of radiography when a round shadow is detected, they rely on 4 signs:
- form of shading;
- localization of darkening relative to nearby organs;
- clarity and thickness of its contours;
- structure of the internal shadow field.
Since the shadow reflected on the image within the lung field may actually be located outside it, assessing the shape of the darkening can greatly facilitate diagnosis. Thus, a round shape is characteristic of intrapulmonary formations (tumor, cyst, infiltrate filled with inflammatory contents). An oval shadow in most cases is the result of compression of a round formation by the walls of the lung.
The structure of the internal shadow field is also highly informative. If, when analyzing the results, the heterogeneity of the shadow is obvious, for example, lighter foci, then with a high degree of probability, it is possible to diagnose the disintegration of necrotic tissue (with disintegrating cancer or disintegration of tuberculous infiltrate) or the formation of a cavity. Darker areas may indicate partial calcification of tuberculoma.
A clear and dense contour indicates the presence of a fibrous capsule, characteristic of an echinococcal cyst. Round shadow syndrome includes only those shadows that are more than 1 cm in diameter; shadows with a smaller diameter are considered lesions.
Ring shadow syndrome
A ring-shaped spot on the lung on an x-ray is the easiest syndrome to analyze. As a rule, a ring-shaped shadow appears on an x-ray as a result of the formation of a cavity filled with air. A mandatory condition under which the detected darkening is classified as ring-shaped shadow syndrome is the preservation of a closed ring when taking pictures in all projections and in various positions of the patient’s body. If in at least one of the series of photographs the ring does not have a closed structure, the shadow can be considered an optical illusion.
If a cavity is detected in the lung, the uniformity and thickness of its walls should be assessed. Thus, with a large and uniform thickness of the contour, one can assume the inflammatory origin of the cavity, for example, a tuberculous cavity. A similar picture is observed with an abscess, when purulent melting of tissue occurs and the contents are removed through the bronchi. However, with an abscess, the remains of pus most often remain in the cavity and their complete removal is quite rare, so usually such a cavity is a tuberculous cavity.
The unevenly wide walls of the ring indicate the process of decay of lung cancer. Necrotic processes in tumor tissue can cause the formation of a cavity, but since necrosis develops unevenly, tumor masses remain on the inner walls of the cavity, creating the effect of an “uneven” ring.
Important! The main difficulty in assessing the ring-shaped shadow is determining the localization of the formation, since in most cases a similar syndrome is observed in extrapulmonary processes (deformation of the ribs, gases in the intestines, gases in the pleural cavity).
ICD-10 code
In the international classification of diseases, a focal formation of the right or left mammary gland (benign lesion) has an ICD code of D24.
Malignant tumor code C50.
It is important to know that it is the type of tumor that will determine all further treatment tactics. Thus, if a woman may only need drug therapy to eliminate a benign tumor, then to get rid of a malignant tumor the patient will need to undergo long-term chemotherapy, hormone therapy and, if necessary, surgery.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The main reason for the development of tumors in the mammary gland in women is called changes in hormonal levels. Additional factors for the occurrence of such diseases are called:
- Increased production of estrogen. It leads to hormonal imbalance, in which an excess of one hormone disrupts the functioning of other hormones.
- The use of hormonal contraceptives without prior consultation and analysis of a woman’s individual hormonal background.
- Long-term use of hormonal contraceptives (longer than 5 years).
- Ovarian dysfunction, which is considered a serious disorder of the reproductive system in women.
- Treatment with hormonal drugs during menopause.
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the internal cavity of the uterus.
- Unstable psycho-emotional state of a woman, frequent stress.
- Poor nutrition, obesity.
- Thyroid diseases
- Diseases of the uterus or appendages.
- Previous abortion.
- Surgical interventions on the pelvic organs.
- Osteochondrosis and spinal diseases.
- Chest injuries.
Symptoms and anatomical differences from the norm
Photos of developing breast tumors can be viewed on medical portals. At the same time, doctors identify the following most common characteristic signs of these pathologies:
- general deterioration of condition, which will manifest itself in the form of weakness, nausea, loss of strength;
- decreased sex drive;
- feeling of chest fullness;
- pain in the mammary glands;
- change in breast shape and size;
- burning sensation in the mammary glands;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- temperature increase;
- the appearance of discharge from the nipples;
- redness of the skin of the chest;
- the appearance of a palpable formation.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptomatic signs indicating the presence of a focal inclusion in the mammary glands have a varied clinical picture and depend on what kind of tumor has formed and at what stage of development it is.
Often, a small formation does not cause any inconvenience at all, so the patient may not even suspect its presence, since tiny lumps are difficult to palpate. As the tumor grows and the disease process intensifies, the patient begins to experience physical discomfort.
Specific symptoms include:
- Pulling pain in the bust area.
- When you move your hand up or down, the skin of the breast becomes lumpy.
- I am concerned about the feeling of burning and swelling in the chest.
- When palpating the chest, a painful lump is felt.
- Often the skin over the growth turns red and turns blue as it grows larger.
- Colorless or bloody exudate from the nipples indicates the formation of a tumor-like focus in the milk ducts of the breast.
- Purulent fluid from the nipples, elevated body temperature and enlarged cervical, axillary and inguinal lymph nodes are characteristic signs of a bacterial infection.
- Severe deformation of the mammary gland indicates a large size of the pathological formation.
Many of these symptoms appear during menstruation, and some of them appear throughout the entire monthly cycle.
Diagnostic measures
At the first suspicion of a breast mass, a woman should contact an experienced mammologist. Traditional diagnosis involves palpation of the mammary glands, taking an anamnesis, and taking blood tests for hormones.
Ultrasound diagnostics are also mandatory. If a malignancy is suspected, an MRI may be performed.
Instrumental research methods
Informative methods of instrumental diagnostics of mammary glands are:
- Mammography . This is a type of x-ray examination with reduced radiation exposure. The procedure is prescribed if clinically necessary. It can show medium and large formations. Small lesions can only be detected by ultrasound.
- MRI . It is used when cancer is suspected. This is a very informative and safe procedure that can examine breast tissue layer by layer.
- Biopsy . It is prescribed for suspected cancer.
Diagnostics
During the preliminary examination, the mammologist conducts an examination, finding out whether the woman is breastfeeding, whether she has a history of breast injury, or whether or not she has had breast surgery.
It is important to talk about all symptoms, especially symptoms such as fever, chills, or fatigue. In some cases, to determine the type of bacteria, a biomaterial or smear with discharge from the chest is taken.
Cost of mammologist services in our clinic
| Appointment with a mammologist with the highest category | 1000 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands with regional lymph nodes in standard mode and using Doppler techniques | 1200 rub. |
| Soft tissue biopsy | 2500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands with regional lymph nodes with technical difficulties | 1500 rub. |
| Make an appointment by phone: 8-800-707-15-60 (toll-free) | |
| *The clinic is licensed to remove tumors |
Interpretation of ultrasound results
Ultrasound examination today is considered one of the most informative diagnostic methods, which is usually prescribed to women under 35 years of age. This procedure should be performed from 5 to 12 days of the menstrual cycle. This way the research will be more accurate.
The mammologist interprets the ultrasound results (more on this with examples). At the same time, the procedure will help to view the tissue of the mammary glands and their ducts, lymph nodes.
Varieties
Benign tumors have different symptoms; doctors classify them as follows:
- diffuse mastopathy;
- nodular mastopathy;
- tumor-like processes and benign tumors;
- leaf-shaped tumor and other acute forms.
Diffuse mastopathy most often has dysplasia in both mammary glands. The main symptoms of this formation, as well as focal mastopathy, are pain in the mammary gland, which becomes stronger before and during menstruation. A substance may be released from the nipples that is not associated with lactation. It depends on the type of mastopathy whether all these symptoms will be present or just one.
Most often, focal and nodular mastopathy occurs in women who are in the premenopausal period. The duration of the menstrual cycle can be more than 35 days, which does not affect the very nature of menstruation. The duration of menstruation itself also increases - 10 days or more.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of focal formations in the mammary gland in a woman primarily depends on the specific disease identified and the type of cells. In case of a cancerous lesion or a large tumor of a benign type, the doctor will most likely suggest surgical intervention (mastectomy, etc.). Also, malignant formation requires mandatory chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Conservative drug therapy involves prescribing the following drugs:
- The drug Andriol . It contains male hormone. A contraindication to treatment with this drug is a suspicion of carcinoma, as well as individual intolerance to the drug substance.
- Means for blocking increased estrogen activity. For this, the patient may be prescribed drugs Tamofen, Valodex . Their use is contraindicated only during pregnancy.
- If there is a lack of progesterone, women are prescribed its synthetic analogues ( Duphaston ).
- To normalize hormonal levels, drugs of the prolactin group ( Ronalin ) are used.
In addition, in order to reduce stress in a woman in a similar condition, she is recommended to take sedatives. These can be tablets or drops ( Novopassit ).
If the cause of the disease is problems with the thyroid gland, the woman should take medications with iodine ( Iodomarin ).
To eliminate inflammation, NSAIDs (Diclofenac) are prescribed.
During the treatment period, the patient should adhere to a well-balanced, healthy diet and have proper rest. Also equally important is the support of loved ones. This will help you mentally prepare yourself to fight the disease.
Types and forms of the condition
Medicine knows several types of manifestations of focal formations in the mammary gland. It is generally accepted that pathological bodies in the right breast are diagnosed much less frequently than in the left gland.
Experts note that tumors in the right half of the bust are characterized by a more dense structure, while they are formed in a certain part of the gland and represent a monocapsule or a group conglomerate (several small nodes). Regarding the size of neoplasms, their overall size has different variations.
Most nodular lumps in the right breast are benign in nature, therefore they do not affect the functionality of neighboring organs and are not capable of metastasis, however, when they increase significantly, they begin to compress the surrounding tissues, thereby impairing their blood supply.
Let's consider the main characteristics of pathological focal nodes in the right and left mammary glands.
Mastopathy
This generalized medical term refers to a number of breast pathologies, which are characterized by the formation of inclusions of various sizes and configurations:
| Type of education | Peculiarities |
| Adenosis | A diffuse type of mastopathy, when there is an active increase in hyperplasia of the glandular tissue of the lobules. |
| Nodular mastopathy | Usually diagnosed in patients with the onset of menopause. |
| Focal mastopathy | It does not pose a clear health hazard, but if treatment is not started in a timely manner, the risk of its transformation into a malignant tumor cannot be ruled out. |
Lipoma
- Formed from the glandular component of the breast.
- Most often it manifests itself in the subcutaneous connective structure, and as it grows it penetrates into the deeper tissues of the mammary gland.
- It is considered a rare type of focal breast compaction.
- It usually develops covertly, with virtually no symptoms.
- Has the property of stopping in sarcoma.
Fibroadenoma
- This inclusion has a clear outline and is divided into lobes.
- Develops from the glandular and fibrous components of the mammary gland.
- Leaf-shaped fibroadenoma is dangerous because it often develops into an oncological form. Other types of this seal remain unchanged.
Avascular inclusion
- A tumor-like body that does not have capillaries and therefore is not supplied with blood.
- Due to the lack of blood supply, the tumor is not capable of rapid growth.
Cyst
- The neoplasm in the form of a capsule belongs to the focal type of breast fibrosis.
- It has a glandular structure of increased density.
- Inside the cystic capsule there is a liquid or thick secretion.
- Basically, the cyst is formed in the vicinity of the milk ducts of the gland, and can be present in the singular or plural.
- The presence of group cysts is defined as polycystic disease.
Sarcoma
- Focal inclusion of a malignant form.
- Consists of supporting or connective tissue.
- It has the ability to rapidly increase and spread metastases.
- Sarcoma has a high risk of death.
Lymphoma
- Malignant neoplasm.
- With this tumor, damage to the lymphatic structure is observed.
- The main symptom of the disease is enlarged lymph nodes.
- As the cancerous focus develops, pathological processes are launched in some organs, in which an increased presence of lymphocytes is diagnosed.
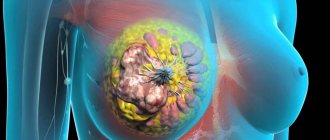
Breast cancer
- This diagnosis means a cancerous formation, the structure of which consists of a glandular component.
- The tumor is extremely hostile in nature.
- It has the ability to rapidly grow and metastasize.
Experts note that there is no particular difference in whether a nodular lesion is present on the left or right of the bust. The degree of danger of the pathological situation depends on the form of the tumor and the stage of its development.
Prevention
Despite the fact that the causes of breast tumors in women are not yet fully understood, the following doctor’s recommendations can reduce the risk of their occurrence:
- Minimize “cleansing” of the uterus in the form of abortions.
- Do not self-medicate with hormonal drugs.
- Have one regular sexual partner to protect yourself from infectious diseases.
- Use contraceptives only after consulting a doctor.
- The first pregnancy and lactation should preferably be before 30 years of age.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle and exercise.
- Be outdoors more.
- Treat inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system in a timely manner.
- Have a preventive examination with a doctor every six months, even if nothing worries you.
- Stick to a healthy diet.
- Avoid stress.
- Be sure to breastfeed your baby after birth.
Forecast
The prognosis for focal formation in the breast in women is individual for each patient. It depends on the specific diagnosis, cause and degree of neglect of the disease. The timeliness of treatment is also important. In such a condition, a woman should follow all medical recommendations.
In general, for a benign tumor after treatment, the prognosis is favorable. The main thing is not to start the progression of the tumor.
Negative prognosis for a malignant tumor that has been neglected. In this condition, the tumor will spread quickly, so the chances of survival are low.
Fortunately, modern medicine can help defeat focal formation. That is why women should be very attentive to their health and undergo preventive ultrasound examinations on time.