What is meant by mammary gland trauma?
There are the following types of damage to the mammary glands resulting from trauma:
- Closed. These include bruise, hematoma of the mammary glands;
- Open. These are wounds of various types (cuts, resulting from burns, bites, punctures);
- Isolated;
- Combined (combined). Such injuries are combined with serious injuries to the chest, for example, with a fracture and/or bruise of the sternum, ribs, with pneumothorax (accumulation of air in the pleural cavity), with hemothorax (the presence of blood in it).
The injury almost always causes internal bleeding, damage to breast tissue, or a combination of both. The most common are bruise and hematoma of the chest.
A bruise of the mammary glands is understood as a closed injury to the breast tissue of a traumatic nature, when there is no significant disruption of their structure.
A hematoma is formed as a result of internal bleeding, which can be:
- mild – it’s a simple bruise;
- severe, resulting in a significant hematoma, a large collection of blood clots that collects outside the blood vessels. Essentially, a hematoma is simply a larger, limited bruise accompanied by rupture of blood vessels.
Hematoma
The prevalence of traumatic injuries to the mammary glands is about 2-3% of all mammological diseases. But these are just statistics. In fact, chest trauma is much more common. It is very easy to get a chest injury at home, at work or during sports. It’s just that a woman does not always attach importance to possible injuries and cannot always remember them.
After breast trauma, patients are usually referred for diagnostic breast imaging to evaluate changes in the breast, either noticed by the patient or a breast surgeon.
What to do if you have a chest bruise
The mammary gland is the most cancer-dependent organ, and any severe damage can lead to the formation of a cyst or worse consequences.
If a woman has a mammary organ injury, she must provide first aid in accordance with the condition of the injury, call a medical team and follow all further instructions from the doctor.
Grandma's first aid kit
Folk remedies are good for I-II degree bruises and as additional treatment measures for more severe injuries.
For severe swelling it helps:
- Compress made from cabbage or birch leaves. The leaves are crushed with a knife or broken with a meat hammer and applied to the sore spot overnight. Old birch leaves can be steamed in boiling water, left until cool and made into lotions.
- Compress of crushed cabbage leaves with sour cream. Sour cream needs to be natural, not a semi-vegetable product.
- Homemade marigold ointment. To prepare it you will need 50 grams of fat and 5 calendula flowers. The petals are torn off, immersed in a base melted in a water bath and kept on fire for 15-20 minutes. The mixture is filtered while hot. Apply once a day at night.
- Homemade ointment with propolis. To prepare it you will need 100 grams of butter (unsalted) and 20 grams of propolis crushed in a mortar (freeze a piece before chopping). Place the propolis and oil in a water bath, heat over low heat for 30 minutes, and strain. Keep the mixture in the refrigerator and apply 2-3 times a day to the sore spot.
- Potato mush. Peel a medium potato, three on a fine grater, apply to the bruise for 5 minutes, rinse with warm water.
During the recovery stage, light massage, thermal procedures, and a compress with camphor alcohol and oil (1:1) help speed up the resorption of the bruise. Such compresses are contraindicated during breastfeeding.
With this we say goodbye to you, we hope we have answered the question in detail and clearly about how to apply bruises on the chest and how to treat breast hematomas. If you still have questions on this topic or have new topics of interest about female breasts, write, we will be happy to help you figure it out.
Treatment of hematoma
If you receive a closed injury, in order to avoid severe hemorrhage, it is recommended to apply a cold compress twice a day for 10-15 minutes. To avoid overcooling your breasts, apply cold through the cloth. To stimulate blood circulation, you can gently massage the damaged area of skin several times a day.
From pharmaceutical preparations, balms and ointments such as “Troxevasin”, “Rescuer”, “Traumel”, etc., which have absorbable properties, will help you. Such products are applied 2-3 times a day until the bruise completely disappears. Also try the well-known “iodine grid” among the people. Its benefit lies primarily in the bactericidal and anti-inflammatory properties of iodine. Using cotton swabs, apply a 5% iodine solution in horizontal and vertical lines at intervals of about 1 cm. Before the procedure, do a skin test to avoid an allergic reaction. To do this, apply a small amount of iodine to the inside of your wrist or forearm. If after 15 - 30 minutes you do not experience severe burning, itching, or redness, then the test has been passed and you can draw a mesh at the site of the hematoma.
Traditional medicine offers many methods for treating hematomas. One of the most popular and well-proven (especially among nursing mothers) absorbent products is a compress of cabbage leaves. It relieves swelling and pain even after serious bruises. Take a cabbage leaf of the appropriate size. Cut it with a knife or beat it with a culinary hammer so that the juice appears on the leaf. Apply it to the sore spot, covering it with gauze or cloth, and leave the compress until the sheet is completely dry, preferably overnight.
Simple hematomas with proper treatment disappear within a week. But remember: bruises in some cases can provoke the formation of cysts and fibroadenomas, so if a lump, lump, or pain occurs, consult a mammologist.
Best regards, Ksenia.
Breast hematoma - a question for a mammologist - 03 online
If you don't find the information you need
among the answers to this question
, or your problem is slightly different from the one presented, try asking
additional question
doctor on the same page, if he is on the topic of the main question. you also can
ask a new question
, and after some time our doctors will answer it. It's free. You can also search for the information you need in
similar questions
on
this page
or through the page
site search
. We will be very grateful if you recommend us to your friends in
in social networks
.
The medical portal ginekoloz.ru provides medical consultations via correspondence with doctors on the website. Here you get answers from real practitioners in your field. Currently, on the website you can get advice in 66 areas: allergist, anesthesiologist-resuscitator, venereologist, gastroenterologist, hematologist, geneticist, hepatologist, gynecologist, homeopath, dermatologist, pediatric gastroenterologist, pediatric gynecologist, pediatric dermatologist, pediatric infectious disease specialist, pediatric cardiologist, pediatric ENT specialist, pediatric neurologist, pediatric nephrologist, pediatric ophthalmologist, pediatric psychologist, pediatric pulmonologist, pediatric rheumatologist, pediatric urologist, pediatric surgeon, pediatric endocrinologist, nutritionist, immunologist, infectious disease specialist, cardiologist, clinical psychologist, cosmetologist, speech therapist, ENT specialist, mammologist, medical lawyer , narcologist, neurologist, neurosurgeon, nephrologist, nutritionist, oncologist, oncourologist, orthopedist-traumatologist, ophthalmologist, parasitologist, pediatrician, plastic surgeon, proctologist, psychiatrist, psychologist, pulmonologist, rheumatologist, radiologist, reproductive specialist, sexologist-andrologist, dentist, trichologist, urologist, pharmacist, physiotherapist, herbalist, phlebologist, phthisiatrician, surgeon, endocrinologist.
We answer 96.86% of questions.
Stay with us and be healthy!
Diagnosis of breast hematoma
In order to detect a hematoma as early as possible, every woman should know and promptly apply in practice methods of self-examination of the mammary glands that are available to any woman.
The self-examination method consists of sequential palpation of all sectors of the mammary gland, as well as the armpits, for the presence of formations.
Self-examination is a very important measure for identifying non-palpable hematoma in the early stages of its development, as well as other neoplasms in breast tissue.
Self-examination of the mammary glands should be carried out monthly during the period of greatest sexual rest - i.e. immediately before the onset of menstruation, as well as immediately after it. The first stage of self-examination is examination in front of a mirror.
The left hand is placed behind the back, and with the fingers of the right hand it is necessary to sequentially palpate the areas of the left mammary gland, moving in a spiral gradually towards the nipple. Then the same manipulation is performed with the right breast.
If you notice a change in the venous pattern, retraction of the skin or nipple, a visually and palpably determined formation, compaction, or nodule, this is a reason to contact a specialist.
Discharge from the nipple, either clear or mixed with blood, is also a cause for concern. The latter should be especially alarming, because This is precisely what may indicate the presence of malignant tumors.
Additional diagnostic methods of examination for suspected hematoma are ultrasound of the mammary glands, as well as microwave mammography. Even a small hematoma is perfectly visualized on the monitor screen, and any qualified specialist can easily carry out a differential diagnosis with other neoplasms.
The selection of therapy for the treatment of hematoma, as well as rehabilitation therapy, is certainly based on the individual indications of the patient.
The doctor also necessarily takes into account the medical history (whether there have been tumor-type diseases of the mammary glands in the past), hereditary predisposition, risk factors, and necessarily the presence of any injuries, especially multiple ones, and other reasons why the development of this disease became possible.
At the Mammology Center, the treatment of each disease is certainly accompanied by rehabilitation therapy, which is compiled directly by the attending physician together with other specialized specialists.
The patient’s progress in the treatment program must be monitored by the attending physician and adjusted if necessary.
We make sure to carry out control diagnostics at the end of treatment in order to exclude possible relapses, as well as assess the quality of the therapy provided.
Bruise on the chest (breast hematoma): treatment, what to do
Bruises on the chest can occur due to bruises during sports activities, doing household chores, during outdoor activities and in other situations. Very often, a woman does not even notice the blow itself, but sees its consequences when the injury already makes itself felt with such a symptom as a bruise.
When breast hematomas appear after a bruise, this sign cannot be ignored, since a bruise of the breast differs from damage to other soft tissues and is more dangerous than, for example, a bruise of an arm or leg.
Clinical picture and other causes
If after any damage a hematoma appears in the mammary gland, then in addition to the bruise, other alarming symptoms may appear.
A lump may be felt under the skin, and painful sensations of an acute or sharp nature may be noted. The tissue at the site of the bruise swells and the skin becomes hot to the touch.
In addition to local hyperemia, an increase in overall body temperature occurs, chills and malaise appear.
Breast hematoma is not always a consequence of soft tissue bruise. Very often, a bruise on the chest occurs after a puncture or after surgery.
This complication occurs quite often in plastic surgery.
If plastic surgery is complicated by hemorrhage in the breast tissue, the patient should be under the supervision of a surgeon until the hematoma on or near the nipple disappears.
Possible risks and consequences
If a breast hematoma is small, it is usually not dangerous. However, it may take a couple of months to treat even a small hematoma if it is located on a woman’s chest. This is due to the structural features of this organ. There is little muscle tissue in the chest, but there are many mammary glands and alveoli, the regeneration of which occurs somewhat more slowly than in muscles.
If the bruise is very large and deep, then it can cause some problems that impair the function of the mammary gland. An old hematoma can lead to the development of nodular mastopathy, so any bruise should be treated immediately after it is identified.
If a hematoma occurs in a woman with breast cancer, it can accelerate the growth of the tumor.
In cases where a bruise appears in a nursing woman, it can block the milk ducts, compress the alveoli, which will lead to lactostasis or even mastitis, therefore, if a hematoma is detected during breastfeeding, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible for consultation, examination and treatment .
It happens that during a breast bruise the ducts are injured, in connection with this the woman notices the appearance of discharge from the nipples.
With this symptom, you need to do a mammogram, since this sign may also indicate oncology, especially if there is a lump in the breast.
Very often, hematomas lead to complications such as the development of an inflammatory process, or infection and suppuration. If this happens, treatment without antibiotic therapy, and sometimes surgery, is impossible.
Diagnostics
If a bruise occurs in the chest area, if it is caused by a contusion, the woman should consult a traumatologist. The doctor will examine the site of injury, the armpit, and palpate the lymph nodes. The doctor pays attention to all features and possible deviations from the norm - the presence of lumps, differences in the size and shape of the breasts, retraction or swelling of the nipple.
The doctor may refer the victim for an x-ray if there was a strong blow to the chest and there is a suspicion of a fracture of the chest. If a fracture is excluded, the patient is sent for an ultrasound examination of the mammary gland, where the doctor will see whether there are infected and purulent areas, determine whether the vessels and milk ducts are damaged, and whether there is a capsule around the hematoma.
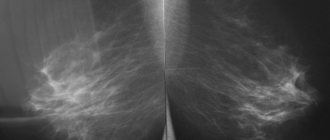
If necessary, the patient is prescribed a mammogram. This type of study gives the doctor the opportunity to assess the consequences of the bruise, as well as see if tumors have appeared in the mammary gland.
Radiothermometry is the most informative method of breast examination, as it helps to see the deep inflammatory process at the very beginning of development.
Only after a detailed examination can the doctor tell you what to do next.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of breast hematoma begins with the application of a fixing bandage. In this case, the chest should be slightly raised so as not to disrupt the blood circulation in it. If the patient is in severe pain, she is prescribed non-steroidal painkillers. If there is no infection or suppuration inside the breast, then the mammary gland must be kept warm and dry.
To make the bruise resolve faster, doctors prescribe ointments, for example, troxevasin or heparin-based. In order to prevent an inflammatory process of an infectious or bacterial nature, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
If the bruise appears during breastfeeding, then when treated with antibiotics, the mother should switch the baby to an adapted milk formula, while carefully expressing her milk every three hours if she plans to maintain lactation until treatment is completed.
For small hematomas, treatment is most often aimed at eliminating the clinical picture.
For large hematomas that interfere with the functioning of the mammary gland, causing severe pain and discharge from the nipple ducts, a surgical intervention is performed, during which the hematoma and accumulated blood clot is removed using puncture and pumping out, if necessary, the purulent contents are pumped out, after which physiological fluid is injected into the resulting cavity solution and antibacterial drugs.
Source: https://vseotravmah.ru/gematomy/sinyak-na-grudi-v-molochnoj-zheleze.html
Diffuse changes in the breast on ultrasound
Mastopathy is a dyshormonal process in which the normal ratio of glandular, connective and adipose tissue is disrupted. There are four types of diffuse mastopathy: glandular, cystic, fibrous, mixed.
READ MORE: Head contusion: signs, consequences and treatment
Glandular echo variant of diffuse mastopathy: increased parenchyma thickness, average echogenicity of glandular tissue; mild phenomena of fatty involution, often ductectasia, discrepancy between the ultrasound type of breast structure and age.
Fibrous echo variant of diffuse mastopathy: the thickness of the parenchyma is increased relative to age norms, a significant increase in echogenicity (as in postmenopause), periductal fibrosis and fibrosis of Cooper's ligaments, the degree of fatty involution corresponds to age, there may be areas of dilated and deformed milk ducts.
Cystic fibrous echo variant of mastopathy: many cysts and groups of cysts of different sizes in the structure of the breast, periductal fibrosis and fibrosis of Cooper’s ligaments, the ultrasound type corresponds to the age of the patient.
Mixed echo variant of mastopathy: increased thickness of the parenchyma, average and increased echogenicity of the glandular tissue, decrease in premammary tissue, weak expression of fatty involution, cysts, periductal fibrosis, often ductectasia, according to the structure of the breast according to the age and hormonal status of the patient.
Ductectasia is characteristic of almost all variants of diffuse mastopathy.
Clinical classification of dyshormonal dysplasia Diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of glandular, cystic, fibrous components, mixed form; Nodular mastopathy; Benign tumors and tumor-like processes - adenoma, fibroadenoma, ductal papilloma, cyst;
Special forms are leaf-shaped tumor. The conclusion of a dishormonal mammary gland may be justified in case of thickening and unevenness of the walls of the ducts, an increase in their diameter, pocket-like expansion of the ducts, and the presence of a hyperechoic connective tissue component.
Fibrocystic mastopathy can be expressed in the form of diffuse, diffuse nodular and nodular (localized) forms.
Nodular mastopathy is a complex and little-studied disease of the mammary gland. Dishormonal mammary glands. Fibrocystic mastopathy can be expressed in the form of diffuse, diffuse-nodular and nodular (localized) forms.
Nodular mastopathy is a complex and little-studied disease of the mammary gland.” Dishormonal mammary glands Fibrocystic mastopathy can be expressed in the form of diffuse, diffuse-nodular and nodular (localized) forms.
Nodular mastopathy is a complex and little-studied disease of the mammary gland. Conclusion dishormonal hyperplasia nodular form (fibrocystic mastopathy) - single or multiple areas of reduced echogenicity with blurred contours, irregular shape.
Clinical manifestations: weakness, chills, fever; pain in the mammary gland; swelling and compaction; local fever and erythema; discharge from the nipple.
The following forms of mastitis are distinguished: serous, infiltrative, purulent. A diffuse form of mastitis or a focal form resulting in an abscess may be observed.
Diffuse form of mastitis on ultrasound: the skin is thickened, the parenchyma and subcutaneous tissue are of increased echogenicity due to edema, ductectasia of 3-4 mm with purulent contents in the lumen, an expanded network of subcutaneous lymphatic vessels is visible in the form of chaotically located anechoic and hyperechoic tubular structures.
Ultrasound signs of the diffuse form of mastitis are nonspecific; they are observed with mastitis and the edematous-infiltrative form of breast cancer. For the differential diagnosis of these conditions, it is important that in the diffuse form of the inflammatory process there is a positive dynamics in the form of a significant improvement in the differentiation of breast tissue after several days of antibiotic therapy.
The nodular form of mastitis is characterized by the formation of an abscess, which is often localized behind the nipple and is accompanied by severe clinical symptoms (pain, redness and tension of the skin, a palpable formation).
The ultrasound picture depends on the duration of the disease.
At the stage of abscess formation in the zone of diffusely changed breast tissue, first a hypoechoic area without clear contours begins to be determined, and then hyperechoic elements of the capsule around it.
By the time abscess formation is completed, a hyperechoic capsule of varying thickness is clearly visualized. The internal structure of the abscess becomes heterogeneous due to areas of necrosis and purulent contents.
Steatonecrosis develops after injury, surgery, puncture pyopsy, vascular pathology (vascular thrombosis and tissue ischemia). There is necrosis of deep fatty tissue and necrosis of subcutaneous fatty tissue.
Steatonecrosis on ultrasound: a complex of fluid-containing masses, an irregularly shaped hypoechoic zone, an area of increased echogenicity in premammary tissue (lipofibrosis). When located superficially, it can cause fixation of the skin, contraction of Cooper's ligaments, and nipple retraction. In this case, the differential diagnosis is made with breast cancer.
Breast injury on ultrasound
There are three phases of development of the process: acute - the first 4-5 days; intermediate - up to 2 weeks; late - after a year.
Acute phase: thickening of the skin, loss of differentiation of breast tissue, increased echogenicity of premammary tissue, microhemorrhages in the form of small hypoechoic inclusions.
Intermediate phase: accumulation of fluid in the peripheral parts of the breast - hypo- and anechoic zones with uneven contours and heterogeneous structure; hematoma formation - an oval or irregularly shaped formation with thick walls and hyperechoic inclusions in the cavity or a complex of cysts with a large number of reflections.
Ways of hematoma development: resorption in most patients (in the absence of positive echo dynamics 2 weeks after injury, a malignant process is excluded); lipogranuloma; post-traumatic cyst; area of steatonecrosis.
Late phase: scar 9 accumulation of fibrous strands); chocolate cyst; microcalcification in the injury area.
Patients after breast injury should be monitored by a mammologist and undergo an ultrasound scan at least 2 times a year.
Breast hematoma on ultrasound
Possible complications and dangers
After a severe bruise to the chest, a woman develops a bruise or hematoma. It is the accumulation of blood clots that can provoke the proliferation of pathogens. This condition can lead to suppuration or an abscess.
The lump that appears after the blow also has consequences for the woman. Often the appearance of a malignant tumor is a consequence of a hematoma in the past.
Cysts and tumors
A severe bruise of the chest can provoke the development of a lump, which can develop into benign and malignant neoplasms.
Less life-threatening diseases include:
- atheroma - a neoplasm that occurs due to blockage of the sebaceous duct;
- granuloma is an inflammatory-purulent neoplasm, which is a hollow capsule containing clear liquid or blood discharge.
A cyst is the result of abnormal proliferation of epithelial and connective components in glandular tissue.
Each of the tumors can be removed surgically, but the very fact of their occurrence indicates that they are at risk for breast cancer.
Fibrosis and others
The following tumors are considered the most dangerous neoplasms:
- fibroadenoma is a benign tumor of the mammary gland of glandular origin, which is one of the forms of nodular mastopathy;
- Breast fibroma is a single dense node in the shape of a ball.
Severe bruising and trauma to the chest can lead to disruption of the lymphatic system, and as a result, lymphoma may occur - a malignant tumor that is dangerous due to widespread metastases.
Breast sarcoma is a malignant tumor of non-epithelial nature that forms in the tissues of the mammary gland. The phenomenon is very rare, but can occur as a consequence of an injury.
Complications during feeding
During breastfeeding, you need to take special care of your bust. Minor bruises of the mammary organ that do not cause pain do not affect feeding in any way.
But if the injury causes pain, then there is a risk of damage to the milk ducts, which can lead to blockage of the ducts or stagnation of milk. If measures are not taken in time, lactostasis may develop - milk retention in the ducts, and this will not only cause severe pain for the mother and the impossibility of normal feeding for the child, but also provoke mastitis - inflammation of the mammary gland.
Treatment of chest injuries
Treatment of bruises and injuries depends on the stage and severity of the process, complaints and examination results.
First of all, the breast must be immobilized (apply a fixing bandage).
Fixation bandage for the treatment of chest injuries
Symptomatic therapy depends on the patient’s complaints and includes:
Ointments, gels for resorption of subcutaneous hemorrhages and hematomas containing heparin (Troxevasin Neo, heparin ointment) are prescribed to injured areas.
- Antibacterial therapy is prescribed only by a mammologist when a secondary infection occurs and an inflammatory process forms (mastitis, abscess).
- If the hematoma is significant, blood is evacuated using a puncture biopsy.
- Physiotherapy (dry heat) is prescribed to resolve the hematoma.
Before visiting a doctor, you can apply a cold compress to your breasts to reduce swelling and pain. Other self-medication before diagnosis of the lesion and consultation with a mammologist is not allowed. Massages and rubbing are not performed in the acute period, as this can increase swelling, pain, and hemorrhage.
Rehabilitation treatment is prescribed in the late period (2-4 weeks or later after the injury, it all depends on the nature of the injury). It includes vitamin therapy, means to improve metabolism, if there are no contraindications, for example, a predisposition to neoplasms.
It is necessary to explain to the patient that she should visit the breast specialist and have a follow-up ultrasound at least once after the initial assessment (4-6 weeks) to ensure that the bruise has improved. Some bruises can take months to resolve as the body slowly reabsorbs blood that has accumulated in the tissues. Experts consider ultrasound most useful in assessing interval improvement in the effects of bruises and hematomas.
Treatment of blunt trauma
How to treat a breast bruise? Dry cold is used as first aid (a bottle or heating pad with cold water or ice cubes in cellophane wrapped in natural fabric will do). The heating pad is applied to the sore spot for 5-15 minutes to prevent tissue hypothermia.
Measures to speed up recovery depend on the extent of the injury.
| Degrees of breast injury | ||
| Degree | Description | Recovery and treatment |
| I | Minor injury, pain tolerable, slight superficial bruise, abrasions. | It heals on its own, you can use ointments to speed up the resorption of bruises. The functioning of the organ during hepatitis is not impaired. |
| II | The pain is severe, the compaction is significant, swelling and hematoma are noticeable. The damage affects the muscles. | A doctor's intervention is required, complex treatment using ointments. Physiotherapy is recommended during the recovery period. For deep hematoma, a course of antibiotic and vitamin therapy (Vit. C, group B, F, retinol) is recommended. For severe swelling, diuretics (diuretics) are prescribed. |
| III | Severe pain, deep hematomas, there are ligamentous injuries. | Breast immobilization and retromammary blockade are required. The use of antibiotics, NSAIDs, agents that accelerate the resorption of bruises and anticoagulants, antithrombotic drugs, and angioprotectors is recommended. |
| IV | Severe pain, deep damage, shock. | In this case, you need to call an ambulance. First, antishock therapy is carried out, and then complex treatment: antibiotics, diuretics, anticoagulants, antithrombotic drugs, physiotherapy. |
Traditional treatment includes the use of ointments that accelerate the resorption of a bruise:
- Troxevasin;
- Heparin ointment;
- Lyoton gel;
- Troxerutin.
Of the above remedies, Troxerutin is considered an effective and inexpensive drug.
MORE: Boric acid solution and powder: instructions for use, price. Use in the treatment of ears and acne -
Of the heparin-containing drugs, Lyoton-1000 gel is considered to be expensive, but the most effective, due to the dosage form (gel) and the high content of the active substance.
In the form of a gel, the drug penetrates faster and deeper into the tissue. In addition, the effectiveness of heparin (the active component of Lyoton gel) depends on the dose. On average, heparin ointments contain 300-500 units of active substance per gram, and Lyoton gel - 1000 units.
When using the ointment, approximately 1 unit of heparin from each gram of product used will reach the damaged vessels of the chest. While when using Lyoton gel it will be 7.2 units per gram.
Creams with natural ingredients have proven themselves to be effective:
- leech extract;
- arnica extract;
- horse chestnut;
- badyaga;
- calendula;
- badger fat;
- camphor oil.
Homeopathic ointments are excellent for coping with swelling and bruising:
Deep hematomas resolve within 1-1.5 months, if there are no complications. For a well-organized large-volume hematoma, a puncture is made and the blood is sucked out.
If there is a risk of bruise suppuration, antibacterial agents are prescribed:
- Augmentin;
- Amoxiclav;
- Doxycycline;
- Unidox Solutab;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Ofloxacin.
If there is a late visit to the doctor and the hematoma suppurates, the lesion is drained (cleansed of pus), and antibiotics are prescribed by injection.
If the damaged area is very painful, NSAIDs (non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs with an analgesic effect) are recommended:
- Voltaren gel;
- Ketoprofen;
- Ibuprofen;
- Fastum gel;
- Nise gel;
- Dolgit;
- Butadion.
For severe swelling, diuretics are prescribed. From herbal remedies it can be a decoction of bear ears, lingonberry leaves or birch buds, from medicines - Furosemide, Torasemide.
Drugs to normalize microcirculation and anticoagulants are prescribed only by a doctor according to indications. To normalize local blood circulation, the following may be prescribed:
- Pentoxifylline;
- Agapurin;
- Trental;
- Vazonite;
- Pentilin.
These products are not recommended for girls under 18 years of age and women with breastfeeding.
To prevent thrombosis, women are recommended to use low molecular weight heparin: Clexane, Enoxaparin, Fraxiparin or Novoparin. These drugs are also not recommended for use during hepatitis B.
Hematomas are removed only if there is excessive bleeding into the glandular tissue and periglandular space. Surgery is also indicated for significant scar changes at the site of injury, when a node similar to a tumor or a false cyst forms. In this case, tissue histology of the removed lesion is required.
Dense formations on ultrasound of the mammary glands
Fibroadenomas account for up to 95% of all benign breast tumors. The dimensions are usually 2-3 cm. The shape is oval, the ratio of the transverse size and the PZR - the PR/PZR index - is more than 1.4.
Fibroadenomas on ultrasound are a solid formation with a clear and even contour; when compressed by the sensor, a symptom of “sliding” of the tumor in the surrounding tissues is noted due to the expanding nature of the growth of fibroadenoma
When testing with oxytacin, the shape of the formation is preserved, the capsule and internal structure, “lateral shadows” and distal enhancement are visualized more clearly.
Some features of ultrasound pictures of FA depending on the structure.
Pericanicular FA is characterized by: round or oval shape; clear, even contours, uniform structure; side shadows; large blocky calcareous inclusions (38%).
Intracanalicular FA is characterized by: oval or lobular shape (consists of several formations); heterogeneous echostructure; uneven, unclear outline; may be isoechoic.
Mixed FAs combine ultrasound signs of both intra- and pericanalicular FAs. When the FA size is more than 6 cm, it is called gigantic. In the structure of such formations, large coral-shaped petrificates are often identified.
When performing color doppler examination, vessels are more often found in FA larger than 2 cm in size. FA is characterized by a circumflex vessel (on average 2-4 vessels). Identification of vessels in previously non-vascularized FA is a prognostically unfavorable sign and allows one to suspect its malignancy.
Phylloid fibroadenoma is a rare benign ibroepithelial tumor of the breast.
Ultrasound signs of phyllodes FA: large size; uneven cyclic contour; hypoechoic heterogeneous internal structure; often - cystic cavities or slit-like cystic inclusions.
Dopplerography reveals multiple arterial vessels in the tumor with high blood flow velocities and a high resistance index. It is possible to differentiate the benign or malignant nature of the formation only histologically.
Lipoma is a node of mature adipose tissue in a connective tissue capsule. More common in pre- and postmenopausal women. Characterized by slow growth. On palpation, there is a soft, elastic subtype formation.
Lipoma on ultrasound: well delimited by a hyperechoic capsule; oval shape; hypoechoic structure, often with linear fibrous structures; when compressed, it is compressible. Differential diagnosis with FA and fatty lobule.
Hamartoma is a rare benign breast tumor. Consists of adipose and fibroglandular tissue, more often in women after 40-45 years. In 60% of cases it is non-palpable. In 65% of cases it is located in the retromamillary area and in the upper outer quadrants of the breast. May be located outside the mammary gland. The size is usually less than 3 cm.
Causes of breast hematoma formation
Almost always the appearance of hematomas is associated with injuries. However, every rule has exceptions.
Possible causes of breast hematoma:
- Chest contusion (sports injury, car accident)
- Rupture of a "fragile" blood vessel in response to minor trauma
- Breast implant surgery (postoperative bleeding)
- Curative (non-cosmetic) breast surgery, such as a lumpectomy or mastectomy
- Core biopsy (core biopsy, core biopsy, cutting biopsy) of the breast (rare), the risk of hematoma formation is approximately 2 times higher when using vacuum aspiration biopsy
An increased risk of breast hematoma is associated with taking medications that thin the blood (aspirin, warfarin and heparin).
There are no hematomas that appear without any reason. Spontaneous bruising on the mammary gland, which forms seemingly for no reason, should be comprehensively examined to exclude serious pathology. For example, “a bruise on the breast for no reason” can appear due to diseases of the blood and blood vessels (varicose veins, von Willebrand disease, thrombocytopenia).
Hematoma in the mammary gland
If a woman has suffered a chest bruise, first aid must be provided immediately on the spot. The chest must be immediately secured using a compression bandage. The damaged mammary gland should be immobilized in an elevated position. The second step, which involves treating a breast hematoma, is applying cold to the site of the bruise. The compress with ice should be kept for about half an hour. This simple technique will make it possible to stop further hemorrhage, since capillary vessels narrow under the influence of cold. Painful sensations will also dull.
It is worth noting that the “ice” compress does not need to be kept on the chest all the time. To prevent tissue hypothermia, ice is removed from the mammary gland every five minutes and, after a short break, is applied again. If the blow falls on the nipple, then the woman may experience a painful shock, but even in the case of a different localization of the bruise, painful symptoms can still plague the victim. In this case, the doctor mainly prescribes a retromammary blockade. In this case, it is used as a method of local anesthesia. The procedure itself consists of several stages:
- Three places are selected on the mammary gland: in the lower extremity, upper and lateral outer region. A 0.5% solution of novocaine is drawn into a syringe and administered subcutaneously.
- Then a long needle is carefully brought into the retromammary space and 50 ml of novocaine (0.25% solution) is supplied to each of the three zones.
- During the process of administering the drug, the doctor or nurse performing the procedure should not feel the patient’s body’s resistance.
- After completing the insertion, remove the needle. Test for correct implementation of the event - no medicine should ooze out of the hole left by the injection. At the same time, the woman’s chest rises slightly and lies as if on a cushion of water.
Simple cyst on ultrasound of the mammary glands
Cysts are the most common pathology of the breast at the age of 35-50 years. They usually regress during menopause, but may appear during therapy with estrogen and steroids. cardiac glycosides.
Cysts are usually up to 5-6 mm in size and can be unilateral or bilateral.
Closely located cysts tend to merge with the gradual formation of a single cavity; multi-chamber cysts with septations may occur.
A simple cyst on ultrasound has thin smooth walls, the contents of the lumen are anechoic, there are no septa or dense nodes in the lumen, and the acoustic signal is enhanced behind.
The lack of distal enhancement may be a consequence of the small size; cysts located among highly echogenic structures; cysts located near the pectoral muscle; cysts with fibrous capsule.
Lack of distal reinforcement; small size; cysts located among structures of high echogenicity; cysts located near the pectoral muscle; cysts with fibrous capsule.
Long-existing cysts are often accompanied by an inflammatory process, which leads to thickening of the walls of the cyst, reflections from the internal structure appear, and the absence of distal enhancement, which does not allow distinguishing a cyst from a solid lesion. Simple cysts are always benign. Asymptomatic simple cysts do not require biopsy; routine mammography and surveillance are recommended.
READ MORE: Uterine prolapse in old age - what to do - Just treat
Atypical cysts - long-term, recurrent, containing calcium. If the cyst wall is thickened, has a heterogeneous structure, or has a parietal component, a puncture is required.
| Photo. A simple breast cyst on ultrasound: A - It is important to focus the device on the object of study - the white triangle (red arrow). On the left, the focus is at the object level, and the device shows an anechoic simple cyst. On the right, the focus is shifted far downward, and one might mistakenly think that a dense structure is forming. B — A trapezoidal cyst expands deeper. B - The panoramic image shows all the signs of a simple cyst - smooth, even walls, anechoic contents, acoustic enhancement behind. |
Treatment process
If a woman has injured her breasts, she must immediately secure the affected area using bandages. Damaged mammary glands must be immobilized and slightly elevated. It is important to apply cold to the injured area. Doctors recommend using special compresses using ice.
You should know that ice compresses do not need to be kept for a long time when a bruise appears on the chest in women. Otherwise, you may damage your skin. To prevent hypothermia, you should remove the ice from your chest from time to time and then apply it again.
If the nipple is damaged during the blow and the woman experiences pain shock, it is necessary to take a painkiller. Doctors are of the opinion that “No-Spa” is the best painkiller that does not cause side effects and effectively eliminates discomfort.
If the pain does not disappear, it is important to immediately seek help from a specialist. In private cases, medical workers anesthetize the mammary glands by injecting novocaine into the muscle tissue. After novocaine treatment, the pain should decrease and the development of hematoma will stop.
Only after pain relief does the doctor begin conservative therapy. The specialist prescribes:
- ultrasound treatment;
- The doctor applies Troxevasin or Heparin ointment to the injured area.
It is important to rub the ointment in with smooth and massaging movements. After a few hours the pain will subside a little.
If the bruise on the chest is yellow, this may indicate that a long time has passed since the injury. Doctors are of the opinion that the hematoma changes color over time - this is a normal physiological reaction of the body.
Symptoms of breast injury
If a woman has chest pain from a blow for a long time, then she needs to pay attention to other symptoms:
- swelling, discoloration, and compactions are visible in the areas where the bruise is located;
- discharge of clear liquid mixed with blood from the nipple if the milk ducts are damaged;
- increase in temperature at the site of injury.
Development of necrosis after hematoma, which leads to septic mastitis.
If a woman’s breast hematoma is small, it will resolve on its own. But if the damage has a large localization or deep penetration, then the risk of developing benign and malignant neoplasms increases. Therefore, if some time after the injury your chest hurts, you should immediately contact a mammologist.
Common Cause
In some cases, hematomas appear on the mammary glands after puncture, but this phenomenon is still very rare. In frequent cases, such hemorrhage is not life-threatening and does not cause serious consequences. A pathological change can only occur if the basic rules of hygiene are violated.
If it is necessary to perform a breast biopsy, it is important to properly prepare for this process. Most often, doctors recommend not taking aspirin and anticoagulants a week before the procedure. This will have a positive effect on blood clotting.
If you do not follow the basic rules of performing a biopsy, the wall of the mammary glands is often injured. As medical practice shows, performing a breast biopsy is a fairly harmless process. If after this procedure liquid discharge comes out of the wound, then do not worry - this is a normal phenomenon that does not require surgical intervention. If bruises appear on your chest, you need to familiarize yourself with the methods of treating them.
Thanks to the puncture, it is possible to accurately determine the nature of the tumors. The procedure can be used to determine whether cancer cells are present. Based on the results of the analysis, the doctor prescribes effective therapy. As a result of a chest contusion, the bruise can cause severe discomfort. In this case, it is important to familiarize yourself with the methods of its treatment.
Symptoms of breast injury
The very first sign of a chest bruise is the manifestation of a subcutaneous or deep hematoma (accumulation of bloody clots in the breast tissue). Over time, the bruise may resolve, but as medical practice shows, necrosis of the fatty component may form in its place.
In addition, other symptoms are characteristic:
| Clinical signs | Features of manifestation |
| Strong pain | Even a minor blow is always accompanied by pain due to the increased sensitivity of the breast tissue. |
| With painful shock, loss of consciousness is possible. | |
| Hematoma formation | Blue skin of the chest in the area of impact. The intensity of the cyanosis depends on the severity of the injury. Manifestation of swelling. The presence of compaction and pain on palpation indicate continued formation of the hematoma. The manifestation of bruising in the nipple-areolar area is accompanied by increased pain. After a few days, the bruise begins to change color, becomes paler, and then fades. |
| Liquid from nipples | They are observed immediately after a bruise or after the development of inflammation in the breast. |
| Serous or purulent discharge from the nipples is a clinical symptom of extensive tissue death, which manifests itself with prolonged absence of therapy or as a result of improper drainage. | |
| Colorless or bloody exudate is a characteristic sign of damage to the milk duct. | |
| High body temperature (hyperthermia) | Occurs when there is significant damage to glandular tissue or as a reaction to stress due to injury. |
| Deterioration in general health | In case of severe injury, the following is observed: - weakness; - nausea; - vomit; - dizziness; - drop in blood pressure. |
The severity of symptoms depends on the degree of injury. Damage to the breast caused by an accident or a fall from a height is often accompanied by serious trauma to the chest or a fracture of the spine. With such a history, the signs of a bruise are very pronounced.
Doctors emphasize that it is important to correctly determine the nature of the pain in the mammary gland after receiving a blow:
- Localization of pain. It appears in the area of bruise in the superficial structure of the breast.
- Distribution area. Usually there is no irradiation, but with suppuration the pain may radiate into the chest.
- Features of manifestation. Most often, the pain is aching, with an abscess a twitching sensation is felt.
- Saturation. In most episodes, the pain is of moderate severity, but with a severe hematoma or the formation of an abscess, an increase in its intensity is observed.
- Duration. Painful discomfort is constant and is present for a long time, but with a mild degree of injury it gradually subsides. With an abscess, pain disappears only after removal of the purulent fluid.
During pregnancy and especially breastfeeding, the pain is much more pronounced:
- In the first case, due to actively occurring processes in the mammary glands during pregnancy.
- In the second case - due to the flow of milk at the moment the baby is latched.
Minor bruises received at home are characterized by the presence of unpleasant discomfort with further manifestation of swelling and bruising. In this case, nausea, dizziness and other neurological abnormalities may not be observed. However, this does not mean that there is no need for medical assistance.
Symptoms of bruise and hematoma of the mammary glands
As a result of closed injuries to the mammary glands, the following symptoms appear:
- Chest pain. The mammary gland is well innervated, and even with minor influences on it, impulses are carried out quickly. The pain can be dull, aching, worse when sleeping on your side, or sharp, severe. If the blow was strong, painful shock with loss of consciousness may develop, which requires emergency medical care with stimulation of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems;
- Hematoma. Bruising and hematoma are accompanied by a change in the color of the skin of the chest. When a bruise occurs, the damaged area first turns red or purple, then changes to blue-violet and, finally, green. Then the bruise turns yellow and goes away. This color change is due to oxidation, the breakdown of blood cells and hemoglobin transformations. Unlike minor contusions and bruises, the “blooming” of a hematoma begins later and lasts longer. The hematoma is accompanied by swelling and pain in the chest;
- Increase in temperature, deterioration in general health. They develop as a result of the body’s reaction to an injury. The following also often occur: weakness and decreased blood pressure, headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting;
- Nipple discharge. They do not develop immediately, but later after a chest injury as a result of tissue necrosis (serous discharge), damage to the ducts (bloody discharge) or the addition of a secondary infection (yellow-green purulent discharge).
The severity of symptoms depends on the degree of damage. If the chest injury is minor, pain, swelling and bruising will mainly develop. For more serious cases – pain, hematoma, deterioration of general condition. In case of serious combined chest injuries with fractures and bruises of the chest, the symptoms increase rapidly with the development of hypotension, nausea and other neurological disorders.
Causes and features of hematoma on the chest
Breast contusion is a closed type injury
If large vessels are not damaged as a result of trauma to the mammary gland, the hemorrhage stops after a short time. The hematoma formed on the soft tissues of the chest gradually resolves and after a few days disappears without a trace. In this case, part of the blood turns into connective tissue of the mammary gland.
Most cases of chest trauma only lead to damage to small vessels - capillaries, which are located immediately under the skin. However, hemorrhage in breast tissue is dangerous due to the high risk of development of pathogenic microorganisms. This is especially true for large hematomas, the size of which is several centimeters. If the hematoma on the mammary gland after the blow has a bright color and stands out sharply on the skin, it is necessary to take measures to treat it. Otherwise, the onset of an inflammatory process and the appearance of compactions are possible, the skin above which acquires an increased temperature and individual signs of hyperemia.
Hematomas on the breast can form due to taking medications that change blood viscosity
Among the most common causes of hematomas are:
- consequences of physical training;
- domestic injuries;
- impacts on hard objects;
- consequences of taking medications that change blood viscosity;
- coagulopathy, indicating disturbances in the process of blood infusion;
- wearing underwear that is too tight.
A hematoma on the chest can be one of the important signs of a malignant formation in the structure of the mammary gland. If the patient is at risk or suspects the onset of a tumor process due to the appearance of accompanying symptoms, an urgent visit to the doctor and immediate diagnosis are required.
Pathological discharge from the nipple - signs of damage to the duct
Most cases of hematoma on the chest are the result of domestic injuries. In addition, bruises can result from damage to the musculoskeletal system or internal organs. In this case, treatment of the hematoma is directly related to eliminating the underlying problem. The chest area is prone to bruising due to its soft structure and lack of bone base. Serious damage in this area can lead to atypical processes - for example, fat necrosis or septic mastitis.
If the injury damages tissue deep inside the gland, the milk duct may be damaged. Signs of this phenomenon are pathological discharge from the nipple, which always attracts attention. Such problems rarely go away without proper treatment. Moreover, they can cause a serious pathological process in the gland, even malignant neoplasms, especially with a genetic predisposition or other risk factors.
In case of severe pain at the bruise site, it is recommended to consult a doctor
Patients who want to make sure that bruises appear are safe should definitely seek qualified medical help. This requirement becomes categorical in the following cases:
- the hematoma is large;
- there is severe pain in the chest at the site of the bruise;
- there is an increase in temperature and hyperemia in the area of injury;
- a painful lump has formed at the site of the bruise;
- a small hematoma does not go away for a long time or increases in size;
- deformation of the mammary gland is noted.
Timely medical assistance will allow you to quickly get rid of the bruise and its consequences. The likelihood of successful treatment increases if you do not delay your visit to the doctor.