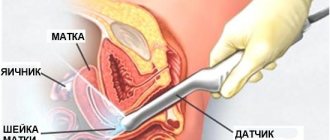
When examined by a gynecologist, epithelial defects of varying appearance are often found on the vaginal mucosa of the cervix. Every second woman is diagnosed with erosion. What are the reasons for the origin of this pathology, when is it urgent to take action, and when is it better to wait? This is a pressing question for women of childbearing age who are planning a pregnancy.
The article will give official recommendations from doctors and describe the experience of women who were treated for erosion using various methods, including surgery. In most cases, the presence of erosion does not affect the pregnancy process in any way; usually the pathology disappears on its own a year after birth. Myths that cervical erosion negatively affects pregnancy and childbirth mainly come from the attending physician, who, for his own peace of mind, is trying to treat a small problem. But is this really necessary or can we wait for self-healing?
The role of the cervix during pregnancy
During gynecological examinations, special attention is paid to the condition of the cervix, because its length, friability and cleanliness of the epithelium determine a woman’s ability to bear a child and give birth without complications. At short stages of pregnancy, the density of internal tissues changes. The number of blood vessels increases to better supply oxygen to the developing fetus. Normally, when pregnancy occurs, the vaginal part closes tightly and remains in this state until approximately 36–37 weeks.
Often, fertilization occurs unplanned, and the woman does not have the opportunity or desire to visit a doctor for an examination. The consequences of such carelessness are accompanied by various risks:
- the presence of infection in the birth canal, including human papillomavirus infection;
- damage to the mucous membrane - erosion, ectopia;
- hormonal disorders;
- incorrect position of the organ or its underdevelopment.
Pathologies of an organic or functional nature affect the course of pregnancy in different ways. The infection can cause inflammatory processes during pregnancy. Considering the fact that a pregnant woman’s immunity is reduced, infectious processes most often worsen and create a threat of miscarriage.
Hormonal disorders cause premature shortening of the cervix, its softening, which also leads to miscarriage, only at a later date. Getting pregnant after a late miscarriage will be more difficult and will require long-term treatment to restore fertility (the ability to conceive).
Incorrect position of the uterus, caused by anatomical features, creates problems during childbirth.
There is debate among women and doctors on forums about how serious the impact of erosion is during pregnancy. Many women are tormented by questions: if erosion occurs during pregnancy, is it necessary to treat it or is it better to wait for childbirth? The situation is resolved individually, because each woman has her own experience and outcome of pregnancy.
The influence of CMM on the birth process
The birth process is affected not only by the size of the uterus and its position, but also by the presence of various pathologies. Erosion is the detachment of the epithelium, therefore, infection can penetrate through damaged covers and the likelihood of infection of amniotic fluid increases. The following microorganisms can affect fetal development:
- Herpes virus. If it is detected in the body, the doctor recommends a cesarean section;
- Chlamydia. When passing through the birth canal, the child also becomes infected;
- Toxoplasmosis. A disease transmitted from domestic animals, most often from cats.
The degree of risk to the fetus directly depends on the stage of pregnancy at which the infection occurred.
If erosion was treated before pregnancy with the help of surgery, without the use of innovative medical methods, then a scar that is hard to the touch appears on the cervix, preventing the normal opening of the cervix during labor. This risks delaying the baby in the birth canal, which can cause hypoxia. If the doctor notices the problem in time, then, in the presence of scar tissue and a modified organ, he will prescribe a method of delivery through cesarean section.
Pregnancy and childbirth with erosion
The appearance of erosion during pregnancy is more typical for nulliparous women, since the mucous membrane is very sensitive to changes in hormonal levels. The presence of erosion can only be determined through a medical examination, since it does not manifest itself in any way in everyday life. In some cases, a woman notices bloody discharge or experiences discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Possible causes of erosion:
- Taking hormonal contraceptives before pregnancy.
- The use of mechanical means for protection - spirals, rings.
- Exposure to chemicals - suppositories, ointments.
Changes in the mucous membrane are caused by artificial termination of pregnancy, diagnostic curettage with the use of instruments that expand the cervical canal.
It is believed that damage to the epithelium cannot affect the course of pregnancy and childbirth. Redness on the walls of the vagina due to hormonal surges characteristic of the period of bearing a child. It is possible to give birth with erosion, but after recovery it is necessary to diagnose the condition of the cervix.
Contraindications
hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
deep vein thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, thromboembolic disorders (pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, stroke), intracranial hemorrhage or a history of these conditions/diseases;
bleeding from the vagina of unknown origin;
incomplete abortion;
porphyria;
established or suspected malignant neoplasms of the mammary glands and genital organs;
when taken orally - severe liver diseases (including cholestatic jaundice, hepatitis, Dubin-Johnson syndrome, Rotor syndrome, malignant liver tumors) currently or in history.
With caution: cardiovascular diseases; arterial hypertension; chronic renal failure; diabetes; bronchial asthma; epilepsy; migraine; depression; hyperlipoproteinemia; lactation period
How do hormonal drugs affect the cervix during pregnancy?
In some cases, with a dangerous condition of the uterine pharynx, medications are used. They affect the tone of the uterus, reducing it, and promote stronger closure of the cervix to prevent miscarriage. It is recommended to carry out hormonal therapy when planning conception, so that dangerous situations do not arise during pregnancy.
Utrozhestan
A drug that normalizes hormonal levels and prevents abortion. Unlike analogues, it is produced on the basis of natural plant raw materials. If there is a lack of progesterone, or the level of male hormones increases, then this drug prepares the woman’s body for conception.
Taking the drug before conception promotes the maturation of the egg, its release from the follicle, successful fertilization and consolidation in the mucous layer of the uterus. In subsequent months, it helps maintain the embryo in the uterine layer until the body itself begins to produce progesterone.
The drug reduces the tone of the uterus, which contributes to the normal process of bearing a child.
If there are signs of erosion, it has a therapeutic effect on the cervical mucosa, normalizing hormonal levels. Available in capsule form that can be used either orally or vaginally.
Magnesia
Magnesium sulfate or magnesium is used during pregnancy:
- when there is a threat of miscarriage;
- if a woman develops a dangerous condition - eclampsia (late toxicosis, gestosis, preeclampsia);
- for swelling.
Indications for use
Utrozhestan is used vaginally to replenish missing progesterone and related conditions:
- hormonal therapy in preparation for in vitro fertilization (luteal phase);
- elimination (reduction) of unpleasant symptoms of premenstrual syndrome;
- hormone replacement therapy after egg donation or oophorectomy;
- conservative treatment of infertility caused by insufficiency of the second phase of the cycle;
- prevention of the threat of miscarriage in the early stages due to hormonal imbalance;
- maintaining the elasticity of the walls of the uterus as the fetus grows;
- elimination of climacteric syndrome during early menopause.
Before taking Utrozhestan, you should consult with your doctor regarding the form of the drug that is most effective in a particular case. Sometimes it is more rational to carry out treatment with capsules (tablets) taken orally.
Systemic therapy with Utrozhestan is prescribed in the following cases:
- high risk of threatened abortion in the early stages as a result of a lack of progesterone;
- prevention of habitual abortion;
- disruption of the egg ovulation process;
- anovulation of the egg and associated changes in the menstrual cycle;
- elimination of severe symptoms of premenopause;
- hormone replacement therapy in elderly women in combination with drugs containing estrogen.
How does orgasm affect the cervix during pregnancy?
One of the common questions that expectant mothers are interested in is whether it is possible to have sex during pregnancy, and is orgasm harmful?
In the normal course of pregnancy, orgasm is not harmful, but on the contrary, beneficial. This is due to the flow of blood to the genitals, the positive emotions that the expectant mother feels. The muscles of the uterus contract moderately - this can be considered preparation for childbirth. The safest period is the second trimester.
There are cases when orgasm negatively affects the pregnancy process. This happens if a woman is at risk of miscarriage. In this case, it is better to refuse sex until the situation returns to normal. With ICI, the pharynx is slightly open, which is a threat, so sharp tremors and a rush of blood can trigger the onset of labor. Excess oxytocin during orgasm is also undesirable if there is a predisposition to premature birth. Oxytocin after 37 weeks can trigger the onset of contractions.
The hormone prostaglandin in seminal fluid helps soften the cervix and open it, so you need to focus not only on your own feelings, but also on the advice of a gynecologist.
Hello! 11 weeks of pregnancy, third pregnancy, always with ICN (pessary, suturing). Now I have been taking Utrozhestan 200 2 times a day since the 5th week. Over the past two days, I have observed scanty light yellow-brown discharge several times. Previously there were white, remnants of Utrozhestan. The ultrasound is perfect, according to the doctor. Neck 40mm, throat moment, T-shaped. What can cause the discharge and what should I do? Switch to Duphaston? Reduce dosage? Thank you
On the Ask a Doctor service, you can consult an obstetrician online on any problem that concerns you. Expert doctors provide consultations around the clock and free of charge. Ask your question and get an answer immediately!
Shortening of the cervix is one of the troubles that an expectant mother may encounter. A woman often does not realize about existing isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI) until the 15th week. A soft, insufficiently long cervix can lead to miscarriage or premature birth. One of the first aid options for this is taking Utrozhestan. The drug helps balance hormonal levels and maintain pregnancy.
How to calculate the dose?
The amount of active substance required to provide a therapeutic effect is calculated by the attending physician individually according to the indications. In the instructions, the drug manufacturer indicates doses that correspond to the expected effect.
| Indications | Daily dose (mg) | A course of treatment | Features of application |
| Prevention of the threat of fetal loss and complications of labor | 200 | 22-34 weeks of pregnancy | Once a day (preferably at night) |
| Threat of early miscarriage | 200-400 | 1-16 weeks of pregnancy (according to indications up to 24 weeks) | In the morning and in the evening |
| As part of complex estrogen therapy | 100 |
| 1 time per day 2 times per day |
| Progesterone deficiency after oophorectomy or egg donation | |||
| Treatment of infertility caused by corpus luteum dysfunction | 200-300 | 17-26 days MC | Once a day at night |
| Hormone replacement therapy after IVF | 200-600 | 1-24 weeks of pregnancy | 1-3 times a day (in combination with human chorionic gonadotropin) |
Utrozhestan is not a contraceptive to prevent or terminate pregnancy. Uncontrolled use of the drug can disrupt natural hormonal levels and cause side effects.
To achieve a positive treatment result, it is advisable to use Utrozhestan capsules several hours after meals. During treatment, you must follow the recommendations of your doctor and undergo regular examinations. The risk group includes patients with a history of:
- diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction);
- liver and kidney diseases (liver dysfunction, renal failure);
- cardiovascular diseases;
- photosensitivity (chloasma);
- eye diseases (retinal damage, partial loss of vision);
- allergy to plant protein (soy, peanuts) and other components of the drug;
- psycho-emotional instability (prolonged depression, post-stress state).
An absolute contraindication to the use of hormonal agents is oncology and uterine bleeding of unknown etiology.
When using a combination of estrogens with progesterone for a long time, it is necessary to take into account the risk of significant side effects, one of which is breast cancer.
How does the drug affect the body of the expectant mother and the fetus?
Utrozhestan is produced in the form of capsules and vaginal suppositories, which are normally tolerated by the expectant mother and do not affect the development of the baby. The drug does not change the production of female hormones and does not cause excess weight gain. It does not affect the hormonal system of the fetus, but it helps many women carry a child to term and give birth on time.
There are numerous reviews of mothers for whom Utrozhestan helped to bear a child with uterine tone, fibroids, and cervical pathologies (including a short cervix). This is a highly effective drug that helps well with an imbalance of female hormones in the body. At the same time, it is important to take the capsules correctly, only under the supervision of an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Contraindications and side effects
If you take capsules longer than prescribed by your doctor, there may be a risk of side effects such as:
- allergic reaction to the active substance in the form of rashes, anaphylactic shock;
- the appearance of cholestatic jaundice;
- migraines, dizziness;
- phenomena of dyspepsia;
- lack of insulin;
- psycho-emotional instability (euphoria, aggression, apathy);
- menstrual irregularities, including absence of menstruation;
- spotting or breakthrough bleeding;
- itching and hyperemia of the vagina, inner thighs;
- changes in the microbial landscape of the vagina, the appearance of discharge;
- soreness of the mammary glands;
- increased appetite;
- hypertension;
- obesity;
- hyperhidrosis;
- decreased libido.
When using Utrozhestan, you need to remember that its simultaneous use with certain medications may interfere with the therapeutic effect. The group of interacting substances includes:
- antibiotics (penicillins, tetracyclines);
- antifungal drugs;
- immunosuppressants;
- antiepileptic drugs;
- anticoagulants;
- sorbents;
- oxytocin;
- barbiturates;
- and other substances.
During treatment with progesterone, the possibility of a shortening of the menstrual cycle or the occurrence of breakthrough bleeding cannot be ruled out. If you have such symptoms, you should consult your doctor regarding further use of the drug. Perhaps the doctor will select a medicine with a similar therapeutic effect under a different name, to which the body will not react with hypersensitivity (for example, Progestogel, Duphaston, Iprozhin, Progesterone).
How to take the drug for a shortened cervix and other pathologies?
The dosage and method of taking the hormonal drug are prescribed by the doctor. It relies on information about the patient’s condition and takes into account the severity of progesterone deficiency in her body. Reception should be carried out strictly according to the instructions. Typically one of the following regimens is prescribed:
- Orally 200-300 mg in several doses. The morning dose can be 100 mg, the rest the pregnant woman drinks during the day.
- If there is a threat of miscarriage, you should take 400 mg at a time and repeat every 7-8 hours until the condition stabilizes under the supervision of a doctor. After improvement, reduce the daily dose to 200 mg. Take the medicine until 36 weeks.
- For vaginal administration of suppositories, the daily dose is 200 mg. If necessary, the doctor will decide to increase the intake to 400 ml or more.
- If there is a threat of premature birth, the drug is prescribed in the period from 22 to 36 weeks at a dosage of 200-400 ml every 12 hours.
- In the early stages (up to 12 weeks), the optimal dose for maintaining pregnancy is 100-200 mg per day. If pregnancy occurs as a result of IVF, it is increased to 300-600 mg.
Contraindications
According to the instructions, the use of Utrozhestan is unacceptable if the patient has a tendency to thrombosis. The medicine should not be used immediately after an abortion. In case of uterine bleeding of unknown etiology, the use of the drug should be discontinued to avoid further complications.
Take the drug with caution for diseases of the cardiovascular system, hypertension, and diabetes. Absolute contraindications to the use of Utrozhestan:
- malignant neoplasms of the genital organs or mammary glands;
- severe problems in the liver;
- hypersensitivity to one of the components of the drug;
- porphyrin disease;
- acute phlebitis;
- breastfeeding period.