After urination, small amounts of residual urine remain in the bladder. Normally, in adult women and men, its amount does not exceed 30–40 ml.
Bladder pathologies
In children, this value is 3–4 ml. If its volume exceeds 50 ml, then this indicates a violation of the normal outflow of urine through the urethra.
Mechanism of urination
The act of urination (innervation) is a combination of the work of the muscular layer (detrusor) of the bladder, which, by contracting, ensures the removal of fluid, and the sphincters of the urethra, which regulate the retention of urine in the process of its accumulation until the desire to perform the act of urination arises.
Depending on the development of pathological changes in any of the structural elements of the urinary tract responsible for the removal of urine, various disorders occur, leading to damage to the detrusor of the bladder with the subsequent development of atrophy and, accordingly, the inability to contract sufficiently.
Important! Although urine amounts greater than 50 mL are clinically significant, the maximum residual amount may exceed 1 liter.
Table: Permissible volume of residual urine by age
| Age | The volume of residual urine is normal |
| Children under 1 month | < 3 ml |
| Up to 1 year | < 5 ml |
| Up to 4 years | < 7 ml |
| Up to 10 years | < 10 ml |
| Up to 15 years | < 20 ml |
| Adults of both sexes | < 50 ml |
Normal residual urine in the bladder: in men, women, children
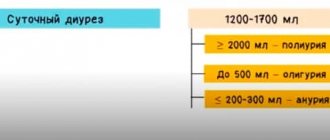
The norm of residual urine for men and women is 30−40 ml. The figure of 50 ml is considered critical. This means that the normal flow of urine is disrupted in a person, and diseases develop. As for the norms of residual urine for a child, they are as follows:
- in newborns 2−3 ml;
- in babies under one year of age 3−5 ml;
- in children 1−4 years old, this norm is 7−10 ml;
- 4−10 years — 7−10 ml;
- 10−14 years - 20 ml;
- for adolescents under 14 years of age, the norm is no more than 40 ml.
Neurological disorders
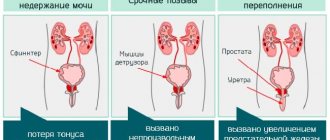
Neurological disorders are always associated with disruption of the part of the nervous system that is responsible for three functions of the bladder:
- reservoir (function that ensures the accumulation of urine in the bladder cavity);
- evacuation (a function that facilitates the removal of urine);
- valve (a function that allows you to hold a certain volume of urine in the bladder).
Damage to any level of the nervous system - from the nerve endings located on the inner surface of the bladder to disturbances in the functioning of the brain - can lead to a number of abnormalities, including hyperfunction of the urethral sphincter. As a rule, the cause of the development of this pathology is damage to the spinal cord due to:
- tumor formations;
- intervertebral hernia;
- spinal injuries;
- congenital pathology of the central nervous system (observed, as a rule, in a child).
Due to difficulties that arise during urination even with a full bladder, atony of the muscle layer develops, which, under constant pressure, loses the ability to contract and push out liquid, accumulating a large volume of residual urine.
Treatment of neurogenic bladder consists of psychological, physical and medicinal methods of influence:
- correction of behavioral lifestyle (streamlining drinking and urination patterns);
- stimulation of urination by massaging the back area;
- physiotherapy;
- drug effects on weakening sphincter tone;
- drugs that regulate the functioning of the central nervous system;
- physiotherapy.
The plexus of nerve endings in the lumbosacral region stimulates the process of urination
Causes of incomplete emptying of the bladder
In men, this syndrome can be a signal of the development of a number of diseases that cause difficulty in the outflow of urine through the urethra:
- Adenoma (benign hyperplasia) of the prostate – the prostate gland hypertrophies and causes compression of the urethra at its entrance to the bladder.
- Prostatitis - inflamed tissue of the prostate gland swells, the volume of intercellular fluid increases, and the urethra is compressed.
- Prostate tumor - can lead to the development of urinary retention only if the tumor grows into the urethra and reduces its diameter.
- Injuries, surgical interventions in the bladder area.
- Neurogenic bladder.
- Cystolithiasis - the presence of stones can cause ureteral obstruction and urinary stagnation.
Additional reasons for innervation may be:
- spinal cord damage;
- endocrine disorders;
- multiple sclerosis;
- enterocolitis;
- pathologies of the peripheral nervous system.
Learn about a kidney CT scan with contrast and how the procedure is performed.
The recipe for monastery tea for the kidneys and the use of the healing drink are described on this page.
Inflammatory and infectious processes
As a rule, the role of inflammatory diseases in the formation of residual urine is the formation of urethral edema or sphincter spasm due to soreness and tissue irritation. A similar reaction can be observed with cystitis, balanitis and urethritis. Prostate inflammation in men occupies a special place among inflammatory diseases that cause persistent urination problems.
Enlargement of the prostate gland, due to an inflammatory process or the formation of a benign (prostatic hyperplasia) or malignant (prostate cancer) neoplasm, causes, in the initial stages of the disease, minor urination disorders, which subsequently lead to more pronounced:
- increased urge to go to the toilet;
- intermittency of the stream when urinating;
- the need for abdominal tension and straining to completely empty the bladder cavity;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Important! With timely consultation with a doctor, prostate adenoma can be successfully treated with the complex effects of medications and physiotherapeutic procedures, and allows you to return to normal life.
Enlargement of the prostate gland towards the bladder, creating an obstruction to the outflow of urine
Diseases in which the syndrome manifests itself
It should be noted that residual urine that is in the bladder is not a disease, but only a symptom. In addition to the diseases mentioned, such a syndrome can also be observed with diverticulum in women and men.
Symptoms of pathology
This is a protrusion in the form of a cavity on the wall of the organ where urine accumulates.
In children, such a pathology as vesicoureteral reflux is very common. With this disease, residual urine is “thrown” up the ureters into the kidneys.
Urinary tract obstruction
The presence of stones in the bladder is one of the most common causes of residual urine. Cystoliasis occurs with equal frequency in both men and women. Only the mechanism of stone formation differs - the male body is characterized by the formation of stones directly in the cavity of the bladder, and the female body is characterized by the migration of stones from the kidneys.
Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder
The reasons for the formation of stones can be internal or external factors:
- chronic infectious diseases of the urinary tract;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- improper diet;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- work in hazardous industries;
- improper drinking regime.
In addition to the main signs of the formation of residual urine, with cystoliasis pain in the lower abdomen with irradiation to the groin, scrotum or perineum is noted. Also a characteristic sign is a sudden interruption of a full stream during urination. Treatment consists of removing stones using medications or lithotripsy, followed by their removal naturally.
Important! Therapy with stone-breaking drugs helps dissolve stones in the kidneys and bladder within 2–6 months, but has many side effects.
The drug Canephron prevents the formation of stones and has a minimum of contraindications
Diagnostics
This process consists of several neurological, urological, laboratory tests and interviews. When you first visit a urologist, you will be prescribed the following procedures.
- Ultrasound of the bladder and pelvic organs. This study is carried out in two phases. The first is when the bladder is full to measure its volume and size. The second ultrasound is 5-10 minutes after emptying. To ensure accurate results, calculations are carried out at least three times. There are special formulas for calculating the amount of liquid, which require the following parameters:
- height,
- width,
- length of the ultrasound shadow of the bladder.
If the patient is currently taking diuretics, or before the examination, drank drinks or ate foods that could irritate the organ for examination, then the doctor must be warned about this, since the diagnosis may be erroneous due to these influencing factors.
Ultrasound is considered a non-invasive method, since the rate of residual urine in men and women is not determined accurately. But it is used more often due to its general availability.
- Clinical analysis of blood and urine, urine culture to determine bacterial infection.
- Cystoscopy and contrast urography – if necessary. The first type of examination is prescribed as a last resort, as it is quite traumatic. But it quite accurately indicates the volume of residual urine, if any was detected.
Do not forget that the calculation of volume and urine analysis for prostatitis and other diseases in which this symptom appears may turn out to be erroneous during ultrasound and other examinations due to nervous strain.
Diverticulum
A diverticulum is a sac-like cavity formed from the wall of the bladder. There are two types of diverticula – true and false. A true diverticulum consists of the mucous and muscular layers of the bladder tissue and, as a rule, is a congenital anomaly.
False diverticulum (acquired) develops as a result of increased intravesical pressure that occurs against the background of pathological conditions accompanied by difficulty urinating and systematic incomplete emptying of the bladder. Due to high fluid pressure, atrophy of the muscle layer develops, the destroyed fibers diverge, and the mucous membrane protrudes into the abdominal cavity under pressure.
The main difference between a false diverticulum and a true one is the absence of muscle fibers in the structure of its wall. The main clinical sign of diverticulum is urination twice with the appearance of cloudy urine.
Treatment consists, first of all, in eliminating the causes causing increased intravesical pressure (if the diverticulum is acquired) and subsequent surgical removal of the deformity.
Complications
If you suspect the presence of excess urine in the body, immediately seek qualified help. After all, the consequences of your delay can cause you many problems. Very often, doctors have to operate on patients, because treatment with drugs cannot help. And all this is only because of the late determination of the final urine. Therefore, the most common complications are:
- inflammation of the kidneys and urethra;
- renal failure;
- stones in the kidneys;
- hydronephrosis.
Urethral stricture
Pathological narrowing of the urethra is called urethral stricture. Metaplasia of the tissues of the urethral mucosa can be caused by various reasons, causing damage of varying severity:
- thermal or chemical burns of the urethra;
- inflammatory processes (cystitis, urethritis);
- injuries or bruises of the perineum;
- injury to the mucous membrane during catheter installation;
- congenital pathologies of the urinary tract.
Due to the replacement of damaged cells with mucous connective tissue, scar formation occurs, which significantly complicates the process of urination, resulting in urine remaining in the bladder.
Stricture of the urethral canal on x-ray
Reasons for the increase
Residual urine can occur due to a variety of reasons. In general, they are divided into three groups:
- obstructive;
- inflammatory-infectious;
- neurological.
Obstructive health problems are considered to be those that prevent urine from leaving the body. For example, stones, tumors, polyps, prostate adenoma in men, uterine fibroids and ovarian cysts in women, as well as narrowing and soldering of the urinary canals. Swelling of the urethra and compression of the bladder muscles, which occur due to inflammatory and infectious diseases, also lead to urine retention. Thus, the prostate, cystitis, and urethritis provoke the occurrence of residual urine.
The last group of reasons includes the loss of urinary control by the central nervous system. In such cases, the bladder itself is healthy, and the problem lies in the muscles of the organ or sphincter, which stop contracting at the right time. The causes of this state of the body are often sclerosis, injuries to the spinal cord and brain, congenital pathologies of the central nervous system, and diseases of the spine. The fact is that antidepressants, antiarrhythmics, diuretics, hormonal drugs, medications for Parkinson's disease, as well as some painkillers negatively affect the tone of the organ.
Signs and complications
Urine, which remains in the bladder cavity after urination, not only causes a large amount of discomfort, but is itself an alarming symptom, the severity of which directly depends on its quantity.
Residual urine is an important clinical sign, as it leads to dysfunction of the upper urinary tract and is a consequence of pathological processes leading to functional disorders of the bladder.
The main symptoms accompanying excess residual urine are:
- increased urge to urinate;
- weak or intermittent stream;
- the need to strain the abdominal muscles in order to begin the process of urination or prevent its interruption;
- inflammatory processes in the urinary tract.
In the absence of timely treatment, the risk of developing inflammatory processes increases, since stagnation creates a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic microflora and the formation of stones. Impaired urine flow can also lead to the development of hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis and renal failure.
When treating acute urinary retention, it is removed using a rubber catheter.
Why is an ultrasound of the bladder performed to determine residual urine?
Ultrasound of the bladder with determination of residual urine is a fairly common procedure among the population of all ages, but more often such a study is prescribed to male patients. This predominance is based on the anatomical features of the structure of the male genitourinary system, and the results play an important role in the selection of treatment.
In this article we will talk about the purposes for which an ultrasound examination of the bladder is performed, how to prepare for it and what the normal indicators should be.
Why is ultrasound prescribed?
Ultrasound of the bladder with residual urine is carried out mainly in the direction of a urologist. Most often, referrals are given to children or men over 35 years old, with inflammation or prostate adenoma.
This diagnostic method is very informative; in addition, the main advantages are its painlessness and speed of execution. In general, the entire study takes about 15-30 minutes. The conclusion is issued on the same day, in a few minutes.
This type of ultrasound examination is prescribed for:
- cystitis;
- urinary incontinence;
- difficulty urinating;
- prostatitis;
- bladder stones;
- prostate adenoma;
- suspected neoplasm;
- bladder injuries;
- violations of contractions of the bladder walls;
- control after treatment.
In addition, ultrasound is used for symptoms of renal colic, the presence of blood in the urine and to examine the urodynamics of the upper urinary tract. Residual urine in a child is associated with problems in the functioning of the bladder.
Most often this is due to a broken connection between the walls of the bladder and the sphincter of the urethra, or to insufficient force of contraction of the walls of the organ. In this case, the doctor should note that it is not the presence of residual urine itself that plays a role, but its quantity.
Determination of residual urine is very important for diagnosis, because this condition impairs the functionality of the upper urinary tract and leads to impaired bladder emptying.
The following symptoms may be observed:
- urinary retention or incontinence;
- interruption of the stream;
- weak stream of urine;
- frequent urge to urinate.
For a more detailed examination, many people practice performing ultrasound of the bladder and abdominal cavity simultaneously. This allows you to assess the functioning and condition of organs and identify possible deviations.
What is assessed during the research process?
During the study, instructions are used according to which the specialist must evaluate the following indicators:
- bladder size and shape;
- contours;
- foreign bodies;
- neoplasms;
- bladder contents;
- presence of inflammation;
- increased tone;
- MP omission;
- pathology of the prostate in men, ovaries in women.
According to ultrasound, the bladder cavity may contain urine, pus or blood. With the help of this study, it is possible to estimate the volume of the organ, moreover, in modern devices this is done automatically.
When residual urine is assessed by ultrasound of the bladder, its residual cannot be more than 10% of the total urine volume. These data play a big role in further diagnosis.
Normally, the organ has a longitudinally rounded shape, depending on whether the image was transverse or longitudinal. In men, the volume of the bladder is 300-700 ml, in women – up to 500 ml. The MP has an echo-negative structure, the walls of the organ are of the same thickness, no more than 4 mm, no foreign inclusions should be observed.
Features of preparation for research
In order to prepare for examining the bladder and determining residual urine, the doctor must tell you in advance about the rules of preparation and the technique of the procedure.
Regardless of the gender and age of the patient, diagnosis occurs as follows:
- The patient assumes a supine position, freeing the lower abdomen from clothing.
- Before diagnosis, it is recommended to drink 1-1.5 liters of fluid and wait for a noticeable urge to urinate (physiological filling also occurs, in which the patient refrains from emptying the bladder for 4-6 hours). For a child, 700-900 ml of liquid one and a half hours before ultrasound diagnostics will be enough. The use of diuretics before an ultrasound is strictly prohibited, as they distort the real picture, causing increased urine output.
- The specialist will move the sensor over the abdomen and evaluate the necessary indicators. After the examination of the bladder has been carried out, the doctor will advise you to empty it, then you need to continue the diagnosis for the presence of residual urine. No more than 10 minutes should pass between examination of a full bladder and diagnosis after urination, since a long break will distort the results of the examination.
The average cost of an ultrasound examination is 300-700 rubles. In some medical institutions, you can undergo diagnostics on your own initiative, without a referral from a specialist.
From the photos and videos in this article, we learned for what purposes the study of MP and the level of residual urine using an ultrasound method is prescribed, we looked at what is assessed during the diagnostic process and what the correct preparation should be.
Frequently asked questions to the doctor
Symptoms
Residual urine is just one of the various symptoms found when the genitourinary tract becomes blocked and becomes inflamed. But if its appearance is associated with neurological disorders, then such a problem is much more difficult to detect, in particular, if the problem is in a small child.
If before this you felt like a healthy person, then the first sign of urinary retention will be the presence of a sluggish urge to urinate. This symptom develops gradually, like organ atony. This can be felt by several signs.
- Pressure in the bubble. Since a small child will not be able to tell about this, you can feel this by an increase in volume and a painful reaction of the child to his examination.
- A feeling of incomplete emptiness.
- Intermittent, sluggish or thin stream when urinating.
- Men may also experience impaired sexual function, swelling of the head of the penis, as well as pain in the pubic or lower back area.
- Pain in the urethra.
- Frequent urge to defecate can also be an indicator that there is residual urine due to prostatitis or other diseases.
If you have a diverticulum, there will be no pressure or pain, but urination will occur “in two steps.” First a large portion will come out, and then a meager one. This process occurs because first the bladder itself is emptied, and then the diverticulum that appears there.
Erroneous results
In determining such an indicator, false positive results often occur. This is due to improper fluid intake. The best option is to collect your urine before visiting your doctor's office. But often, between the collection of fluid and a visit to the diagnostic room, a certain time period passes, during which a person may accumulate the next portion of urine in the organ and need to go to the toilet again.
Factors such as the use of diuretic medications or taking a large amount of liquid the day before the test can also negatively affect the results. So, if a patient drinks a diuretic before undergoing an examination, urine begins to quickly accumulate in his body, the amount of it is about 10 ml per minute.
Often a person cannot take a test in a hospital because he experiences discomfort in such conditions, so the test may show an excess of residual urine.
For a reliable result, it is recommended to conduct the examination three times or more.
This will make it possible to correctly determine the indicator and make an accurate diagnosis.