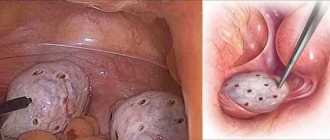
An ovarian cyst is a capsule filled with secretory fluid. It is one of the most frequently diagnosed pathologies of the female reproductive system. There are no cells inside the cavity, and the change in the size of the ovarian cyst occurs due to an increase in the volume of secretion.
In most cases, the cause of formation is a hormonal imbalance, but it can develop as a result of inflammation of the appendages.
What is a cyst: how is it formed?
An ovarian cyst is a benign neoplasm, which is a cavity on a stalk. The capsule is filled with liquid contents and is capable of increasing in volume as a result of the accumulation of secretions.
There are several types of cystic formations, differing in origin and internal contents:
- Follicular. It is formed at the site of an unopened follicle capsule.
- Corpus luteum cyst. Replaces the unregressed corpus luteum.
- Paraovarian. Arises from the supraovarian appendages. This is a large ovarian cyst, can reach 5 cm or more.
- Endometrioid. It is an accumulation of menstrual blood. The endometrial cells act as the shell of the capsule.
- Dermoid. Its contents are represented by fragments of embryonic tissue.
- Mucinous. Multi-chamber neoplasm filled with thick mucus.
Pathological and normal cyst sizes
The conventional norm is considered to be a capsule volume of up to 2 cm. Exceeding this figure can be considered as a potentially dangerous formation for women’s health, since the development of such conditions as:
- shell rupture;
- leg torsion;
- suppuration;
- development of hemorrhage and others.
The size of an ovarian cyst is considered large if it exceeds 6 cm in diameter. Many experts recognize such formations as dangerous, but it all depends on its type.
It is important to remember that a large ovarian cyst, if ruptured, can cause massive internal bleeding.
2 cm
An ovarian cyst of 2 cm in volume does not pose a particular danger to women’s health. For example, if it is a follicular variety, then it will resolve on its own within one to three menstrual cycles.
Most often, cystic formations of this size are treated with medication. The woman is prescribed hormonal medications.
3 cm
Treatment of ovarian tumors with a volume of 3 cm is carried out with the help of medications. Hormone therapy was recommended for the patient. Surgery is practiced when necessary.
4 cm
An adnexal cyst on the left or right ovary of 4 cm is most often a parovarian neoplasm. It tends to increase and can reach significant volumes.
Dangerous for a woman, as it can be complicated by torsion of the leg. Symptoms of the condition include:
- cramping pain localized in the lower abdomen;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- increased body temperature;
- tachycardia;
- tension of the anterior abdominal wall.
If such symptoms develop, the woman is recommended to undergo urgent surgical intervention.
5 cm
When diagnosing an ovarian cyst measuring 5 cm, you must regularly visit the gynecologist’s office. This should be done once every six months. The patient is recommended to periodically determine hormonal levels, which makes it possible to monitor changes that have occurred.
6 cm
An ovarian cyst of 6 cm is considered large. Quite often, gynecologists take a wait-and-see approach, monitoring changes in the patient’s general health.
To determine how dangerous this neoplasm is for her, a woman is prescribed additional examinations:
- blood and urine tests;
- CT and/or MRI;
- blood test for tumor markers;
- puncture;
- diagnostic laparoscopy.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor decides whether to perform removal surgery or not.
Ovarian reserve
A woman’s age is one of the important factors influencing the effectiveness of ART methods, since this parameter is directly related to the quality of the eggs located in the ovaries.
This parameter is not absolute, since a 45-year-old woman could have good quality eggs and still be fertile at this point - although this particular situation is more unusual than usual.
On the other hand, in some cases there are women who even at the age of 25 have “low-quality” eggs, even needing donor eggs.
These extreme examples, however, quite existing, led to the need for some way to assess the quantity and quality of eggs in women of different age groups.
It was for this purpose that the concept of “ovarian reserve” was introduced, since it became necessary to evaluate a woman’s reproductive age, not as the absolute number of years from the date of her birth, but as her real existing ability to become pregnant.
Ovarian reserve is the number of eggs in women at a given time that can be used for fertilization.
But how to count them, they are located in the ovaries? For this purpose, a number of functional tests have been proposed, which you can learn a little about in this section.
Counting the number of antral follicles
Antral follicles are small follicles (2-8 mm in diameter) that we can see, measure and count using ultrasound. Transvaginal ultrasound is the optimal method for counting these small structures.
The fact is that the number of antral follicles has a direct relationship with the number of primordial follicles, visible only during microscopic examination, located in the ovaries. Each primordial follicle contains a precursor to an egg, which may become one in the future.
Thus, counting antral follicles visible on ultrasound replaces microscopic examination of the ovaries for accurate assessment of the number of oocyte precursors.
Counting antral follicles using ultrasound is a simple and accessible method for assessing ovarian reserve.
Figure 1 on the left shows an ovary (outlined in blue) in which antral follicles were counted at the beginning of the menstrual cycle (outlined in red). In this projection of the ovary, 16 such follicles are visible.
What is the “good” number of antral follicles?
Based on a number of studies by foreign authors, the following pattern has been revealed:
| Number of antral follicles | Expected response to ovulation stimulation and the effectiveness of ART techniques |
| Less than 4 | Very low quantity. Poor or no response to stimulation. Enrollment in an IVF program should be seriously considered. Very low chance of pregnancy. |
| 4-7 | Low quantity. There may be a slight response to stimulation. It is preferable to use very high doses of FSH for stimulation. Unsuccessful attempts. |
| 8-10 | Slightly reduced quantity. A large number of unsuccessful attempts. |
| 11-14 | Normal (but average) amount. The response to stimulation is reduced, but, as a rule, sufficient. Group with a favorable prognosis for pregnancy. |
| 15-26 | Normal good quantity. Excellent response to ovulation stimulation. It is preferable to use low doses of FSH. Best efficiency. |
| More than 26 | A high amount characteristic of polycystic ovary syndrome. The use of low doses is necessary due to the risk of hyperstimulation syndrome. In some cases, the eggs are of low quality, which reduces the chance of pregnancy. |
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) on days 2-3 of the menstrual cycle
This indicator is also an important marker of the state of the ovarian reserve.
According to domestic data, the following concentration limits are distinguished:
- 3-8 IU/l is normal, a good response to stimulation is expected;
- 8-10 IU/l – the response can range from normal to moderately reduced;
- 10-12 IU/l – low ovarian reserve, reduced response to stimulation;
- 12-17 IU/l – poor response to stimulation and low pregnancy rate;
- More than 17 IU/l is a very poor response to stimulation.
Calculation of ovarian volume
The formula for calculating ovarian volume is as follows:
Ovarian volume = 0.532 x length x width x thickness.
What can data tell us about ovarian volume? If a woman has an ovarian volume of less than 8 cm?, then low ovarian reserve is assumed, if more than 12 cm? – high ovarian reserve.
anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) and inhibin B
The most informative test is one that allows you to determine the content of anti-Mullerian hormone. In women, the production of this hormone occurs in granulosa cells and reaches a maximum in preantral and antral follicles 4 mm in diameter.
In larger follicles, as well as in follicles more than 8 mm in diameter, there is no secretion of this substance.
Figure 2 schematically shows the actions of AMH in the ovary:
The growth of follicles is shown schematically. It has been shown that anti-Mullerian hormone is produced by primary and preantral follicles and has mainly 2 types of effects on the ovary: 1 - suppresses the primary stages of follicular growth, 2 - suppresses FSH-dependent growth and selection of preantral and small antral follicles.
Based on a number of studies, it has been established that the content of AMH in the blood serum is directly related to the content of antral follicles, that is, based on the analysis data, the state of the ovarian reserve can be assessed. It has also been shown that the lower the content of this hormone in the blood, the worse the ovarian response to ovulation stimulation.
An interesting fact is that anti-Mullerian hormone can be used not only to assess the state of the ovarian reserve, but also to assess the pathophysiological state of the ovaries, for example, to confirm the presence of polycystic ovary syndrome, since in this disease the pool of small antral follicles is increased. This indicator can not only be a marker of the presence of the disease, but also a criterion that will allow assessing the severity of disorders in polycystic ovary syndrome.
The study of anti-Mullerian hormone content can be carried out on any day of the cycle, since its content practically does not change during the cycle.
According to other scientists, it is better to study the content of anti-Mullerian hormone on days 3-5 of the cycle.
These data can be used in preparation for ART in order to objectively assess the condition of the ovaries, as well as select the correct stimulation protocol.
Based on an assessment of a number of the above indicators, a conclusion can be made about the state of a woman’s ovarian reserve:
Low ovarian reserve is assumed if:
- the patient’s age exceeds 35 years;
- FSH level at 2-3 d.m.c. more than 10IU/l;
- the number of antral follicles is less than 10 mm in diameter at 2-3 d.m.c. less than 5 in each ovary;
- ovarian volume less than 8 cm³;
- low levels of anti-Mullerian hormone.
High ovarian reserve is expected if:
- the patient's age is less than 35 years;
- FSH level at 2-3 d.m.c. less than 8IU/l;
- the number of antral follicles is less than 10 mm. in diameter by 2-3 d.m.c. more than 10 in each ovary;
- ovarian volume more than 12 cm³;
- high levels of anti-Mullerian hormone.
Next: » Laparoscopy and IVF
See also:
Infertility treatment services at the “I’m Healthy!” Clinic
- Consultation with MD, professor of obstetrician-gynecologist
- Consultation with Ph.D. reproductive specialist
- Assessment of couple fertility and diagnosis of infertility factors
- Consultation with MD urologist-andrologist
- Examination of the spouse and preparation of a “fertility passport” in accordance with international standards
- Expert ultrasound of the pelvic organs with Doppler ultrasound
- Checking the patency of the fallopian tubes (ultrasonohysterography, hysterosalpingography)
- Assisted reproductive technologies (artificial insemination, IVF, ICSI, PIXI)
Step-by-step steps to diagnose infertility
Step-by-step steps for the IVF program
Source: https://www.ya-zdorova.ru/iskusstvennoe-oplodotvorenie/ovarian-reserve/
Examination and course of treatment
Diagnosis of pathology involves the following activities:
- collection of patient complaints;
- two-handed examination in a gynecological chair;
- Ultrasound examination using a transabdominal or transvaginal method;
- collection of punctate from the posterior vaginal vault;
- determination of tumor marker CA-25;
- CT or MRI;
- pregnancy test to rule out ectopic gestation.
The treatment your doctor chooses depends on your current tests. If there is a chance of malignancy, then surgery is mandatory. In this case, the size of the capsule does not matter.
If the formation does not pose a danger and is not accompanied by the development of complications, then the woman is prescribed a course of drug therapy. The duration of treatment with hormonal drugs is two to three months. Recovery occurs in 90% of cases.
If the therapy does not bring the expected result or the capsule has increased in size, the woman is indicated for surgical treatment.
The laparoscopic technique is most often practiced. For large tumors, classic intracavitary surgery is used.
Complete removal of the ovaries is performed in exceptional cases.
Normal ovarian volume according to ultrasound formula
The health of a woman’s reproductive system is very important for every representative of the fairer sex, especially if she plans to have children in the future. This is due to the fact that a disruption in the functioning of any organ will invariably lead to the development of various gynecological diseases, not excluding infertility.
The ovaries, which are glands, are responsible for the production of sex hormones, the process of egg maturation, as well as the release from the follicle.
Paired reproductive organs are located on both sides of the uterus, which in turn is located in the pelvis.
Some may be interested in how to calculate the volume of the ovary, since this parameter can change at different ages and the state of the female reproductive system.
When it bursts
The capsule bursts at different sizes. In approximately 50% of cases, the provoking factor is internal inflammation.
The walls involved in pathological processes become thinner and lose their integrity even under the slightest load. Physical exercise, weight lifting, running, etc. can provoke a rupture.
You also need to be careful when having sex. Too active friction or deep penetration can also cause capsule rupture.
Ovarian cystic neoplasms are a gynecological pathology that requires constant medical monitoring. That is why, if pain in the lower abdomen or cycle disorders occurs, it is necessary to obtain qualified medical advice.