Hypo- and hyperechoic formation in the liver on ultrasound
The health of the liver is the health of the whole organism, because it is this organ that is responsible for neutralizing harmful substances that regularly enter inside. When the liver stops functioning normally, other organs and systems “give up” behind it. The body is at risk of intoxication. The specificity of this organ is that until serious changes occur in it, it will not make itself felt by pain, since it has no pain receptors. That is why it is necessary to monitor the condition of the liver by regularly examining the organs using the harmless and informative ultrasound method.
Diagnostic methods
The only way to detect a hypoechoic area is to resort to ultrasound diagnostics. In this case, the examination is carried out with a special device that emits ultrasonic waves.
Ultrasound is a painless and completely safe procedure
In contact with internal organs, ultrasonic waves are reflected and returned. Thanks to this, everything that happens is displayed on the monitor. Subsequently, the doctor deciphers the results obtained.
Ultrasound is harmless regardless of the patient's age. The method can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The method does not require special preparation. An exception is abdominal ultrasound examination. In this case, sometimes you need to fill your bladder or follow a diet.
Before performing an ultrasound, an acoustic gel is applied to the area being examined. The product promotes better glide. Does not interfere with visualization and does not cause an allergic reaction.
After diagnosis, you need to remove the remaining gel. This can be done using dry wipes. The doctor will decipher the indicators and confirm or deny the likelihood of the presence of hypoechoic tissue.
From this video you can learn more about benign formations in the mammary gland:
What is the essence of the ultrasound method
During the examination of an organ, the device, or rather its sensor, which is in contact with the patient’s skin, produces ultrasound waves, they are directed to the organ and reflected from it. They return with a different frequency. These return waves are picked up by the same sensor. After instant processing, a picture based on the sent and returned frequencies is projected on the device’s screen.
The data obtained by this method gives the diagnostician a lot of information about the condition of the organ and its pathologies. Using ultrasound, it is possible to find out the following parameters of the liver:
- Organ location.
- Its dimensions.
- Structures – external and internal. You can learn a lot from this indicator, in particular the presence of tumors of various types. To determine structural changes, the echogenicity index is used. It is different for each organ, including the liver.
Sometimes organs may show areas with less echo density; they are called hypoechoic. Such non-physiological lesions can have different sizes, numbers, and shapes. Such a lesion of the liver is a very dangerous phenomenon; if the cause of the formation of the pathological focus is not treated in a timely manner, there is a possibility of liver failure, which leads to serious consequences.
Hyperechoic inclusions in the ovary: what is it - Dermatologist
A hyperechoic formation in an ultrasound image indicates tissue compaction. If such a symptom is detected, the doctor prescribes an additional examination. Compaction can be a sign of a tumor, stones, or calcifications.
Treatment tactics
When cystic bodies with low echogenicity are detected, treatment may vary depending on the type of tumor, its size, the likelihood of malignancy and the occurrence of complications.
If the ovarian cysts are small, doctors in most cases choose a wait-and-see approach, which consists of monitoring the anechoic body.
If the tumor grows to a large size, drug treatment or surgical intervention is prescribed.
To summarize, it must be said that if the conclusion of the ultrasound results says that anechoic elements are present in the appendages, you should not panic. Most often they turn out to be cysts that need to be treated.
Only if the cystic body is distinguished by the presence of blood vessels can we talk about the likelihood of developing a malignant process.
To finally get a diagnosis, it is recommended to visit the treating gynecologist, who, based on ultrasound, will determine the type of disease and its nature.
We recommend you learn: Ovarian cyst in the fetus, what to do
Source: https://tihuzlpoliklinika.ru/gormony/giperehogennye-vklyucheniya-v-yaichnike-chto-eto-takoe.html
Symptoms of pathological formations on the organ
The main recommendation for those who have problems with the functioning of the organ is to undergo regular examinations. Moreover, the ultrasound method is optimal, because it does not harm the body, and there are no restrictions on the number of times it is performed.
If there have been no problems with liver function before, then you need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Painful sensation in the area of the right ribs.
- There is an unpleasant bitter taste in the mouth.
- Periodic sensations of nausea and vomiting occur.
- The skin appears yellowish.
- Changes in body temperature occur for no reason.
- Performance drops sharply.
- Mucous membranes change color.
One, and even more so, several such symptoms are a signal to see a doctor as soon as possible. If measures are not taken in a timely manner, complex consequences are possible, including organ rupture, which will lead to death. Although the threat is very serious, drug treatment has a lasting and positive result.
Types of neoplasms
Any foci of non-physiological acoustic density indicate to the diagnostician problems with the functioning of the organ. This means that the blood is cleansed and pumped more slowly. As a result, toxins accumulate, which negatively affects not only the liver, but the entire body. Various diseases develop; cystic neoplasms and tumors may be suspected on the liver itself.
Formations with reduced acoustic density
A hypoechoic formation is a pathological focus on the liver, which has a lower density than that of the organ. When ultrasonic waves pass through this area they slow down their speed. On the device’s monitor, this will be shown as a darker spot than the rest of the organ. Such neoplasms are a signal of the development of pathological processes, most likely a destructive process.
The following diseases and neoplasms can show themselves this way:
- Cirrhosis.
- Cystic neoplasm.
- Thrombosis.
- Abscess.
- Adenoma.
- Carcinoma.
A detailed description of the detected focus of reduced echo density makes it possible to determine which category the pathological focus belongs to. Characteristics:
- Cirrhosis will manifest itself as nodular neoplasms of small diameter, while the outlines of the organ will be tuberculate.
- The cyst will be described as a roundish cavity with fluid inside.
- Thrombosis of the collar vein will be described as a formation that has an elongated shape and a loose constitution.
- Abscess - ultrasound will show deformed edges of the organ, gas bubbles will appear in its structure.
- In case of adenoma, a pseudocapsule will be visible, the tissue of which will be more dense. The lesion will be smooth with clear boundaries.
- Carcinoma is a cancerous tumor. It will show itself not only as a neoplasm on the organ, but also as metastases that spread to neighboring organs.
Additional Research
Since gnopoechoic areas are often malignant neoplasms, additional studies are needed to confirm or refute the diagnosis. But still, based on the data obtained, it is already possible to draw a conclusion and make a diagnosis, and therefore prescribe treatment. In any case, if diagnosed in the early stages of development, the disease will be easier to cure, no matter what the tone is. If additional tests are prescribed, they must be completed.
Hyperechoic neoplasms
These areas will have increased acoustic density; on the monitor they will be much lighter than other organs. Such neoplasms are also dangerous, because they can be:
- Hemangioma is a collection of blood vessels, the so-called “tangle”, it forms a benign tumor.
- Primary cancer - it develops as a result of the penetration of metastases from other organs.
Conclusion. Diagnosis of liver tumors using the ultrasonic wave method is the most effective and safest method. With its help, both malignant and benign neoplasms are identified.
1uzi.ru
Anechoic ovarian cyst: what is it and how to treat
An anechoic ovarian cyst is what sonologists – ultrasound diagnostic specialists – call a darkening visible on an ultrasound examination in the area of the organ. This is not a diagnosis or a disease. Although under this effect of a hardware examination there may be a temporary normal phenomenon of the female body, a cyst or a cancerous tumor.
The fact is that a similar picture is given by being filled with liquid, which happens every month during the cycle. But there should be no darkening before, during or after menstruation. If during this period an ultrasound showed an anechoic cyst, it means that there is a pathology in the body. Which one should be diagnosed by the attending physician.
Just as bats determine the world around them by the waves returning from objects, so the ultrasound of diagnostic equipment creates a picture of organs based on the reflection of the signal. The fact is that the liquid located inside the cavities, tissues with a large water content, absorbs ultrasound waves.
As a result, this place will be dark on the monitor. The denser the fabrics, the lighter they are. Therefore, bones appear brightest and are hyperechoic. The same applies to hollow organs, mainly filled with air and gases.
Hence the name echogenic - reflective, anechoic - the opposite meaning.
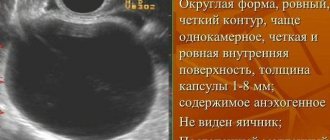
Interesting fact! A cyst is a formation with walls and contents, round or oval in shape, and can be single or multi-chambered. From here we get that any cysts with fluid inside are anechoic. Not every one is filled with fluid and appears as a dark spot on the monitor, just as not everything that is anechoic is a cyst.
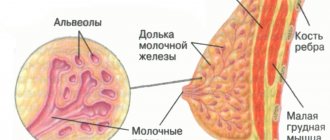
During ultrasound diagnostics, similar formations are found in the mammary glands, kidneys, thyroid gland and other organs.
Cyclic changes and echogenicity
During the period close to ovulation and some time after, the ovary on ultrasound may look like a dark spot for the following reasons:
- Follicle maturation is the normal state of the ovary during the period of ovulation. As the egg forms, the follicle in which it exists grows. By the end it reaches 2-2.5 centimeters in diameter. Next, the egg is released.
- The formation of the corpus luteum is a subsequent stage in the normal process of the reproductive system. After the egg has left the follicle, the so-called corpus luteum is formed in its cavity. It produces the hormone progesterone, which promotes pregnancy. Gradually, the temporary gland decreases and by the beginning of the next menstruation it stops working.
Now let's look at diseases in which a dark spot in the ovary area is a symptom:
- Follicular cyst. A formation that appears due to the accumulation of fluid inside the follicle. They are thin-walled and have a round shape.
- Paraovarian - formation on the surface of the ovary. It grows from the epididymis and is located closer to the area where the fallopian tube attaches.
- Dermoid cyst. A congenital pathology, which is characterized by the presence of a “pocket” in different places of the body where the rudiments of teeth, skin, and hair are located.
- Luteal. When the corpus luteum forms, a larger than usual amount of fluid is collected. Sometimes it may not resolve with the onset of menstruation.
- Serous cyst. A bubble in the upper layer of the organ.
- Endometrioma is a formation of endometrium containing blood. Location inside or near the ovary. Their interesting feature is that during menstruation, they also release blood. Such cysts are a consequence of the spread of endometriosis pathology.
It is not a cyst, but it is similar in general parameters to a cystoma; it is also anechoic. This is a benign formation of the type of multi-chamber, heterogeneous accumulation of tissue, which can be filled with fluid. Predisposed to rapid cell growth and division. The following types are noted:
- Mucinous cystoma. Formed from glandular tissue. Numerous cavities are filled with viscous semi-liquid mucin;
- Cystadenoma. Formation from papillary epithelium. Reminds me of papillomas. They grow quickly, causing various consequences.
There are many types of cysts, even ovarian cancer, which is found in 20% of women, can be anechoic. With the onset of menopause, the risk of cancer increases.
Some of the above formations are hypoechoic, wave absorption is incomplete, and there is some reflection. The areas in the picture are dark, but not black.
Interesting fact! There is such a thing as an avascular cyst - a formation that does not have blood flow. For example, cancerous tumors always have blood circulation.
Clinical picture of an ovarian cyst
At first there are no symptoms, but as the size increases, the formation begins to manifest itself:
- Pulling, pressing in the lower abdomen;
- Pain on the right or left side;
- Feeling of full bowels;
- Discomfort when emptying the bladder, false urges;
- If sharp pain occurs in the form of contractions, nausea and vomiting appear, and the body temperature rises - these are signs of torsion or rupture of the cyst, urgent medical attention is needed.
Diagnosis of pathology consists of a gynecological examination, medical history and ultrasound examination. Additional tests may include testing hormone levels, as well as identifying tumor markers.
For different types of cysts, a different approach is required in each case:
- Observation is applied to formations that can resolve over time. These are luteal and follicular cysts.
- Drug therapy with hormonal drugs is effective for hormone-dependent formations.
- Aspiration - liquid is pumped out through a puncture and ethanol is injected into the cavity, which promotes gluing of the walls.
- Surgery. Dangerous formations, cancerous tumors, dermoid cysts that cannot resolve, endometrioma are removed along with the affected ovary. In the case of oncology, the appendage and fallopian tube are sometimes removed.
Surgeries to get rid of cysts are performed laparoscopically even during pregnancy.
If an anechoic cyst is diagnosed on ultrasound, you should not immediately worry. First of all, you need to compare the date of diagnosis with the period of your cycle.
The gynecologist will prescribe additional research at a time when there should not be dark spots for natural reasons. If this time the formation remains, you will have to prepare for long-term treatment, possibly surgery.
Leaving a cyst unattended is dangerous; its rupture can lead to peritonitis and death.
Diagnosis of an anechoic ovarian cyst and whether it needs to be treated Link to main publication
Source: https://StopKista.ru/yaichnik/anehogennaya.html
Terminology analysis
After conducting an ultrasound examination, many begin to panic when they hear specific terms, such as hyperechoic formations in the liver. But don’t worry, as this term refers to the characteristic signs of the disease.
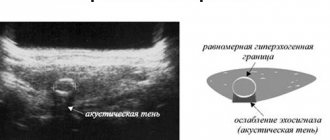
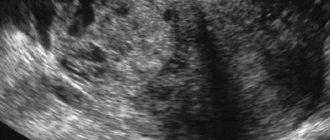
So, let's start with the concept of what a hypoechoic formation in the liver is on ultrasound (synonym hypodense) - this is an area with a lower density in the tissue of the organ. Typically, on an ultrasound monitor, the hypoechoic zone appears as a dark spot. This is often what a cyst looks like, or its varieties, which are a formation whose cavity is filled with fluid.
Click to enlarge.
A dark spot on an ultrasound is a focus of low density, indicating a disease and the presence of pathologies in the organ.
Hyperechoic formation in the liver (synonymous with hypervascular formation) is a formation in which echo density is increased, i.e. They have a higher ability to reflect ultrasonic waves. On an ultrasound monitor, such formations are displayed as white spots. More often these are benign tumors, hemangiomas (discussed below) and also malignant tumors.
An anechoic formation is an inclusion in an organ that does not reflect ultrasound and is filled with fluid. This pathology clearly manifests itself on ultrasound and has a round shape. In 90% of cases, the term anechoic is applicable to the cyst. Thus, a liver cyst is clearly diagnosed.
Diffuse tissue changes show structural changes in organ tissue, as a result of severe lesions, dysfunction (both minor and noticeable). Diffuse changes in the liver are a multifaceted concept that is not a diagnosis, but only helps to get a complete picture of the disease and choose the right treatment.
Changes can affect the entire organ. If a part of the liver is characteristically changed, they say that these are diffuse focal changes in the liver (focal changes in tissue).
So, during diagnosis, the identification of an abnormal focus indicates a disruption in the normal functioning of the body. This is dangerous because the process of blood purification can proceed at a slow pace, which threatens the accumulation of toxins and the development of other diseases. It is also necessary to study the characteristics of the disease.
When I have been treated with sofosbuvir and daclatasvir, can I smoke cigarettes?
The concept of hypoechogenicity
Ultrasound examination is a modern and reliable method for diagnosing pathologies of the pelvic organs. An ultrasound sensor, examining organ tissue, senses high-frequency vibrations and then scans the image onto the screen. The ultrasound method is similar to echo, which is why the study is also called echography.
Women often ask what the hypoechoic formation written in the ultrasound report means. A hypoechoic formation in the ovary is a dark spot on the screen, that is, echogenicity is reduced.
Important! The hypoechoic formation appears darker on ultrasound than other tissues located nearby. This is due to the slow delivery of sound waves to areas of low echogenicity. Often these areas are cystic formations or tumors.
Not only can a cyst be hypoechoic, the doctor also sees other areas on the ovaries with reduced acoustic density. They may be:
If we are talking about a cystic formation, then the pathology is noticeable on ultrasound as a formation that has uneven thin walls, inside of which liquid exudate is noticeable. The diagnostician determines the size of the inclusion, but laparoscopy, cystoscopy or biopsy will help to more accurately determine the occurrence of the anomaly.
An uneven thin-walled formation on ultrasound is a cyst, fibroma, or malignant tumor.
Types of formations
Tumors can be benign or malignant. Vascularization is an indicator of benignity, which is why benign tumors are called hypovascular. We will look at those that are most often diagnosed by doctors.
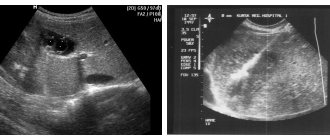
A hepatic cyst is a capsule filled with a clear liquid or a jelly-like mass (which is less common); the walls of the cyst are lined with epithelium. On ultrasound it looks like an oval formation with a dark cavity. It can be asymptomatic and located in different layers of the organ, varying in size.
Liver adenoma is benign, develops in the vessels of the liver, and is a capsule filled with cells and epithelium of the liver. Very often occurs in women as a result of long-term use of hormonal contraceptives. It has a dense structure and on ultrasound looks like a lighter formation relative to the tissues of the organ. An adenoma, under the influence of certain factors, can degenerate into a malignant tumor, so proper treatment is mandatory.
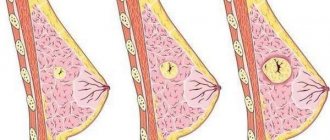
Stages of hemangioma. Click to enlarge.
Hemangioma is a benign vascular tumor. Capillary hemangioma is a vascular formation consisting of separate cavities. Cavernous hemangioma (similar to a cyst in nature) - combines into larger ones and fills with blood. It does not degenerate into malignant, and does not threaten human health if it is small in size. Otherwise, diagnosis and treatment are necessary.
Liver angioma is another type of vascular tumor. They are tumors consisting of many small lymphatic and blood vessels. Damage to liver tissue can cause serious complications. Congenital angiomas occur due to developmental defects and pathologies, can reach large sizes, and in their case, surgical intervention is necessary. Angiomas in old age can be asymptomatic and do not reach large sizes
Lipoma is a benign tumor, similar in structure to a cyst, consisting of a capsule filled with white fatty secretion. Lipoma also does not develop into a malignant tumor and is not dangerous if it is small in size. It occurs due to a violation of cellular metabolism in the organ, as a result of which fat accumulates in excess. In case of rapid growth, treatment is necessary, which consists of surgery, since lipoma cannot be treated with medication.
Cystadenomas are rare, develop, as a rule, in the right lobe, are similar to a cyst and have a multilocular cystic structure. The reasons for its occurrence are not fully understood. The mass formation causes obvious symptoms and puts pressure on the organs. On ultrasound it appears as anechoic formations with septa. Cystadenoma can only be treated surgically.
As for symptoms, benign liver tumors generally grow slowly, unlike malignant ones, and do not have pronounced symptoms. These tumors and cysts, especially in the case of small sizes, rarely lead to serious disruption of general health.
Treatment of benign neoplasms depends on the etiology of the pathology and the effect on the body. In some cases, they are limited to observation, diet, and drug treatment, while in others, surgical intervention is necessary.
Symptoms of cystic formation
If a woman has been prescribed sonography, which visualizes a hypoechoic inclusion, the symptoms may have already appeared or will not take long to appear. Symptoms depend on the size and type of cystic formation. A cyst formed on the ovary is characterized by slow growth, which is why there are often no signs of the disease, so a woman consults a doctor late, when all the unpleasant aspects of the pathology are felt.
The cyst can reach a large size, and on ultrasound you can see a thin-walled round or oval neoplasm filled with fluid.
Symptoms indicating the presence of a cyst in a woman:
- menstrual irregularities;
- feeling of soreness in the lower abdomen;
- increased pain during physical activity;
- infertility;
- bloody vaginal discharge not associated with menstruation, but smoothly transitioning into it;
- profuse menstruation with severe pain and release of clots.
Complications of the cyst:
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen;
- muscle spasms;
- defecation disorder;
- flatulence;
- accumulation of irritants in the peritoneal cavity;
- torsion of the cyst stalk - the likelihood of tissue necrosis;
- rupture of the cyst - danger of infection and abscess.
Briefly about malignant tumors
Among malignant tumors, there are primary ones, which grow from the cells and structure of the organ in which they develop, and those that are introduced by metastases of other organs (since the blood is filtered through this organ) - the so-called secondary ones. Among the primary tumors there are: liver adenocarcinoma, carcinoma (formed in the parenchyma), hepatoblastoma (in children), chylangiocarcinoma (formed in the cells of the bile ducts), angiosarcoma and others.
Risk factors for the development of these tumors are parasitic infections, cirrhosis, hepatitis forms B and C, syphilis, chronic alcoholism, and severe poisoning with chemical compounds.
By undergoing diagnosis as early as possible, it is possible to treat a malignant tumor at an early stage, since success in treatment depends on timely detection of the disease. Every six months it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound and undergo the necessary tests.
Calcifications in the liver
Among neoplasms, it is worth special mentioning the uncommon phenomenon of calcifications in the liver. This is the deposition of calcium salts in organ tissues. Calcification of the liver occurs due to severe infections. The body, as it were, “protects” the affected areas by “sealing” it with salts; this is a kind of protective reaction of the body. Calcifications vary in size.
Clinical manifestations and symptoms may not be observed and can only be identified by ultrasound results. Calcifications are dangerous because their accumulation causes the appearance of malignant carcinoma.
kistaplus.ru
What it is?
Hyperechogenicity characterizes such a part of the organ in which a bright spot is visualized during ultrasound due to the ultra-fast reflection of light waves. This is due to the fact that the tissue of such an organ has a higher density in a certain area. Such hyperechoic formations can indicate both minor deviations and dangerous pathologies. Light inclusions are more often detected in the following conditions:
- benign tumors (hemangiomas);
- cancer (primary) or metastases to the parenchyma from a tumor in another organ, for example, with damage to the ovary, prostate, large intestine;
- adenoma;
- abscess;
- hyperplasia;
- local fatty inclusion or stone;
- hemorrhagic cyst.
More often, increased echogenicity is observed in the fairer sex. The size of the formations depends directly on their type, and sometimes reaches 20 cm. There are two main types of hyperechogenicity:
- diffuse, affecting the entire liver parenchyma;
- focal or local, affecting certain areas.
Causes
Heredity, an unhealthy lifestyle, and metabolic problems provoke the appearance of a hyperechoic formation in the liver.
Medicine does not know the exact reasons for the formation of hyperechoic inclusions, but the main ones include the following:
- heredity;
- taking hormonal drugs in the female half of humanity;
- diabetes;
- excess weight;
- thyroid diseases;
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis;
- metabolic disorders;
- intoxication due to alcohol poisoning;
- uncontrolled long-term medication use.
The structure of the liver in such diseases is heterogeneous, i.e. there are tubercles of various sizes, which entails changes in the liver cells and bile ducts, connective tissues. These are quite serious changes that require urgent examination and treatment. With slight echogenicity, drastic measures are not required, but the condition of the organ must be constantly monitored.
Treatment of the anomaly
A patient who has a hypoechoic inclusion on ultrasound sonography is concerned about what the pathology is and what additional measures are needed to make a more accurate diagnosis.
Attention! Hypoechoic formations are not prone to rapid growth, but you cannot hesitate and you need to contact a gynecologist as soon as possible to prescribe treatment to avoid malignancy. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the cause that caused the development of the pathology, and then begin conservative or surgical treatment of the foreign inclusion.
If a hormonal disorder contributes to the development of a cyst, hormonal medications are prescribed. While taking medications, the tumor regresses after 3-4 cycles. As additional therapy, it is recommended to take a vitamin-mineral complex, immunomodulating drugs, and physical therapy. Treatment methods help restore the functions of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands and ovaries. The use of oxygen for therapeutic purposes normalizes the mental state and stimulates metabolic processes.
If conservative treatment does not bring results, the cystic formation progresses, surgery is prescribed to remove the anomaly - usually this happens through laparoscopy - a minimally invasive method, thanks to which recovery occurs faster.
If the parameters of the cyst are large, radical surgery is performed: the cyst is excised along with the ovary. This type of operation is performed only in extreme cases, when a woman consults a doctor at a late stage of the disease and cystic complications are noticeable or the patient no longer plans to have children.
Symptoms of hyperechoic formation in the liver
Hyperechoic inclusions with small sizes do not appear in any way, but as they grow, signs such as:
Hyperechoic formations in the liver affect the size of the organ, digestion, well-being, and the condition of the skin.
- pain in the right side of a tearing, aching or stabbing type;
- palpable increase in liver size;
- nausea, vomiting;
- heartburn, bitterness in the mouth in the morning;
- poor appetite, unexplained distortion of taste;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes;
- itchy skin;
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system.
These symptoms do not specifically indicate the presence of hyperechogenicity, as they may indicate other pathologies. But their appearance gives grounds for contacting a gastroenterologist or hepatologist. Doctors will assess the intensity and nature of the clinical picture, determine the range of necessary tests and make an accurate diagnosis, on the basis of which they will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic method that will allow you to identify such inclusions is ultrasound. This examination method will detect light areas, their number, size and location. Based on the nature of the changed area and its contours, one can suspect malignant or benign formations. But there are additional procedures that will help in making an accurate diagnosis and determining the specific cause of the appearance of a hyperechoic area:
- blood test for biochemistry (to determine markers of hepatitis or intrahepatic activity);
- CT or MRI;
- puncture biopsy;
- angiography.
Features of hypoechoic ovarian cyst
A quarter of all hypoechoic inclusions are neoplasms on the ovarian appendages, which can be retention (functional), endometrioid (“chocolate”), dermoid cyst or cystadenoma. Ultrasound is difficult to determine inclusions in the ovary, so additional diagnostics are required.
If an ultrasound examination reveals a benign tumor, complex treatment is prescribed using hormonal drugs, immunostimulating agents, vitamins - it all depends on the nature of the disease and the patient’s individual indicators. After therapy, the benign tumor resolves or becomes smaller. Malignant tumors continue to progress and are tracked in the pelvic area as extraneous hypoechoic inclusions.
Ultrasound diagnostics evaluates the appearance of the tumor and its structure. The following types of tumors differ in structure:
- Homogeneous;
- Heterogeneous;
- Contains individual hyperechoic elements.
Note! Often, bodies of a homogeneous structure turn out to be a type of malignant tumor, heterogeneous ones - a diffuse type of cancer; serous ovarian cystadenoma is suspected if a hypoechoic tumor includes hyperechoic inclusions.
To clarify the diagnosis, during an ultrasound examination, the adjacent ovarian tissues are carefully examined with distal enhancement of the echo channels, and Doppler sonography determines the level of blood flow. With the help of additional manipulations, the benign quality of the inclusion is established and it is decided whether the patient needs additional examination. Moreover, for a detailed examination, MRI, CT, laparoscopy and blood tests for tumor markers are sometimes required.
Features of treatment
Hyperechogenicity is not a disease, but a sign of an altered liver structure due to a possible pathology, to eliminate which you need to know the exact diagnosis and degree of liver damage. Liver diseases are treated in several ways: with medication, diet therapy or surgery. If the formation is no more than 5 cm, then there is no need for therapy. The condition is constantly monitored and measures are taken if the tumor grows rapidly.
Diet food
Basic principles of the diet for hyperechogenicity:
- the daily calorie intake should not exceed 2500;
- You cannot consume more than 100 g of proteins and fats, and 350 g of carbohydrates;
- food and drinks should be warm;
- exclude fatty, sour, smoked, salty foods from the diet;
- a taboo is placed on onions, garlic, chocolate, baked goods, alcohol, carbonated drinks, sour fruits and vegetables, fried meat and fish;
- It is better to give preference to boiled vegetables, lean fish and meat, cereals, rye crackers, milk, and soups with vegetable broth.
Medicines and surgeries
The essence of therapeutic therapy for increased echogenicity is to cure the cause and restore the full functioning of the affected organ. Medicines are prescribed depending on the root cause of the disease and are often used in combination:
- antispasmodics that relieve pain;
- antibiotics that stop and prevent bacterial infections and abscesses;
- diuretics to remove excess fluid during ascites;
- hepatoprotectors to normalize metabolism;
- disaggregants that improve the condition of blood vessels.
When a tumor is detected, antitumor therapy is prescribed, the choice of which is influenced by the presence of metastases and the type of tumor.
Sometimes the patient requires surgery to remove, for example, a tumor that affects neighboring organs and their full functioning. Removal is required if the formation has caused severe pain in the abdominal area and is constantly growing. But in less dangerous cases, a properly selected diet, giving up bad habits and changing your lifestyle is enough.
infopechen.ru
Methods of treating pathology
When a hypoechoic inclusion appears in the ovary, treatment is selected depending on the type of neoplasm. If luteal or follicular cysts are detected, it is recommended to monitor the condition over time. If they do not go away on their own, then hormonal therapy is prescribed. It is advisable to remove detected tumors and other types of cysts.
To treat pathology manifested by a hypoechoic formation in the ovary, laparoscopic surgery is prescribed. During this procedure, the doctor can see the tumor and remove it. If cancer is suspected, the uterus and appendages are removed and chemotherapy and radiation treatment are prescribed.
This access allows the tumor to be incised without breaking its capsule and all organs to be viewed.
Causes of hypoechoic formation
As an indicator of ultrasonography, a hypoechoic formation can have any location. The causes of hypoechoic formation are also different and completely depend on the etiology and pathogenesis of the diseases that develop in patients.
For example, a hypoechoic formation in the pancreas is considered a diagnostic criterion for identifying pathologies such as cysts, hemorrhagic pancreatitis, mucinous cystadenoma (which is prone to malignancy), adenocarcinoma of the head of the pancreas, and metastases from malignant tumors of other organs.
Hypoechoic formation in the liver and gallbladder
Healthy liver tissue is moderately hyperechoic, and hypoechoic formation in the liver can occur in cirrhotic lesions; focal steatosis; cysts (including Echinococcus multilocularis); biliary abscess; hepatocellular adenoma; focal parenchymal hyperplasia; hepatoma and small cholangiocellular adenocarcinoma.
Hypoechoic formations are also visualized in cases of diffuse metastases of pancreatic, ovarian, mammary gland, testicular, and gastrointestinal cancer spreading to the liver.
In the ultrasound diagnosis of gallbladder pathologies, the structure of its walls is of particular importance, since in the absence of damage to the organ they are visualized in the form of three layers: external and internal hyperechoic and middle hypoechoic.
Among the causes that cause hypoechoic formation in the gallbladder are polyps, adenocarcinoma (with an intact outer layer of the bladder), lymphomas (tumors of the lymph nodes), and angiosarcoma.
Hypoechoic formations of the spleen
Normally, the echogenicity of the spleen is uniform, although slightly higher than that of the liver. But due to the high vascularization, ultrasound of the spleen is performed with a contrast agent, which accumulates in the parenchyma and makes it possible (at the end of the parenchymal phase) to visualize focal lesions and hypoechoic formations of the spleen.
Such formations include:
- acute intraparenchymal hematoma due to rupture of the spleen (due to abdominal trauma);
- hemangiomas (benign vascular formations) with splenomegaly;
- splenic infarctions (infiltrative or hematological);
- spleen lymphoma;
- metastases of various origins (most often soft tissue sarcoma, osteosarcoma, kidney, breast or ovarian cancer).
As experts note, echinococcal, tapeworm and dermoid cystic formations of the spleen can have a mixed echostructure.
Hypoechoic formation in the kidney, adrenal glands and bladder
A hypoechoic formation in the kidney can be detected when inclusions in the parenchyma include cystic formations (including low-quality ones), hematomas (in the initial stages), pyogenic perinephric abscesses (at the stage of necrosis) or cavernous tuberculosis of the kidney.
According to endocrinologists, detecting a hypoechoic formation of the adrenal gland is not an easy task, and ultrasound, unfortunately, does not always cope with it. For example, verification of the diagnosis of adenoma in primary aldosteronism, as well as pathological proliferation of adrenal cortex cells in hypercortisolism (Cushing's disease) is based on symptoms. Ultrasound accurately detects a fairly large pheochromocytoma, as well as lymphoma, carcinoma and metastases. So, it is most advisable to examine the adrenal glands using CT and MRI.
With the development of benign leiomyoma, transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder or pheochromocytoma (paraganglioma) of the bladder, which is accompanied by arterial hypertension and hematuria, an ultrasound examination visualizes a hypoechoic formation in the bladder.
Hypoechoic formation in the abdominal cavity and pelvis
Pathologies localized in the abdominal cavity, in particular in the intestinal section of the gastrointestinal tract, can be easily examined by ultrasound: the diseased empty intestine has thickened hypoechoic walls, contrasting with the surrounding hyperechoic adipose tissue.
The far from complete list of reasons causing a hypoechoic formation in the abdominal cavity visualized by ultrasound includes:
- a hernia protruding into the inguinal canal;
- intra-abdominal hematomas (traumatic or associated with coagulopathies);
- serous and purulent phlegmon of the peritoneum or retroperitoneum;
- abscess of the terminal ileum with transmural ileitis (Crohn's disease);
- inflammation of the mesenteric lymph nodes (mesenteric lymph nodes);
- B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma or Burkitt's lymphoma;
- metastasis to the visceral lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity;
- carcinoma of the cecum, etc.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and uterus reveals formations with low acoustic density in women - in the presence of fibroids, adenomas, cysts or endometriosis of the uterus; functional or dermoid cysts of the appendages. A hypoechoic formation in the ovary occurs with a hemorrhagic cyst, as well as tubo-ovarian abscess (purulent inflammation in the fallopian tubes and ovaries), follicular lymphoma and carcinoma.
In men, pathologies with such a diagnostic indicator are testicular cancer, testicular lymphocele, varicocele of the cord, and during an ultrasound of the prostate in patients with a benign adenoma or cancer of this gland, a hypoechoic formation of the prostate gland is visualized.
Hyperechoic formation: causes of development and characteristic signs - Diagnosis
A hyperechoic formation in an ultrasound image indicates tissue compaction. If such a symptom is detected, the doctor prescribes an additional examination. Compaction can be a sign of a tumor, stones, or calcifications.
The concept of echogenicity
The ultrasound method is based on the use of ultrasound. It is able to pass through the tissues of the human body and be reflected from them. This property is called echogenicity. Each organ has its own echogenicity.
In the ultrasound image, the internal organs range in color from white to black. Most are gray, which indicates uniform echogenicity. Dense tissues reflect ultrasound quickly, which is why they are white in the image. Normally these are cartilage and bones. The property is called hyperechogenicity.
Soft tissues and blood vessels reflect ultrasound slowly and appear dark gray in the image. The liquid does not reflect ultrasonic waves at all and turns black.
What are hyperechoic tissue inclusions?
Hyperechoic inclusions are formations in tissues that appear white in the image. They are similar in density to cartilage or bone. A healthy person should not have such inclusions. Hyperechoic formations are:
- tumors;
- stones;
- sand;
- calcifications.
Hyperechoic structures can appear in any organ. They are clearly visible because they differ in density from the surrounding tissue. Particularly dense inclusions have an acoustic shadow, also determined by ultrasound. The shadow appears due to the sharp transition from very dense fabric to soft one. It is located on one side of the pathological formation and looks like a dark gray spot.
Reasons for education
Hyperechoic formations appear due to pathological processes:
- inflammation;
- rebirth;
- accumulation of salts;
- stone education.
One disease can have several causes.
Features depending on the organ
Hyperechoic formations appear in various organs of the human body. They are found in soft tissues or inside cavities. Formations are distinguished according to the following characteristics:
- form;
- size;
- contours;
- intensity of brightening in the image.
Based on these criteria, the specialist suggests a particular disease.
Liver
The hyperechoic neoplasm here is a tumor; more often it is malignant. Represented by a light spot of irregular shape.
Completely clear liver tissue combined with a decrease in size is a sign of cirrhosis. This is a disease in which normal liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue.
Liver cysts can be detected due to the reverberation effect. Once in the cavity, ultrasound is reflected several times from its walls and attenuates. The image shows the light walls of the cyst with a darkening in the center.
Read a detailed article about formations in the liver.
In the video you will see the hyperechoic walls of the liver portal system:
Gallbladder
Hyperechoic formations of the gallbladder are located inside it or on the wall.
- Sludge is a thick hyperechoic suspension of bile at the bottom of the bladder. Represented by a white stripe along the bottom contour.
- Polyp. Formed by cholesterol deposits, it grows from the wall of the organ. It has a wide base and elongated shape. Size up to 4 mm.
- The stone is compressed bile salts. It looks like a bright white spot at the bottom of the bubble. There is always an acoustic shadow. The shape of the stones is often round.
It is easy to distinguish sludge or stone from a polyp. The stones move when the body position changes, but the polyp remains in place.
Uterus
A hyperechoic focus in the uterine muscle is a fibroid or malignant tumor. With fibroids, an increase in the organ itself and its deformation are simultaneously observed.
A hyperechoic formation may be a uterine polyp or a menstrual blood clot. To confirm this, an ultrasound should be done 3-4 days after menstruation.
If a hyperechoic formation is detected, shaped like the letter T, this is an intrauterine contraceptive. It has clear contours and is located in the middle of the organ.
Breast
Dense neoplasms in the mammary gland occur against the background of hormonal imbalances or inflammation:
- fibrous mastopathy - rounded light formations with an acoustic shadow;
- mastitis - linear areas of clearing or nodes;
- malignant tumor is a formation with unclear contours.
To distinguish between neoplasms, mammography and puncture are performed.
Bladder
Most often, stones are found here - small light inclusions with an acoustic shadow. They have different shapes and sizes. At the initial stage of urolithiasis, sand is detected - a hyperechoic suspension.
The bladder is affected by the infectious disease schistosomiasis. Many pinpoint hyperechoic inclusions are found in its wall.
Kidneys
Hyperechoic formations are often stones. Small white inclusions located in the cups provide an acoustic shadow. They have a round or coral shape.
A kidney tumor is usually located on its surface. It is represented by a light, rounded growth. A benign tumor has an even lighter rim - the capsule.
Thyroid
The hyperechoic area is a tumor of the thyroid gland. A light, round formation with clear contours. Inside there may be even denser areas - calcifications.
Ovaries
A dense formation in the ovary with unclear contours and a dark border around it is cancer. A tumor with a capsule around it and a heterogeneous structure is a teratoma. This is a congenital ovarian cyst containing fat, hair, and teeth.
Ultrasound of the fetus
When examining pregnant women, the fetus sometimes reveals a GEF - a hyperechoic focus - in the left ventricle of the heart. Most often, it does not matter for the further development of the fetus. The GEF in the heart is an accumulation of calcium salts or an additional chord - an outgrowth of the ventricular wall.
But sometimes it is a sign of chromosomal abnormalities. If a woman has risk factors, she undergoes additional examination. A needle is inserted into the amniotic sac and a small amount of water is taken for analysis.
The same examination can be done in the placenta. The analysis identifies any genetic abnormalities.
Watch a video about fetal GEF:
Anechoic formation in the ovary, what is it, located inside the structure of the organ during pregnancy
For many patients, an anechoic formation in the ovary sounds like a terrible death sentence.
In fact, such a conclusion is not a diagnosis, but only indicates the presence in the area of the appendages of an element that does not reflect ultrasonic waves.
Most often, anechoic inclusions are the norm, however, in medical practice, formations with low echogenicity may indicate the course of a pathological process.
What is an anechoic structure in the appendages
Echogenicity is the main concept used during ultrasound examination of all organs of the body. Inclusions with low echogenicity do not reflect sound directed at them by the transducer. This indicator depends on the morphological structure of the organ being studied.
There is such a pattern: the more liquid there is in an object, the lower its echogenicity. Such bodies appear as a dark spot on the ultrasound screen. Hyperechoic inclusions, in turn, are light areas.
An anechoic formation in the ovary can be:
- yellow body
- follicular, endometrioid or serous cyst,
- fetus during pregnancy.
Many women who have received ultrasound results are interested in the question of what anechoic formations in the ovaries are. The fact is that sonologists only describe how each element of the appendage displays ultrasound.
The treating gynecologist must determine the type of formation and its nature. If such a formation turns out to be the corpus luteum, this is not a pathology, because it appears in the ovary almost every menstrual cycle. Its formation indicates that ovulation has occurred.
The peculiarity of such a body is that it contains a certain amount of fluid, so the inclusion appears dark on the ultrasound monitor. It is worth remembering that this neoplasm appears only after the egg has been released from the follicle.
Its presence when the next menstruation is delayed may indicate that conception has occurred.
Anechoic formations often turn out to be cystic bodies. An anechoic ovarian cyst is considered benign if it contains no vessels. Follicular cysts appear on ultrasound as dark spots with precise boundaries. Endometrioid ovarian cysts are distinguished by a light-colored capsule and heterogeneous contents.
Important! Dermoid cysts are echo-positive formations, so they are easy to distinguish from other types of cystic bodies. If a low echogenic mass is found in a woman before six weeks of pregnancy, it may be a fetus. We recommend you find out: Retention formation of the right ovary, what is it and Hydatid ovary, what is it
Features of anechoic neoplasms on ultrasound
Most often, an echo-negative formation in the appendage area turns out to be an ordinary cyst, which goes away on its own through several menstrual cycles. If blood vessels are found in its composition, the patient should undergo further examination to exclude a malignant tumor.
In most cases, it is possible to distinguish a benign cyst from a cancerous tumor without additional tests. The fact is that cystic bodies are avascular. This means that they have no blood supply. The type of cyst is also determined quite easily.
Thus, follicular formations are characterized not only by low ultrasound imaging, but also by ovarian tissue along the periphery. Their diameter can vary from 25 to one hundred millimeters.
Inside such a neoplasm there is anechoic content, and behind it there is an effect of amplifying the ultrasound signal.
Please note: If a pathology is detected, doctors recommend an echobiometric study over time. This allows you to avoid complications and start treatment on time.
Anechoic formations that appear after ovulation may indicate cysticity of the corpus luteum. On the echogram, such pathologies are located behind, to the side or above the uterus. Their sizes range from thirty to 65 millimeters.
There are four types of morphological structure of such a cyst:
- anechoic element with a homogeneous structure,
- homogeneous formation with low echogenicity and complete or incomplete septa of irregular shape,
- homogeneous elements of an anechoic type with mesh or smooth parietal structures, the diameter of which is 10-15 millimeters,
- formation, the structure of which has zones with medium echogenicity.
Source: https://ndc-sergiev-posad.ru/prochee/giperehogennoe-obrazovanie-prichiny-razvitiya-i-harakternye-priznaki.html