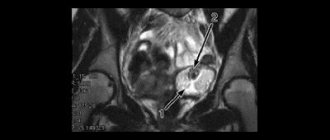
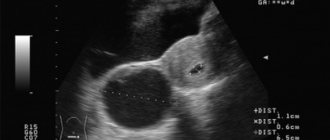
Hyperechoic inclusions in the ovary are neoplasms that have a high density and are not able to transmit ultrasound waves during examination of the pelvic organs.
Hyperechogenicity is the property of certain objects to reflect ultrasonic waves beyond measure. Such areas appear on the ultrasound monitor as light spots. If an extraneous inclusion is displayed on the screen as a dark area, then we are talking about a hypoechoic area. Hyperechoic formations have increased density. These include mature teratomas, calcifications and oncological tumors.
What is a hyperechoic formation in the ovary
A hyperechoic formation is a specific area with increased density, which is detected on ultrasound not only in the ovary, but also in the reproductive organ, liver, etc. Sound waves from such an area are displayed beyond measure, which is explained by its features. To clarify the diagnosis, various additional studies are usually carried out.
Small hyperechoic inclusions in the ovaries can be calcifications, but most often formations with increased density are tumors (benign or malignant). To avoid the development of an oncological process, the patient is recommended to undergo a dynamic ultrasound, take a blood test for the CA 125 tumor marker, and, if necessary, contact an oncologist.
Types of formations with hyperechoic inclusions
Cysts are often encountered in gynecological practice. In most cases they are functional. A luteal cyst usually has a round shape and a thick wall, with intense blood flow along the periphery of the ovary. Its dimensions range from 3 to 7 cm. Moreover, its internal filling can be completely anechoic or contain hyperechoic inclusions (blood clots). As a rule, a luteal cyst regresses spontaneously over several menstrual cycles.
Mature teratomas most often have sizes from 2 to 12 cm. They differ from each other in their internal contents. The monitor screen may show just one hyperechoic component, which is fat, or several cystic and hyperechoic areas, as well as a dense area that gives an acoustic shadow. Finely streaked inclusions or thin and long structures with increased density are most often hair located inside the dermoid. Sometimes a “comet tail” can be traced behind them.
Malignant hyperechoic inclusions
In fact, malignant ovarian tumors appear on ultrasound as large formations. Most often they are double-sided and have an irregular shape. Their capsules are distinguished by thick and lumpy walls. Such inclusions have several partitions and are often characterized by multiple papillary growths. One type of ovarian cancer is stromal cell tumors.
On the monitor they are defined as bilateral formations, the diameter of which is 5-20 cm, have an oval shape, a smooth outer shell and a dense consistency. In addition, they are characterized by a heterogeneous internal structure, in which hyperechoic areas and hypoechoic areas are determined.
Hyperechogenicity of the neoplasm is not the only possible sign of ovarian cancer on ultrasound. A doctor may suspect a malignant tumor if, according to the results of the study, it:
- has thick septa with fragmentary thickenings;
- having a round or oval shape, contains liquid inside, and has dense wall inclusions with an uneven surface;
- is large and cystic, characterized by papillary growths;
- has uneven boundaries and an unequal internal structure.
If ovarian cancer is suspected, the patient's well-being is assessed. Symptoms indicating the probable presence of cancer are:
- two-sidedness of the pathological process;
- an increase in the size of the abdomen as a result of the accumulation of fluid in it, as well as certain groups of lymph nodes;
- the presence of tumor infiltrates in the pelvis.
If the entry “hyperechoic formation in the ovary” is a dermoid cyst
A dermoid cyst is also called an ovarian teratoma. It is a special capsule that contains all kinds of tissue, sometimes even a whole head of hair or bone. Where do they come from? The fact is that in the ovarian tissue of every woman there are embryonic rudiments, and it is from them that a dermoid cyst grows for reasons still unknown to science. hyperechoic formation in the ovary increases
slowly, the woman does not even feel any discomfort. It has a round or oval-elongated shape, and its diameter ranges from 5 to 15 cm.
Sometimes a dermoid cyst is confused with an endometrioid or corpus luteum cyst. To clarify the diagnosis, MRI is used. Sometimes also short-term observation for a couple of months can exclude the formation of the corpus luteum.
Characteristic symptoms of the pathology
Most often (in 60% of cases) the anechoic formation turns out to be an ovarian cyst. Among them there are functional (these include follicular and luteal) and organic (endometrioid, dermoid).
Functional cysts
A follicular cyst forms in the follicle if ovulation does not occur. The wall stretches, the tumor can reach significant sizes, while there are no painful symptoms. Within 1-3 months, the cyst usually resolves as the cycle improves.
Luteal (corpus luteum cyst) can be detected in the 2nd half of the cycle. A sign of its appearance is the existence of an anechoic formation in the ovary immediately before menstruation. Unlike the corpus luteum of pregnancy, it is round, the diameter of the dark spot gradually increases.
In this case, the woman experiences an asymmetrical enlargement of the abdomen, and a slight nagging pain appears. The cycle becomes irregular, the functioning of the bladder and intestines is disrupted.
Addition: There is also another type of hypoechoic formations located outside the ovary. The paraovarian cyst is attached to it by a thin stalk. It is filled with liquid. Its development is not related to the processes of the cycle, but can complicate the functioning of the organ. When the leg is twisted, the cyst enlarges and severe pain occurs due to impaired blood supply and irritation of the peritoneum.
Organic cysts
These are benign tumor-like structures that do not disappear on their own within 2-3 months. Their appearance does not depend on the stage of the menstrual cycle, however, just like functional ones, they most often grow after the onset of puberty, giving various complications. In this case, inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages, cyst ruptures, and tissue necrosis occur due to twisting of the base of the cyst. If neoplasms appear on both sides, the woman faces infertility.
Endometrioid (chocolate) occurs when cells of the overgrown endometrium fall on the surface of the ovary. They begin to divide, forming a cavity filled with menstrual blood. During menstruation, the walls of the cyst bleed. Menstruation becomes more abundant and longer. Further development of such cysts leads to infertility due to the formation of scars in the tissues, as well as adhesions between the appendages and other organs. Dysfunction leads to disruption of the general hormonal levels and malfunction of the thyroid gland.
Dermoid cyst (teratoma) is a congenital pathology. The dense round capsule contains the remains of organic tissue from which the embryo is formed. There is mucus inside it. The anechoic formation can reach a diameter of 15 cm.
Video: Types of ovarian cysts, when surgery is necessary
Cystadenomas
On ultrasound they look the same as cysts.
The serous is filled with a yellowish liquid of protein origin (seeps through the internal membranes of the organs). The average size is 16-20 cm. There is no danger of malignant degeneration.
Mucinous. Its contents are thick mucus. The ultrasound image shows several cameras. The tumor can reach large sizes and can degenerate into cancer.
Papillary. Multi-chamber cavity, covered from the inside with papillae. The size of the tumor itself does not exceed 12 cm, but it often spreads to neighboring organs and degenerates into ovarian cancer (especially in women over 45 years of age).
Carcinoma (cancerous tumor)
It is an anechoic formation in the ovary, the appearance of which is indicated by the presence of a developed network of blood vessels. It does not have clear dimensions or a specific shape.
Video: Types of ovarian tumors
Symptoms of a dermoid cyst
While the dermoid cyst is small in size, it has no signs. When it increases, symptoms such as nagging pain in the lower abdomen may be observed. If you regularly visit a gynecologist, then such an echogenic formation in the ovary
is detected in the initial stages of development. The formation can also put pressure on neighboring organs, which can cause problems with the bladder (frequent urination) and intestines (constipation or diarrhea). If the cyst becomes inflamed, your body temperature may also increase.
The fact is that as the formation grows, it begins to displace healthy ovarian tissue. At first, no changes are observed, but then the tumor compresses the vessels, cutting off nutrition to the ovary. As a result, healthy tissue is replaced by scar tissue (connective tissue), which is more resistant to deficiency of nutrients and oxygen. At the same time, there may not be any changes in the body, because the second, unaffected ovary can easily cope with the load placed on it. Therefore, a dermoid cyst is often discovered when it almost completely replaces healthy ovarian tissue.
The danger of an ovarian dermoid cyst is also that it can twist, which is accompanied by sharp and severe pain in the lower abdomen. Occasionally, such a formation can become malignant.
Hypoechoic formation - as determined by ultrasound
If possible, pelvic examination in women is recommended to be performed transvaginally, since it is the most informative. An alternative method is transabdominal, where the sensor is placed on the lower abdomen.
Before a transvaginal examination, you must empty your bladder. The procedure is carried out with the woman lying on her back, with her knees bent. The doctor places a disposable ultrasound condom on the sensor, applies the gel, and then carefully inserts it into the vagina. Normally, the examination is painless and does not take more than 30 minutes.
If a transabdominal ultrasound is prescribed, then 1 hour before the examination you should drink about 1 liter of water to create an acoustic window between the uterus and the bladder. During the procedure, the doctor examines and measures the uterus and ovaries. When a neoplasm is detected, its echogenicity, structure, shape, contours are assessed, the diameter is measured and the blood flow is examined.
How is education treated?
A dermoid cyst can only be treated surgically, because its contents cannot be absorbed, as is the case with functional cysts. The sooner the formation is removed, the greater the chance of saving healthy ovarian tissue.
When choosing a surgical intervention technique, many factors are taken into account, including the size and location of the formation, the stage of neglect of the process, the presence of suppuration or inflammation in the cyst, as well as its torsion, which generally requires emergency surgery. An important criterion is also the age of the patient and the nature of the formation (malignant or benign).
If a hyperechoic formation in the ovary
discovered in a young woman, the preferred method is cystectomy or resection, which allows maximum preservation of healthy tissue. In menopausal women, the affected ovary, sometimes both, and the fallopian tubes may be removed.
Increasingly, laparoscopy and laparotomy are used to remove cysts. After any of the operations, therapeutic treatment is prescribed, which sometimes includes hormonal drugs.
If a dermoid cyst is discovered during pregnancy, treatment is also selected on an individual basis. If a pregnant woman’s tumor grows rapidly, it can be removed, but only after the 16th week. If the cyst suppurates or twists, it is removed at any stage of pregnancy. Otherwise, if no growth is observed, the cyst must be removed after the birth of the baby in order to avoid their malignancy.
What is a hypoechoic formation?
On an ultrasound monitor, a hypoechoic inclusion is visualized if there are areas with reduced echogenicity of tissues. Echogenicity is compared with the acoustic density of healthy areas. This means that the emerging tumor reflects the ultrasound signal directed at it less well.
The doctor will see darkened areas on the screen. They can be gray, dark gray or almost black. For decoding, specialists have developed a special scale that displays 6 shades of gray. Each pixel of the image obtained on the screen corresponds to a specific shade of gray; it will depend on the type of tumor and the strength of the ultrasound signal.
What a formation with low echogenicity may be
A hypoechoic formation in the ovaries, identified by ultrasound, may be:
- cyst;
- yellow body;
- follicle;
- vascular tumor (hemangioma).
If the identified neoplasm has uneven contours, it may turn out to be a fibroma or a malignant tumor. Fibromas look like dense hypoechoic homogeneous structures; anechoic inclusions are sometimes visible in them. Benign tumors (teratomas, cystadenomas) look like dense inclusions with papillary growths and rounded walls. They may have one or more cameras inside. Malignant neoplasms give a similar ultrasound picture.
If a heterogeneous echostructure is detected in the ovary, the doctor may suspect the appearance of an endometrioid cyst; it can be oval or round in shape. Its internal structure is hypoechogenic; numerous point components are visible in it - a fine suspension.
Anechoic formations during pregnancy
Most often, pregnant women are diagnosed with a corpus luteum cyst, which, after the formation of the placenta (at about 14 weeks), disappears on its own and without consequences. However, a dermoid cyst that can twist when the uterus enlarges, a cystadenoma, or a malignant neoplasm can also be detected. In such cases, surgical intervention is required. Until 18 weeks, it is performed using laparoscopy. At later stages, only laparotomy is possible. In some cases, the tumor is removed during a cesarean section.
If an endometrioid cyst is detected, then surgical treatment is postponed until after childbirth, since with the onset of pregnancy, when menstruation disappears, the cyst stops growing.
Hyperechoic formation in the ovary: what is it?
On the monitor of an ultrasound diagnostic device, hyperechoic formations appear as light or almost white spots. They can take the form of linear, point or volumetric inclusions. Light spots indicate the appearance of high-density structures through which ultrasonic waves do not pass.
What could be a formation with high echogenicity?
Hyperechoic inclusions in the ovary may be:
- malignant or benign neoplasms;
- salt deposits.
If hyperechoic areas are detected in the ovaries, the woman is recommended to constantly monitor the condition by performing ultrasound scans over time. If the hyperechoic zone increases in size, then doctors recommend consulting with an oncologist and donating blood to determine the level of the CA-125 tumor marker.
A heterogeneous structure with hyperechoic inclusions is characteristic of a dermoid cyst. In its cavity, echo zones are visualized, characteristic of the accumulation of fat, bone tissue, and hair.
During the examination, the septum on the ovary with a hyperechoic structure should alert you. This is one of the indirect signs of a malignant tumor. With oncology, the septa will be dense with visible fragmentary thickenings. They have a heterogeneous structure and uneven boundaries.
Hyperechoic formation: causes of development and characteristic signs - Diagnosis
A hyperechoic formation in an ultrasound image indicates tissue compaction. If such a symptom is detected, the doctor prescribes an additional examination. Compaction can be a sign of a tumor, stones, or calcifications.
The concept of echogenicity
The ultrasound method is based on the use of ultrasound. It is able to pass through the tissues of the human body and be reflected from them. This property is called echogenicity. Each organ has its own echogenicity.
In the ultrasound image, the internal organs range in color from white to black. Most are gray, which indicates uniform echogenicity. Dense tissues reflect ultrasound quickly, which is why they are white in the image. Normally these are cartilage and bones. The property is called hyperechogenicity.
Soft tissues and blood vessels reflect ultrasound slowly and appear dark gray in the image. The liquid does not reflect ultrasonic waves at all and turns black.
What are hyperechoic tissue inclusions?
Hyperechoic inclusions are formations in tissues that appear white in the image. They are similar in density to cartilage or bone. A healthy person should not have such inclusions. Hyperechoic formations are:
- tumors;
- stones;
- sand;
- calcifications.
Hyperechoic structures can appear in any organ. They are clearly visible because they differ in density from the surrounding tissue. Particularly dense inclusions have an acoustic shadow, also determined by ultrasound. The shadow appears due to the sharp transition from very dense fabric to soft one. It is located on one side of the pathological formation and looks like a dark gray spot.
Reasons for education
Hyperechoic formations appear due to pathological processes:
- inflammation;
- rebirth;
- accumulation of salts;
- stone education.
One disease can have several causes.
Features depending on the organ
Hyperechoic formations appear in various organs of the human body. They are found in soft tissues or inside cavities. Formations are distinguished according to the following characteristics:
- form;
- size;
- contours;
- intensity of brightening in the image.
Based on these criteria, the specialist suggests a particular disease.
Liver
The hyperechoic neoplasm here is a tumor; more often it is malignant. Represented by a light spot of irregular shape.
Completely clear liver tissue combined with a decrease in size is a sign of cirrhosis. This is a disease in which normal liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue.
Liver cysts can be detected due to the reverberation effect. Once in the cavity, ultrasound is reflected several times from its walls and attenuates. The image shows the light walls of the cyst with a darkening in the center.
Read a detailed article about formations in the liver.
In the video you will see the hyperechoic walls of the liver portal system:
Gallbladder
Hyperechoic formations of the gallbladder are located inside it or on the wall.
- Sludge is a thick hyperechoic suspension of bile at the bottom of the bladder. Represented by a white stripe along the bottom contour.
- Polyp. Formed by cholesterol deposits, it grows from the wall of the organ. It has a wide base and elongated shape. Size up to 4 mm.
- The stone is compressed bile salts. It looks like a bright white spot at the bottom of the bubble. There is always an acoustic shadow. The shape of the stones is often round.
It is easy to distinguish sludge or stone from a polyp. The stones move when the body position changes, but the polyp remains in place.
Uterus
A hyperechoic focus in the uterine muscle is a fibroid or malignant tumor. With fibroids, an increase in the organ itself and its deformation are simultaneously observed.
A hyperechoic formation may be a uterine polyp or a menstrual blood clot. To confirm this, an ultrasound should be done 3-4 days after menstruation.
If a hyperechoic formation is detected, shaped like the letter T, this is an intrauterine contraceptive. It has clear contours and is located in the middle of the organ.
Breast
Dense neoplasms in the mammary gland occur against the background of hormonal imbalances or inflammation:
- fibrous mastopathy - rounded light formations with an acoustic shadow;
- mastitis - linear areas of clearing or nodes;
- malignant tumor is a formation with unclear contours.
To distinguish between neoplasms, mammography and puncture are performed.
Bladder
Most often, stones are found here - small light inclusions with an acoustic shadow. They have different shapes and sizes. At the initial stage of urolithiasis, sand is detected - a hyperechoic suspension.
The bladder is affected by the infectious disease schistosomiasis. Many pinpoint hyperechoic inclusions are found in its wall.
Kidneys
Hyperechoic formations are often stones. Small white inclusions located in the cups provide an acoustic shadow. They have a round or coral shape.
A kidney tumor is usually located on its surface. It is represented by a light, rounded growth. A benign tumor has an even lighter rim - the capsule.
Thyroid
The hyperechoic area is a tumor of the thyroid gland. A light, round formation with clear contours. Inside there may be even denser areas - calcifications.
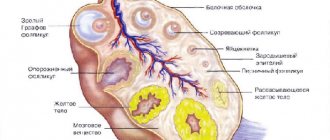
Ovaries
A dense formation in the ovary with unclear contours and a dark border around it is cancer. A tumor with a capsule around it and a heterogeneous structure is a teratoma. This is a congenital ovarian cyst containing fat, hair, and teeth.
Ultrasound of the fetus
When examining pregnant women, the fetus sometimes reveals a GEF - a hyperechoic focus - in the left ventricle of the heart. Most often, it does not matter for the further development of the fetus. The GEF in the heart is an accumulation of calcium salts or an additional chord - an outgrowth of the ventricular wall.
But sometimes it is a sign of chromosomal abnormalities. If a woman has risk factors, she undergoes additional examination. A needle is inserted into the amniotic sac and a small amount of water is taken for analysis.
The same examination can be done in the placenta. The analysis identifies any genetic abnormalities.
Watch a video about fetal GEF:
Anechoic formation in the ovary, what is it, located inside the structure of the organ during pregnancy
For many patients, an anechoic formation in the ovary sounds like a terrible death sentence.
In fact, such a conclusion is not a diagnosis, but only indicates the presence in the area of the appendages of an element that does not reflect ultrasonic waves.
Most often, anechoic inclusions are the norm, however, in medical practice, formations with low echogenicity may indicate the course of a pathological process.
What is an anechoic structure in the appendages
Echogenicity is the main concept used during ultrasound examination of all organs of the body. Inclusions with low echogenicity do not reflect sound directed at them by the transducer. This indicator depends on the morphological structure of the organ being studied.
There is such a pattern: the more liquid there is in an object, the lower its echogenicity. Such bodies appear as a dark spot on the ultrasound screen. Hyperechoic inclusions, in turn, are light areas.
An anechoic formation in the ovary can be:
- yellow body
- follicular, endometrioid or serous cyst,
- fetus during pregnancy.
Many women who have received ultrasound results are interested in the question of what anechoic formations in the ovaries are. The fact is that sonologists only describe how each element of the appendage displays ultrasound.
The treating gynecologist must determine the type of formation and its nature. If such a formation turns out to be the corpus luteum, this is not a pathology, because it appears in the ovary almost every menstrual cycle. Its formation indicates that ovulation has occurred.
The peculiarity of such a body is that it contains a certain amount of fluid, so the inclusion appears dark on the ultrasound monitor. It is worth remembering that this neoplasm appears only after the egg has been released from the follicle.
Its presence when the next menstruation is delayed may indicate that conception has occurred.
Anechoic formations often turn out to be cystic bodies. An anechoic ovarian cyst is considered benign if it contains no vessels. Follicular cysts appear on ultrasound as dark spots with precise boundaries. Endometrioid ovarian cysts are distinguished by a light-colored capsule and heterogeneous contents.
Important! Dermoid cysts are echo-positive formations, so they are easy to distinguish from other types of cystic bodies. If a low echogenic mass is found in a woman before six weeks of pregnancy, it may be a fetus. We recommend you find out: Retention formation of the right ovary, what is it and Hydatid ovary, what is it
Features of anechoic neoplasms on ultrasound
Most often, an echo-negative formation in the appendage area turns out to be an ordinary cyst, which goes away on its own through several menstrual cycles. If blood vessels are found in its composition, the patient should undergo further examination to exclude a malignant tumor.
In most cases, it is possible to distinguish a benign cyst from a cancerous tumor without additional tests. The fact is that cystic bodies are avascular. This means that they have no blood supply. The type of cyst is also determined quite easily.
Thus, follicular formations are characterized not only by low ultrasound imaging, but also by ovarian tissue along the periphery. Their diameter can vary from 25 to one hundred millimeters.
Inside such a neoplasm there is anechoic content, and behind it there is an effect of amplifying the ultrasound signal.
Please note: If a pathology is detected, doctors recommend an echobiometric study over time. This allows you to avoid complications and start treatment on time.
Anechoic formations that appear after ovulation may indicate cysticity of the corpus luteum. On the echogram, such pathologies are located behind, to the side or above the uterus. Their sizes range from thirty to 65 millimeters.
There are four types of morphological structure of such a cyst:
- anechoic element with a homogeneous structure,
- homogeneous formation with low echogenicity and complete or incomplete septa of irregular shape,
- homogeneous elements of an anechoic type with mesh or smooth parietal structures, the diameter of which is 10-15 millimeters,
- formation, the structure of which has zones with medium echogenicity.
Source: https://ndc-sergiev-posad.ru/prochee/giperehogennoe-obrazovanie-prichiny-razvitiya-i-harakternye-priznaki.html
Reasons for appearance
The causes of hyper- and hypoechoic inclusions in the ovaries are varied. When a cyst appears, a hypoechoic structure will be visible on the ultrasound monitor. The causes of cysts include:
- hormonal imbalances;
- abortions;
- early onset of menstruation;
- injuries;
- genetic predisposition.
Unfavorable working conditions, frequent stress, poor nutrition, and an unfavorable social environment can have an impact. The risk of developing cysts is higher in women who smoke compared to non-smokers.
The causes of the development of malignant ovarian tumors are not well understood. The likelihood that an identified hypoechoic area will turn out to be cancer will be higher in women who:
- refused to remove previously identified cysts and tumors;
- chronic inflammation that developed in the pelvic organs was not treated;
- took oral contraceptives uncontrollably.
Atherosclerosis, obesity, hypertension and late menopause in combination with the early onset of menstruation are among the provoking factors for the development of tumors.
Methods of treating pathology
When a hypoechoic inclusion appears in the ovary, treatment is selected depending on the type of neoplasm. If luteal or follicular cysts are detected, it is recommended to monitor the condition over time. If they do not go away on their own, then hormonal therapy is prescribed. It is advisable to remove detected tumors and other types of cysts.
To treat pathology manifested by a hypoechoic formation in the ovary, laparoscopic surgery is prescribed. During this procedure, the doctor can see the tumor and remove it. If cancer is suspected, the uterus and appendages are removed and chemotherapy and radiation treatment are prescribed.
Treatment methods
Treatment is carried out in cases where the hypoechoic formation in the ovary begins to rapidly increase in size, and the risk of complications and severe consequences increases. When choosing treatment tactics, the doctor takes into account the woman’s age, the nature of the menstrual cycle, and the type of disorders.
Waiting tactics. If there are no obvious pain or serious disturbances in the functioning of neighboring organs, then, as a rule, a wait-and-see tactic is used. Repeated ultrasounds are performed within 2-3 months. During this time, functional cysts usually disappear on their own.
Conservative therapy with hormonal drugs. Restoration of hormonal levels and elimination of ovarian dysfunction is carried out when endometrioid cysts and, in some cases, large functional cysts are detected.
Preparations containing balanced doses of progesterone and estrogens are used. Among them: oral contraceptives (Zhanin, Yarina), combined synthetic analogues of female hormones (Marvelon, Anteovin Duphaston).
Vitamins E and A are also prescribed.
Physiotherapy is used to reduce the size of cysts. Methods such as electrophoresis and magnetic resonance therapy are used.
Aspiration of cysts. The method is used only when the doctor is sure that the fluid-filled neoplasm is not a tumor. A device with a special needle is inserted into the cavity of the cyst through the vagina, with the help of which part of the contents is sucked out. In order for the cyst to be destroyed, it is filled with ethyl alcohol. The extracted fluid is sent for histological examination.
Surgical removal of anechoic formations is carried out in case of detection of tumors of various types, dermoid cysts, endometriosis that cannot be treated with hormones. Operations are performed using laparoscopy, and if the tumor is too large, then laparotomy.
Note: There are many traditional medicines that help reduce cysts and even get rid of them. The recipes use herbal preparations, pine buds, raspberry and currant leaves, as well as walnuts, honey, and flaxseed oil. However, you can start self-medication only if you are completely confident in the diagnosis.
What do hyperechoic inclusions mean?
Ultrasound examination involves viewing tissues regarding their echogenicity or ability to absorb or reflect radiation. If an area with high reflectivity is noted, then its density is higher than normal, which increases the likelihood of developing a pathological process.
On the monitor, areas with increased echogenicity are marked with light spots , which helps to detect the exact localization of a possible pathological process. Ultrasound can detect tissues with increased density, determine the size of the tumor and its contours, but to identify the predominant cellular structure, biomaterial analyzes are needed.
What can hyperechoic inclusions be?
If an ultrasound of the ovaries reveals hyperechoic inclusions, this does not mean that a serious and dangerous disease is developing, although there is still a certain probability. Among the possible pathologies that may appear on ultrasound as areas with high reflectivity, the following categories can be distinguished:
- Salt deposits or calcification.
- Benign formations.
- Oncology or malignant tumors.
Ultrasound alone is not enough for an accurate diagnosis of any disease from the above categories, but this method may be the reason for further more detailed studies.
Salt deposits or calcification
Salts can accumulate in almost any tissue, including the ovaries. The formation of deposits is provoked by various processes and not always pathological. The reasons may be previous injuries or inflammation, as well as poor nutrition and metabolic disorders. The formations are not considered life-threatening; they are often treated conservatively, and nutrition can be adjusted.
On ultrasound, calcium deposits or calcifications are sometimes visible as polyps, so it is important to conduct additional diagnostics to determine the exact structure of the problem area.
Benign lesions
Hyperechoic inclusions in the ovary may indicate cystic formations. They can be of different sizes, localization. More often it is an accumulation of connective tissue, glandular tissue, and fatty compounds, which form a kind of “pouch.” There is liquid content inside it.
A cyst can be triggered by past inflammation that has caused tissue damage. There is a possibility of formation of a formation at the site of adhesion.
It is in the ovaries that a luteal cyst can form; it is formed mainly from the corpus luteum. In most cases, it does not require treatment, as it is reduced after several menstrual cycles.
For cystic formations of significant size and constant growth dynamics, surgical intervention is prescribed. If there are direct indications for surgical intervention, then it is dangerous to neglect the doctor’s recommendations, since there is a risk of tumor growth and transformation into a malignant one.
A teratoma can form on the ovaries, which appears on ultrasound as hyperechoic inclusions. The tumor is predominantly composed of gonocytes or embryonic germ cells. It develops according to a benign type, but there is a possibility of acquiring malignancy.
Oncology or malignant tumors
If a malignant tumor is suspected, a biopsy is prescribed, as well as a number of other studies that help identify structural changes. Modern capabilities make it possible to take biomaterial without cavity incisions and practically without traces, in particular, by laparoscopy.
Ultrasound of the ovaries and the reproductive system in general is one of the most informative, allowing to identify pathological formations at the earliest stages. That is why the study is recommended not only for existing health problems, but also as a preventive measure.
{SOURCE}
Anechoic ovarian cyst: what is it and how to treat
An anechoic ovarian cyst is what sonologists – ultrasound diagnostic specialists – call a darkening visible on an ultrasound examination in the area of the organ. This is not a diagnosis or a disease. Although under this effect of a hardware examination there may be a temporary normal phenomenon of the female body, a cyst or a cancerous tumor.
The fact is that a similar picture is given by being filled with liquid, which happens every month during the cycle. But there should be no darkening before, during or after menstruation. If during this period an ultrasound showed an anechoic cyst, it means that there is a pathology in the body. Which one should be diagnosed by the attending physician.
Just as bats determine the world around them by the waves returning from objects, so the ultrasound of diagnostic equipment creates a picture of organs based on the reflection of the signal. The fact is that the liquid located inside the cavities, tissues with a large water content, absorbs ultrasound waves.
As a result, this place will be dark on the monitor. The denser the fabrics, the lighter they are. Therefore, bones appear brightest and are hyperechoic. The same applies to hollow organs, mainly filled with air and gases.
Hence the name echogenic - reflective, anechoic - the opposite meaning.
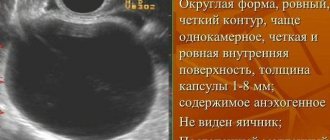
Interesting fact! A cyst is a formation with walls and contents, round or oval in shape, and can be single or multi-chambered. From here we get that any cysts with fluid inside are anechoic. Not every one is filled with fluid and appears as a dark spot on the monitor, just as not everything that is anechoic is a cyst.
During ultrasound diagnostics, similar formations are found in the mammary glands, kidneys, thyroid gland and other organs.
Cyclic changes and echogenicity
During the period close to ovulation and some time after, the ovary on ultrasound may look like a dark spot for the following reasons:
- Follicle maturation is the normal state of the ovary during the period of ovulation. As the egg forms, the follicle in which it exists grows. By the end it reaches 2-2.5 centimeters in diameter. Next, the egg is released.
- The formation of the corpus luteum is a subsequent stage in the normal process of the reproductive system. After the egg has left the follicle, the so-called corpus luteum is formed in its cavity. It produces the hormone progesterone, which promotes pregnancy. Gradually, the temporary gland decreases and by the beginning of the next menstruation it stops working.
Now let's look at diseases in which a dark spot in the ovary area is a symptom:
- Follicular cyst. A formation that appears due to the accumulation of fluid inside the follicle. They are thin-walled and have a round shape.
- Paraovarian - formation on the surface of the ovary. It grows from the epididymis and is located closer to the area where the fallopian tube attaches.
- Dermoid cyst. A congenital pathology, which is characterized by the presence of a “pocket” in different places of the body where the rudiments of teeth, skin, and hair are located.
- Luteal. When the corpus luteum forms, a larger than usual amount of fluid is collected. Sometimes it may not resolve with the onset of menstruation.
- Serous cyst. A bubble in the upper layer of the organ.
- Endometrioma is a formation of endometrium containing blood. Location inside or near the ovary. Their interesting feature is that during menstruation, they also release blood. Such cysts are a consequence of the spread of endometriosis pathology.
It is not a cyst, but it is similar in general parameters to a cystoma; it is also anechoic. This is a benign formation of the type of multi-chamber, heterogeneous accumulation of tissue, which can be filled with fluid. Predisposed to rapid cell growth and division. The following types are noted:
- Mucinous cystoma. Formed from glandular tissue. Numerous cavities are filled with viscous semi-liquid mucin;
- Cystadenoma. Formation from papillary epithelium. Reminds me of papillomas. They grow quickly, causing various consequences.
There are many types of cysts, even ovarian cancer, which is found in 20% of women, can be anechoic. With the onset of menopause, the risk of cancer increases.
Some of the above formations are hypoechoic, wave absorption is incomplete, and there is some reflection. The areas in the picture are dark, but not black.
Interesting fact! There is such a thing as an avascular cyst - a formation that does not have blood flow. For example, cancerous tumors always have blood circulation.
Clinical picture of an ovarian cyst
At first there are no symptoms, but as the size increases, the formation begins to manifest itself:
- Pulling, pressing in the lower abdomen;
- Pain on the right or left side;
- Feeling of full bowels;
- Discomfort when emptying the bladder, false urges;
- If sharp pain occurs in the form of contractions, nausea and vomiting appear, and the body temperature rises - these are signs of torsion or rupture of the cyst, urgent medical attention is needed.
Diagnosis of pathology consists of a gynecological examination, medical history and ultrasound examination. Additional tests may include testing hormone levels, as well as identifying tumor markers.
For different types of cysts, a different approach is required in each case:
- Observation is applied to formations that can resolve over time. These are luteal and follicular cysts.
- Drug therapy with hormonal drugs is effective for hormone-dependent formations.
- Aspiration - liquid is pumped out through a puncture and ethanol is injected into the cavity, which promotes gluing of the walls.
- Surgery. Dangerous formations, cancerous tumors, dermoid cysts that cannot resolve, endometrioma are removed along with the affected ovary. In the case of oncology, the appendage and fallopian tube are sometimes removed.
Surgeries to get rid of cysts are performed laparoscopically even during pregnancy.
If an anechoic cyst is diagnosed on ultrasound, you should not immediately worry. First of all, you need to compare the date of diagnosis with the period of your cycle.
The gynecologist will prescribe additional research at a time when there should not be dark spots for natural reasons. If this time the formation remains, you will have to prepare for long-term treatment, possibly surgery.
Leaving a cyst unattended is dangerous; its rupture can lead to peritonitis and death.
Diagnosis of an anechoic ovarian cyst and whether it needs to be treated Link to main publication
Source: https://StopKista.ru/yaichnik/anehogennaya.html