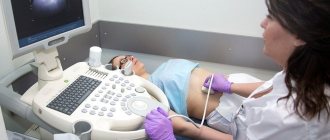
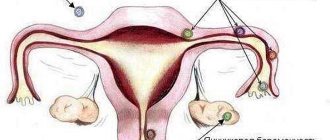
A benign tumor of the corpus luteum - luteal tumor - is understood as an anomaly that develops during the period of reproductive functioning of the female body. Cases when a corpus luteum cyst is diagnosed during pregnancy are quite common. This type of tumor is most often discovered accidentally during the first ultrasound examination of the fetus.
Why does a corpus luteum cyst occur in early pregnancy?
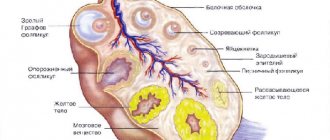
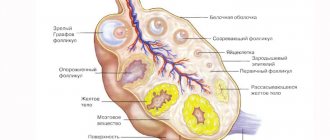
After ovulation, the egg is released from the follicle, and its granulosa cells begin to actively grow, causing the appearance of the corpus luteum. It is responsible for the production of progesterone from the period of ovulation until the time when the placenta forms in the pregnant woman.
It also happens that the corpus luteum appears already at the beginning of pregnancy. It is a cavity containing a yellow-red liquid inside. Doctors believe that the appearance of ovarian cysts can be provoked by the following factors:
- Following strict diets or, conversely, eating too much food.
- Constantly being in stressful situations and fear.
- A sharp change in climatic conditions.
- Overweight or underweight.
- Abuse of harmful substances (alcohol, cigarettes, drugs).
Often, eliminating from your life the factor that provokes the appearance of an ovarian cyst in a pregnant woman contributes to its self-resorption.
There is a list of more serious reasons that can affect the appearance of a cyst in a pregnant woman:
Gynecological:
- ovulation was artificially stimulated;
- the woman has previously had an abortion;
- IUD was installed for contraception purposes;
- the birth took place naturally or was performed by caesarean section;
- The woman was taking emergency contraception.
- Diseases of other organs, often responsible for hormones.
- The treatment of the disease associated with the female reproductive system was not fully carried out.
- Working conditions at the workplace were harmful.
- Hormonal imbalance in the body that occurs with the onset of pregnancy.
- Sex life:
- was started at an early age;
- occurred on the days of menstruation;
- been with many partners;
- was absent for a long time.
There is also a theory that the formation of cysts has a hereditary predisposition, and the onset of hormonal changes in the body when a woman is expecting the birth of a child directly contributes to this.
What is the corpus luteum?
This formation is so called because of the yellowish color of the substance it contains - lutein. This temporary gland acts as the guardian of pregnancy in the early stages, until the placenta is fully formed and can function independently. This is approximately 10 - 12 weeks from conception. Then the gland slowly dissolves.
The formation of the corpus luteum inside the follicle occurs not only during pregnancy. This happens once per cycle in the second half. In the next, something new is formed. When pregnancy does not occur, it atrophies. It also happens that VT persists from the previous cycle, this phenomenon is called persistence. The pathological process is explained by the fact that the hormone progesterone continues to be produced, lengthening the second phase of the cycle. And new, dominant follicles are not formed.
The table below shows the stages of development of the corpus luteum:
Also, many people wonder whether a corpus luteum cyst can cause delayed menstruation? The answer to this question is yes.
When a corpus luteum cyst appears, the released gestagen hormones can cause a delay in menstruation.
Signs and symptoms of corpus luteum cyst growth during pregnancy
Often, the presence of an ovarian cyst does not manifest itself in any way, so the pregnant woman learns about it from the doctor only after an ultrasound examination. Characteristic signs and symptoms indicating its growth at the beginning of pregnancy are:
- Pain in the lower abdomen (pulling, tingling in nature).
- Excessive fatigue.
- Increased body temperature.
- Lack of desire for intimacy.
- Disturbance of adequate sleep.
- Urge to vomit.
- Bleeding that started in the uterus.
- The presence of characteristic discharge from the external genitalia.
Important!
If a woman experiences similar symptoms, it is very dangerous to delay a visit to the doctor! This will help avoid cyst rupture and maintain pregnancy.
Prognosis and prevention
Usually, if there are tumors in the ovaries, pregnancy is possible.
If regression or planned tumor removal has occurred, the prognosis for the patient is favorable. To prevent complications, it is necessary to regularly visit the gynecologist's office and have an ultrasound scan. It is better to prevent pathology than to treat it later. To prevent the disease, it is recommended to follow these tips:
- You should not take hormonal medications or oral contraceptives on your own.
- It is necessary to treat inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system in a timely manner,
- It is advisable to lead an active lifestyle, give up bad habits, get adequate rest and nutrition,
- Avoid abortions, being in places with high harmful conditions, and regularly lifting heavy objects.
Simple recommendations will help prevent many women's problems.
How can an ovarian cyst during pregnancy be dangerous for the health of the woman and the unborn child?
Having an ovarian cyst in the early stages of pregnancy is not considered normal. If it exceeds the permissible dimensions (7 cm for a singleton pregnancy and 9 cm for a multifetal pregnancy), the following complications may appear:
- rupture of the membrane of a cystic neoplasm and entry of its contents into the peritoneum;
- necrosis (if torsion of the cyst-like formation occurs);
- internal hemorrhage will begin in the ovary.
All this provokes migraines, dizziness, fatigue and nausea in the pregnant woman. Immediate surgical intervention will be required to prevent inflammatory processes in the peritoneum, peritonitis, sepsis, and also to avoid death for both the fetus and the expectant mother.
Causes
Doctors do not name the exact reasons for the development of a cyst of the corpus luteum of the right ovary or the left one during pregnancy. However, it is known that in this case the walls of the follicle are filled with liquid instead of glandular tissue. Predisposing factors include:
- Inflammatory processes of the appendages or uterus;
- Fertility drugs that affect the ovaries;
- Circulatory disorders;
- Failures of the hormonal system;
- Abortion;
- Experienced stress, tense emotional state;
- Poor nutrition;
- The use of emergency contraceptives with a shock dosage of hormones;
- Harmful working conditions.
What to do if a corpus luteum cyst hurts in early pregnancy?
At the beginning of pregnancy, the presence of a cyst is practically not noticeable. If the expectant mother experiences pain, she should immediately go to her doctor for examination. This may be a signal that the cyst has ruptured or its stem has become torsioned, which is an indication for surgery.
Pregnancy with corpus luteum cyst
Pathology can occur both simultaneously with conception and after 16-20 weeks of gestation in the absence of regression of the corpus luteum. In any case, such a patient requires additional examination and more careful monitoring. Treatment may not be prescribed in the following cases:
- slow growth of education or lack of its increase;
- good health of the pregnant woman;
- cyst diameter no more than 5 cm;
- normal hormonal levels.
A woman needs to carefully monitor her condition and avoid situations that could lead to a rupture of the pathology. To prevent its growth, visiting baths, saunas, and taking hot baths is prohibited. Pain from a corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy can be relieved by taking antispasmodic drugs or products containing magnesium.
Indications for surgery:
- active cyst growth;
- diameter more than 8 cm;
- the risk of infection or malignancy;
- likelihood of leg torsion or apoplexy.
In the absence of acute conditions, the intervention is performed after the first trimester using laparoscopy. After surgery, therapy is prescribed to support the viability and development of the fetus.
During a cesarean section, a woman in labor may ask to have the cyst removed to avoid subsequent surgery.
Treatment
Most cases of existing ovarian cysts at the beginning of pregnancy do not require therapy. It dissolves on its own by the 12th to 20th week of pregnancy, when the placenta takes over the production of progesterone, or after delivery.
A yellow cyst, in general, does not pose a danger to the fetus and the expectant mother, but specialists should observe its tendency to grow using ultrasound. If the cyst is large in diameter, then the pregnant woman is prescribed a test that can detect the level of progesterone in the blood. If it is not enough, then treatment is carried out using progesterone-containing drugs (“Utrozhestan” or “Duphaston”). Usually they are drunk until the moment when the placenta is fully formed and it begins to independently produce progesterone. This happens by the 20th week maximum.
When the cyst grows so large that it may pose a threat, specialists may decide to operate on it surgically. This helps reduce the risk of complications in the future. Surgery is also performed if the cyst has ruptured or its stem is twisted. The operation is called laparoscopy. It is permitted during pregnancy and is performed under general anesthesia. Complications after the procedure are very unlikely, and the patient will be able to go home the very next day.
To make sure that the baby is not in danger, after laparoscopy the pregnant woman is recommended to undergo a course of hormonal therapy that can help keep the fetus viable.
The main task of the luteal body
The normal monthly cycle has two phases - luteal and follicular, when changes occur in the endometrium of the uterus and ovaries that provide the necessary conditions for preparing the egg for fertilization and pregnancy.
The first day of your period is considered the beginning of the menstrual cycle and, accordingly, the follicular phase, which lasts approximately 2 weeks. During this time, the next dominant egg and follicle mature, and the glandular cells of the mucous membrane increase in the uterus. By the time the egg matures, the pituitary gland releases the greatest amount of luteinizing hormone into the blood, as a result of which ovulation occurs, more precisely, the rupture of the Graafian vesicle with the subsequent release of the egg. This ends the first phase of the monthly cycle and the second begins.
In the luteal phase, the pituitary gland secretes follicle-stimulating hormone minimally, the follicle begins to reduce, and from its granulosa cells, under the influence of luteinizing hormone, a corpus luteum is formed, which reaches a size of 2-3 cm and is an endocrine temporary gland.
It produces progesterone and a small amount of estrogens, which prevent the formation and release of another new egg, reduce the contractile activity of the uterus and its tone, increase the production of endometrial glands, preparing it for the preservation and implantation of a fertilized egg.
This time also lasts approximately 2 weeks. During pregnancy, the corpus luteum continues to function for about another 3-4 months, otherwise menstruation begins, and by the end of the luteal phase it undergoes reverse development and begins to sprout connective tissue fibers with the appearance of a scar.
How to behave if you have a corpus luteum cyst in early pregnancy?
If, while waiting for the birth of your baby, an ovarian cyst is diagnosed, you must:
- Try to limit yourself to physical exercises (even those allowed for pregnant women);
- Ensure sexual rest.
Important!
If you experience abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and other symptoms characteristic of a cyst rupture, you should immediately call emergency medical help. Not only the life and health of the unborn child, but also the pregnant woman herself may be at risk!
Ovarian apoplexy
The term “ovarian apoplexy” means a sudden hemorrhage, accompanied by rupture of ovarian tissue and intra-abdominal bleeding. Due to the fact that in the phase of ovulation, the formation and flowering of the corpus luteum, the blood supply to the gland is extremely intense, hemorrhage usually occurs during this period.
There is a fairly large list of causes of hemorrhage, including:
- congestion in the pelvic organs;
- inflammatory diseases of the female reproductive organs, leading to impaired blood supply;
- varicose veins located on the ovaries;
- intense physical activity accompanied by heavy lifting;
- decreased blood clotting rate;
- blunt abdominal trauma.
As a rule, the site of bleeding is the corpus luteum or corpus luteum cyst. When diagnosing ovarian rupture, the first-line diagnostic method is ultrasound. The assessment of the echographic picture depends on what day of the menstrual cycle the study is performed, in comparison with the visually assessed condition of the other ovary.
As a rule, with hemorrhage, no abnormalities in the size of the affected ovary are detected. The size of the corpus luteum is within normal limits and does not exceed the diameter of the follicle in the preovulatory phase. Depending on the intensity and duration of bleeding, a certain amount of free fluid (blood) is detected in the abdominal cavity.
If there is a luteal cyst on the ovary, then the doctor will not see any changes in its shape and volume during ultrasound. To obtain more detailed information, it is necessary to perform a loparoscopy, during which the doctor not only sees the affected ovary, but can also repair ruptures in the luteal gland or, in extreme cases, in case of severe bleeding, remove the entire ovary.
Treatment of ovarian apoplexy provides for the possibility of recovery without the use of surgery (applying a cold compress to the ovarian area, using antispasmodics, ascorbic acid to increase blood clotting). However, such tactics do not allow for full restoration of the body due to the impossibility of removing blood from the retroperitoneal space and suturing ruptured glands, which subsequently causes the development of adhesions, repeated rupture of the corpus luteum and the inability to get pregnant.
Important! In addition to monitoring folliculogenesis, the capabilities of diagnostic and therapeutic ultrasound include dynamic monitoring of the state of the luteal cyst, its behavior in response to the use of drug therapy, as well as performing the imaging function when collecting follicles for IVF. Hormonal stimulation of ovulation before IVF leads to the formation of several follicles, and, accordingly, several corpus luteum
Hormonal stimulation of ovulation before IVF leads to the formation of several follicles, and, accordingly, several corpus luteum
Today, ultrasound in gynecology has expanded its diagnostic capabilities so significantly that it has become part of the standard algorithm performed in hospitals and clinics. Increasing the frequency of resolution and improving the quality of the resulting ultrasound images makes it possible to visualize extremely small formations in organs, including polycystic ovary syndrome in the early stages of development.
The loss of clarity of the outlines of the follicle with the premature development of echogenic formations in its cavity and in the absence of ovulation makes it possible to confidently diagnose the luteinization of a non-ovulated follicle, that is, the development of the corpus luteum before ovulation. Timely diagnosis allows not only to identify the cause of infertility, but also to carry out a number of therapeutic measures aimed at restoring reproductive function and preventing the development of the disease.
Sources:
What if a corpus luteum cyst bursts in early pregnancy?
The worst thing that can happen to an ovarian cyst is its rupture. In this case, the woman will feel pain and cramps from the lower abdomen, which gradually become more and more unbearable. The result will be hemorrhage into the ovary and peritoneum, as well as a high risk of peritonitis. The pregnant woman becomes pale and loses blood, which meanwhile enters the peritoneum. As a result, vomiting begins, and the woman may even lose consciousness. Her pulse becomes faster, and her blood pressure, on the contrary, goes down. Medical assistance not provided in a timely manner can cost the life and health of the expectant mother and child.
The cyst is removed surgically under general anesthesia. If the operation is started in a timely manner, then it will not pose a threat to the fetus and the pregnant woman, however, after a rupture, the process of pregnancy development will have to be constantly monitored. This will help you react in time if any threat appears.
Symptoms and diagnosis
A corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy is often not accompanied by any symptoms. In some cases the following are noted:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- spotting;
- pain during sexual intercourse and physical activity.
In general, we can say that the symptoms of ovarian corpus luteum cysts are similar to those of ectopic pregnancy and other types of cysts.
A corpus luteum cyst can form in either the right ovary or the left ovary, depending on where ovulation occurs.
This phenomenon is diagnosed using ultrasound examination. A doctor may suspect the presence of a tumor formation during a routine gynecological examination, when the size of the cystic formation is noticeable upon palpation. Normally, VT is 6–8 cm in size and has a round shape.
A cyst can be difficult to distinguish from other neoplasms or an ectopic pregnancy. Therefore, they often resort to laparoscopy. This method is more informative and is used if there are suspicions of serious complications associated with the growth of the cyst, its size and filling of the cavity with fluid.
What are the dangers of having a corpus luteum cyst during pregnancy?
- During pregnancy, a corpus luteum cyst (especially if it is large) often puts pressure on the appendages and uterus, and the woman may experience severe pain radiating to the lower back.
- If the size of the formation is too large, the membrane may rupture and liquid contents may spill into the abdominal cavity.
- When the pedicle of the cyst is torsed, necrosis of the organ tissue occurs.
- Internal hemorrhage into the ovary may occur.
The woman feels severe pain, dizziness, nausea, and possibly vomiting. This threatens with serious consequences: sepsis, inflammation of the abdominal cavity and peritonitis. Up to and including death.
Effect on pregnancy test result
A neoplasm up to 7 cm in size is capable of producing hormones necessary for the progression of conception. Therefore, it is difficult to say whether a corpus luteum cyst can influence the results of a pregnancy test, giving a positive result, because it causes increased production of the hormone progesterone, and not human chorionic gonadotropin.
The test responds to inflammatory processes in the ovaries, especially the development of malignant tumors. A luteal neoplasm is not one of these, but if it is abnormally large in size, it can cause a second weak line, which will be a false positive result.
The “yellow” ovarian formation is not prone to malignancy (malignancy), which means there is no risk of degeneration into cancer, as a result of which the disease has a positive prognosis. But to avoid various complications, you need to visit a gynecologist at least twice a year and systematically undergo an ultrasound examination.
ETIOLOGY (CAUSES) OF APOPLEXIA
*Among the etiological factors leading to this pathology are the following: neuroendocrine disorders; inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs, which cause sclerotic changes in the ovaries; stagnant processes in the pelvis; varicose veins of the ovaries and physical activity in the middle of the menstrual cycle or a week before menstruation; abnormalities in the position of the genital organs; pelvic tumors; disorders of the blood coagulation system; abdominal injuries; vaginal examinations; violent sexual intercourse. During the menstrual cycle, conditions favorable for the occurrence of apoplexy are formed: ovulation, abundant vascularization of the tissues of the corpus luteum, premenstrual hyperemia of the ovary. They can lead to the formation of a hematoma, which, when ruptured, causes bleeding into the abdominal cavity. The volume of blood loss can be from 50 ml to 2-3 liters. Apoplexy of the right ovary occurs more often, which is associated with better blood supply and a larger number of venous vessels compared to the left ovary./
Ovarian apoplexy can be caused by exogenous and endogenous causes. Endogenous causes include: incorrect position of the uterus, compression of blood vessels, leading to disruption of the blood supply to the ovary, compression of the ovary by a tumor, adhesions and inflammatory processes in the pelvis.
Exogenous causes include violent sexual intercourse, horse riding, abdominal trauma, vaginal examination, surgery, and enema. However, in some patients, ovarian rupture may occur at rest or during sleep.
The risk of ovarian bleeding increases in patients taking anticoagulants for a long time.
Therefore, in patients admitted with acute abdominal pain while taking anticoagulants, ovarian apoplexy must be excluded.
Treatment methods
The therapy is complex, using radical and conservative methods. You need to understand that complete recovery will not be achieved.
Supervision has a supportive meaning, aimed at stabilizing the condition, optimizing vital functions and prolonging biological existence.
Drugs are used to eliminate symptoms, as well as etiotropic effects (on the root cause):
- Antihypertensive drugs. ACE inhibitors, calcium antagonists, beta blockers. Used to normalize blood pressure and maintain vascular tone. Classic combinations are Diltiazem or Verapamil, Perineva, its analogues, also Moxonidine, Physiotens.
- Cardioprotectors. Supports the functional activity of the heart and prevents further destruction.
- Antiarrhythmics like Amiodarone. Against the background of changes in the frequency of contractions of the muscle organ.
- Potassium and magnesium complexes. Normalize metabolic processes.
As part of the treatment of other conditions, antibiotics (for myocarditis and infectious and inflammatory pathologies) and corticosteroids are prescribed.
It is better to select drugs in a hospital for quick correction and monitoring of side effects.
Surgery is required only for associated complications. There is no point in treating cardiosclerosis surgically.
A big role in therapy is given to lifestyle changes. At any stage.
- Quitting smoking and alcohol are also strictly contraindicated.
- Normal physical activity (at least an hour of exercise therapy, walking or other minor exercise).
- Full sleep. 8 hours per night. Moreover, a quarter or more of the rest should occur before 23.00, this is the best time.
- Water regime - 2 liters per day, but no more, so as not to overload the body.
- Salt - no more than 7 grams. There should not be a complete exclusion of the sodium compound. It plays a key role in ensuring metabolism.
Diet correction. There are no strict dietary restrictions; you need to minimize the amount of fatty foods, fried, smoked foods, and completely abandon semi-finished and canned foods, because it is impossible to control the amount of salt in them.
Attention:
Therapeutic methods do not lead to a complete cure, but provide a good chance of maintaining vital functions at an acceptable level.