How to detect polyps: symptoms
The content of the article
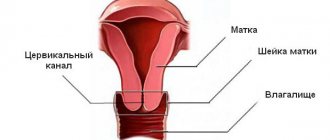
Polyps are benign formations on the mucous membrane. They have a drop-shaped or irregular shape. They usually form on the mucous walls of hollow organs and, after growth, hang into the lumen.
Polyps can be attached to a broad base, but more often they have a long, thin stalk that lengthens as the polyp grows. The length of the neoplasm can reach tens of centimeters.
In most cases, there are no symptoms of pathology; mucosal growth is detected during a gynecological examination. It happens that a polyp blocks the cervical canal. In this case, disturbances occur with the monthly cycle, and there may be pain after intimate relationships.
Polyposis can be diagnosed using uterine ultrasound and hysteroscopy. Thanks to these methods, the doctor can clearly assess the size, condition, and location of the polyps.
Diagnosis of diseases with a hysteroscope
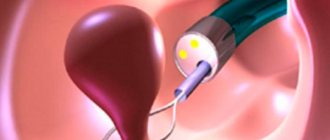
Hysteroscopic diagnosis determines the presence of pathological changes in the uterine cavity. Using a diagnostic hysteroscope, the disease itself and the stage of its development are determined. If abnormal formations are detected, a small piece of tissue is removed for subsequent laboratory analysis (biopsy). This manipulation is carried out in order to identify the oncological or benign nature of the tumor that has arisen.
Diagnostic, otherwise office hysteroscopy does not require hospitalization of the patient, and is performed under local anesthesia and does not injure the mucous membrane. During a biopsy, mechanical intervention is minimal and does not cause serious damage. The time interval for the procedure varies from 10 minutes to half an hour.
The office diagnostic procedure is done to confirm the diseases suspected by the gynecologist:
- an increase in the number of cells in the inner layer of the uterine wall (endometriosis);
- benign hormone-dependent tumor (fibroids);
- cancerous tumors;
- pathological growth that arose due to incomplete release from the fetal membrane in the postpartum period (placental polyp);
- inflammatory process in the surface layer of the endometrium (endometritis);
- focal benign growth of the uterine mucosa (endometrial polyp) or the lining of the cervical canal (cervical polyp);
- adhesions in the uterine cavity (intrauterine synechiae);
- foreign objects in the organ;
- the formation of a through hole in the wall of the uterus (perforation) due to mechanical damage;
- benign proliferation of endometrial glandular cells (hyperplasia).
The doctor determines the presence of indications for diagnostics after a gynecological examination.
In addition, the doctor prescribes an endoscopic examination of the uterine cavity according to the complaints that the woman makes. These include: irregular periods, abnormal vaginal discharge, pain associated with a recent medical or vacuum abortion, and systematic miscarriages.
Removal of cervical polyp: preparation for surgery
Preparation for surgery is a mandatory step in removing a cervical polyp. It includes the following steps.
- Passing a gynecological examination, taking smears for infectious diseases.
- Treatment of detected diseases, allowing to exclude postoperative infection.
- Having a colposcopy is a procedure in which the cervix is examined under a microscope.
- Submission of a cytological smear.
- General blood analysis.
The gynecologist provides the patient with an exact list of tests that must be taken before removing cervical canal polyps. A few days before surgery, you should not have sex, use vaginal pills, or suppositories.
Unforeseen complications
In most cases, hysteroscopy is well tolerated by women. Possible negative consequences may manifest themselves as follows:
- prolonged bleeding;
- inflammation of the endometrium;
- incessant pain.
Uterine bleeding is one of the severe complications of manipulation
Such symptoms indicate complications that arose during the operation or its poor quality (the formation was not completely removed, the walls of the uterus were damaged, or an infection occurred). In this case, hospitalization is necessary, most often with emergency surgery. Feedback from patients about the procedure was mostly positive. Negative emotions, for the most part, are caused not by the hysteroscopy itself, but by the discomfort after the operation.
How to remove a polyp of the cervical canal - traditional methods
How is a cervical canal polyp removed? One possible method is curettage. The procedure is prescribed after the end of menstruation, one day before the start.
Anesthesia is used before the operation - one of the reasons why the technique is not suitable for many women. The cervix is exposed, the formation is removed with a special clamp, and the movements are unscrewing. This is followed by cutting out the pedicle of the formation and scraping the canal with a curette. Hysteroscopy is a less traumatic method of removing a cervical polyp, which is most widespread. The formation is removed using a hysteroscope - a device that allows you to keep the process under control (observation on a monitor).
Liquid nitrogen is used to cauterize the area of tissue where the polyp was located.
Excision of the polyp stalk may be necessary if the growth of the membrane is located next to the external os of the canal. The procedure ends with curettage of the canal mucosa if the doctor suspects that the formation is malignant. In this case, anesthesia is used. Hysteroscopy takes only a few minutes, eliminates relapse in 99% of cases, and does not imply subsequent bed rest. Damage to the mucous membrane is minimal.
Carrying out endoscopic surgery
The operation is performed under general anesthesia (intravenous or mask). The anesthesiologist selects the correct anesthesia depending on the individual characteristics of the patient (presence of allergies, physical condition), and the time planned for the procedure. The operation usually lasts between 40 and 60 minutes, during which the woman's heart activity and breathing are monitored by the anesthesiologist.
The presence of hypersensitivity to anesthesia drugs is discussed in advance with the anesthesiologist.
After putting the patient into a state of medicated sleep, the gynecologist treats the genitals with an antiseptic and begins the first stage of the operation - expansion of the uterine cavity. The doctor, at his own discretion, uses one of the methods to enlarge the organ:
- gas, using a hysteroflator - a medical device that supplies carbon dioxide into the uterine cavity;
- liquid, using solutions: Ringer's, glucose, glycine or saline.
The next surgical phase is the introduction of a hysteroscope, surgical instruments and a detailed examination of the uterus, inside the cervical cervical canal. Using medical forceps, foreign objects are removed. In the case of hysteroscopy of an endometrial polyp or other area of the reproductive organs, the doctor advances the hysteroscope to the desired area. Once the abnormal growth is identified, it is clamped and resected.
The final step is to remove the instruments from the uterine cavity. The cervix closes independently, without additional manipulation.
Removal of a polyp of the cervical canal - modern techniques
How are polyps on the cervix removed for nulliparous girls planning a pregnancy in the future? Gentle techniques are used - laser and radio wave removal, cryodestruction.
- A laser as a tool for removing polyps of the cervical canal is ideal. The choice of this technique eliminates the formation of scars and ensures the fastest possible healing. With the help of a laser, not only the growth of the membrane is eliminated. The vessels are also cauterized, which avoids bleeding. The possibility of recurrence of the polyp is practically excluded, damage to the mucous membrane is minimal.
- A radio wave knife is another modern tool that is used to remove polyps of the cervical canal; reviews prove that it is minimally traumatic. Fast healing, absence of scars - radio waves are considered the safest way to get rid of formations on the cervix.
- Cryodestruction is a procedure that involves the removal of a benign tumor using liquid nitrogen. The substance is brought to a minimum temperature, then the effect is applied to the area where the polyp is located. Contact with nitrogen leads to the death of formation cells. As a result, the polyp is detached, and the bed is cauterized to prevent bleeding. The duration of healing is determined by the diameter of the polyp stalk; it may take several months.
A gynecologist will tell you how to remove polyps on the cervix in a particular case.
Reviews
Veronica: Today I am preparing for the in vitro fertilization procedure. That's how life happened. To fully collect information, I was sent to an office hysteroscopy with a biopsy. The preparation took five days. I passed numerous tests, had an ultrasound and an ECG (it is mandatory after 35 years). Taking into account my wishes, the diagnosis was carried out under anesthesia. She fell asleep and woke up already in the room. Two hours later, the gynecologist described the results to me in detail and prescribed a course of antibacterial therapy. Side effects include bloody discharge, which bothered me for about four days, and dizziness from the anesthesia. Otherwise I felt good. I believe that this diagnostic procedure is the most informative and will not be superfluous for any woman, even if nothing bothers her.
Maria: Based on the results of the ultrasound, the gynecologist suspected I had endometrial polyps and prescribed a hyteroscopy for diagnostic and treatment purposes. In one procedure, my uterine cavity was examined, the presence of a polyp was diagnosed, and it was successfully eliminated. The operation was performed under general anesthesia, and I spent just over a day in the hospital. All this time there was a very tight feeling in my lower abdomen. She took antispasmodic drugs. The discharge continued for a week, then it all stopped. A follow-up examination was carried out two weeks later. The gynecologist has no complaints about my health. I feel good.
Irina: I underwent the hyteroscopy procedure to remove the polyp quite easily. I shouldn't have been afraid. The pain in the lower abdomen was no stronger than during menstruation, the discharge stopped quickly. The only unpleasant moment was coming out of anesthesia. Perhaps my dose was not calculated quite correctly. I felt sick for more than a day and had a very bad headache. But when it comes to women’s health, I am now absolutely confident in myself.
What consequences are possible?
Even the choice of a gentle technique does not completely eliminate postoperative consequences.
- Discharge after removal of a polyp of the cervical canal is a normal phenomenon that should not be alarmed. They will be abundant only in the first two days and may contain blood clots. For about another 10 days, discharge in a small amount is possible.
- Pain in the lower abdomen is a consequence that can last up to two weeks (most often it goes away in a few hours). If necessary, you can manage pain by taking painkillers.
- The next menstruation is delayed by about a month.
Removal of a cervical polyp is a common gynecological procedure, which does not exclude (if a gentle technique is chosen) pregnancy in the future. Don’t worry if the doctor has made a similar diagnosis; it’s not at all difficult to cope with.
And the presence of a polyp or the postoperative period does not impose restrictions on leading an active life. It is only important not to refuse treatment, and choose the most suitable method; a gynecologist will help you choose it.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Rehabilitation
When the operation is completed, the patient is transferred to the ward. The length of stay in the hospital depends on the complexity and extent of the surgical intervention, and the reaction to the injected anesthetic.
Two weeks after the operation, you must visit the doctor for a follow-up examination.
The symptoms that a woman experiences after hysteroscopy are bleeding for a week, weakness, aching pain, as during menstruation. To alleviate the general condition, the gynecologist prescribes antispasmodic drugs (Spazgan, No-shpu). In order to prevent infectious and inflammatory processes, it is recommended to undergo a course of antibacterial therapy. Restoration of the epithelial cover of the uterus is carried out with the help of hormonal drugs (Duphoston, etc.).
During the rehabilitation period, a woman is contraindicated in physical activity, hypothermia, and sexual intercourse for two weeks. The day of hysteroscopy should be considered the beginning of the menstrual cycle. Pregnancy after surgery is possible as early as the next month.
Uterine polyposis, manifestation of the disease and treatment
Uterine polyposis is a fairly common phenomenon today. It is a focal hyperplasia of the endometrium of the organ, characterized by the proliferation of mucosal neoplasms (polyps) that are benign in nature.
The polyp looks like a rounded growth on a stalk (the base can be either thin or thick). In most cases, the development of polyposis in the uterus is a process that does not threaten the woman’s life, but it has a tendency to transform into cancer (the risk of becoming malignant is 1-2%).
Features of pathology and its varieties
Features of the pathological process
The pathological process can be diagnosed in women at any age, starting from 11-12 years (i.e. after the onset of puberty). The peak is observed in patients over 45 years of age (during premenopause). Polyps can be single or multiple (this distribution is called polyposis).
The size of the neoplasm varies from a few millimeters to 2-3 cm. In appearance, they are more like cylinders with a porous surface and can be yellowish or burgundy with a purple tint. They are distinguished by a very thin membrane, through which the blood vessels feeding the neoplasm are clearly visible.
USEFUL INFORMATION: What is the lifespan of a woman's eggs?
Each polyp consists of a central vascular canal, endometrial glands and stroma.
The main classification of polyps is based on location and morphology.
- According to their location, they are divided based on the focus of localization, thus, it happens: polyposis of the cervix and body of the organ.
- According to their morphological type they are:
- glandular (forming in endometrial tissue from the cells of its glands). It is also called uterine endometrial polyposis; this type of pathology is mainly observed in young girls;
- fibrous (they are formed from connective tissue cells). Most often they are diagnosed in women over 45 years of age;
- glandular-fibrous (this mixed type is most often diagnosed in women after 30-35 years);
- placental (more rare cases, develop if after childbirth or a spontaneously terminated pregnancy, a piece of placental tissue remains in the woman’s body). They are dangerous neoplasms that cause serious consequences, including infertility;
- adenomatous (such polyposis of the uterine cavity or cervix is the most dangerous; it is these neoplasms that transform into malignant ones). This is a precancerous condition.
Why do polyps develop?
There may be several reasons for the formation of polyps in the cervical canal. These are genital infections, changes in the vaginal microflora, disruption of the normal functioning of the ovaries, hormonal surges, endocrine diseases, as well as mechanical damage. A woman can receive injuries during sexual intercourse, masturbation, or during childbirth if they are accompanied by specific obstetric manipulations.
By the way! Installation of an intrauterine device can also seriously injure the mucous membrane of the cervical canal and provoke the formation of polyps.
Indications
Usually, uterine polyps do not cause concern until they grow to an impressive size and lead to generalization.
Curettage of neoplasms on the uterine mucosa is carried out according to the following indications::
- menstrual irregularities;
- periodic nagging pain;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- heavy intermenstrual discharge (liquid, transparent);
- problem with conception.
The main indication is a diagnosed polyp based on the results of hysteroscopy and ultrasound. Polypous neoplasms, when unpleasant symptoms appear, significantly affect a woman’s quality of life, leading to infertility or aggravation of the menopausal period.
Treatment with traditional methods
It is possible to cure polyps using traditional methods, but it will take more time. The use of herbs normalizes hormonal levels and tumors resolve on their own.
Some of the most effective herbal remedies include:
- celandine - used in the form of decoctions for douching;
- nettle – included in herbal teas with general strengthening effects;
- chamomile - an anti-inflammatory agent for douching or drinking as tea;
- garlic - crush a clove, wrap it in gauze and insert it into the vagina overnight, it may cause a burning sensation, but then it goes away;
- herb hogweed - considered rare, can only be purchased from professional herbalists, contains plant analogues of hormones;
- mixtures based on propolis - a powerful remedy that can get rid of chronic infections, used in the form of suppositories at night in the vagina, you can add aloe;
- the ASD-2 fraction is a specific method, since the product is officially intended for animals and is sold in veterinary pharmacies, it has a very pungent and unpleasant odor, but there are studies and experiences of people who were cured of cancer by this drug;
- nutritious vitamin mixtures to boost immunity - pumpkin seeds and boiled egg yolks, decoctions of wild berries, nuts with honey.
Traditional methods can be combined with traditional and homeopathy. The advantage of traditional methods is that, in parallel with the local effect on the mucous membrane, positive changes occur throughout the body with the help of vitamins and microelements.
You can be treated with a variety of compresses on the cervix or abdomen. For example, horsetail is steamed over boiling water, wrapped in gauze and placed on the stomach. It is necessary to cover with a warm blanket and lie until it cools down. This is an external treatment method that normalizes the cycle and relieves inflammation.
A salt compress also helps. 10% salt solution (per liter jar of water - 3 tablespoons of salt). It is necessary to wet a cotton cloth in several layers in the solution and apply it to the lower abdomen. Do not cover with plastic, but you can wrap it with cloth and walk until it dries. Do it several times a day. Using salt compresses you can reduce adhesions on the seams.
Interesting! During the war, a salt compress was used to treat wounded people who developed gangrene when there were no antibiotics. Within a few days, the wound turned pink and began to heal.
Soda douching is useful for fungal infections associated with a polyp. Baking soda reduces the acidity of the vagina and prevents infection from developing.
Tampons with aloe and honey, onion tampons, honey and viburnum - are used inside the vagina. Mix the components in equal parts, apply to a gauze pad and administer in the evening before bed.
The duration of treatment depends on the degree of polyp growth and size. On average – 4 – 6 months. Taking herbs and tinctures - in courses of 7 - 10 days, then a 10-day break.
Attention! Under the influence of traditional methods of treatment, the polyp may burst and begin to smear with ichor. It's not scary and it's worth continuing the procedure.
Recovery after surgery
Initial recovery will take approximately four weeks. For the first week, the operated patient must take antibiotics to prevent the development of infection. If pain interferes, you will have to take painkillers, and anti-inflammatory drugs block the inflammatory process.
Polyps signal by their appearance that not all is well in the production of hormones
. It is necessary to monitor blood composition to identify hormonal imbalances. Stabilization of hormonal levels will require treatment from three months, sometimes treatment lasts up to a year. Ozonation with applications with special oil and physiotherapy promote accelerated restoration of the epithelium.
General recommendations for the rehabilitation period:
- Do not physically strain;
- Baths, saunas, steam baths and solariums are prohibited;
- Daily shower;
- Sexual activity is prohibited without the permission of a gynecologist;
- You cannot use vaginal tampons.
Contraindications for removal
The main method of treating polyps is removal, since there is a possible risk of degeneration into a malignant neoplasm. Conservative treatment and observation is possible only for single polyps of small size (up to 0.5 cm), not adenomatous.
Contraindications for surgery:
- pregnancy and lactation;
- active inflammatory and infectious processes of the female genital organs (preliminary sanitation is required);
- menstruation;
- bleeding from the genitals;
- malignant neoplasms.
Reasons for the formation of polyps in the uterus
The causes of polyps are not exactly known. According to scientists, neoplasms can arise under the influence of several factors:
- hormonal deficiency;
- concomitant diseases associated with the level of hormones in the body - ovarian cyst, fibroids, endometriosis;
- chronic infections of the genital tract, transmitted during childbirth (this may explain the occurrence of polyps in little girls);
- low immunity;
- polyps are companions of diseases such as ectopia, colpitis, cervicitis, ectropion, leukoplakia;
- bacterial infections (cervicitis) of the genital organs against the background of reduced immunity;
- viral diseases – human papillomavirus (HPV), herpes;
- fungal – mycoplasmosis, thrush;
- ureaplasma, chlamydia.
If mechanical damage to the cervical mucosa occurs after frequent abortions, this is fraught with the appearance of polyps as a protective reaction of the body. Birth trauma can also lead to disruption of the integrity of the endometrium. During the process of cervical dilatation and childbirth, tissue ruptures occur and the mucous layer is damaged. If suturing was performed incorrectly, growths may subsequently appear in the cervix. Postpartum fluctuations in hormones in the body contribute to the beginning of the process of polyp growth.
During pregnancy, with a decrease in immunity, chronic diseases and infections worsen if the pregnancy was not planned and no treatment was carried out.
Important! One cause does not cause disease. A combination of several factors leads to the growth of polyps.