Tears during childbirth: causes
Unfortunately, the occurrence of ruptures during childbirth cannot always be avoided. However, you need to pay attention to a number of factors that increase the risk of trauma to the birth canal. Fortunately, many of them are fixable.
Age of the woman giving birth (after 35 years)
With age, tissues gradually lose their elasticity. This also applies to the perineal area. The pelvic floor muscles become less elastic and the skin becomes less stretchable, which increases the risk of ruptures during childbirth.
Inflammatory diseases
Vulvitis, vulvovaginitis and other inflammatory diseases make tissues loose and fragile. Normally, the walls of the vagina, due to their folding, are able to stretch, which is very important when the baby passes through the birth canal. Infections, especially those that persist for a long time or are poorly treated, lead to the loss of this ability. Thus, if during childbirth the vaginal walls do not stretch well, this leads to ruptures.
Professional sports
Women who have been professionally involved in sports have well-pumped muscles (including the pelvic floor). On the one hand, this is a plus, since trained pelvic floor muscles prevent the development of prolapse of the uterus and vaginal walls. On the other hand, the muscles lose the necessary elasticity, which increases the risk of tears during childbirth.
Perineal injuries
If there are scars on the perineum that appeared as a result of injuries during the first birth or any operations, the risk of ruptures during childbirth is quite high. This is explained by the fact that in the area of the scar there are no muscles or normal skin. It is represented by ordinary connective tissue, which does not have elasticity and the ability to stretch.
Incorrect behavior of a woman during childbirth
The period of pushing is one of the most important stages in childbirth. The baby's head presses on the pelvic floor, causing an irresistible desire to push. To avoid trauma to the birth canal, you need to overcome this desire and breathe through the contraction. At this moment, the expectant mother is required to have maximum concentration and strict adherence to all the recommendations of the doctor and midwife. Incorrect behavior of a woman can cause ruptures during childbirth.
Causes of ruptures during childbirth that occur directly during labor
High crotch
A high perineum is a physiological feature of a woman, which manifests itself at the time of childbirth and can cause ruptures. This obstetric term means that the distance between the entrance to the vagina and the anus is quite large. At the moment of eruption of the head, the tissues of the perineum are stretched on the baby’s head, preventing him from “passing through”.
Perineal swelling
When labor is weak, contractions are chaotic in nature and do not increase in strength, frequency and intensity, determining the normal course of labor. In such a situation, the baby stands in one plane for quite a long time, which leads to impaired blood circulation in nearby tissues and, as a result, to swelling of the perineal tissue. This disrupts their elasticity and makes them more fragile.
Large fruit
Sometimes the baby’s size is slightly larger than standard or the pregnant woman’s pelvis is slightly smaller. In these cases, a discrepancy between the sizes of the fetus and pelvis can cause ruptures during childbirth.
Rapid labor
In some cases, labor is so intense that the baby moves through the birth canal too quickly and the surrounding tissues do not have time to stretch enough and are torn.
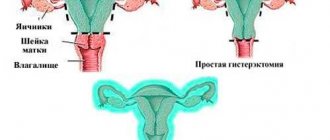
Adhesions after hysterectomy
Often, when uterine fibroids are detected, as well as in cases of advanced and untreatable disease of the pelvic organs, doctors remove the uterus.
Hysterectomy is an operation to remove the most important organ for a woman - the uterus. After this, the main problem may be the appearance of adhesions. To avoid this, a woman needs to undergo certain procedures. Physiotherapy is the main help in resolving scars, making them elastic. Also, a woman needs to move actively to avoid the appearance of new synechiae.
If, after the surgical intervention, the patient develops a fever, the scars become inflamed and swollen, and bleeding begins, then an urgent visit to the doctor is required.
If the patient is not treated properly and does not pay attention to these symptoms, she may develop intestinal obstruction. This pathology leads to another operation.
Types of breaks
Cervical rupture
Cervical rupture during childbirth occurs when a woman in labor begins to push early. The cervix does not have time to fully open for the baby to begin to smoothly descend to the pelvic floor. Premature attempts lead to an accelerated course of this process and injury to the cervix.
Tears in the vaginal walls
Ruptures of the vaginal walls in most cases occur due to injury to their mucous membrane. In more serious situations, muscle rupture occurs. Very often this is a consequence of inflammatory diseases or rapid labor.
Posterior commissure rupture
When the posterior commissure ruptures, the skin of the perineum between the entrance to the vagina and the rectum is injured. The cause may be perineal ruptures in previous births, tissue swelling, incorrect behavior of the woman in labor, or a large fetus.
Uterine adhesions and pregnancy
Many women cannot become pregnant due to adhesions of both the uterus and ovaries. But if this does happen, then adhesions can greatly overshadow the pregnancy. They manifest as unpleasant sensations and pain.
Causes of adhesions during pregnancy
There are a number of reasons why adhesions may appear during pregnancy:
- presence of infections;
- endometriosis;
- presence of blood in the abdominal cavity;
- undergone operations.
Causes of adhesions during pregnancy
In addition to pain, the following symptoms also appear:
- constipation or diarrhea;
- temperature increase;
- nausea and vomiting.
Basically, these symptoms appear with the clinical picture of third-degree adhesions. The chronic course of the disease is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen and disruption of intestinal function. The adhesive process is often asymptomatic, which complicates treatment.
If pregnancy occurs, and the presence of adhesions is discovered after this, then this indicates that the main organs are functioning as they should. But it is quite difficult to treat detected adhesions during this period. Only a doctor can prescribe treatment for a pregnant patient. A special approach is required so as not to harm the child.
To reduce pain, a pregnant woman is recommended to have a special diet to reduce the load on the intestines and ensure its patency.
The main treatment for adhesions during pregnancy:
- Use with extreme caution medications for pain relief.
- The use of anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent inflammatory processes.
- Special physical exercises to prevent the appearance of new adhesions.
- If these procedures do not help, then their dissection is required.
The dissection may be carried out due to the fact that the commissure is close to the uterus and as the organ grows, severe pain begins. This also leads to the appearance of inflammatory processes that the woman had before, but did not manifest themselves in any way.
The main thing during pregnancy is to trust doctors and not self-medicate in order to carry and give birth to a healthy child.
Types of cuts
Perineotomy
An incision, 2-3 cm long, is made directly towards the rectum. The indication for perineotomy is a high perineum.
Episiotomy
An incision of the same length is made slightly to the side, at an angle of 45 degrees to the line connecting the entrance to the vagina and the anus.
Indications for episiotomy:
- birth in a breech presentation: the pelvic end of the baby is smaller in diameter than the head, so it is necessary to prevent premature extension of the head and its “stuck”;
- premature birth: in order to reduce pressure, shorten the period of pushing and avoid traumatizing the fragile baby;
- operative delivery (vacuum extraction of the fetus, application of obstetric forceps): to avoid deep ruptures and severe trauma to the birth canal; shortening the period of pushing: for myopia or certain diseases of the cardiovascular system in the expectant mother, in order to reduce the load on the body or if the child’s well-being deteriorates during childbirth.
Incisions are made without anesthesia. Don't be afraid of this. The fact is that the skin of the perineum loses sensitivity due to compression and overstretching. In addition, the pain signal from childbirth itself overrides all other possible pain impulses, since the main task for the body is to give birth at any cost. Therefore, when the doctor picks up scissors, the woman in labor purely psychologically stresses herself out. In fact, she will not feel pain during the dissection of the perineum.
Suturing of cervical ruptures is also performed without anesthesia, since there are no nerve endings there, and therefore the woman cannot experience pain. Suturing the perineum after a cut or rupture, as well as suturing ruptures in the vaginal walls, is performed under local anesthesia or spinal anesthesia (if it was used during childbirth).
Diagnostics
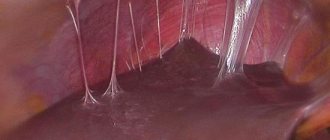
The main diagnostic method is hysteroscopy. This is an endoscopic research method that allows you to assess the condition of the uterus from the inside. A tube with a video camera is inserted into it, which transmits the image to the monitor in real time.
Other methods:
- hysterosalpingography - injection of a contrast agent into the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes, followed by X-ray examination;
- Ultrasound of the pelvis;
- MRI.
GHA
Historically, the first diagnostic method was hysterosalpingography. It was with its help that Asherman first diagnosed this disease, described it and proposed the first classification.
This method is inexpensive, does not require anesthesia, and is performed on an outpatient basis. It is also good because it allows you to assess the patency of the fallopian tubes, and this is a mandatory procedure for everyone who has applied for infertility.
On an x-ray, uterine synechiae look like filling defects - single or multiple, of different sizes and shapes. Dense adhesions divide the uterine cavity into chambers. But the contrast agent enters them through the ducts, so the cameras can be visualized./p>
The sensitivity and specificity of HSG in the diagnosis of adhesions is about 80%. This means that the risk of missing an existing pathology is about 20%. In addition, there is a 20% chance that the identified synechiae will actually turn out to be another disease.
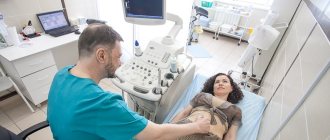
Ultrasound
Ultrasound identifies synechiae as dense strands of connective tissue. Less common are anechoic structures in the form of cells. In general, the information content of the method is low. Ultrasound can reveal only total damage to the cervical canal and uterine cavity. The study is carried out in the secretory phase of the cycle, with mature endometrium.
A more advanced ultrasound technique is the combination of three-dimensional ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound. This test is more informative than hysterosalpingography. It shows 90% sensitivity and 99% specificity.
MRI
MRI is rarely used. This is a clarifying technique. Its main advantage is the ability to visualize the uterine cavity above the level of adhesions.
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is the gold standard for diagnosing uterine synechiae in women of reproductive age. It visualizes the uterine cavity, allows the doctor to determine the condition of the endometrium, the type of adhesions, and location. Diagnostic hysteroscopy can immediately become therapeutic: using this method, the doctor can dissect adhesions.
Prevention of ruptures
As mentioned earlier, some of the factors that increase the risk of rupture during childbirth can be eliminated.
First, cure inflammatory diseases of the vagina and cervix, if any.
Secondly, train the pelvic floor muscles so that they become more elastic and can more easily endure stretching. Exercises in the form of alternating contraction and relaxation will help achieve this.
Thirdly, there are special cosmetic oils that nourish the skin of the perineum, thereby making it more elastic.
Fourthly, set yourself up correctly for childbirth. A woman must understand that childbirth is hard work and much will depend only on her. Adequacy and complete trust in the doctor are key points in the behavior of the expectant mother during childbirth. For expectant mothers who want to prepare for childbirth in advance, our school conducts a course “Ready for Childbirth!” In three hours you will learn how to behave correctly during childbirth, what methods of self-anesthesia are available, and how a husband can help his wife during childbirth.
Perineal rupture: consequences
Unfortunately, perineal tears vary in depth. Sometimes the injury can be so severe that it permanently disrupts the normal functioning of a woman's body. Here are the most severe consequences of perineal rupture:
bleeding
inflammation of the vagina, cervix and generalization of infection
prolapse and prolapse of the cervix and vagina
incontinence of gases and feces (with a 3rd degree rupture)
sexual dysfunction
Lacerations and perineal or episiotomy during childbirth
As you know, labor pain has a wonderful property - it is quickly forgotten. Therefore, many women, remembering the birth of their child, only talk about how doctors “cut” them, as a result of which their life became more difficult in the first month after childbirth. As a rule, in this case we are talking about perineo- or episiotomy. We will tell you what these operations are, why they are needed and, most importantly, what a woman can do to avoid them or make these injuries less painful.
What is the perineum?
The pelvic floor, or perineum, is the internal support of our body, of all our internal organs. It consists of three layers of muscles. The muscles of the lower (outer) layer are arranged in the form of a figure eight, the rings of which encircle the vagina and anus. The middle layer is represented by the triangular muscle. Finally, the upper (inner) layer forms the pelvic diaphragm. This is the paired and most powerful muscle of the pelvis, whose fibers create a real dome.
Such a complex structure and the close connection of the perineum with the genitourinary organs mean that this area is subject to heavy loads and plays an important role in the functioning of the organs located in the pelvis.
General information
Vaginal ruptures are a pathological condition in obstetrics and gynecology, which is characterized by damage to the walls of the vagina, accompanied by pain, bleeding or the formation of hematomas. Damage to the upper and lower thirds of the organ is most often observed. This is due to the fact that vaginal rupture often occurs against the background of uterine or perineal rupture. Isolated injuries and ruptures of the middle third are less common, since this area has relatively greater elasticity and is less connected to the surrounding tissues. Most cases of vaginal rupture are considered violent. Most often, obstetric pathologies or rough sexual intercourse act as etiological factors.
When is a perineal incision necessary?
There are the following indications for perineal dissection:
Threatening perineal rupture
(occurs with a large fetus, high perineum, rigidity - poor extensibility of perineal tissue, etc.). Most often, the rupture begins at the posterior commissure and then moves to the perineum and vaginal walls. The rupture does not begin suddenly - it is preceded by changes in the appearance of the perineum.
Signs indicating an impending rupture include characteristic protrusion of the perineum, cyanosis, swelling, and then pallor of the skin. If obstetricians notice signs of a threatening rupture, they make an incision. This is done because the smooth edges of an incised wound heal better after suturing than the rough edges of a laceration.
Premature birth
- to avoid pressure from the perineal tissues on the fragile bones of the premature baby’s skull.
The need to shorten the period of exile
due to the condition of the mother in labor (high blood pressure, congenital and acquired heart defects, myopia, etc.).
Intrauterine fetal hypoxia
(the incision helps relieve pressure from the perineum on the baby's head and speed up the birth process).
Surgical delivery
(if necessary, use forceps or a vacuum extractor).
Breech presentation of the fetus
- to avoid difficulties in the birth of a head whose size exceeds the size of the already born buttocks.
Choosing a perineal incision method
Episiotomy or perineotomy
Perineal incisions can be of two types: perineotomy - an incision directed directly towards the rectum, and episiotomy , in which the incision is directed to the side (if you imagine the perineum as a dial, then we can say that perineotomy is performed at 5 or 8 o'clock).
The method of dissection of the perineum during childbirth is chosen taking into account the characteristics and pathological changes of the perineum, the obstetric situation, and the size of the fetus.
Perineotomy
carried out during the normal mechanism of labor in case of a threat of rupture of the “high” perineum (increased compared to the norm the distance between the posterior commissure of the labia majora and the anus), as well as in case of premature birth.
Indications for episiotomy
are the threat of rupture of the “low” perineum (when the distance between the rectum and the entrance to the vagina is small), acute subpubic angle (the angle at which the bones of the pubic symphysis meet), breech presentation of the fetus, cicatricial changes in the perineum, obstetric operations (application of obstetric forceps, vacuum -extractor).
Lateral episiotomy - an incision strictly to the side - is carried out only in case of pathological changes in the perineum that do not allow the use of another method of dissection (for example, for tumors) - such incisions heal worse.
Perineotomy and episiotomy are performed in the second stage of labor, when the presenting part of the fetus has sank to the pelvic floor and tension in the perineum appears, before its rupture occurs. The operation is performed by a doctor; in emergency cases, in his absence, by a midwife.
The perineotomy operation does not require pain relief, since ischemia (lack of blood supply) of the perineal tissue leads to loss of pain sensitivity. Before dissection, the skin of the perineum is treated with tincture of iodine. The incision is usually made with scissors at the moment the fetal head erupts. Its length is on average 2-3 cm. Blood loss, as a rule, is small. Restoration of the cut perineum is carried out after the birth of the placenta.
Diagnosis and treatment of vaginal ruptures
Diagnosis of vaginal ruptures is based on the collection of anamnesis and complaints of the patient, an objective examination and the results of laboratory tests. As a rule, anamnesis and an objective examination of the genital tract are sufficient to make a diagnosis. From the anamnestic information, damage to the vagina may be indicated by aggressive or forced sexual intercourse, polytrauma, the use of obstetric aids during childbirth, as well as concomitant ruptures of the uterus or perineum. A visual examination of the external genital organs may reveal an increase in size and blueness of the labia, bleeding from the vaginal cavity.
During vaginal examination, signs of vaginal rupture are defects in the mucous membrane or protrusion of the wall, corresponding to a submucosal hematoma. In cases of vaginal ruptures in its distal third and the area of transition into the fornix, a manual examination of the uterus is performed to exclude ruptures of its lower segments. Laboratory data, as a rule, are not very informative, especially in the presence of minor vaginal ruptures. In a general blood test, in case of massive blood loss, signs of hemorrhagic anemia can be determined (a drop in the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells), and with the development of inflammatory complications, neutrophilic leukocytosis and an increase in ESR.
Therapeutic tactics for vaginal rupture depend on the nature and severity of the damage. For minor submucosal hematomas, medical intervention is often not required - the hemorrhages resolve on their own. Small ruptures in the walls that do not cause clinical manifestations also heal on their own. For more massive hematomas or severe ruptures in the walls, surgical intervention is required. The main methods of pain relief are epidural anesthesia or intravenous anesthesia. Massive hematomas are opened and emptied, and hemostasis of damaged arterial or venous vessels is performed. Large vaginal tears accompanied by bleeding are repaired with separate sutures or a continuous catgut suture. Also in such cases, in order to prevent infection of the wound, the woman is prescribed antibacterial drugs.
Caring for seams
To identify injuries, after childbirth the doctor must examine the soft tissues of the birth canal. Regardless of whether it was a tear or a cut, the integrity of the tissue is necessarily restored. Whether pain relief will be used, and which one, depends on the degree of damage to the birth canal.
If a woman has only cervical ruptures, then no anesthesia is required, since there are no pain receptors in the cervix. Cervical tears are sutured with absorbable sutures (catgut or vicryl). There is no need to remove them.
If ruptures of the vagina and labia minora are detected, they are sutured, usually under local anesthesia. As with cervical ruptures, absorbable threads are used as suture material.
If the perineum has been damaged, depending on the depth of the wound, either local anesthesia or intravenous anesthesia is given (in this case, the woman falls asleep for a short time). If epidural anesthesia was used during childbirth, the woman is simply given an additional dose of anesthetic.
The integrity of the perineum is restored layer by layer. First, the muscles - deep and superficial - are carefully compared, then sutures are placed on the skin. If the sutures are applied with catgut, they do not need to be removed, but if with silk thread, the sutures are removed 5-7 days after birth.
During the postpartum period, sutures on the perineum and labia are treated with hydrogen peroxide and a solution of potassium permanganate or brilliant green once a day. This is done by a midwife in the postpartum ward. If the ruptures in the soft tissues of the birth canal were deep, then antibacterial drugs may be prescribed due to the proximity of the rectum and the possibility of infection.
Traditional methods of treating adhesions
Often, medical methods are not always effective; after surgery, adhesions may appear again. Then they resort to traditional medicine. The most popular herbs for treatment are:
- Plantain. Basically, the treatment uses seeds, which are poured with boiling water and used for one to two months.
- St. John's wort. Often more effective for adhesions in the fallopian tubes. A decoction of it helps to get rid of them completely.
- Tinctures made from cinquefoil and milk thistle also help in the treatment of adhesions in the uterus.
The most famous home treatment is the treatment of adhesions with boron uterus. This medicinal plant has a good anti-inflammatory, antitumor, as well as a resolving agent, and many other healing capabilities. It has already helped many women get pregnant, although doctors gave no hope. It’s not for nothing that it’s called women’s herb. It is used both in alcohol tincture and by brewing.
Alcohol tincture is sold at the pharmacy, but you can prepare it yourself. For this, take 50 grams. herbs and pour 500 gr. vodka and 300 gr. water. All this is infused in a dark place. Then he drinks a course of 10 days. For tincture on water, you need to pour 1 tbsp. l. herbs with a glass of boiling water, leave for 2-3 hours and then apply.
Alcohol tincture is more effective, since in addition to everything else, it also calms the nerves. If a woman has been using this drug for some time and feels a deterioration in her health, then the process has gone in a good direction. There was pelvic inflammation and treatment began. This remedy is recommended by doctors as well as medication.
All these are the most famous herbs for the treatment of adhesions in the uterus using folk remedies. The main thing is to start treatment on time and then the result will not be long in coming.
Kegel exercises
Kegel exercises are quite simple. All women can do them. They serve to strengthen the muscles of the vagina and perineum, preparing them for childbirth, and help during the postpartum period.
Slow compressions.
Tighten your perineal muscles and slowly count to three. Relax. It will be a little more difficult if, holding the muscles, hold them in this state for 5-20 seconds, then gradually relax.
"Elevator".
We begin a smooth ascent on the “elevator” - squeeze the muscles a little (1st floor), hold for 3-5 seconds, continue the ascent - squeeze a little harder (2nd floor), hold - etc. to its limit - 4-7 “floors”. We go down in the same stages, pausing for a couple of seconds on each floor.
Abbreviations.
Tighten and relax your muscles as quickly as possible.
Pushing.
Push down moderately, as if you are having a bowel movement. This exercise, in addition to the perineal muscles, also causes tension in some abdominal muscles. You will also feel the anus tightening and relaxing.
Start your workout with ten slow squeezes, ten contractions and ten pushes, five times a day. The exercises should be repeated at least 25 times during the day. You can do the exercises almost anywhere - while walking, watching TV, sitting at your desk, lying in bed.
When starting out, you may find that your muscles don't want to remain tense during slow contractions. You may not be able to perform the contractions quickly or rhythmically enough. This is because the muscles are still weak - control improves with practice. If your muscles get tired mid-exercise, rest for a few seconds and continue.