More than half of the diseases “on the female side” are somehow related to pathology on the ovaries. Some of them do not create any inconvenience. For example, a corpus luteum cyst is often found only during a random ultrasound. However, the risk of complications always exists. Such a new level in the development of pathologies can be a cyst filled with blood - a hemorrhagic ovarian cyst. In this article we will look at how ovarian cysts occur, symptoms and treatment. Women whose hemorrhagic type of cyst is actively developing require surgical intervention. When it is really necessary, and when you can get by with conventional medications, we will consider further.
Features of the structure
Medical statistics say that hemorrhagic formation of the right ovary is most often diagnosed. This is explained by the fact that this side is closer to the large artery, from which blood usually enters the body of the tumor.
If a left ovarian cyst is detected, the treatment method does not change.
Let's consider the main features of a hemorrhagic neoplasm:
- Arises as a complication of a progressive follicular cyst or corpus luteum cyst (the tumor stretches or ruptures, resulting in hemorrhage into its cavity);
- There are no blood vessels passing through the cyst;
- Develops in the second half of the menstrual cycle, when bleeding occurs in a mature follicle or corpus luteum;
- Not a single case has been recorded in which a benign tumor transformed into a malignant one;
- Sometimes it resolves on its own or with appropriate treatment with medications;
- It is often diagnosed in teenage girls during the start of the menstrual cycle.
Cystic formation of the ovary in 99% of all cases is localized on one side. Bilateral pathology is observed only when dominant follicles mature in two uterine appendages at once.
Reasons for education
Medical experts have not yet fully identified what contributes to the development of this disease. However, there is an opinion that cystic formation occurs as a result of the presence of diseases that provoke hormonal imbalance. In addition, development is associated with the following pathologies:
- Deterioration in the performance of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, hypothalamus or pituitary gland;
- The presence of inflammation or infection in the pelvic organs;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Use of certain pharmacological drugs (emergency contraceptives, birth control pills, ovulation stimulants, etc.);
- Poor blood circulation in the ovaries;
- Medical abortion, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy;
- Too early arrival of menstruation (before 11 years);
- Excess weight, anorexia;
- Serious mental disorders, constant stress and depression;
- Constant and intense physical activity.
Diagnostics
If any abnormalities related to the functioning of the reproductive system are detected, the woman should immediately go to see a gynecologist.
A qualified doctor, to determine a progressive disease, performs the following diagnostic procedures:
- Finds out about the symptoms that worry the patient;
- Examines and palpates the abdominal area;
- Examines a woman on a gynecological chair;
- Refers the patient for testing (blood, urine and secretory fluid from the vaginal cavity are examined);
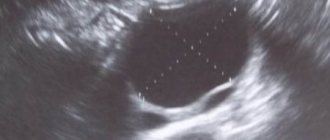
- Conducts ultrasound examination of the pelvic organ;
- Sends the woman for magnetic resonance imaging;
- Performs laparoscopy (sometimes it turns into a laparoscopic operation and the cystic neoplasm is immediately excised).
Based on the patient’s complaints and the results of the diagnostic examination, the gynecologist makes an accurate diagnosis, then he selects the safest and most effective treatment.
Possibility of conception
After laparoscopy, pregnancy can be planned only 4 months after surgery and six months after laparotomy. This is necessary in order for the entire body and ovarian tissue to fully recover. The stitches should heal completely.
For modern medicine, an ovarian cyst is a pathological condition. It can be cured if the patient consults a doctor in time. Surgical intervention, as a rule, occurs using a gentle method. This allows the woman to become pregnant in the future and successfully bear the fruit.
Pregnancy after cyst and tubal obstruction: diagnosis, treatment and symptoms
Previous article
Sunbathing if you have a breast cyst
Next article
Symptoms
The presence of a hemorrhagic cyst is indicated by the following symptoms:
- A sudden onset of intense pain in the lower abdomen on the left or right side (depending on in which ovary the formation is localized). Pain may radiate to the groin, lower extremities, or anus;
- A feeling of heaviness in the pubic bone or groin area;
- The appearance of a burning sensation in the stomach (occurs due to bleeding from the tumor);
- Frequent urge to urinate;
- Periodic, false urge to have a bowel movement;
- Menstrual irregularities;
- The appearance of bloody discharge during the intermenstrual period;
- Excessively long and intense periods or, conversely, scanty and short;
- Deterioration of general condition (fatigue, weakness, drowsiness);
- Increase in abdominal volume.
If the above signs of a benign tumor appear, the girl should immediately contact a gynecological office to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Why is a hemorrhagic ovarian cyst dangerous?
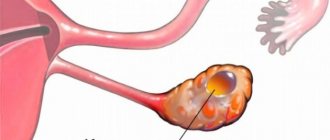
When the cyst becomes large, torsion of the cyst may occur. The likelihood of such a development of events also depends on the length of the pedicle with which the formation is connected to other organs. This leg consists of a part of ligaments, veins and arteries. When torsion occurs, part of the intestine and fallopian tubes may become attached to such a formation.
When the cyst changes orientation in space, the veins that supply the membrane are first compressed.
Blood stagnation occurs in them. The cyst grows rapidly in size, since the arteries are still functioning and actively pumping blood. The larger the cyst grows, the more it twists the leg. Eventually, blood flow may stop completely. IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
There are two scenarios:
- Rupture of an ovarian cyst, when there is no outflow of fluid and the membrane is quite thin.
- Necrosis and progression of peritonitis in acute torsion.
Twisting the leg is considered an emergency. Sharp pain that spreads to the coccyx area, spasms and nausea are indications for urgent hospitalization. A hemorrhagic cyst often ruptures, since it is already filled with blood and the membrane is quite thin.
Complications and consequences
If you do not promptly pay attention to the state of your women’s health and ignore the symptoms that manifest themselves in the presence of a cystic formation, then you can provoke serious consequences that are dangerous for normal functioning (sometimes even life-threatening).
The most common complication of a hemorrhagic cyst is the rupture of its body and the release of the fluid that was in it.
This occurs as a result of its long-term progression, when it reaches quite impressive sizes (more than 10 cm). Sometimes tumor rupture can be triggered by surgical interventions, preventive examinations, intense sexual intercourse or excessive physical exertion on the abdominal area. The consequence of a violation of the integrity of the cyst is peritonitis. It represents inflammatory processes in the peritoneum. To save the patient’s life, it is necessary to immediately clean the abdominal cavity together with excision of a benign neoplasm.
In addition to rupture, a large tumor puts pressure on nearby pelvic organs and can impair their functionality. Due to this condition, the girl’s reproductive system begins to malfunction and infertility develops.
If the cystic formation progresses during gestation, there is a high probability of spontaneous abortion. That is why the condition of the girl and the cyst is being carefully monitored. Sometimes, to save the fetus, doctors perform laparoscopy and eliminate the pathology.
Prognosis for hemorrhagic cyst on the ovary
Hemorrhoidal ovarian cyst has a favorable prognosis. Timely treatment will avoid complications. The patient’s body functions normally within a day after the operation. Small incisions heal quickly. To prevent the seams from coming apart, you will have to go without a hot bath for some time.
Problems arise when the cyst has burst and blood has entered the abdominal cavity. Then you need to additionally pump out the liquid and disinfect it to avoid inflammation.
For girls who have not yet given birth, the remnants of healthy ovarian tissue are preserved if possible. For women who have given birth, the appendages are usually removed. But there is no need to be alarmed; the second ovary is usually enough for reconception. And timely consultations in gynecology will allow you to take control of this process and avoid complications.
After the operation, you need to take a course of pills to restore ovarian function. This usually takes 1-2 months, after which the patient can be considered healthy. While taking medications, regular examinations are carried out to exclude relapse.
What treatment is prescribed
The most humane method of therapy is prescribed exclusively by the attending physician, based on the patient’s age, her condition, as well as the type and diameter of the cystic formation.
Surgery is not always necessary; in some cases, the cyst may resolve after taking medications.
Treatment with pharmacological agents is possible if the tumor has a small diameter, is not subject to inflammatory processes and is not accompanied by pronounced symptoms. In such situations, the task of the attending physician is to prescribe safe and high-quality hormonal therapy. To eliminate hemorrhagic cysts, the following drugs are used:
- Combined contraceptives. These include: Janine, Belara, Novinet, Yarina, Jess, etc. The action of the medications is aimed at facilitating the work of the ovaries, reducing the size of the tumor and preventing its re-formation;
- Duphaston is a hormonal agent that copes well with regulating the amount of hormonal elements in the body. It also negatively affects the cyst, slows down its growth and provokes its resorption. Taking Duphaston is advisable if the cause of the pathology is a hormonal imbalance.
In addition to taking pharmacological medications, the doctor tells the woman what usual activities are currently prohibited (visiting the sauna, physical activity, exposure to high temperatures, etc.). It is recommended to apply a cold compress to the stomach area every day. Throughout the treatment, the girl periodically undergoes ultrasound examination, which helps the doctor monitor the condition of the tumor.
If the tumor has reached an impressive size or the use of drugs does not bring any positive results, then it is useless to treat with medication. In such situations, surgery is performed.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fT9C7Ctifyg
The most common methods of surgical intervention:
- Laparoscopic is a gentle method that involves making three holes in the stomach and removing the cyst using a laparoscope and miniature instruments. This technique is usually prescribed for small tumors;
- Laparotomy is an abdominal operation, during which the tumor is removed through a large incision (10-15 cm) in the abdominal area. This method of intervention is carried out in emergency situations (cyst rupture, twisting of its stem, inflammatory reactions).
After the operation, the doctor prescribes special medications and gives useful recommendations to prevent relapse of the disease.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is presented in the following cases:
- a complication of the pathological condition has occurred;
- A cystic formation was detected in a patient under the age of 15 years. Due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics, there is a high risk of complications;
- if drug therapy has led to an increase in the node by more than 10 cm.
Main types of surgical operations:
- laparotomy. It is carried out in case of complications or detection of malignant neoplasms in the uterus. With a large hemorrhagic node;
- laparoscopy. A gentle method of surgical intervention, due to small access. Prescribed for small cysts and in the absence of complications.
Prevention of formations
In order to avoid the unpleasant consequences of the disease and itself, you must adhere to the following preventive rules:
- Visit the gynecological office at least twice a year;
- Follow the rules of intimate hygiene;
- Consult your doctor before any use of hormonal medications;
- Use contact contraception (condoms) to prevent unwanted pregnancy and infections in the body;
- Avoid promiscuity;
- Contact your gynecologist if you experience any symptoms indicating a dysfunction of the reproductive system.