Before you start looking for answers to the question: how to lower androgen levels in women and whether hyperandrogenism can be cured, it is necessary to understand the causes and mechanism of development of this disease. Hyperandrogenism is a fairly common pathology that affects the functioning of the endocrine system, affecting about 20% of women worldwide.
What are androgens, where are they secreted in men and what hormones do they include?
The hormones responsible for the development of the body of a full-fledged man or woman are estrogens, that is, female sex hormones and androgens. These two groups of active substances determine a person’s hormonal background. Despite the priority concentration of only one of the groups, all hormones are present in both the male and female body. How male sex hormones are formed and released in the body, what the androgenic effect is and what the function of androgens is in the stronger sex and women will be discussed below.
General purpose and functions
Androgens in men begin to be actively released during puberty, that is, during puberty. It was during this period that their multidisciplinary influence was most noticeable. The main androgenic effects in the male body:
- Anabolic and anti-catabolic androgenic effects. Their essence is that androgenic hormones promote the burning of fat deposits and the formation of muscle mass.
- Another androgenic effect is the acceleration of glucose metabolism and a decrease in its concentration in the blood.
- Androgen hormones help to form subcutaneous fat tissue according to the male type. As a rule, fat is deposited in men on the abdomen. In contrast, in the fair sex, subcutaneous fat is deposited in the thighs, buttocks, and breasts.
- An additional androgenic effect is the ability of androgenic hormones to reduce the concentration of cholesterol in the blood. Of course, the antiatherogenic effect is more inherent in estrogens; any androgen hormone released also reduces blood cholesterol levels.
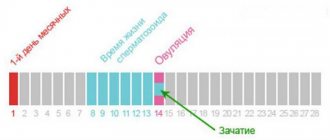
- The most important purpose of androgens is considered to be the ability to influence sexual function and fertility, that is, a man’s ability to conceive a child. Androgenic effects include the formation of libido and normal erection. Spermatogenesis also largely depends on male sex hormones.
Testosterone, released during puberty in boys, is responsible for the formation of the child’s body according to the male type. The release of testosterone, etc. causes the appearance of beards and mustaches in adolescents, leads to the appearance of the odor of sweat (during puberty, many adolescents have a more intense and pungent odor of sweat, even in comparison with mature men), promotes enlargement of the genitals, the appearance of pigmented nipples , formation of the bone skeleton: men, as a rule, have a developed shoulder girdle, while their pelvis remains narrow. It is under the influence of the main androgen - testosterone - that the timbre of the voice is formed: in men it is lower and rougher than in women.
Classification
The most well-known male hormone is testosterone, but there are other hormones and their precursors. For example, androstenedione. It is a precursor, that is, a substrate for the subsequent synthesis of sex hormones, that is, androgens in men and estrogens in women. The precursor itself is synthesized in the adrenal glands. The strength of its androgenic effect is weak (about 20% of testosterone), but the level of androstenedione is also important. During diagnosis, it serves as a marker for the formation of testosterone itself.
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA-S) is the next sex hormone. DHEA-S also has low activity (no more than 10% of the potency of testosterone) and is the basis (that is, substrate) for the formation of other sex hormones. Despite the low true activity of DHEA-S, the biological activity of the total hormone content is quite high due to the high concentration of dehydroepiandrosterone.
The main androgen is testosterone.
The substance is produced in Leydig cells located in the testes. They begin to function in the prenatal period. It is a change in the normal level of any androgen that leads to pathology of the structure and function of the genital organs.
Normal levels of hormones in the blood of men
The normal level for adult men is 133-441 mcg/dl (or 250-990 pg/ml), the normal level for women under 50 years old is 32-204 mcg/dl, the normal blood level for women under 49 years old is 30-333 mcg/dl. dl.
In addition to hormone levels, it is important to calculate the free androgen index to understand hormonal status. The level shows exactly how much of the hormone is currently freely available.
What is virilization
Androgen deficiency and excess estrogen in the blood cause virilization of men. There is a congenital and acquired deficiency in the production of any androgen. The condition occurs when:
- Klinefelter's syndrome. The disease is caused by a gene deficiency. Signs of the disease appear in boys at an early age. Excessive height, long legs, and a high waist can cause parents to be wary. At puberty, they do not have male-type growth, their testicles and penis do not develop, and their voice has a high timbre. Klinefelter syndrome is often accompanied by intellectual disability.
- Androgens in the blood may decrease if the testicles are not descended into the scrotum (cryptorchidism). Outside the scrotum, the temperature of the testicles rises and the normal function of the organ is disrupted, that is, normal testosterone production becomes impossible. The initial sign of cryptorchidism is the absence of a testicle on palpation in the scrotum. Later, parents may notice that a boy, due to a lack of any androgen, may have excess body weight, a high voice, and a lack of male-type hair. Sometimes cryptorchidism at birth is a temporary phenomenon, and the testicles descend into the scrotum without outside intervention after a short time.
- Similar changes can be observed with orchitis. Inflammation of the testicle occurs with “mumps”, that is, mumps, which develops after a trauma to the scrotum, against the background of decreased changes. Symptoms of orchitis: increased body and testicular temperature, local swelling, headaches, general intoxication.
- Kallmann syndrome. Congenital pathology accompanied by cryptorchidism and decreased androgen production. Sometimes the syndrome is accompanied by hypogonadism, six-fingered fingers, and the presence of a cleft upper lip and hard palate in the child (“cleft lip” and “cleft palate”).
- Pituitary insufficiency. The pituitary gland is a gland that secretes hormones and controls the production of testosterone and androstenedione. The causes leading to pituitary insufficiency are often tumor processes.
A deficiency can be suspected based on numerous signs. Symptoms of a deficiency of male sex hormones may include hot flashes, palpitations, chest pain, increased sweating, bone pain, decreased muscle mass and an increase in the amount of subcutaneous fat. From the genital area, erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, premature ejaculation, anorgasmia, and impaired spermatogenesis may be observed. On the part of the nervous system, there is increased fatigue, depression, and memory loss.
Sometimes the lack of androgenic effect is due to the presence of androgen insensitivity syndrome in a boy. The disease occurs when there is a spontaneous mutation of the gene responsible for the insensitivity of receptors to their effects.
Immunity can be complete or partial. Depending on the severity of the syndrome, androgen deficiency is expressed to varying degrees. Complete insensitivity leads to the formation of a male-type phenotype.
We recommend reading: Hormone replacement therapy for women after 40, 50, 60 years, during menopause, HRT after removal of the uterus and ovaries, pros and cons, drugs, herbal medicine, reviews
Due to the important effects that androgens have in the body of men, even a slight suspicion of their deficiency or excess can lead to serious changes in the body. Therefore, it is imperative to find out the cause of the disease and begin treatment as soon as possible, especially when it comes to adolescents going through puberty. However, you cannot start therapy with drugs that have an androgenic effect on your own. All treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a physician.
Nowadays, drug treatment and surgical intervention are practiced. In the first case, Cabergoline, Parlodel, Bromocriptine, Metergoline or Pergolide are prescribed. The last two are considered easier than the others. They are used in combination with other substances. Every six months, control treatment is necessary after examining the causes and consequences of a violation of the level of this hormone. In some cases, the cause of increased prolactin takes a long time to eliminate. This is due to diseases of the thyroid gland, kidneys or liver. In such cases, surgery is most often prescribed. As the disease progresses, which is accompanied by oncological manifestations, testosterone is additionally prescribed. In rare cases, radiation therapy is prescribed. This is relevant if other treatment methods are unsuccessful.
Stopping drinking alcohol, smoking, and taking sedatives will help temporarily lower prolactin levels. It is also important to avoid stressful situations. It should be understood that exceeding prolactin levels is extremely dangerous for men. It is fraught with visible deviations in the functioning of male organs. The sooner the prolactin level stabilizes, the easier it will be to prevent the consequences of the resulting disorders.
Therapy of adrenogenital syndrome
Treatment of adrenal hyperandrogenism is aimed primarily at normalizing hormonal levels and eliminating external negative manifestations of hormonal imbalance. Increased levels of androgens in the body are neutralized with the help of drugs that increase the amount of female hormones (for example, Dexamethasone, Metipret).
Hormonal therapy in women directly depends on the patient’s plans for the future. If a woman does not plan to conceive a child, then oral contraceptives with an antiandrogenic effect are prescribed (for example, “Zhanine”, “Yanina”). To eliminate skin manifestations, the oral contraceptive “Diane-35” is useful, which is prescribed in conjunction with the drug “Androkur” to enhance the effect. However, the result will appear only after three months of therapy. If you are planning a pregnancy, medications are prescribed that activate the release of the egg. In the absence of a therapeutic effect, surgical intervention in the form of a wedge-shaped resection of the ovaries is possible in order to stimulate the release of the egg. Surgery is also indicated in the presence of adrenal tumors (tumors must be surgically removed).
Medicinal herbs are used as folk remedies for regulating hormonal levels. There are a lot of plants that have a beneficial effect on metabolic processes and help normalize hormonal balance (angelica, black cohosh, licorice root, mint, peony, sacred twig, etc.). However, the use of herbal remedies is possible only as a complement to medical therapy; it is impossible to independently eliminate the pathology with folk remedies.
Mechanism of androgenization
In general, the pathology of androgenization consists of a significant increase in the production of male sex hormones. As the concentration of testosterone derivatives increases, their effect on the woman’s body increases. Tissues become more sensitive to the effects of such substances as the number of receptors associated with these hormones increases.
The result is the formation of typically male characteristics in a woman, which, of course, are less pronounced compared to the physiological norm for men.
Foods that help reduce testosterone
They highlight a list of healthy and tasty foods that effectively help regulate the amount of sex hormone. Some tips:
- The menu must include milk and its derivatives (cream, cottage cheese, cheese).
- If a woman’s testosterone levels are very different from the norm, then she needs to eat more protein. It is found in chicken meat and fish.
- Doctors do not recommend following a vegetarian diet.
- You should not eat foods that contain free testosterone (garlic, eggs, legumes, almonds and hazelnuts).
- Foods that contain low molecular weight granulated sugar (white bread, potatoes, cereals) help reduce the concentration of the hormone.
- You can and even need to eat sweets, but only those types that are made with fructose. For example, natural honey, dates, peaches, apples, plums and so on.
- There should not be long pauses between meals, because reducing the level of glucose and insulin in the blood significantly increases testosterone production.
Types of pathology
Depending on the cause, level and mechanism of development of the pathology, the following types of hyperandrogenism are distinguished.
- Ovarian. Characterized by disorders of genetic or acquired origin. Ovarian hyperandrogenism is characterized by rapid development and sudden onset of symptoms. In the ovaries, androgens are converted to estrogens by the enzyme aromatase. If its functioning is disrupted, a deficiency of female sex hormones and an excess of male hormones occurs. In addition, ovarian hyperandrogenism can be provoked by hormonally active tumors of this localization.
- Adrenal. This hyperandrogenism is caused by adrenal tumors (most often androsteromas) and adrenogenital syndrome. The latter pathology is caused by genetic abnormalities of the gene that is responsible for the formation of the enzyme C21-hydroxylase. The deficiency of this substance over a long period of time can be compensated by the work of other hormone-producing organs, so the condition has a hidden course. With psycho-emotional stress, pregnancy and other stress factors, the enzyme deficiency is not covered, so the AGS clinic becomes more obvious. Adrenal hyperandrogenism is characterized by ovarian dysfunction and menstrual irregularities, lack of ovulation, amenorrhea, and insufficiency of the corpus luteum during egg maturation.
- Mixed. A severe form of hyperandrogenism combines ovarian and adrenal dysfunction. The trigger for the development of mixed hyperandrogenism is neuroendocrine disorders and pathological processes in the hypothalamus. It manifests itself as disorders of fat metabolism, often infertility or miscarriage.
- Central and peripheral. Associated with dysfunction of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, disruption of the nervous system. There is a deficiency of follicle-stimulating hormone, which impairs the maturation of follicles. As a result, androgen levels increase.
- Transport. This form of hyperandrogenism is based on a deficiency of globulin, which is responsible for binding sex steroids in the blood and also blocks excessive testosterone activity.
Based on the site of origin of the pathology, the following types of hyperandrogenism are distinguished:
- primary - originates in the ovaries and adrenal glands;
- secondary - the center of origin in the pituitary gland.
According to the method of development of pathology, the following are distinguished:
- hereditary;
- acquired.
According to the degree of concentration of male hormones, hyperandrogenism occurs:
- relative - the level of androgens is normal, but the sensitivity of target organs to them is increased, and male sex hormones tend to convert into active forms;
- absolute - the permissible norm of androgen content is exceeded.
Causes of adrenal hyperandrogenism
The main reason for the accumulation of androgens in the body is a congenital defect in the synthesis of enzymes, which prevents the conversion of steroids. Most often, this defect is caused by a deficiency of C21-hydroxylase, which synthesizes glucocorticoids. In addition, hormonal imbalance is a consequence of the influence of hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex or tumor-like formations (some types of adrenal tumors are capable of producing hormones). The most common diagnosis is the presence of congenital adrenal hyperandrogenism. However, sometimes there are cases of the development of hyperandrogenism due to tumors of the adrenal glands that secrete androgens (Cushing's disease).
Role in the female body
Androgens in women are produced in the adrenal glands and ovaries. These organs produce the bulk of them. It is important to remember that hormone synthesis does not occur in adipose tissue.
In women, androgens play a central role in maintaining hormonal balance. After the onset of puberty, they initiate the growth of pubic hair and in the armpits.
The weaker sex needs substances for the production of the main hormone - estrogen - and the possibility of full-fledged sex: the emergence of sexual desire and a feeling of satisfaction.
They regulate the functioning of human internal organs and systems. In particular, the reproductive, renal and muscular systems, heart and bones slow down bone loss.
General information
Virilization (masculinization) of adrenal origin is caused by excessive production of androgenic hormones by the adrenal glands and leads to external and internal changes that are atypical for the patient’s gender. Androgens are essential in the body of an adult woman because they are responsible for important transformations in the body during puberty. In particular, they produce estrogen synthesis, and also help strengthen bone tissue, muscle growth, participate in the regulation of liver and kidney function, and the formation of the reproductive system. Androgens are produced mainly by the adrenal glands and in the female body by the ovaries, and in the male body, respectively, by the testicles. A significant excess of the normal levels of these hormones in women can significantly upset the reproductive system and even provoke infertility.
Signs of excess androgens in a woman and how to reduce their level with folk remedies
Male sex hormones, which is what is meant when we talk about androgens, are also present in women at any age. What depends in the body on the level of androgens in women. When androgens in women do not exceed normal levels, this allows them to remain healthy, preserving their external beauty. An overabundance of steroids indicates an endocrine disorder and provokes the manifestation of qualities more suitable for a man. Hormonal disruption does not go unnoticed; the increased level of androgens turns a sophisticated lady into an overly masculine person in appearance and demeanor.
Before puberty
Before puberty, hyperandrogenism is caused by genetic disorders or hormonal imbalances during fetal development. Clinically manifested by defective anatomy of the external genitalia and pronounced male secondary sexual characteristics.
Adrenal hyperandrogenism in newborn girls is manifested by false hermaphroditism - the vulva fusions, the clitoris becomes excessively enlarged, and the fontanelle becomes overgrown already in the first month. Subsequently, girls experience:
- long upper and lower limbs;
- high growth;
- excessive amount of body hair;
- late onset of menstruation (or absent altogether);
- secondary female sexual characteristics are weakly expressed.
We recommend reading: TSH - normal hormone level and interpretation of test results
Diagnosis is difficult to carry out with this pathology and ovotestis - the presence of male and female germ cells, which happens with true hermaphroditism.
During puberty
During puberty, girls with hyperandrogenism may experience:
- acne on the face and body - blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles;
- seborrhea - excessive production of secretions by the sebaceous glands;
- hirsutism - excessive hair growth on the body, including in “male” places (on the arms, back, inner thighs, chin);
- NMC - unstable menstrual cycle, amenorrhea.
During reproductive age
If the pathology manifests itself during reproductive age, all of the above symptoms may be joined by:
- baryphonia - deepening of the voice;
- alopecia - baldness, hair loss on the head;
- masculinization - an increase in muscle mass, a change in the figure according to the male type, redistribution of subcutaneous fat from the thighs to the abdominal area and the upper half of the torso;
- increased libido - excessive sexual desire;
- breast reduction - small mammary glands, lactation continues after childbirth;
- metabolic disorder - expressed in insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipoproteinemia, obesity;
- gynecological problems - disruptions in the menstrual cycle, lack of ovulation, infertility, endometrial hyperplasia;
- psycho-emotional disorders - tendency to depression, feeling of loss of strength, anxiety, sleep disturbance;
- cardiovascular disorders - a tendency to hypertension, episodes of tachycardia.
All these symptoms are combined into one concept - viril syndrome, which implies the development of male characteristics and the loss of female characteristics by the body.
In menopause
In women at the onset of menopause, hyperandrogenism syndrome occurs due to a decrease in estrogen levels. By this time, many people notice the appearance of “male hair,” especially in the chin and upper lip. This is considered normal, but it is necessary to exclude hormone-producing ovarian tumors.
Causes of androgenic alopecia
The male sex hormone testosterone is produced in the testes. Under the influence of 5a-reductase, testosterone is converted into a more active dihydrotestosterone and, during puberty, promotes the development of primary and secondary male sexual characteristics, has an anabolic effect, in particular, stimulates an increase in muscle mass.
Synthetic analogues of testosterone are used as medications - testosterone propionate (administered intramuscularly once a day), methyltestosterone (prescribed in tablets under the tongue).
Androgen drugs stimulate protein synthesis in the body, which is manifested by an increase in skeletal muscle mass. In addition, they promote bone calcification.
Androgen drugs are used:
- as a replacement therapy for insufficient sexual development,
- with impotence (with prolonged use of androgens, atrophy of the cells that produce testosterone occurs).
- Androgen drugs are also prescribed to women with breast cancer.
Side effects: sodium and water retention, edema, hypercalcemia, nausea, cholestatic jaundice, depression, paresthesia; in women – masculinization (growth of facial hair, deepening of the voice). When androgen drugs are prescribed to boys with insufficient sexual development, the closure of the epiphyses of long bones is accelerated and growth slows down.
Androgen drugs are contraindicated in prostate cancer.
Antiandrogen drugs: cyproterone, flutamide (block androgen receptors). Used for prostate cancer.
Finasteride (Proscar) inhibits 5a-reductase. Used for benign prostatic hyperplasia; prescribed internally.
Androgenic alopecia is a type of baldness, the main cause of which is considered to be hypersensitivity of the hair follicle to dihydrotestosterone, the active form of testosterone - the male sex hormone.
Increased sensitivity of follicles to testosterone is transmitted at the genetic level, and in 75% of cases from the mother. Thus, androgenic alopecia can be considered a hormonal disease with a hereditary predisposition.
Baldness in men of the androgen-dependent type begins in the frontal and parietal regions.
In women, the cosmetic defect first affects the central parting, then the thinning moves to the crown.
At the beginning of the manifestation of the pathology, the hairs become thinner, lose vitality and shine, and then gradually begin to fall out.
Androgenetic alopecia develops slowly, the first symptoms of the disease can be detected closer to 30 years, after 10-15 years visible areas of baldness form.
A characteristic feature of androgenetic alopecia is the preservation of the amount and thickness of hair in the nape area. The follicles of this zone are not sensitive to dihydrotestosterone, so fluctuations in the level of the hormone do not affect their functioning.
Androgens are a collective term for male sex hormones. They are produced in the body of representatives of both sexes, but in women in much smaller quantities.
Thanks to androgens, and to a greater extent testosterone, in men:
- Muscle tissue is more developed;
- Hair growth occurs according to the male type - more hair on the face and body;
- The development of the mammary glands is not expressed;
- Rough voice and stronger stamina.
Androgens take part in metabolism and maintain normal sugar levels. Male hormones are divided into weak and strong. The latter include testosterone and its weakened version, dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
With a genetic predisposition (the presence of an enzyme called 5-alpha reductase in the scalp), androgens lead to the development of androgenic alopecia.
Estradiol
Androgens and estrogens are hormones with common metabolic processes, but they have opposite effects.
Estrogens are responsible for the life cycle of hair. Estradiol is produced in large quantities during pregnancy; under its influence, the growth phase of the strands lengthens. And this is why pregnant women’s curls practically stop falling out.
Within 2-4 weeks after childbirth, estrogen levels drop and almost all hairs that are in the growth phase begin to fall out simultaneously, which leads to their noticeable thinning.
Read on: How to treat hair loss while breastfeeding.
If you experience excessive hair loss with signs of dysfunction of internal organs, you should first consult a therapist. The doctor prescribes diagnostic procedures, consultation with an oncologist, endocrinologist, dermatologist.
A trichologist provides effective assistance for androgenetic alopecia; if necessary, the help of a cosmetologist, physiotherapist, or massage therapist is required.
Manifestations of androgenetic alopecia depend on the severity of symptoms, gender and additional changes in hair structure.
A characteristic sign of the pathology is damage to the hair follicles only in the parietal and frontal regions of the head; it is in these areas that there is an enzyme sensitive to dihydrotestosterone.
Androgenic alopecia in women causes:
- Reducing the amount of vegetation in the forehead and crown area. In most cases, complete loss of curls does not occur;
- Pathological changes in the menstrual cycle. Androgens counteract the work of estrogens, which disrupts the physiological regulation of menstruation;
- Acne. The rashes affect any part of the body, but in most cases, acne forms on the face and back;
- Hirsutism is the appearance of hair in areas atypical for a woman’s body - on the chest, cheeks, chin, back.
Androgenetic alopecia in men is manifested only by thinning strands on the crown and forehead.
The life cycle of each hair is regulated by the influence of a certain amount of hormones.
Curl development is divided into two stages:
- GROWTH PHASE
. Lasts from three to 10-12 years. The increase in hair length in this phase is stimulated by certain substances - growth factors;
- LOSSOUT PHASE (INVOLUTION)
. Normally, its duration takes up to 100 days. When hair loss occurs, only the hair root gradually undergoes decay; it receives fewer nutrients, which leads to its atrophy and weakening, as a result of which the hair naturally falls out.
In the parietal and frontal parts of the scalp there is a special substance - the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, under its influence androgens are transformed into dihydrotestosterone. It is this active form of testosterone that affects the normal course of all phases of hair development.
Androgenetic alopecia occurs when the amount of hormones increases or skin cells become more sensitive to them. In this case, dihydrotestosterone blocks growth factors, and the life cycle of curls is reduced several times - in severe cases, up to 5-8 weeks.
During the hair loss phase, under the influence of androgens, the hair follicle is damaged, which accordingly disrupts its functioning and leads to increased hair loss.
This occurs as a consequence of spasm of skin capillaries as a result of exposure to dihydrotestosterone.
Violation of microcirculation in turn causes:
- Follicle dystrophy;
- Thinning of curls and their discoloration;
- Premature transition of hair into the resting phase, which prevents its lengthening.
During the resting phase, the curls become “dead,” which causes them to fall out profusely when washed and combed. At the beginning of the disease, colorless and thin hairs hide bald spots, so the problem does not seem so obvious. But gradually the bulb dies off completely, leaving connective tissue in its place, from which hair no longer grows.
With androgenic alopecia, hair loss may not be critical - only up to 100 hairs per day, read more about hair loss norms. But due to the death of the follicles, after a few years, areas of the head completely devoid of vegetation are noticeable.
With androgenetic alopecia, the clinical picture will differ in men and women. Most often, the pathology is detected in men, and, as a rule, its first signs can be detected closer to 30 years of age.
According to statistics, signs of androgenic alopecia can be found in 20-90% of women. But their hair loss is not as pronounced compared to men, and the problem mainly worsens during menopause and after it, that is, at 50-55 years old. Read more on this topic - how to stop hair loss during menopause.
This is primarily due to the stimulating effect of estrogen on the follicles, which partially neutralizes the functions of dihydrotestosterone.
Androgenetic alopecia is common in women of any nationality and race.
There are three main forms of the disease in women:
- I – SHAPE – BY STRIP TYPE
. The density of the strands begins to decrease along the central parting. If a woman uses a side parting, then the hair will thin in this place. Gradually, the thinning area moves closer to the temples;
- O – SHAPE (LIKE A NEST)
. Thinning also begins from the parting area, but follicular degeneration simultaneously affects both the parietal and frontal regions. Due to this, the bald spot simultaneously moves to the forehead and back of the head, forming an even focus or otherwise a rounded spot-nest;
- REDUCTION ACCORDING TO MALE TYPE
. Rarely detected. In the frontal and parietal zones, the hair becomes thinner, thinner and gradually falls out, forming a bald spot, more typical for men. This variant of androgenetic alopecia is distinguished by a fairly rapid course - complete atrophy of the follicles can occur in 3-4 months.
To determine the degree of hair loss in women, the Ludwig scale is used, its main criteria:
- The temporal region is almost never negatively affected by dihydrosterone;
- The anterior hairline does not change (no posterior shift is observed);
- Thinning and bleached hairs alternate with curls of normal structure, due to this the overall thickness of the hairstyle decreases, but, as a rule, there is no complete hair loss.
When examining a group of women over 50 years old, altered curls (devoid of color, short, thinning) were found in almost everyone, but not all of them had obvious signs of androgenetic alopecia.
In men, the incidence of androgenetic baldness reaches 95%:
- In a quarter of the subjects, noticeable bald spots appear by the age of 20;
- Two out of three men experience noticeable thinning by age 35;
- After 50 years, three out of four men already have a significant degree of baldness.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS, also known as ovarian hyperandrogenism, is a syndrome that is accompanied by dysfunction:
- ovaries - increased production of androgens, estrogens, no ovulation;
- adrenal cortex - hypersecretion of the same androgens;
- pancreas – produces a lot of insulin;
- pituitary gland;
- hypothalamus.
The disease consists of the development of an anovulatory menstrual cycle. In healthy women, a follicle grows in the ovary, which contains an egg in its body. The follicle matures, bursts and releases the egg. In PCOS, atresia (growth arrest) or underdevelopment of the follicle occurs. A cyst is formed from its remains.
The phenomenon repeats itself during almost every cycle. The resulting cysts literally fill the endocrine glands. As a result of the development of cysts, the ovaries increase in size and gradually lose their function. The consequence of these processes is infertility.
Infertility
Apart from reproductive problems, the dominant symptoms are:
- hirsutism described above;
- obesity;
- acne;
- increased pigmentation - mainly on the neck, above the upper lip, along the hairline on the forehead;
- clitoral hypertrophy;
- seborrhea.
What are the indications for the test?
Your doctor may order a test if you have problems such as:
- infertility;
- obesity;
- skin problems;
- osteoporosis;
- adrenal cancer;
- changes in the menstrual cycle;
- ovarian tumors;
- bleeding from the uterus.
As a rule, gynecologists, andrologists and endocrinologists send the test. However, you don’t have to wait for a referral from a doctor, if you have any of the signs of an increased amount of androgens, you can take the test yourself in any clinic.
There are a certain set of rules that should be followed before donating blood. In particular, fluorography and x-rays, as well as ultrasound and physiotherapy, should not be done before the test. If you are taking any hormonal medications, you should stop taking them for a while, if possible and if this does not harm your health. Otherwise, the test may be inaccurate.
In addition, the day before the test it is better not to eat or subject the body to high stress, not to take fatty foods, alcohol and refrain from smoking. It is worth paying attention to the characteristics of the female body; it is advisable to take the test between the 5th and 8th day of menstruation.
After you take the tests, you will be given a form on which your results will be written, and the results that a healthy woman should have. This way, you can independently assess your hormone levels. However, you should not make hasty conclusions and worry if you see deviations, because they do not always indicate a disease.
Its level can be influenced by dietary habits, lifestyle and season. For example, in spring the readings will always be lower than in winter. Hormone levels can be affected not only by physiological reasons, but also by psychological ones. So, if you are depressed, if you have experienced an emotional shock, then the level of the hormone can rise sharply. It is important to take the test in the morning because it is at this time that the maximum amount of the hormone is concentrated in your body.
Strong and courageous: how natural is it?
Hyperandrogenism - good or bad, the answer is clear. The increased production of androgen hormones in women, which are more typical for the male part of humanity, is a dangerous imbalance that can manifest itself from “harmless” hirsutism to virile syndrome. In any case, even a slightly increased level of androgens disrupts the functioning of the female body, which is fraught with the manifestation of the most common symptoms.
It is hyperandrogenism that is one of the links in the pathogenesis of the development of disease of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles. A high level of androgens in the female body provokes blockage of the excretory ducts, which is often observed during puberty. Androgen hormones in adolescents provoke characteristic rashes on the face, but disappear by a certain age. If symptoms of seborrhea and acne persist in a mature woman, this is a reason to undergo examination by an endocrinologist and gynecologist, since in most cases this may indicate polycystic ovary syndrome.
Androgens in the female body can provoke hirsutism. Which for most ladies is a serious blow to their appearance. A girl with excess hair on her body and face does not look attractive, especially if it is located in places more common for men. In addition, the hair changes from soft (fluff) and light to terminal, hard and coarse.
Symptoms of elevated androgen levels in women can manifest themselves in the presence of alopecia and baldness. What is typical for men becomes a disaster for women when they develop “bald spots” on the crown, temples or frontal part of the head. Examination and analysis of symptoms indicates prolonged and high hyperandrogenism, which occurs when there are neoplasms in the body that secrete androgens.
How to lower androgens with herbs?
Treatment with folk remedies for hyperandrogenism is carried out with various medicinal herbs that can block androgen receptors or suppress their production. These include:
- Medicinal dandelion roots (pharmacy herbal tea).
- Basil: a handful of leaves are soaked in 500 ml. hot water overnight. Drink half a glass in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Licorice (licorice horst dragee).
- Cohosh (pharmacy drugs Klimadinon, Estrovel, Remens).
- Mint: 50 g of mint leaves are immersed in 300 ml. hot water, infuse and take half a glass 2 times a day.
- Wheat germ: consume fresh daily in the morning.
- Flax seeds can be purchased at the pharmacy. They are taken 1 tablespoon 1 time per day.
- Sage: tea bags of pharmaceutical sage are consumed 3 times a day, first immersed in 200 ml of boiling water.
- Unripe oats are used in the form of a decoction: for 1 glass of oats - 1 liter of water, boil for half an hour, then leave for 3 days. Take half a glass 2 times a day.
- Green tea can be drunk in its traditional form or in capsules (extract).
It is necessary to treat elevated androgens over a long period of time and comprehensively, strictly following all doctor’s instructions. Herbal components should only complement and not replace traditional therapy. Folk remedies are not effective in treating insulin resistance.
Source
Consequences for the body
Estrogens are responsible not only for “female appearance” and the realization of reproductive potential, but also protect the body from many pathological conditions. An imbalance between estrogens and androgens can lead to the following consequences:
- problems with pregnancy - infertility, early and late miscarriage;
- increased risk of developing cancer - endometrial, breast, cervical;
- gynecological diseases - dysfunctions, ovarian cysts, endometrial hyperplasia and polyps, cervical dysplasia, mastopathy occur more often;
- somatic diseases - a tendency to hypertension and obesity, strokes and heart attacks occur more often.
Caution - antiandrogens!
It is important to remember that, despite the availability of herbal treatment with antiandrogenic effects, their prescription, as part of a comprehensive infertility treatment program or as preparation for IVF, should be administered by a qualified reproductive specialist, gynecologist, and andrologist.
Herbal medicine is not a panacea for any form of infertility! This is only an additional, auxiliary method that helps make special adjustments to modern protocols for getting rid of infertility.
androgens, infertility
How to diagnose hyperandrogenism
Before starting therapy, you need to conduct the necessary research to find out the cause of androgenization. Among the main diagnostic tests are:
- determination of the concentration of the following hormones in the blood - estradiol, testosterone, gonadotropin, androstenedione, dehydroepiandrosterone, prolactin, progesterone;
- determination of insulin content;
- Ultrasound examination of the ovaries and adrenal glands.
As a last resort, a tomography of the genital organs and abdominal cavity is performed.
Complications
Adrenal hyperandrogenism is a serious pathology that can lead to significant complications. With congenital hyperandrogenism, abnormal development of the genital organs occurs. Disorders of the reproductive system can lead to miscarriage, chronic inability to bear a child, and infertility. With hyperandrogenism resulting from adrenal tumors, there is a risk of developing malignant neoplasms and metastasis.
When do estrogens go away?
The level of estrogen in women determines many things, the symptoms of their deficiency determine various pathologies, the lack of female sex hormones leads to disruption of the functioning of organs and systems, as well as to premature aging.
A decrease in estrogen often leads to poor health, in particular:
- Blood pressure surges.
- Violation of thermoregulation, throwing you either hot or cold.
- Bad mood, loss of strength and constant weakness.
We recommend reading: Is it possible to get pregnant while taking birth control pills: the likelihood of pregnancy
Hormonal imbalance can affect the entire body, a person begins to “lose ground” and from being energetic, full of vitality and plans, will turn into a “wreck”, suffering from memory deterioration and lack of concentration.
Symptoms of a decrease in estrogen in adulthood, especially after menopause, are expressed in a decrease in bone density, which is why complex fractures are so common in the postmenopausal period.
Lack of estrogen during puberty provokes delayed sexual development, increased hair growth is observed, menstruation arrives late, and infertility subsequently develops.
Inability to conceive is the main symptom of a lack of estrogen in women; it is this circumstance that brings them to a gynecologist, forcing them to undergo a list of studies and subsequently appropriate treatment.
Anabolic steroid
Anabolic steroids are compounds similar in chemical structure to androgens. Just like androgens, they stimulate protein synthesis and bone calcification. At the same time, the specific androgenic effect of these substances is less pronounced.
Nandrolone (retabolil) is administered intramuscularly once every 3-4 weeks for muscular dystrophy and osteoporosis.
- in children - accelerated growth of epiphyseal plates, premature ossification, growth retardation, early puberty, virilization;
- in women - masculinization, deepening of voice, ovulation disorders, hirsutism, male pattern alopecia, acne; during pregnancy – teratogenic effect;
- in men - irritability, increased aggressiveness, mood swings, depression, increased and then decreased libido, decreased testosterone production, testicular atrophy, sterility (suppression of spermatogenesis; recovery after a few months),
When using anabolic steroids, there may be an increase in blood pressure (sodium retention), liver dysfunction, and an increased risk of coronary insufficiency.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, an increase in the level of male hormones - especially in the early stages - causes spontaneous abortion.
The cause of interruption of gestation is a pathological change in hormonal levels. The fertilized egg cannot attach to the uterine endometrium and is rejected.
By 12–14 gestational weeks, the corpus luteum, which is responsible for the development of pregnancy and the production of testosterone, fades away. It is replaced by the placenta. From this moment on, the risk of miscarriage due to high androgen levels is sharply reduced.
Repeated danger occurs at 18–20 weeks and at the end of gestation, when an excess of male hormones can lead to early discharge of amniotic fluid and the onset of labor.
Treatment
Therapeutic tactics are determined depending on the disease provoking hyperandrogenism.
Most often, combined oral contraceptives are prescribed. With the development of adrenogenital syndrome, treatment with glucocorticosteroids is necessary.
If the cause of the pathology is hypothyroidism or an increase in prolactin levels, then the patient needs drug correction of the original sources. Stabilization of hormonal levels will occur on its own.
Doctors often turn to herbal androgens for women. These are substances of natural origin, and therefore their use is accompanied by a minimum number of side effects.
Among plants and herbs, saw palmetto, stevia, angelica, and licorice root have a good antiandrogenic effect.
Replacement therapy
If manifestations of low testosterone levels bother the patient, a urologist-andrologist or endocrinologist may prescribe replacement therapy. The reason for this should be a combination of objective signs (for example, a decrease in testosterone levels in the blood) and subjective ones - if the patient is not satisfied with his quality of life, productivity, mood, sexual activity.
Androgen replacement therapy has contraindications and side effects that the doctor must also consider. Testosterone is contraindicated for people with thrombosis, strokes and heart attacks, as well as a history of gynecomastia and cancer.
Testosterone is most often found in the blood serum in an inactive state. Therefore, to prepare therapy, it is necessary to undergo several types of hormone tests. This will be free testosterone - present in the blood, but not bound to proteins; general testosterone - attached to transporter proteins; luteinizing hormone (LH) - it stimulates the cells of the gonads that produce testosterone; and prolactin - increased levels of this hormone can reduce the level of LH and, as a result, androgens.
A decrease in testosterone levels in older age is a normal story, as “normal” as a life expectancy of 45-50 years. Nature cares about people only during their reproductive activity - the state of health and quality of their life after 45 years of age is of little concern to her. But over the past hundred years, life expectancy has increased—and along with it, our ideas about when it’s time to retire have changed.
Therefore, if you want to maintain good health in body and spirit, continue to do what you love or, for example, run a country, in consultation with your doctor, you can choose hormonal therapy and help your body cope with the challenges posed by the modern world. Especially for Giktimes readers, a consultation with an endocrinologist or urologist-andrologist at the Atlas clinic with a 15% discount.
Drug treatment
You cannot lower the concentration of androgens in the blood on your own, as improper use of medications will lead to dire consequences. Most often, drugs in tablet form are used for these purposes:
Nutrition for hyperandrogenism
Often the cause of this disease is a woman’s poor diet, which excludes animal foods from the diet. How to reduce? You can reduce androgen if you completely abandon vegetarianism and include meat and food of animal origin in your nutrition program.
A woman with high testosterone needs to consume dairy products and white bread daily. The menu should also include fried vegetables, honey, soy and vegetable oils. Food should be seasoned with a small amount of salt, and sugar should be added to tea or coffee.
If a woman is overweight, then to lose weight she should choose any method other than diet. Many experts advise doing yoga. It will help cleanse and restore the body, and also contribute to the proper functioning of the endocrine system. Pilates classes will also have an effect.
Every woman needs to monitor the level of testosterone in the body, prompt diagnosis and treatment. Reduced levels of the male hormone negatively affect the functioning of the body. Therefore, it is better when the hormone levels are normal.
Disease prevention
Speaking about the prevention of hyperandrogenism, experts first of all advise women to radically change their lifestyle. If you are overweight, you need to properly adjust your diet. Important: fasting during hyperandrogenism is strictly contraindicated. Moderate nutrition, giving up bad habits and an active lifestyle are the best way to promote good health and normal metabolism.
Creating a positive psychological mood, communicating with family and friends, varied hobbies and playing sports are necessary conditions for improving a woman’s health and creating her psychological comfort.