Discharge from candidiasis in men and women
Discharge is one of the most characteristic symptoms of candidiasis in women and men. In both cases they have a white tint and a cheesy consistency. It occurs infrequently in men; the most common symptom of candidiasis is itching, dry skin of the genital organs. Such symptoms can be triggered by the following predisposing factors:
- microflora imbalance;
- prolonged stress;
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics, cytostatics, immunosuppressants, hormonal drugs;
- exposure to pathological conditions: diabetes mellitus;
- hormonal fluctuations: menopause (including male), pregnancy, lactation;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- errors in nutrition: the presence of a large amount of sweets, simple carbohydrates, baked goods, yeast products, fermented milk products with fungal starter.
Considering that the disease is very common, it is important for women to know what discharge may occur with thrush. Discharge from candidiasis in women and men can be not only white or yellowish in color. Depending on the accompanying disorders, biological material may have a brown, pink, reddish, greenish tint. Thrush is not always accompanied by discharge, which may indicate chronicity of the pathological process. The main manifestations of the disorder are itching, swelling, hyperemia of the genital organs, discomfort after sexual intercourse.
Possible diseases
Very often, foamy discharge in women is a sign of infection of the external or internal genital organs. Most often, this symptom occurs with trichomoniasis and bacterial vaginosis, less often with candidal vaginitis - thrush.
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis (trichomoniasis) is a genitourinary infection common among the fair sex. According to WHO, up to 10% of the world's population is infected. Every year, new cases of the disease are registered in 170 million people.
The causative agent of the infection is Trichomonas vaginalis. It is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person during unprotected sexual contact and settles on the mucous membrane of the genital tract. If the typical localization of trichomonas in men is the urethra, prostate gland and seminal vesicles, then in women inflammation of the urethra and vagina usually occurs.
The incubation period of the disease is 7-30 days. Typical symptoms of infection in representatives of the fair half of humanity are:
- foamy discharge;
- itching, burning, pain in the area of the urethra and vagina;
- vulvar hyperemia;
- pain during and a few minutes after urination;
- discomfort, pain during sexual intercourse;
- sometimes – pain in the lower abdomen.
There are two forms of the disease - acute and chronic. During primary infection, acute trichomoniasis develops, accompanied by pronounced clinical symptoms. Discharge from the genital tract is profuse, foaming, yellow or greenish, with an unpleasant putrid odor. Often the disease is combined with other STDs (gonorrhea, chlamydia, gardnerellosis) due to common routes of infection.
If trichomoniasis was not diagnosed in time and the patient was not provided with the necessary treatment measures, the disease becomes chronic. At this stage, itching, soreness and other pathological symptoms decrease, and the volume of discharge decreases. The patient feels much better, but the pathological process in her genitourinary system continues.
Chronic trichomoniasis is dangerous not only for its hidden course, which promotes the spread of infection, but also for the high risk of complications. Most often, women develop trichomonas salpingoophoritis, which ultimately leads to irreversible infertility.
Bacterial vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis (the term gardnerellosis is also mentioned in the literature) is the second most common cause of foamy discharge. The disease is not caused by an inflammatory process in the vagina, but by a significant violation of the ratio of “beneficial” and “harmful” microflora of the genital organs. With this pathology, the physiological level of lactobacilli, which normally constitutes up to 95% of the vaginal biocenosis, critically decreases and is replaced by opportunistic microorganisms - anaerobes and gardnerella.
Number and type of discharge
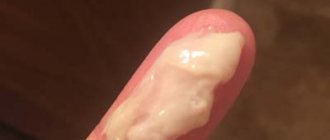
When a patient wants to know for sure what discharge from thrush looks like, doctors often draw an analogy with kefir or cottage cheese. If the disease proceeds without complications, then in the classic course of candidiasis the discharge has the following characteristics:
- White color;
- curdled consistency;
- moderate amount;
- smell reminiscent of dairy products;
- after the discharge dries, yellowish stains remain on the underwear.
In the early stages of candidiasis, small white grains can be found in the liquid discharge material. If there is no quality therapy, the grains will turn into lumps. White clots accumulate on the walls of the vagina and formations are formed that are similar in appearance to a curdled mass. Strong and abundant discharge disturbs a woman and causes discomfort.
With chronic thrush, there may be no discharge at all and the disorder is discovered by chance, during a routine gynecological examination. A similar phenomenon is also characteristic of the latent course of the disease. There are no changes in vaginal mucus; white patches can be so insignificant that they often go unnoticed.
Treatment and prevention
After determining the exact diagnosis of the infectious pathogen, the gynecologist begins to develop an individual treatment system, which will significantly depend on the specific pathogen, concomitant diseases, and the degree of infection of the external genital organs.
Metronidazole has long been considered one of the best drugs for the treatment of trichomoniasis. Moreover, local forms of drugs are ineffective because they cannot completely get rid of the infection. Use tablets for oral use. The dose and duration of therapy are considered by the gynecologist on an individual basis.
During vaginosis, treatment is usually based on taking Clindamycin and Metronidazole. The combination of these drugs makes it possible to successfully remove excessive amounts of pathogenic organisms. Metronidazole suppresses the appearance of nucleic acids in the causative agent of the disease, and Clindamycin blocks the formation of protein. In addition, the treatment regimen for vaginosis may include the following:
- vitamin complexes;
- healing and strengthening drugs;
- use of lactobacilli.
The basis of treatment for thrush is antimycotics. They can be used both vaginally and orally. The following drugs can be used:
Important: Topical preparations for the treatment of candidiasis, which are based on vegetable or mineral oil, may damage condoms. During therapy, you need to use a different method of contraception or abstain from sexual intercourse for a short time.
In addition, women are required to follow doctor's prescriptions regarding diet (exclude fresh baked goods and sweets from the diet) and lifestyle (maintain personal hygiene and use comfortable underwear made from natural materials). To strengthen the immune system, plant adaptogens and vitamin complexes are used.
Any vaginal discharge with or without odor is a reason to observe how the body is working. There is no need to be embarrassed by this problem. Today, methods of treating nonspecific vaginal diseases are safe and make it possible to achieve the desired effect in a short time.
Abundant foamy discharge in women indicates that an infection has entered the genitals, as a result of which the microflora has been disrupted. The reasons for this problem can be different: weak immunity, taking medications, disruptions in the endocrine system, violation of personal hygiene rules. All this allows pathogens to attack the body. If the infection penetrates the uterine cavity, inflammation of the endometrium may develop.
Difference from natural secretions
White discharge often occurs in women before menstruation and has nothing to do with vaginal candidiasis. It is at this time that the amount of mucus secreted changes and its consistency may change. Small particles may be present in the biological material - this is exfoliated endometrium. If the consistency and appearance of the discharge has changed, but there are no accompanying symptoms of thrush, this can be considered a variant of the norm.
The appearance of discharge on underwear or panty liners may be a sign of thrush
Thrush is characterized by white spots or an abundant cheesy mass, which is accompanied by itching, burning, and unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen. A white coating remains on the linen; itching cannot always be eliminated with the help of baths based on chamomile and soda. This indicates the widespread spread of the pathological process, the rapid growth and multiplication of the fungal infection.
Discharge with blood
Blood impurities are not always regarded as a pathology; their volume, the phase of the cycle and the general condition of the woman are important. If there is a slight discharge with blood in the middle of the menstrual cycle, then this is a sign of the release of a mature egg from the ovary. Blood impurities are insignificant and gradually disappear.
White vaginal discharge mixed with blood in the second half of the cycle should be regarded as a likely sign of beginning menstrual bleeding.
If there was no menstruation for a long time, and then blood appeared, then this is a possible symptom of a miscarriage - an urgent consultation with a gynecologist is required.
Among women
In order to detect the disease in time, women should know which discharges they have normally and which ones require contacting a gynecologist. Moderately liquid discharge of a transparent color, without lumps, grains, or itching is considered normal for women. This is a natural physiological fluid that occurs in response to various hormonal changes in the female body: ovulation, pregnancy, the beginning or end of menstruation.
Natural female secretions include:
- epithelial cells covering the uterus, which are regularly renewed;
- mucus contained in the cervical canal: the cervix is equipped with special glands that synthesize mucus, which perform a protective function and protects the organ from the effects of pathogenic microorganisms;
- representatives of friendly and opportunistic microflora, which are normally found in a woman’s vagina.
Doctors note that normally the mucus discharge is scanty, odorless and without foreign impurities . Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, environmental factors, and nutrition, the discharge may acquire a slight yellowish tint. Discharge with a denser consistency, colored in a distinct yellow, brown, pink, or green tint is an alarming signal that requires consultation with a doctor.
A change in the color of vaginal discharge may indicate the progression of the inflammatory process or the addition of a bacterial infection.
Particular attention is paid to the smell of discharge:
- a sour smell may indicate active growth and reproduction of a fungal infection;
- a fishy smell indicates the active growth and reproduction of gardnerella against the background of reduced local immunity, progression of vaginal candidiasis and dysbacteriosis. The progression of vaginosis is provoked not only by the smell of fish, but also by the mucus turning green;
- The smell of metal often accompanies bloody discharge. This characteristic of discharge is especially dangerous in the middle of the cycle, when there are several weeks left before the onset of menstruation;
- smell of rot may indicate the progression of the oncological process.
An unpleasant odor is a sign not only of thrush, but also of many serious and dangerous diseases.
Clear, odorless discharge does not require specific therapy. All a woman needs to do to support her reproductive system: observe the rules of personal hygiene, refrain from self-medication, and undergo a regularly scheduled examination by a gynecologist. Natural discharge normally does not cause psychological or physical discomfort.
White discharge appeared. Should we sound the alarm?
Contrary to popular misconception, vaginal discharge is an absolutely natural state of intimate affairs for a healthy woman who has entered reproductive age. The female body, trying to prevent infections from entering the genital organs, produces a certain amount of special secretion. This secretion cleanses and moisturizes the vaginal mucosa, preventing possible discomfort from dryness and a feeling of tightness.
In most cases, the consistency of such discharge may be slightly viscous or smearing. There is practically no characteristic smell. The color of the discharge can vary from clear to white or slightly yellowish in different women and at different periods of the menstrual cycle. The amount of mucus secreted is usually small, except when a woman is pregnant or in the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle - after ovulation and before the onset of menstruation.
This also applies to cases where a woman is sexually aroused, has recently given birth and is breastfeeding. Then the discharge becomes more abundant than usual, sometimes changing color a little, becoming slightly white. The volume of daily secretions, as a rule, rarely exceeds 1 ml. The discharge does not cause any discomfort. Once on panties, they can leave small, faint stains that can be washed off without difficulty.
When does it make sense to see a doctor, and how can he help?
If the discharge has acquired an unusual, pungent odor, changed color, consistency, or is accompanied by symptoms such as itching, burning, pain, then you should definitely see a gynecologist. Such changes may indicate the presence of a vaginal infection, the development of an inflammatory process, or the onset of an infectious disease. Attentive attitude to your body and timely contact with a specialist will help to avoid the development of the disease and stop the process at the initial stage.
The gynecologist will prescribe smear tests and bacterial cultures, which will help find out the true cause. It is strictly forbidden to resort to antibiotics, folk remedies or other self-medication measures at this stage. The insidiousness of infectious diseases is that, despite exactly the same symptoms, one disease can quite successfully masquerade as another. But the approach to treatment is radically different, and the use of inappropriate methods can seriously aggravate the course of the disease.
If you notice strange white vaginal discharge, don't panic. Seeing a doctor will speed up recovery: as a rule, treatment of white discharge almost always has a good prognosis.
Possible causes of white milky discharge
Here are just a few common reasons. It should be noted that this is only a small fraction of the possible factors influencing the occurrence of white vaginal discharge. Therefore, diagnosing yourself or hoping that everything will go away on its own is blatant negligence towards your body. A woman should monitor her feminine health with special diligence. After all, this is not only the key to the birth of healthy offspring, but also the prolongation of one’s beauty and youth for many years.
So, when you don’t need to be afraid of heavy milky vaginal discharge:
— After sexual intercourse.
It happens that after sexual intercourse a woman notices the presence of white milky discharge. These may be remnants of natural lubrication released by the body during sex. If sexual intercourse was unprotected, then in the next few hours, sperm residues may be released from the genitals in the form of white or yellowish clots. This is a completely normal occurrence and should not cause concern.
— During pregnancy.
If you are expecting a child, then the usual clear discharge may intensify, become thicker and more viscous. This is due to the active work of the hormone progesterone, and is not a problem requiring the participation of a doctor.
When milk discharge is a sign of illness:
— Candidiasis.
The notorious thrush. The course of the disease is accompanied by abundant white discharge, reminiscent of flakes of freshly prepared cottage cheese, often with a sour odor. The cause of candidiasis is an increase in the number of microorganisms of the genus Candida or the penetration of pathogenic strains of the fungus into the body. The discharge includes dead epithelial tissue, vaginal mucus, and fungus. This fungal infection destroys the normal microflora of the mucous membrane and provokes the appearance of milky vaginal discharge, accompanied by itching and burning in the vagina. A woman infected with the fungus may experience pain during urination and sex. You cannot become infected with candidiasis either sexually or through personal hygiene items - this fungus lives in almost all of us, but under favorable conditions it begins to attack the body.
— Bacterial vaginosis.
Beli. This disease is characterized by copious grayish or white creamy vaginal discharge with a repulsive odor. Most often this smell is characterized as the smell of rotting fish. The discharge is a mixture of vaginal mucus, epithelial tissue and microbial masses. Bacterial vaginosis is a non-inflammatory process, which is accompanied by a decrease or absence of lactoflora. It is replaced by polymicrobial associations of anaerobes and Gardnerella. This disease can cause menstrual irregularities.
— Trichomonal colpitis.
Milky white discharge consists of epithelium, vaginal mucus and leukocytes. This disease is an inflammatory process in the vagina. Inflammation can easily affect the uterus, cervix or appendages, causing serious problems such as infertility or cervical erosion. Trichomoniasis can be contracted not only through sexual contact, but also through household contact.
Follow the rules of intimate hygiene, do not ignore the changes occurring in your body, do not engage in self-diagnosis: then your women's health will always be in order. Be healthy and happy!
Women are sensitive creatures, so any change in the body raises questions and sometimes gives rise to fears. And, of course, the area of reproductive health worries women, perhaps most of all.
Such delicate processes in the body as discharge do not go unattended. Let's look at this in more detail. odorless - any woman knows what it is. But nevertheless, discharge will tell a lot about health, since, although it is a process provided for by nature, it can be a beacon of what is happening in the body.
First, let's define why we need white odorless discharge, what function does it serve?
By the way, if the discharge is odorless and does not resemble milk or cottage cheese in consistency, this does not mean that everything is fine. They may not have any odor, but if they are abundant or not mucous, but, say, transparent, like water, then this is another reason to go to the doctor. The smell does not always appear.
A sensitive barometer of reproductive health and general condition of the body.
Many women today are concerned about the causes of milky vaginal discharge. Every regular on various Internet forums strives to express their knowledge about the origin of this unpleasant phenomenon; in addition, there are all kinds of expert consultations directly online.
In general, a variety of measures are being taken to find out once and for all what kind of female disease milk discharge symbolizes.
In men
The male reproductive organs function in tandem with numerous glands: sebaceous, seminal, and sweat. They are localized on the surface of the skin and under it, in the pelvic area. Each gland produces its own secretion, which affects the functioning of the entire male body. Normal discharge occurs in men under the influence of the following factors:
- sexual arousal: transparent, odorless mucus is produced, the volume depends on the individual characteristics of the man’s body;
- functioning of the sebaceous glands with subsequent secretion of smegma;
- After sexual intercourse, it produces seminal fluid.
Men pay attention to the same indicators as women. A small amount of odorless mucus discharge, foreign impurities and coloring is normal and does not require specific therapy. If you experience curdled, yellow, green, brown, pink discharge with an unpleasant odor, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Pathological mucus may indicate the progression of sexually transmitted, inflammatory diseases, as well as traumatic lesions.
With or without sour odor
The smell of vaginal discharge is an important sign for a comprehensive health assessment. A woman should know the following:
- white discharge without odor and itching is normal for any stage of the menstrual cycle and trimester of pregnancy;
- white discharge with a sour odor is a normal variant, since lactic acid bacteria are present in large quantities in the vagina, which produce lactic acid and cause a specific sour odor, but there is no discomfort;
- white, thick, odorless discharge - typical of the second stage of the menstrual cycle, when the concentration of progesterone increases;
- abundant white odorless discharge in the middle of the menstrual cycle is a possible sign of ovulation and a favorable period for conception; in a pregnant woman - a possible sign of labor beginning;
- White discharge in women with the smell of fish or rotting is a symptom of pathology in the reproductive system.
If a woman develops white discharge with an odor that was not there before, then it is necessary to contact a women's doctor and have a culture of the discharge done to identify pathogenic microflora of the cervix and vagina.
White, odorless discharge in women is a physiological process that only requires compliance with female intimate hygiene.
For other diseases
White discharge with accompanying itching, burning and discomfort is a classic indication of progressive candidiasis. However, thrush may be accompanied by other physiological conditions and disorders, which leads to the coloring of biological material in other colors.
Green discharge is considered one of the most dangerous and may indicate the development of purulent inflammation. They often occur when a secondary infection occurs, as well as against the background of advanced diseases of the reproductive system. Discharge with a pungent, unpleasant odor is especially dangerous.
Brown discharge is a characteristic sign that is observed at the end of menstruation. After the bleeding is completed, residual blood is released, which coagulates and turns the curdled discharge brown. However, there are other possible reasons for this coloration, especially if brown discharge occurs in the middle of the cycle:
- progressive or chronic inflammatory process;
- oncological diseases;
- hormonal imbalance;
- sexually transmitted infections.
During pregnancy, this can be an alarming symptom associated with placental abruption.
Bloody discharge not associated with menstruation, especially during pregnancy, can be a dangerous signal. If they appear, you should immediately seek medical help.
If vaginal candidiasis is accompanied by blood-streaked discharge, this may indicate the development of the following pathological conditions:
- hormonal imbalance;
- cervical erosion;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- progression of endometriosis or fibroids.
Sometimes spotting is caused by the onset of menstrual bleeding. In other cases, this is an alarming signal that indicates violations of the reproductive system.
Yellow discharge is often associated with the use of antibiotics, as well as the use of multivitamin complexes, which include B vitamins. Such a reaction of the body is transient and often resolves itself after stopping the use of the medication. However, with prolonged yellowish discharge, it is necessary to exclude the progression of endometriosis or adnexitis. In this case, such coloring is associated with the destruction of leukocytes against the background of a long-term inflammatory process.
With pinkish discharge, cheesy formations mix with a small amount of blood. The main reasons for this clinical picture:
- the onset of menstrual bleeding;
- cervical erosion.
Pink discharge is not observed every cycle, but occurs periodically, once every 3-6 months. This is an alarming symptom that requires consultation with a gynecologist and a comprehensive diagnosis.
Vaginal discharge | types, causes, treatment Polyclinic
Vaginal discharge is the result of the work of glands located in the vaginal mucosa. By the nature of the discharge, you can assess the condition of the female genital organs.
Normal vaginal discharge is not considered a disease, as it is necessary for the normal functioning of the reproductive system.
In the vestibule of the vagina and near the cervix there are secretory glands that produce mucus necessary to moisturize the mucous membrane and form healthy microflora.
Healthy discharge is formed in a small volume, it is transparent, odorless and not accompanied by pain or itching. When the type of discharge changes, this indicates the presence of a pathological process in the female genital organs.
Types of discharge
Depending on the amount of mucus produced, discharge is divided into scanty, abundant and normal.
Scanty is a discharge that is not enough for the normal functioning of the vagina and external genitalia. The mucous membranes begin to dry out and crack. During sexual intercourse, friction and pain are felt. Scanty discharge is the result of hormonal changes due to age, endocrine disease, or taking hormonal medications.
Heavy discharge is a discharge that leads to a constant feeling of moisture in the vagina. They are noticeable on underwear.
Heavy discharge can be diagnosed in young women during ovulation in the middle of the menstrual cycle; it is transparent and does not have an unpleasant odor. During pregnancy, especially before childbirth, the discharge also becomes more abundant.
These are healthy discharges and should not be feared. If the consistency, volume, color or smell of the discharge changes, this indicates the beginning of a pathological process.
Discharge that sufficiently moisturizes the vagina and does not cause discomfort is considered natural. If there is normal discharge, additional moistening of the vagina before sexual intercourse is not required.
The consistency of the discharge varies from watery, mucous, curdled and foamy.
- Liquid discharge - watery and mucous - odorless and colorless is considered normal. Watery discharge occurs in the middle of the cycle during ovulation; mucous discharge appears during sexual intercourse and serves as a lubricant.
- Thick, cheesy discharge indicates the presence of a fungal infection. Doctors usually diagnose candidiasis. The discharge resembles liquid cottage cheese, it is not uniform in consistency.
- Foamy discharge indicates the presence of a bacterial infection. This is especially dangerous if they have an unpleasant odor or distinct color. Foamy discharge is a hallmark of trichomoniasis.
Based on the color of the discharge, there are clear (normal), white, bloody, yellow, green and brown.
- Clear discharge is normal. They are usually invisible on underwear and on the body.
- Thick white discharge indicates the presence of candidiasis (thrush). In a healthy state, white discharge may appear before childbirth.
- Bloody and brown discharge is the most dangerous, as it signals the presence of blood in the vagina. Normally, they occur only during menstruation. When taking hormonal contraception, especially in the first months, the appearance of intermenstrual bleeding is acceptable; this is considered normal and indicates the body’s adaptation to artificial hormones. In other cases, spotting indicates the presence of a serious pathology or the onset of bleeding.
- Yellow and green discharge indicates the presence of an infectious-inflammatory process.
Based on the smell, discharges are differentiated: odorless, sweetish, sour, and unpleasant.
- The phrase “odorless discharge” is conditional, since all human discharge is characterized by some odor. In a healthy state, this smell is pleasant and subtle. It is individual for each person. Since a person feels it constantly, he eventually stops feeling it. If a woman does not smell the discharge, it can be stated that it is odorless discharge.
- Discharge with a sweetish or sour odor most often indicates thrush. Candida fungi use sugar for nutrition, love it and live in an environment rich in sugar.
- Foul-smelling discharge is caused by a bacterial infection. They often smell like stale fish. The characteristic fishy smell is produced by anaerobic bacteria. The stronger the smell, the stronger the infection.
Reasons for appearance
Intimate secretions serve as a kind of indicator of the health of the female sphere.
With natural discharge that does not cause discomfort, we can conclude that the organs of the female reproductive system are healthy. However, regular examinations by a gynecologist at the beginning of the cycle are still necessary. Many pathological processes occur without symptoms; their presence can only be demonstrated by a gynecological examination and laboratory tests.
Several factors can influence the appearance of discharge in a healthy woman. These are stress, climate change, taking hormonal drugs, taking strong medications, allergic reactions. Personal hygiene can also affect the nature of the discharge.
A woman should be concerned when the discharge changes in consistency, acquires a strange color or smell, or changes in intensity. Often such discharge is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, itching, pain in the perineum, irritation of the external genital organs, and discomfort when urinating.
There are some symptoms that can be used to preliminarily identify the disease. Of course, an accurate diagnosis is only possible with a doctor after examination and laboratory diagnostics, but the appearance of some can give a more or less accurate picture of the disease.
White curdled discharge with a sweet or sour odor indicates candidiasis. Other symptoms of candidiasis are:
- burning, itching in the vagina and external genitalia;
- swelling of the vagina after sexual intercourse;
- pain when urinating and during sexual intercourse.
Excessive yellow or bloody discharge with an unpleasant odor may indicate bacterial vaginitis. This is an inflammation of the vagina caused by a violation of the microflora. This means that local immunity cannot restrain the growth of pathogenic bacteria; they attack vaginal cells, and the inflammatory process begins. Characteristic symptoms of bacterial vaginitis:
- redness, itching and swelling of the genitals;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- painful intercourse;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- weakness and fatigue;
- frequent urination.
Excessive foamy leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor may indicate trichomoniasis. The causative agent of the disease is Trichomonas. The following symptoms are also observed:
- irritation of the genitals and inner thighs;
- erosion of the mucous membranes of the intimate area;
- pain when urinating;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain during sexual intercourse.
Homogeneous yellow-green discharge with an unpleasant odor may be a sign of gonorrhea. This is an acute infectious disease caused by gonococcus and sexually transmitted. Symptoms of gonorrhea are:
- itching and pain in the urethra and vagina;
- increased body temperature;
- separation of pus from the vagina;
- frequent painful urination;
- enlarged and painful lymph nodes;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- loss of appetite.
Serous-purulent discharge with blood often indicates the presence of a cyst in the uterus or its appendages. Symptoms of a cyst, in addition to bloody discharge, are:
- discomfort in the vagina;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- increased menstrual flow;
- menstrual irregularities;
- painful menstruation.
Bright yellow and green discharge in copious amounts with a very unpleasant odor signal endometritis. This is an inflammation of the uterus caused by bacteria or injury. Symptoms of endometritis:
- acute pain in the abdomen, in its lower part;
- fever with chills;
- increased heart rate;
- painful urination;
- weakness;
- enlargement of the uterus caused by tissue inflammation;
- heavy and painful periods;
- infertility.
Brown discharge during delayed menstruation can indicate a pathological course of pregnancy, for example, an ectopic pregnancy. The likelihood of this pathology can be judged by the following symptoms:
- absence of menstruation;
- sharp or cramping pain in the lower abdomen, usually on the side;
- toxicosis and other signs of pregnancy.
This is a very dangerous condition that requires immediate medical attention. Even if the pregnancy is intrauterine, but there is spotting, you should immediately consult a doctor, as this is a sign of a threat of miscarriage.
Which doctor should I contact if I have abnormal vaginal discharge?
If you have discharge of an unnatural color, smell or consistency, you should visit a gynecologist. The doctor will ask about symptoms, conduct a visual examination, take a swab from the vagina and make a diagnosis based on the test results.
Analysis of vaginal discharge will show whether there is a bacterial, viral or fungal infection, and what the degree of infection is. After this, an ultrasound examination of the organs of the reproductive system is prescribed. An ultrasound will show the size of the organs of the female system, their position, the presence of neoplasms, for example, cysts or tumors, and will help to specify the diagnosis.
In addition, the doctor prescribes a general blood test, cytological examination and/or colposcopy.
In case of a cyst or tumor, additional consultation with an oncologist will be required. If heavy discharge occurs due to stress, it is useful to consult a psychologist. If sexually transmitted diseases are detected, a consultation with an immunologist will be required.
For long-term illnesses, it is useful to consult an immunologist and assess your immune status. If there is heavy discharge due to allergies, it is recommended to consult an allergist.
In children, unhealthy discharge is assessed by a pediatric gynecologist and pediatrician.
How to treat abnormal vaginal discharge
Treatment of problematic discharge should always be carried out with the participation of a doctor after a thorough diagnosis.
For bacterial infection and inflammation associated with it, antimicrobial drugs are prescribed. Antibiotics are prescribed orally and locally in the form of suppositories, creams, and ointments.
For fungal infections, antifungal drugs are prescribed. It is worth remembering that thrush is a local manifestation of extensive fungal damage to the body, and its treatment is not limited to suppositories and creams. The bulk of the fungus is located in the intestines, so it is worth treating the entire body as a whole, and not just the vagina.
For viral infections, antiviral drugs are prescribed. Viruses are dangerous organisms, and doctors have not yet learned how to effectively treat them. Increasing immunity plays a vital role here.
If tumors appear, they can be treated conservatively or removed. Here, the decisive role is played by the nature of the neoplasm - benign or malignant - and the speed of its development.
In case of intrauterine pregnancy with a threat of miscarriage, the patient is sent to the hospital, the condition of the uterus, placenta, and fetus is examined. In case of an ectopic pregnancy, immediate removal of the fertilized egg from the woman’s body is required.
In any case, when unhealthy discharge appears, very careful hygiene is required, since many pathological discharges corrode the skin of the genitals. Sometimes the doctor prescribes baths with medicinal solutions and douching.
There are many traditional methods for treating discharge. They sometimes help, but sometimes they can blur the clinical picture and complicate the diagnosis and treatment of the disease. Among the folk methods, washing with herbal decoctions is considered safe and useful.
Chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort relieve inflammation, increase local immunity and soothe irritated skin. Under no circumstances should foreign objects be inserted into the vagina, as some folk recipes advise.
This can harm the microflora and injure the already irritated vaginal mucosa.
How to prevent abnormal vaginal discharge
The first rule for preventing painful discharge is regular hygiene. You need to wash yourself every time after visiting the toilet and in the evening before going to bed.
Washing is carried out with clean warm water and special products for intimate hygiene. Regular soap can destroy natural microflora and promote the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
Hot water kills beneficial lactobacilli, and cold water can worsen a viral infection.
Underwear should be changed daily. Linen should allow air to pass through and absorb moisture, so it is recommended to use linen made from natural fabrics - cotton, linen. Synthetic underwear cannot be worn constantly.
Tight underwear and thongs contribute to irritation of the genital skin and reduce local immunity. Gynecologists do not recommend using panty liners, as they interfere with air exchange.
It's better to change your underwear more often.
Nutrition also influences the nature of discharge. Consuming large quantities of sweet foods increases blood sugar and promotes the rapid proliferation of Candida fungi.
Source: https://www.polyclin.ru/vydeleniya-iz-vlagalishcha/
Treatment
To get rid of discharge from candidiasis, it is necessary to direct efforts to suppress the growth and development of the fungus. Often, after treatment, pathological discharge disappears. To do this, they use an integrated approach: they use medications for local and systemic effects, diet, and observe personal hygiene rules. It is important to eliminate the source of stress, normalize work and rest, sleep, and restore normal functioning of the immune system.
Preparations for external treatment of thrush:
- women are prescribed suppositories with antimicrobial, antibacterial, fungicidal substances: Pimafucin, Clotrimazole, Polygynax, Mikozhinax;
- men are shown creams for treating affected areas of the penis: Pimafucin, Triakutan, Clotrimazole.
Both men and women are prescribed medications for a systemic effect on the disease: Fluconazole, Diflucan, Pimafucin.
After a course of antifungal therapy, efforts are directed toward restoring the natural microflora. For this purpose, probiotics are prescribed, which include friendly lacto- and bifidobacteria. Therapy must be supplemented with a diet: sugar, refined foods, starchy vegetables and overly sweet fruits, store-bought sauces, spicy, fatty, fried foods are excluded from the diet.
Treatment of foamy discharge, drugs
To select adequate therapy, it is important to establish the causes of foamy discharge. If trichomoniasis has caused foamy discharge, drugs from the 5-nitromidazoles category are used for treatment.
In this case, long-term therapy is carried out, and it does not always give good results. Sometimes bacteria are highly resistant to the product used.
- In such a situation, the doctor prescribes a second course of treatment using drugs from a different group.
Often the lack of effect of therapy is associated with constant infection from a sexual partner. Moreover, in men the disease is often asymptomatic. This is why it is so important to treat partners at the same time.
During the treatment of trichomoniasis, it is better to stop drinking alcohol and completely avoid sexual intercourse. Pregnant women should be treated under strict medical supervision, since medications negatively affect the development of the fetus.
If foamy mucous discharge appears due to bacterial vaginosis, treatment is selected only after laboratory diagnosis. As a rule, therapy includes several stages.
- Most often, doctors prescribe antimicrobial agents in the form of tablets, suppositories, and creams. During treatment, it is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol, as this often causes vomiting and abdominal pain.
At the second stage, it is imperative to restore the healthy microflora of the vagina. Eubiotics are used for this. These drugs contain beneficial lactobacilli that suppress the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
General information about trichomoniasis
The disease is caused by the protozoan parasite vaginal trichomoniasis. The vagina is the most common site of infection in women, and the urinary tract in men. The parasite is transmitted through unprotected sex with an infected partner.
Trichomoniasis is the most common but curable infectious disease. Women are more susceptible to infection.
Clear thick discharge
The lactobacilli contained in it give the vaginal discharge its transparent appearance. As already noted, clear or white thick discharge without itching, as well as without an unpleasant odor, rarely means a serious pathology. More often, their appearance is associated with changes in the nature of hormonal levels.
Transparent, resembling thick, viscous mucus, discharge is often provoked by a change in the composition and viscosity of the cervical mucus, when it becomes very dense or liquefies.
If the presence of a mucus-like secretion in the cervical canal is necessary for protection, then why does the cervical “plug” change its density? It turns out that the exudate of the cervical glands provides one of the important stages of conception - the transportation of sperm from the vagina to the uterine cavity. The cervical “plug” has a porous structure; the higher its density, the smaller the pore size. During the period of ovulation, when conception becomes possible, the viscosity of the mucus decreases and the size of the pores increases, so sperm penetrate into the cervical cavity and uterus. Cervical mucus also filters out high-grade sperm.
With hormonal dysfunction, normal changes in the viscosity of the cervical contents can provoke problems with conception. In the diagnosis of infertility and hormonal disorders, methods for determining the degree of viscosity of cervical secretions are often used.