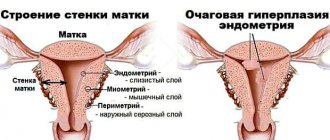
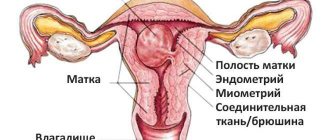
Endometrial hyperplasia is a pathological process that is expressed in thickening of the inner mucous membrane of the uterine cavity. Areas can appear in isolated places (then polyps or focal hyperplasia are formed) or diffusely throughout. Symptoms in patients:
- heavy and prolonged menstruation;
- the appearance of clots during menstrual periods;
- delays of up to 2 weeks or more;
- painful periods;
- spotting outside of menstrual periods.
Pathological growth of the mucous membrane occurs for various reasons. As a rule, disturbances in the balance of sex hormones with excess estrogen are found. This is precisely what the basic principles of treatment are based on - normalizing hormone levels with the help of various drugs.
Curettage is a diagnostic procedure, not a method of treatment . It is carried out to collect material (pieces of tissue) and its subsequent histological examination. This way you can exclude the malignant nature of the growth and select the most rational conservative therapy. After it, the symptoms temporarily disappear, but soon return.
Diagnostic curettage
In some cases, you can still try to start treatment without curettage, namely:
- if hyperplasia is suspected in young girls under 40 years of age;
- menstruation is not very heavy;
- symptoms started recently.
Suspicion of hyperplasia in women of premenopausal age and menopause always requires preliminary curettage , otherwise the malignant process can be missed.
As a rule, the course of treatment is at least 3 months , after which it becomes much better, or it is necessary to take more serious diagnostic and therapeutic measures.
The following groups of drugs can be prescribed:
- oral contraceptives;
- gestagens and progestogens.
When taken regularly, the level of endogenous estrogens drops along with drug-induced sleep of the ovaries, which leads to a therapeutic effect. The following drugs are often prescribed:
- "Regulon"
- "Janine"
- "Yarina"
- "Jess"
- "Klayra" and others.
They are taken one tablet daily at a fixed time for 21-28 days, depending on the drug. In the last 7 days, menstrual-like discharge should occur. If they are not abundant, then the therapy is effective. If a woman does not notice improvement within 2-3 months, it is necessary to reconsider the treatment or diagnosis.
In some cases, experts prefer gestagenic drugs. The essence of this treatment is to restore the balance between estrogens and gestagens. Are used:
- "Duphaston" 1-2 tablets from the 10th to the 25th days of the cycle or continuously;
- “Norkolut” from the 10th to the 25th days of the cycle or constantly 1-2 tablets;
- "Progesterone" in the form of injections.
In parallel with hormonal drugs, it is recommended to initially take hemostatic tablets on menstrual days: “Etamzilat”, vitamin C, “Ascorutin”, “Vikasol”, “Ditsinon”, “Tranexam” and others.
For the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia, the Mirena intrauterine hormonal system is used. This is a coil with a reservoir for progestogen, which can be gradually released, creating constant doses of the hormone in the blood. It is established for 5 years. The day before, it is advisable to confirm the diagnosis of hyperplasia histologically. Mirena is especially effective for a combination of hyperplasia and adenomyosis (endometriosis of the uterine body).
GnRH antagonists are a more severe group of drugs that act at the level of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus of the brain. Taking gonadotropic hormone agonists creates a state of artificial menopause in a woman’s body. Accordingly, there may be complaints of hot flashes, headaches, feeling hot, sweating and other symptoms of menopause. After the end of treatment, ovarian function gradually returns, all complaints also go away.
The following drugs are used:
- "Buserelin"
- "Zoladex"
- "Diferelin" and others.
The drugs are available in the form of solutions for intramuscular and subcutaneous injections, as well as in the form of sprays for nasal use. Treatment regimens usually include a single dose of medication every 28 days. The course is at least 3 months.
Androgens may be prescribed to women approaching menopause. To begin with, gestagens are used, and then androgens, so the body gradually plunges into menopause and menstruation never occurs again, and hyperplasia also regresses. Testosterone and Methyltestosterone are prescribed.
Doses and regimens are set individually. Usually the course lasts at least 2-3 months.
Options for action after completion of therapy:
- completion of treatment and regular examinations with ultrasound examination;
- prescribing another group of drugs;
- curettage or hysteroscopy to clarify the diagnosis;
- surgical treatment if the above methods are ineffective.
Ultrasound.
Endometrial hyperplasia Restoration of the reproductive system after taking hormonal drugs occurs quite quickly , but everything depends on the characteristics of the woman’s body.
In some cases, menstruation does not occur; additional treatment with hormonal drugs may be required.
If treatment is aimed at causing persistent menopause, menstruation does not occur at all.
Traditional methods can also be used to combat endometrial hyperplasia , but it is better to use them on the recommendation of a doctor and only with a confirmed diagnosis.
Recipes with boron uterus:
- Tincture. Take 20-30 g of dried herb and pour 500 ml of vodka or alcohol. Place in a cool, dark place and leave for 2-3 weeks. After this, strain the solution and take 20-30 drops orally 2-3 times a day.
- Decoction. Pour 1-2 tablespoons of the herb into 500 ml of boiling water and place in a water bath. Keep this for about 60 minutes. Drink 1 tbsp. l. morning, afternoon and evening.
For the burdock recipe, you need to take fresh roots and squeeze 1 liter of juice from them. The same should be done with the golden mustache . Mix 2 ingredients and take a tablespoon twice a day. The course is at least 4-6 months.
Nettle based recipes:
- Tincture. You need to take 200 g of grass and pour 500 ml of vodka or alcohol. Place in a dark and cool place for 2-3 weeks. Take 1 tsp. twice a day for several months.
- Infusion. You need to take 2-3 tbsp. spoons and pour 500 ml of water, put in a water bath for 20-30 minutes. Take 100 ml up to 5 times a day.
Read more in our article about the treatment of hyperplasia without curettage.
GPE - what is it?
GPE is a hyperplastic process of the endometrium. This is an oncological pathology, but is considered a benign formation and affects the mucous layer of the uterus.
Among gynecological pathologies, GPE in gynecology is characterized by thickening of the endometrium, which envelops the walls of the uterus. As a result of this, mucosal cells grow in an unusual way, which entails an enlargement of the uterus.
According to medical data, 70% of the fair sex diagnosed with GPE eventually develop uterine cancer. Because of such irreversible consequences, you should not resort to self-medication and delay a visit to the doctor.
Classification
First of all, the disease is classified according to the severity of hyperplastic processes:
- simple hyperplasia, in which there are no atypical cells, the structure of the endometrium is active, its components grow evenly, and vessels are also evenly distributed in the stroma. The degree of cystic expansion of some glands is moderate;
- complex or complex hyperplasia. In other classifications it is called adenomatosis. Not only does the glandular epithelium grow, but the structure of the glands also changes. There is no balance between the proliferation of glands and stroma.
In accordance with pathomorphological and cytological features, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- simple glandular - there is no cystic expansion of the glands or there is in some areas, then this is the glandular-cystic stage of this form;
- glandular-stromal - proliferation affects glandular and stromal structures. Only the superficial layer thickens, the basal layer remains unchanged;
- atypical glandular or adenomatous - proliferative changes can reach the basal layer of the endometrium, and a varied morphological picture is observed.
According to the severity of the ongoing processes, the disease can be mild, moderate and severe. Depending on the degree of prevalence, there are diffuse and polypoid hyperplasia or, as it is also called, local or focal. According to the WHO classification, endometrial hyperplasia without atypia is distinguished; an atypical type of pathology is also distinguished, in which atypical cells are found in the mucous layer.
Causes
The main reason that leads to hyperplasia in the endometrium is a hormonal imbalance in the female body.
Most often, neoplasms form in response to an increase in estrogen levels. An increase in the production of this hormone is observed during hormone replacement therapy.
But you can’t put all the blame on hormonal imbalance. No less important factors influencing hyperplasia may be:
- heredity and predisposition to the formation of neoplasms in the uterus;
- inflammatory processes affecting the ovaries and appendages (occurring in a chronic form);
- infertility;
- irregular menstruation;
- overweight;
- HIV;
- diabetes;
- polycystic ovary syndrome.
How is the disease diagnosed?
When diagnosing a pathology such as focal endometrial hyperplasia, a woman’s complaints are taken into account. The doctor must be aware of the course and regularity of menstruation, the amount of blood lost, the presence of pain or discharge between menstruation.
Externally, pallor of the skin is revealed due to anemia, which develops against the background of prolonged blood loss, as well as neoplasms in the breast, such as fibroadenoma, which indicates a hormonal imbalance. During the initial examination, the uterus, vaginal walls, color and consistency of the endometrium, the presence of polyps and other formations are visualized.
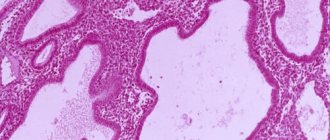
But the result of diagnosis is modern methods of visualizing internal organs - ultrasound, hysteroscopy, curettage, as well as blood tests for hormone levels.
Diagnostic curettage procedure - curettage
Diagnostics using curettage allows you to directly study particles of the endometrium that has undergone hyperplasia. The procedure is an invasive intervention that requires tests and particularly careful preparation. Curettage for hyperplasia is carried out in a hospital setting under general anesthesia using intravenous anesthesia. The use of anesthetics is not required only if the manipulation is performed immediately after a miscarriage or childbirth, when the cervix is dilated.
Curettage of the inner layer is carried out using a dilator, which opens the cervical canal. Using a surgical spoon (curette), a small part of the endometrium is carefully scraped off from different areas. A vacuum aspirator is used less frequently.
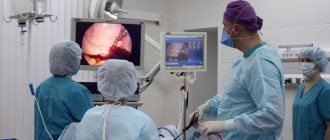
The manipulation is carried out almost blindly; a hysteroscope is rarely used for control purposes. It allows you to display an image on a monitor, where the areas of tissue sampling are clearly visualized.
In the case of focal hyperplasia, curettage is not advisable, since during manipulation there remains a risk of taking endometrial particles from healthy areas. If the entire surface is affected, collecting tissue from any part of it will allow an accurate examination of the material.
Manipulation is considered not only diagnostic, but is also used in the treatment of various diseases, including endometrial hyperplasia. During the procedure, the upper affected layer of the uterus is removed, which allows you to quickly stop the bleeding.
Forms of hyperplasia
For the most specific selection of tactics for getting rid of gynecological diseases, endometrial hyperplasia was conventionally divided into categories that are characterized by special symptoms. This allows you to more accurately diagnose the advanced stage of the disease.
Hyperplastic processes of the endometrium are classified into the following types:
- simple (there is a noticeable enlargement of the glands, which does not disturb their architecture);
- complex (there is a heterogeneous accumulation of glands in the endometrium);
- complex and simple with atypia (the size of the glands increases, and symptoms of destruction of the structure of the cell nucleus become noticeable in the endometrium).
Among the three types of illness mentioned above, it is with atypia that the chances that the illness will develop into uterine cancer increase.
There is also a classification of endometrial hypertrophy according to forms, namely:
- glandular;
- glandular-cystic;
- cystic;
- focal;
- adenomatosis.
The most harmless and mild form of the disease is considered to be the glandular form. The probability that the disease will become malignant is no more than 6%. This form is characterized by active division of cells and compaction of the endometrium.
In this case, the glands have an uneven location; they may be noticeably pressed against each other, which does not prevent the release of the contents of the glands.
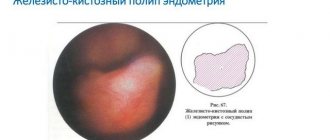
The glandular cystic form is characterized by cell proliferation, which impedes the outflow of mucus. As a result, the glands take on a cyst-like shape.
With the cystic form, the cells not only proliferate, but also increase in size. These changes make them look very much like blisters. Despite such transformations, the epithelium of the gland from the inside has the same appearance, which does not allow this form to transform into oncology.
The peculiarity of the focal form is that endometrial cells grow unevenly, forming separate foci that are susceptible to the effects of hormones.
With this form, the chances of the formation of a cancerous tumor increase, and if the changes are not uniform, then the form of the disease is otherwise called diffuse.
The most dangerous form of endometrial hyperplasia, which often ends in cancer, is adenomatosis. It is impossible to cure it with medications; the only way out is to remove the uterus.
Taking into account which form of the disease is diagnosed in a woman, appropriate treatment is selected for her, ranging from hormonal drugs to surgical intervention.
Mixed
Mixed endometrium is a hypoplastic type of disease, which is diagnosed during endometrial histology. The procedure is often prescribed to girls whose attempts to become pregnant for a year or longer have not been successful.
Features of this form of the disease are:
- insufficient development of the functional layer;
- identifying areas where secretory changes have occurred.
In most cases, the disease is diagnosed:
- in young girls diagnosed with ovarian hypofunction;
- in women with the onset of menopause.
Endometrial hyperplasia
This disease is characterized by changes in the endometrium, which often lead to malignancy. At the same time, the stromal and glandular layers of the endometrium stop “cooperating” with each other, which contributes to nuclear atypia.
Endometrial hyperplasia is classified into:
- simple (transforms into cancer in 1% of patients);
- complex (cancer develops in 3% of patients);
- simple with atypia (cancer patients 8%);
- complex with atypia (cancer is diagnosed in 29% of patients).
At risk for endometrial hyperplasia are girls who:
- critical days come earlier than expected;
- menopause is delayed;
- excess body weight.
- there is no desire to have a child.
Endometrial polyps
Endometrial polyps are a form of hyperplasia, during the development of which a growth is formed from the endometrium without malignancy. Very often, this form of the pathological process is diagnosed in girls aged 30-35 years.
It is impossible to identify the reasons that contribute to the formation of such growths. But there are factors that contribute to the formation of polyps, namely:
- high rates of estrogen production;
- injury to the uterus;
- termination of pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- high blood pressure;
- excess body weight.
The first signal that polyps are forming in the female body is the absence of menstruation. The symptom may be menstrual bleeding that occurs between periods.
With this pathology, women complain of pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen, and the nature of the pain is similar to contractions.
Please note that the formation of polyps is not always accompanied by pronounced symptoms; sometimes there may be no signs of the disease at all.
To avoid complications, you need to regularly visit a gynecologist; this is the only way to diagnose the problem in a timely manner.
Adenomatosis
Adenomatosis is a form of hyperplasia, which is characterized as a precancerous condition.
If you start a therapeutic course in a timely manner at this stage, in more than 90% of cases you will be able to avoid cancer.
This form of hyperplastic process promotes the proliferation of endometrial cells, resulting in an imbalance of hormones and, accordingly, a decrease in the protective properties of the body.
At the initial stages, the disease may not show symptoms, which is why it often goes unnoticed and appropriate treatment is not carried out for a long time.
You can get rid of the disease only after hormone therapy or surgery.
Traditional methods of treating endometrial hyperplasia without curettage
Traditional methods can also be used to combat endometrial hyperplasia, but it is better to use them on the recommendation of a doctor and only with a confirmed diagnosis. For this purpose, various herbs can be used in the form of tinctures, infusions, decoctions for oral administration or on vaginal tampons.
Hog queen
The recipes are as follows:
- Tincture. You need to take 20-30 g of dried herb and pour 500 ml of vodka or alcohol. Place in a cool, dark place and leave for 2-3 weeks. After this, strain the solution and take 20-30 drops orally 2-3 times a day.
- Decoction. 1-2 tablespoons of the herb should be poured into 500 ml of boiling water and placed in a water bath. Keep it like this for about 60 minutes. Drink 1 tbsp. morning, afternoon and evening.
Burdock
You need to take fresh burdock roots and squeeze 1 liter of juice from them. The same should be done with the golden mustache. Mix 2 ingredients and take a tablespoon twice a day. The course is at least 4-6 months.
Nettle
Recipes based on the plant are as follows:
- Tincture. You need to take 200 g of grass and pour 500 ml of vodka or alcohol. Place in a dark and cool place for 2-3 weeks. Take 1 teaspoon twice daily for several months.
- Infusion. You need to take 2-2 tablespoons and add 500 ml of water, place in a water bath for 20-30 minutes. Take 100 ml up to 5 times a day.
Herbal infusions
To prepare one of the effective drugs, you need to take the following ingredients:
- serpentine root;
- shepherd's purse;
- calamus root;
- cinquefoil root;
- knotweed grass;
- nettle leaves.
All components must be mixed based on the ratio 1:1:2:2:2:2. Then take 2 tablespoons of the mixture, pour 500 ml of boiling water, boil and place in a thermos for several hours. Drink 100 ml 1-2 times a day.
We recommend reading about how menstruation occurs with a polyp. From the article you will learn about what a polyp is, its effect on the menstrual cycle, conservative and surgical treatment of a polyp in the uterine cavity.
And here is more information about how menstruation occurs with a spiral.
Endometrial hyperplasia is a serious disease that is based on hormonal disorders. Based on this, treatment also involves taking medications that balance the ratio between estrogens and gestagens. For more effective and safe treatment, preliminary curettage or at least a biopsy of the endometrium is still recommended.
In some cases, treatment regimens may be prescribed without this, for example, in young girls or with unexpressed symptoms of the disease. It is also possible to supplement treatment regimens with folk recipes: boron uterus, burdock, nettle, as well as infusions of various herbs.
Symptoms
At the initial stages of the development of the hyperplastic process, the symptoms of hyperplasia are very difficult to ascertain, and the situation becomes especially complicated when polyps form. There are cases when a girl finds out about the presence of a disease during a regular examination by a gynecologist.
The main signs of endometrial hyperplastic process are irregular menstruation and intrauterine bleeding. In this case, the following are observed:
- frequent fluctuations in menstruation (there may be shifts or a complete absence of discharge throughout the month);
- heavy bleeding (more often occurs as a result of a long delay);
- unstable nature of discharge;
- spotting between periods (especially worrying for women after menopause);
- before critical days, spotting is observed;
- increasing the duration of critical days (discharge does not stop for 7 days or more).
The progression of the disease is often accompanied by pain, which intensifies with intimacy. Girls also complain of anemia, pallor, decreased activity and performance. Dizziness occurs no less often, appetite decreases, and lethargy appears.
Features of the uterine mucosa with hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia is a pathological process that is expressed in the thickening of the inner mucous membrane of the uterine cavity under the influence of various factors. Areas can appear in isolated places (then polyps or focal hyperplasia are formed) or diffusely throughout. The condition is accompanied by the following complaints:
- heavy and prolonged menstruation;
- the appearance of clots during menstrual periods;
- delays of up to 2 weeks or more;
- painful periods;
- spotting outside of menstrual periods.
Pathological growth of the mucous membrane occurs for various reasons.
As a rule, disturbances in the balance of sex hormones with excess estrogen are found. This is precisely what the basic principles of treatment are based on in normalizing hormone levels with the help of various drugs. We recommend reading about the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia after curettage. From the article you will learn about when you need to do curettage, the technique of curettage, its consequences and the recovery period.
And here is more information about the diagnosis and treatment of endometrial polyp in the uterus.
Diagnostic methods
Before selecting a therapeutic course regimen, the attending physician must examine the patient and listen to her complaints. With hyperplasia, it is very important to investigate the situation in order to avoid the transformation of the neoplasm into cancer.
Today, medicine knows several gynecological pathologies that are similar in their symptoms. That is why, to make the most accurate diagnosis, the doctor must:
- examine the patient in a gynecological chair;
- visually examine the vagina;
- conduct an ultrasound of the uterus and appendages;
- perform a transvaginal scan;
- using an optical device to examine the walls of the uterus (the device is inserted through the cervical canal);
- prescribe the patient the necessary tests.
During the examination of patients, each doctor is faced with the task of identifying echo signs of hyperplasia, which will make it possible to most accurately determine the areas of the mucous layers that have been affected.
All test results obtained during the examination are used during curettage.
When carrying out this procedure, the doctor must take a biopsy sample for a cytological examination, the results of which will determine the nature of the tumor (benign or malignant).
In addition to the basic methods of diagnosing the disease, doctors may prescribe additional procedures. Additional diagnostic measures include hysteroscopy and hydrosonography.
Please note that ultrasound is recommended to be performed at the end of menstruation, which will allow the functionality of the mucous membrane to be assessed as accurately as possible.
Menstrual cycle after endometrial removal
Curettage is a planned diagnostic procedure; it is rarely performed urgently in case of a condition that threatens a woman’s life. The manipulation is performed 2–4 days before the start of a new cycle; tissues are not taken for examination during menstruation.
After curettage of the endometrium, menstruation does not begin immediately; in the future, cycle disruptions may occur. Within 5–7 days, there is a spotting that occurs due to microdamage to the mucous membrane. Full periods should begin on the 10th day after endometrial removal.
The following cases are considered violations:
- bleeding continues for 10 days or more;
- heavy bleeding begins;
- menstruation suddenly stops;
- a yellow and green secretion with an unpleasant odor appears;
- low-grade fever or low-grade fever is observed;
- there is pain in the lower back or abdomen.
Complications of classical curettage may include:
- cycle failure after removal - usually prolongation to 35 days or more;
- formation of adhesions;
- a decrease in the volume of menstrual discharge, which can be observed against the background of spasm of the cervical canal.
You can plan a pregnancy after removal of the uterine layer no earlier than 3 months later.
Treatment
The first thing that should be noted is that the selection of therapeutic measures for endometrial hyperplastic process largely depends on the woman’s age.
Treatment of patients of different age groups is carried out according to different schemes. Thus, the methods are classified into the following groups:
- girls of reproductive age (hormones are often prescribed, oral contraceptives are used as usual);
- women with menopause (curettage or hysteroscopy is performed, after which hormones are prescribed);
- patients before menopause;
- patients after menopause (long-acting gestogens are used for treatment under ultrasound and cytology every 9 months).
It does not matter at all what tactics and medications were used to treat, a period of complete recovery is achieved. But, despite the positive dynamics, such patients are still being monitored for 5 years.
Complications
Many girls with this diagnosis are interested in the possible consequences of endometrial hyperplasia. Despite all the possible dangers, the worst outcome is infertility.
But endometrial hyperplastic processes pose a danger not only for girls planning a pregnancy. If you do not receive proper treatment, the disease transforms into cancer, the treatment of which takes a lot of time and requires enormous patience from the patient.
In addition, malignant neoplasms cannot always be removed and completely cured. Most cancer patients die in agony.
It is also worth talking separately about the recurrence of endometrial hyperplasia, which is a clinical problem that requires a solution at the stage of choosing treatment tactics.
To avoid relapse, they resort to surgical intervention, but this also does not provide a 100% guarantee that the disease will not recur.
If a relapse occurs during the atopic form of hyperplasia, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound to indicate the extent of the lesions. Curettage and therapy with hormone-containing drugs are also required. If such tactics do not produce results, removal of the uterus is required.
Why is it dangerous?
Many women treat this disease irresponsibly until they find out how dangerous hyperplasia is for their health, and what consequences can be expected if this pathology is not cured in time. Experts say that it is dangerous to underestimate hyperplasia, since it can cause the following complications:
- an atypical form can develop into cancer;
- the disease may recur again;
- infertility will be diagnosed during reproductive age;
- against the background of bleeding, chronic anemia develops.
Forecast
To talk about a possible prognosis for endometrial hyperplastic process, it is necessary to take into account the form and stage of the disease. Depending on these factors, we can talk about a favorable prognosis.
If the form of the disease was diagnosed in a timely manner and can be treated, the likelihood of relapse and malignancy is unlikely.
Patients who receive a positive prognosis have a chance of complete restoration of reproductive, sexual and menstrual functions.
You can get a favorable prognosis for simple, glandular, glandular-cystic and cystic forms. Also, patients who have developed polyps receive a similar prognosis.
Please note that the favorable prognosis depends on the age of the patient: the younger the girl, the lower the risks. If a simple form of the disease occurs with disruptions of the endocrine system and metabolic processes, the prognosis can significantly worsen.
In cases where the disease recurs, it is impossible to talk about a positive outcome, because a surgeon intervenes, during which the uterus is removed and some functions fail, which cannot be restored.
If the hyperplastic process is diagnosed after the onset of menopause, the prognosis will be unfavorable. This is due to the fact that at a more mature age, hyperplasia often becomes malignant, which is considered a precancerous form.
When the disease does not respond to conservative methods of therapy, the patient is prescribed surgery. This can be done by curettage or removal of the uterus.
In this case, the prognosis will be unfavorable not only for the woman’s health, but also for the functionality of the reproductive system, the functionality of which will be impossible to restore.
Also, speaking about the prognosis, one cannot fail to take into account concomitant diseases. If, along with hyperplastic processes, the patient is diagnosed with hypertension, the prognosis worsens, because this increases the likelihood of relapse.
The same situation applies to concomitant diseases of the endocrine system.
Therapy
The main treatment for any form of hyperplasia is hormonal. With the correct selection of drugs, it is possible to inhibit the stage of proliferation of endometrial cells, stop bleeding and stabilize hormonal levels.
When using contraceptive methods as a treatment for hyperplasia, ovulatory cycles are restored, the ratio of progesterone and estrogens is stabilized, and the thickness of the uterine layer decreases.
After using hormones, the following is prescribed:
- laser ablation – removal of hyperplasia foci with a laser pulse;
- cryodestruction – cauterization of areas of thickened endometrium.
Radical treatment is hysterectomy. Removal of the uterus along with the appendages (less often without them) is carried out only after preliminary hormone therapy and in the absence of effect.
ethnoscience
Treatment of hyperplasia with folk remedies is only permissible in combination with hormone therapy. The following herbs and natural ingredients are used:
- flaxseed oil - used in the acute phase of hyperplasia, taken orally for one month;
- aloe tincture with honey - used both for oral administration and for douching, preparing suppositories;
- peony extract, burdock juice, nettle or cucumber tincture;
- boron uterus - considered the most effective remedy, reduces the active growth of the endometrium, improves immunity, suppresses the source of inflammation.
An important condition in the treatment of the disease is adherence to the principles of diet therapy. The diet includes foods rich in fiber, fatty acids, and vitamins. The consumption of sweets, fatty foods, and the use of spices is reduced. To maintain water balance, the daily fluid intake is at least 2 liters.
Any form of hyperplasia requires an integrated approach and the correct selection of hormone-containing drugs. According to various data, hysterectomy is used as a method of therapy in no more than 5% of cases. In women under 40–45 years of age, appendages are left during surgery to delay the onset of menopause.
Prevention
To avoid the development and progression of endometrial hyperplastic process, follow these recommendations:
- regularly visit a gynecologist for preventive examinations;
- do not delay treatment of menstrual irregularities;
- eliminate neuroendocrine disorders in a timely manner;
- control metabolic processes (if the metabolism is slow, you need to “accelerate” it to the required norm);
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- if you do not want to get pregnant, use contraceptives;
- avoid abortion.
If it was not possible to avoid hyperplasia, maximum efforts must be made to minimize the risks of complications. To do this, you need to diagnose the disease in time and begin treatment at the initial stage under the supervision of a doctor.
Screening
Screening is a combination of various research methods that make it possible to diagnose malignant tumors in their early development, when the disease does not manifest itself in any way.
The purpose of the procedure is early diagnosis of asymptomatic pathology and its treatment.
Screening programs are carried out taking into account the feasibility for those forms of malignant process that are recognized as problematic in the country or region, taking into account the number of patients and the number of deaths.
According to statistics, in the Russian Federation, screening studies are used to diagnose lung, breast, gastrointestinal, and cervical cancer.
This is due to the fact that the number of patients with such types of cancer makes up the majority, and the mortality rate from them beats all indicators.
An example of a screening test for diagnosing breast cancer is a mammogram, for colon cancer - an occult blood test, for cervical cancer - a cytological study.
Statistics
The increase in the percentage of women diagnosed with hyperplastic processes in the uterine mucosa is associated with an increase in the average age of the fair sex, unfavorable environmental conditions, and an increase in the number of chronic somatic diseases, most of which are caused by hormonal changes.
5% of gynecological diseases are due to hyperplasia of the endometrial layer, so this pathology is considered to be very common. The disease is diagnosed in teenage girls and women of reproductive age, but most of it is diagnosed at the age of 35-55 years; some authors claim that this pathology occurs in half of the cases in premenopausal women and during menopause.
In recent years, the number of patients with hyperplasia and cancer of the uterine body has been increasing simultaneously; the latter ranks 4th in prevalence among malignant tumors in women and 1st among oncological formations specifically in the reproductive system.
During menopause
Menopause is a period when hormonal changes occur in a woman’s body, as a result of which reproductive abilities fade and contribute to the development of various pathologies.
In order to promptly diagnose pathological changes at such a vulnerable time for a woman, you need to regularly undergo the following examinations:
- undergo an ultrasound scan every six months;
- monitor hormone levels by taking tests;
- if there is minimal probability or suspicion of progression of the disease, consult a doctor and have the uterine cavity curetted.
As a rule, for the treatment of hyperplasia after menopause, it is customary to use vitamin complexes containing vitamins A and E. A woman may also be prescribed sedatives and antidepressants.
Oral contraceptives, for example Duphaston or Utrozhestan, are no exception, which need to be taken for six months. After the age of 46, the gynecologist prescribes Buserelin, Zoladex.
If we talk about surgical treatment of pathology, then after menopause, a woman is prescribed cryodestruction and laser therapy. If such gentle procedures do not have the desired effect, a hysterectomy is prescribed.
The connection between pathology and the cycle
Normally, the menstrual cycle is divided into 3 phases:
- proliferation - at this time the functional layer grows and thickens;
- secretion – the inner uterine layer matures;
- desquamation - detachment of the functional layer with its subsequent removal in the form of menstrual bleeding.
The first phase begins at the beginning of menstruation. Somewhere in the middle of the cycle, the egg matures and leaves the follicle; this period is characterized by the release of a transparent, stretchy mucus secretion. From this moment, the reproductive cell is ready for fertilization; if conception does not occur, then under the influence of hormones the functional layer peels off and is released along with the egg during menstruation.
All changes during the menstrual cycle occur under the influence of sex hormones:
- proliferation is caused by estrogen;
- progesterone promotes the onset of the secretory phase.
Under the influence of hormones in the proliferation phase, planned cell destruction occurs - apoptosis; this process does not allow the endometrial layer to grow larger than the required size. Apoptosis is triggered only if ovulation has occurred, that is, the concentration of sex hormones has reached a certain level. If there was no ovulation in the cycle, then the effect of estrogen on the endometrium decreases, and it increases in thickness, in which case GPE is diagnosed.