The female body is a real mystery, sometimes even for the women themselves. But if you treat it with love and observe the changes, listen to the sensations, then it is quite possible to learn to understand the signals of the body. Knowledge of the processes by which the female body lives is especially necessary when a girl is going to become a mother or wants to avoid an unwanted pregnancy without harm to her female health.
One of the indicators that days favorable for conception are approaching is discharge during ovulation. What is this substance and why does it change? What else can mucous discharge indicate and why should it be treated with special attention?
Basic Concepts
Before covering the topic in detail, let’s briefly go over the main terms that will be mentioned in the article:
- ovulation is a favorable time when a woman’s egg is ready for fertilization, lasts 1-2 days;
- a follicle is a membrane in which an egg is formed and matures; on the day of ovulation it ruptures;
- fertility - a woman’s ability to conceive a child, the most optimal age is considered to be 23-31 years old, but in practice the age range is much wider - the main desire and, of course, health;
- cervical fluid - is formed in the cervix, has a number of important functions for pregnancy; women observe the secretion of cervical fluid before and during ovulation on their underwear;
- The corpus luteum is a temporary gland that appears at the site of the follicle after fertilization and is responsible for the production of progesterone (the hormone that maintains an interesting position) until the placenta is formed.
Important! Without ovulation, pregnancy is impossible. Not every menstrual cycle is accompanied by ovulation. Isolated cases when the egg does not mature (menstrual cycle without ovulation) are considered temporary rest and do not require treatment.
Typical discharge pattern
The first signs of ovulation are characterized by more abundant discharge, as well as its consistency and color. Their frequency directly depends on how many gonotropes are produced by the pituitary gland.
If there is a period of discharge during the maturation of the egg, then there must be some norms that characterize it.
The nature of discharge after menstruation and before ovulation:
- In the initial period, these secretions contribute to the appearance of a mucus plug in the cervix. It serves as protection against bacteria dangerous to the female body, as well as sperm. In medicine, this phase is called sterile, since there are no secretions as such yet.
- Before ovulation, the mucus plug begins to gradually soften. It looks viscous and transparent, gradually comes out of the cervix and flows out of the vagina.
- On the day of ovulation itself, the discharge thickens. Women can recognize ovulation quite easily, since the consistency of the mucus on this day becomes of medium viscosity, it is colored cloudy white and is viscous, which is clearly visible in the photo. The mucus looks like egg white.
During the ovulatory period, the vagina is maximally moisturized and the woman herself feels it. Her sexual desire increases, nature itself calls on her to become a mother.
How many days before pregnancy can occur? Conception is possible on the very day of ovulation and another 24 hours. If sperm enter the uterus a few days before ovulation, they can fertilize the egg on that day, because their survival is up to 5 days. If there is no fertilization, the egg dies.
Vaginal discharge as a method of contraception and pregnancy planning
It is noteworthy that the pattern of changes in the state of the cervical fluid was noticed and described by a man, John Billing, a doctor from Austria. Therefore, the so-called cervical method of pregnancy planning is known in medical circles as the Billing method.
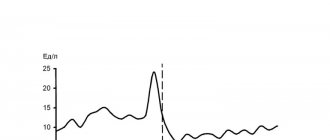
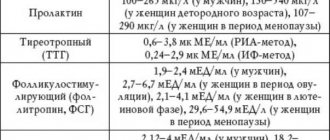
So, fluctuations in the level of sex hormones lead to constant (periodic) changes in the female body. The onset of ovulation is indicated by surges in luteinizing hormone (LH). It is responsible for the production of female sex hormones by the ovaries and is very important for the onset of ovulation.
Immediately before the egg, ready to be conceived, leaves the follicle, the level of this hormone increases several times. That is, ovulation occurs within 24 hours after LH reaches its maximum in the blood. The uniqueness of this phenomenon formed the basis of the operating principle of the ovulation test.
There is a rather poetic comparison: during one female cycle, a woman experiences four seasons. Which can rightfully be considered, if not scientific, but a very accurate description. Throughout the entire cycle, not only a woman’s mood or well-being can change dramatically, but also food preferences, the degree of sexual desire, and so on.
According to medical signs, the indicator of all changes is the state of the cervical fluid. For example, on fertile days, mucus becomes similar to raw egg white - this is the comparison often used by both doctors and ladies themselves. To the touch - like a pulling discharge, that is, the substance from the vagina can stretch between the fingers, forming a kind of thread.
Thus, periodic monitoring of changes gives a woman the opportunity to “predict” the day of ovulation. This is equally good for those who want to get pregnant and for those who are not yet planning to become parents.
This method of natural contraception has the right to exist, but with some reservations: you should not rely on it if the cycle is irregular or the female body has experienced stress of any nature (psychological shock, surgery, illness, etc.).
Important! The mucous membrane of the female genital organs reacts very quickly not only to hormonal changes, but to literally all changes: medications, stress, overload, changes in diet. Therefore, relying on the nature of the discharge as the only and reliable method of contraception is not recommended.
Read below to learn how to distinguish normal discharge from signs of dysfunction in the female genital organs.
What is the ovulatory phase?
Every woman of reproductive age gets her period. The body is renewed and the process of preparing for a possible pregnancy begins. First, an egg develops in the ovary, and in the middle of the cycle it matures and the follicle in which it was located bursts.
The release of an egg from the follicle is called ovulation. This is the ovulatory phase of the menstrual cycle, which lasts up to 48 hours.
The lifespan of the egg is 24 hours, maximum 48. It moves along the fallopian tubes towards its “tailed friend”. If you had unprotected sex a few days before ovulation, there is a high probability of pregnancy. After all, sperm can live up to 5 days in the female body.
It is in one of the fallopian tubes that this meeting takes place and then the fertilized egg moves into the uterus to attach to its wall and develop there for the entire 9 months. If conception does not occur, she dies.
If a woman becomes pregnant during this period, the hormone progesterone, which is called the pregnancy hormone, comes into its own, and the preparation of the endometrium for embryo implantation begins.
Why do there be discharges and why know their features?
If you listen to your body, you can avoid unwanted pregnancy, notice the symptoms of the disease in time, plan a pregnancy and find out about its occurrence. The nature of the discharge before and after ovulation also has its own significance and can tell a lot about a woman’s health.
By observing yourself for several months, you will be able to determine natural changes in your well-being and identify characteristic sensations. Although every article on a women's topic necessarily contains the phrase: every woman's body is individual - but there are also patterns in weight.
So, why do various sticky substances appear on underwear? What role do they play in the female body?
Cervical fluid (CF) as a kind of “conductor” of male germ cells to a mature egg. After completion of sexual intercourse, male caudate cells appear on the mucous membrane of the cervix. Due to the increase in estrogen levels, the mucous membrane changes on the eve of ovulation and ideal conditions are created for the “meeting” of sperm.
Only after contact with the mucous membrane of the cervix do male reproductive cells acquire the ability to fertilize an egg. The so-called “capacitation” phenomenon.
Discharge during ovulation provides sperm with the ability to survive for several days in anticipation of ovulation. And unsuitable (dead) cells, after fertilization or death of the egg, dissolve as unnecessary. After the corpus luteum begins to produce progesterone at a rapid pace, the mucous membrane loses its “conductor” abilities. The following main functions of the cervical substance can be distinguished:
- provides sperm with additional energy to reach the egg;
- selection and preservation of the viability of the highest quality sperm;
- creates conditions for the advancement of male germ cells into the internal female genital organs only during the most favorable period for pregnancy;
- serves as a protective shield from the leukocytes of the female body and the aggressive environment of the vagina itself.
A woman can determine the consistency of cervical fluid on her own using two fingers. At different stages of the cycle it has different ductility from 1 to 8 centimeters. In addition, its characteristics may be influenced by other factors not related to the approach of ovulation. For example:
- seminal fluid;
- all kinds of infections;
- excited state;
- certain medications.
Discharge on the day of ovulation is distinguished from seminal fluid and substances that are released during sexual arousal by the fact that it does not dry out (on a napkin or hand). CJ is more viscous and does not change its consistency throughout the entire time until you wash it off.
Traces of bright blood - what to fear
So, if there is blood discharge during ovulation, we have clarified this. If there are bright smears of a scarlet, bloody hue, you should consult a doctor as early as possible. If they are detected 4-6 days after the end of the ovulation phase, you need to find out the cause of the failure. It can be:
- cervical erosion;
- tumors in the uterus;
- the process of inflammation in the genital tract;
- taking contraceptives.
Such traces of blood discharge during and after ovulation should alert a woman
What should the discharge be like?
Let us recall that the menstrual cycle consists of several stages that have a clear sequence:
- the egg is born and matures in a special shell in the form of a sac (follicle);
- rupture of the follicle membrane and the transition of a female cell ready for pregnancy into the fallopian tube - ovulation;
- the movement of a female cell along the fallopian tube in “waiting” for sperm, 1-2 days allotted by nature for conception - fertile days;
- transition of the embryo to the uterus and secure attachment there, or death of the unfertilized egg;
- menstruation - if pregnancy has not occurred.
At each stage of the female cycle, cervical fluid of a certain composition is present in the vagina, which directly determines the course of fertilization. What should the discharge be like depending on the approach of the “key day” of the menstrual cycle?
"Dry" or "clean" period. The fluid becomes thick and viscous and completely covers the cervix, protecting it from the penetration of pathogenic bacteria. At this stage there is no discharge.
Ovulation is almost here. As soon as the maturation of the egg is nearing completion, the mucous plug gradually liquefies and partially comes out, clearing the way for sperm. Then ladies may see a white, creamy discharge. They are thick and sticky.
Fertile days. The cervical fluid becomes watery and transparent, giving the woman a feeling of wetness in the vagina. During ovulation, it also changes in chemical composition; a favorable environment (alkaline) is created in the female genital organs to preserve male reproductive cells in “good health” for as long as possible. The substance becomes liquid enough for the penetration and movement of sperm 3 days before ovulation.
Ovulation. The cervical substance becomes similar to raw egg white. They also stretch well.
The key to women's health is not only rest, good nutrition and a healthy lifestyle, but also the vigilance and attention of the woman herself.
There are several simple rules for self-observation. It is necessary to carefully examine the discharge (3 times) on the day of completion of menstruation: carefully take a sample from the vagina with a clean finger; take a closer look and characterize the substance in all respects (stickiness, how liquid, viscous or dry). To assess ductility, spread your fingers apart. Check how dry your underwear is during each visit to the toilet.
It is advisable to keep a diary of your observations. This will help you determine your own level of normal discharge and notice deviations in time.
Possible causes of brown spotting in the middle of the cycle
There are many prerequisites for this phenomenon, from stress to oncology. Other circumstances and symptoms will help lead to an assumption.
Physical exercise
Exhausting sports, heavy bags, and work beyond our strength lead to the rupture of small capillaries in various places. At the moment of ovulation, there is a fairly loose layer of endometrium in the uterus. Sudden tension can provoke its slight withdrawal. Then a bloody or brown spot appears. Or the remnants from the last menstruation, which lingered on the walls, come out.
Carefully! Such factors can lead to serious bleeding.
Stress
Mental stress and mental pain have no less effect than a heavy barbell. However, their mechanism of action is related to hormones; under the influence of a malfunction, slight bleeding occurs in the form of brownish discharge.
Injuries
The mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix is easily damaged during sex, hygiene procedures, and the use of a gynecologist's speculum. Rough movements and a small amount of lubrication lead to cracks in the walls, which gradually bleed.
Pharmacology
Birth control pills, IUDs, and vaginal suppositories provoke changes in vaginal secretion in consistency and color. Some women, having discovered light brown copious oily discharge in the morning, do not think that this is the remains of a suppository containing iodine. After Clotrimazole or Lomexin, pink discharge is noted by 70% of patients.
Hormonal drugs, including IUDs, specifically disrupt the cycle in the first months of use. Brown and pink spotting is observed in the middle and instead of menstruation. If after 5-6 months the situation does not stabilize, then you need to consult a doctor.
Attention! Endocrine disorders are caused not only by taking medications, but also by unhealthy changes in body weight - obesity or dystrophy.
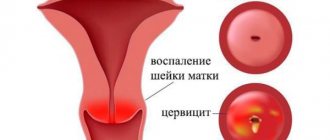
Inflammatory diseases
With adnexitis or salpingitis, on any day of the cycle, bloody smears may appear, as well as smelly green discharge, copious liquid, thick white. Depending on the type of infection that provoked inflammation in the tissues. The treatment will be long and multifaceted.
Erosion
Brown spotting after sex is the first symptom of cervical damage. Among other processes, dysplasia is observed here - a precancerous change and an oncological tumor. They get rid of the problem using cauterization with a laser, electrocoagulator, chemistry, liquid nitrogen, the best option is treatment of the cervix with Surgitron. In case of malignant degeneration, supravaginal amputation is performed.
Endometriosis
The growth of the menstrual lining of the uterus, when a very thick loose layer is observed and even clots seep through the wall into the abdominal cavity and other organs. It manifests itself as long, heavy and very painful menstruation. Bloody brown discharge also occurs in the middle of the cycle.
Education
Tumors, fibroids, endometrial and cervical canal polyps provoke uterine spasms and the release of a small amount of blood. Polyps bleed on their own, especially those that protrude from the cervix into the vagina. At the same time, nagging pain and an increase in menstruation in the number of days are noted. As with erosion, brown discharge occurs after sexual intercourse with polyps, but more often they are scarlet or pink.
Carefully! Adenomatous formations eventually become cancerous.
Pregnancy
Should this phenomenon be considered a symptom of conception? Definitely not. Brownish spotting may appear during gestation if there is at least one of the above pathologies. There is no reason to consider the discharge as implantation bleeding, because it occurs 10-12 days after ovulation, closer to the next menstruation. If in doubt, you can always do a test, although only after a couple of weeks.
Malfunctions of the central fluid
This substance can be both the key to the successful achievement by the strongest sperm of a mature egg, and an obstacle to the desired pregnancy.
An insufficient amount of liquid may form or it may acquire an undesirable structure: too viscous, jelly-like. Such violations of the natural consistency are most often the result of drug treatment. In this case, after the necessary examination, the doctor prescribes hormonal correction.
Even CF that is normal in thickness and viscosity can “resist” the desired pregnancy. If the female body produces antibodies to antigens (contained in seminal fluid and the sperm themselves). In this case, the ability of sperm to move is lost.
Even if ovulation has occurred, the sperm and the mucous membrane of the female genital organs are in perfect order, then under a microscope you can observe how the male reproductive cells have frozen or “trembled” in place. Then, after identifying the cause of the production of such antibodies, treatment is prescribed.
Important! Ovulation without discharge cannot result in a long-awaited pregnancy. Often the absence of cerebral fluid is the cause of difficulties in planning pregnancy.
What kind of discharge should you see a doctor for?
A woman should not delay visiting an antenatal clinic when vaginal discharge deviates from the norm and may be symptoms of pathology. The most incorrect and often common decision of women is self-medication. Often, instead of consultation, lovely ladies prescribe treatment for themselves based on articles and reviews on the Internet, advice from friends or pharmacists.
Important! Many diseases have similar symptoms, but completely different treatments. There are also obvious (noticeable) signs of the disease, and hidden processes that only a doctor can determine. Therefore, self-medication is often ineffective.
In addition, it is imperative to take into account the characteristics of a woman’s body when choosing treatment, so as not to aggravate the situation, which also speaks in favor of qualified help.
Negative changes in vaginal discharge include:
- bright yellow shades of discharge during ovulation;
- itching and burning of the genitals, which are accompanied by discharge, pain during sexual intercourse;
- discharge of any color and density with an unpleasant odor;
- a lot of discharge after ovulation;
- dark brown, bloody discharge before ovulation;
- The discharge has a consistency close to cheese mass or resembles curdled milk.
To summarize all of the above, a woman should not endure discomfort, any inconvenience, “incorrect” discharge, including this deviation from the norm. Therefore, you should not save time and, as many people think, money. It is better to immediately contact the antenatal clinic. This will give the woman the opportunity to get answers to all questions, proper treatment, and psychological peace of mind.
As life practice shows, those who saved time and money by self-medicating then spend even more to cure advanced diseases and the consequences of self-prescriptions.
What else can affect discharge during ovulation?
When a girl usually ovulates painlessly and bloodlessly, but suddenly a small spot appears, what should she do? If this does not happen systematically, then small drops of blood may appear during ovulation during intense physical activity. The discharge will be mixed with blood, but in the next cycle everything should return to normal.
Sometimes the cause of bleeding on the day of ovulation can be simple stress and nervous tension.
In some cases, blood during ovulation “reminds” that:
- a woman takes hormonal contraceptives;
- the presence of an intrauterine device;
- use of medications.
Bloody discharge after ovulation or during this process often indicates the consequences of using intrauterine contraception and a deficiency of hormones, in particular the hormone progesterone. Its deficiency can cause complications such as infertility and involuntary termination of pregnancy.
As a rule, such discharge makes itself felt a week after ovulation and is expressed as scanty brownish discharge. To normalize hormonal levels, a woman should be prescribed medications that stabilize progesterone levels, including affecting the normal course of discharge and ovulation.
These are the drugs:
- Utrozhestan;
- Duphaston;
- Progesterone.
You need to carefully monitor how many days the bleeding continues after ovulation. If they are not abundant, then do not worry too much and immediately contact a specialist.
But if the discharge is profuse and does not stop for quite a long time, then women should immediately contact a gynecologist.
The doctor can tell you more about the fertilization of the egg, the symptoms before ovulation, the approaching maturation of the egg, and diseases that occur in the female genital area in hidden forms. If the tests indicate disorders in the reproductive system, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Brown discharge
During ovulation, discharge of this color can have a number of reasons, and it is best to consult a specialist for advice. Among the main reasons, doctors name:
- estrogens, if their level in the blood exceeds the norm, then the discharge may be brownish in color;
- infection of the female genital organs, which requires serious attention from doctors;
- if discharge during ovulation occurs temporarily (no more than 48 hours), then there is nothing to worry about - this is a consequence of the rupture of the follicle and the release of a mature egg;
- The cause of discharge can also be medications that can affect women’s cycles, hormonal drugs;
- the intrauterine device can cause brown and even red discharge;
- decreased thyroid activity.
But at the same time, spotting during ovulation, which does not cause inconvenience and does not become intense, may be a consequence of follicle rupture. But you shouldn’t hope that “maybe it will blow by.” It is better to be vigilant once again.
Blood discharge during ovulation
Discharge during ovulation, which is bloody in nature, can cause a woman to fear for her health. Brown discharge during ovulation, which may appear for several days as the egg matures, is normal. But many representatives of the fairer sex may confuse dark or light brown discharge during ovulation with symptoms of implantation discharge.
With the beginning of each cycle, new eggs mature, packaged in follicle capsules. Over time, one dominant follicle stands out among them, from which a mature egg is released. Women can trace such symptoms before the onset of ovulation and the next day.
Ovulation and its brown discharge should not be similar to menstrual discharge. During ovulation, blood discharge is released in very small quantities - literally a few drops. If a woman notices that the bleeding is profuse, then she needs to immediately contact a gynecologist on the same day.
If spotting exists, ovulation may be painful. When the follicle matures, it becomes larger in size, and the girl may feel pain on the right or left, depending on which ovary the egg is located in. When rupture occurs and the egg is released, drops of blood may appear. Essentially, this is a minor injury and blood is a natural occurrence.
Discharge after ovulation increases quantitatively. At this time, due to the increase in progesterone levels, the discharge has a cloudy and viscous consistency, can resemble gruel and lasts, as a rule, up to seven days. But for women there is no certain limit in terms of scarcity or viscosity, which is explained by the characteristics of her body.
What are the signs of successful conception?
What happens if conception occurs? When a couple plans a pregnancy according to “all the rules,” that is, the woman has passed all the necessary examinations (pathologies and infections are excluded), then the nature of the discharge can determine the onset of pregnancy without resorting to a traditional test.
In the first 6/12 days after fertilization, the embryo moves to the uterus for further development of pregnancy. When the embryo attaches to the wall of the uterus, small vessels may be damaged. This phenomenon has a complex name - implantation bleeding. Although it sounds scary, in practice it is just small brownish discharge that a woman can mistake for the premature onset of menstruation. They can be observed on days 20-26 of the female cycle.
Such discharge may range in color from light brown to reddish. They are usually scanty and last several hours or days. They have a number of characteristics not typical for normal menstruation. Brown discharge after fertile days does not turn into more abundant discharge and lasts much less.
Other discharge after ovulation
Heavy discharge after ovulation is not always a good sign, especially if it is associated with discomfort, foul odor or itching. Grayish, greenish or bright yellow discharge indicates inflammatory processes.
Brownish marks on laundry are considered “not scary.” This is a consequence of a few drops of blood entering the vagina after the follicle ruptures.
Creamy or white discharge after ovulation does not indicate pregnancy. This is a signal: the egg is completely ready for fertilization.
An unexpressed yellow color without unpleasant manifestations (smell, itching, temperature) indicates an excess of progesterone. But there is a fine line here; yellowness may also indicate a bacterial infection. You need to pay attention to the presence of other symptoms.
THERE IS DISCHARGE, but NO PREGNANCY
Unfortunately, disruptions occur not only in our plans for life, but also in the body. Even with all the correct preparations, accurate determination of fertile days, when there are all the signs, discharge after ovulation, pregnancy may not occur. There can be many reasons for this: from overwork and stress to hormonal disorders and illnesses.
Most likely, menstruation will come with some delay. Perhaps fertilization of the egg took place, but something went wrong. The embryo failed to gain a foothold; there was a deficiency of progesterone or other reasons in the mother’s body. Therefore, discharge and minor pain in the lower abdomen were present, and the pregnancy itself did not develop properly.
Dear ladies, no matter what the mucus secretion is, and no matter how well you have studied all the features of your body, do not neglect routine examinations by the gynecologist.
Why is there no ovulation?
There may also be cases when, even if there is viscous discharge for several days, similar in consistency to egg white, there is no ovulation. Judging by the signs, the discharge during ovulation is exactly the same in color, consistency and abundance.
This phenomenon can be attributed to disorders in the female reproductive system. It is caused by a malfunction of the hypothalamus, pituitary system and ovaries, hormonal imbalance or nervous strain.
If you don’t ovulate once or twice a year, there’s no need to worry. With an anovulatory cycle, the corpus luteum does not develop, the egg does not mature, but the menstrual cycle is not disrupted. If anovulatory cycles occur more frequently during reproductive age, you should consult a gynecologist.
If a woman who can still have children has a cycle failure and does not ovulate, then this manifestation can be attributed to:
- oligomenorrhea;
- amenorrhea;
- uterine bleeding.
The listed violations of the ovulation process are not present.
Before making a diagnosis, a specialist conducts a full examination of the female body, a radiologist performs an ultrasound, and a smear of the discharge is taken in the laboratory.
To summarize, we can draw the following conclusion: ovulation and discharge are two inextricably linked processes.