- What is an anovulatory cycle?
- Signs of an anovulatory cycle
- Diagnosis of anovulatory cycle
- Causes of anovulatory cycle
- Treatment of anovulatory cycle Hormone therapy
- Traditional methods
| Nature has given the fair sex the opportunity to have children. To achieve this, a whole range of functions develops and is realized in the female body. It affects the work of both the genital organs and the endocrine glands; during a special period of pregnancy, the entire body is rebuilt in a special way. |
Ideally, a woman’s readiness for pregnancy and childbirth is observed after puberty and until menopause. This period is called reproductive age. At this time, in accordance with the monthly female cycle, readiness and ability to become pregnant is observed. Today, if there is sexual activity, a woman herself is able to control the prospect of childbearing by correcting hormonal levels or the entry of sperm into the genital system. At the same time, the desire and readiness to prolong the family often encounters obstacles, one of which is the so-called anovulatory cycle.
The anovulatory cycle is a problem of modern gynecology
The anovulatory cycle is a serious problem for practicing obstetricians-gynecologists and reproductive specialists. In order to understand the anovulatory cycle - what it is, and why doctors in all countries are concerned about it, let’s look at what the norm is.
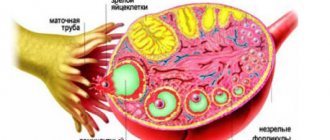
The menstrual cycle is a regularly occurring change in a woman’s body aimed at the possibility of conception. The external manifestation of cyclic changes is bloody discharge from the genital tract - menstruation. Normally, every woman's menstrual cycle consists of two phases: follicular and luteal. The follicular (otherwise known as follicular) phase begins on day 1 of the cycle, which corresponds to the beginning of menstruation. Under the influence of FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone), the growth and maturation of the follicle occurs - a special structural component containing the egg. With a 28-day cycle, the duration of this phase is usually 13-14 days.
The follicular phase ends with ovulation. At this moment, the follicle ruptures and the mature egg is released into the fallopian tube. At this stage, the highest concentration of luteinizing hormone is determined, the secretion of which increases starting from the 7th day. During a short period of ovulation, lasting 36-48 hours, fertilization and further development of pregnancy are possible. After ovulation, the next phase begins - the luteal phase.
With the transition to a new phase, the ratio of hormones changes. The level of LH and FSH decreases, the concentration of estrogen increases. Under the influence of estrogen, the endometrium - the mucous membrane lining the uterine cavity - begins to grow, preparing a place for a fertilized egg. Along with this, the ruptured follicle is transformed into a hormonally active corpus luteum, producing the hormone progesterone. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum undergoes reverse development, the level of estrogen and progesterone decreases and endometrial rejection occurs - menstruation.
Thus, a two-phase ovulatory cycle is normal for a woman of fertile age. A cycle in which ovulation does not occur is called anovulatory. Lack of ovulation is not always a pathology. Normally, it is typical for periods of pregnancy and lactation, as well as with the onset of menopause. While maintaining a regular menstrual cycle, 3-4 anovulatory cycles per year are considered as normal.
In a situation where, for one reason or another, anovulatory cycles predominate over ovulatory ones, we speak of chronic anovulation. Without solving this problem, the chances of getting pregnant are reduced to zero, which forces women to seek help from specialists.
Causes of anovulatory cycle
Hormonal disorders
The leading causes of anovulation are endocrine disorders. The following take part in the regulation of the normal menstrual cycle: cerebral cortex; special brain structures - the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, in which hormones are produced (including LH and FSH); ovaries, which produce estrogens, androgens and progesterone; as well as the uterus. A breakdown in any of the links leads to disruption of the menstrual cycle.
The hormone-producing structures of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus work in direct connection with each other. The production of FSH, which is responsible for the formation and maturation of the follicle, occurs in the pituitary gland and is regulated by the hypothalamus. Any imbalance of hormones prevents the formation or growth of follicles, which makes it impossible for the egg to mature and further fertilize it. Dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary system occurs as a result of injuries, tumor processes, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, empty sella syndrome, prolactinoma.
Pathology of the thyroid gland
In addition to the menstrual cycle, the work of the hypothalamic-pituitary system is closely related to the work of the thyroid gland. The synthesis of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland is also controlled by the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Diseases such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt the delicate balance of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones, as well as estrogen and progesterone, thereby causing menstrual irregularities, including anovulation.
Vitamin D deficiency
As you know, vitamin D can enter the body from the outside with food, or be formed in the skin under the influence of sunlight. In both cases, it undergoes a number of changes, forming various metabolites. One of these metabolites, D3, is involved in the process of follicle formation - folliculogenesis.
Vitamin D receptors are found in all organs and tissues of the reproductive system (ovaries, endometrium, myometrium). The physiological concentration of vitamin D and its metabolites contributes to adequate ovarian production of estrogen and progesterone, as well as stability of the menstrual cycle.
Acquired diseases
Since ovulation occurs in the ovaries, any damage to this organ can lead to anovulation, even with normal hormonal levels. Factors contributing to decreased fertility include chronic inflammatory diseases (adnexitis), polycystic disease, and tumor growths.
Pathogenesis of the condition
During the anovulatory cycle, periods of follicle growth that differ in time and characteristics occur. However, timely rupture of the follicle and the subsequent release of a mature egg does not occur, and an unruptured follicle can persist for a long time before undergoing degeneration (reverse development).
The follicle itself produces estrogen hormones, which causes hyperestrogenism - oversaturation of the blood with estrogen. In this case, a decrease in the gestagenic component will be observed, since the formation of the corpus luteum, responsible for the production of progesterone, is impossible without rupture of the follicle. Fluctuations in hormone levels characteristic of a normal menstrual cycle do not occur. Their concentration in the blood becomes monotonous, and the cycle itself in this case is called monophasic. Developing bleeding in this case is usually called not menstruation, but a menstrual-like reaction.
Since the endometrium has a large number of estrogen receptors, a constant increased concentration of these hormones will cause increased growth of the inner lining of the uterus, which can be complicated by pathological conditions such as endometrial hyperplasia or polyps.
What is anovulation
With hormonal disorders, ovulation may be absent. In an anovulatory cycle (a cycle without ovulation), the follicle does not mature, or it matures, but for some reason does not burst. Accordingly, there is no egg, and conception is impossible.
In this case, the cycle is not two-phase, but monophasic. The basal temperature in the second phase is low: it does not rise above 36.9. The basal temperature chart is anovulatory if BT throughout the cycle ranges from 36.2 to 36.9 and does not rise in the middle of the cycle. There are even situations when BT has fallen after expected ovulation, that is, it becomes lower than in the first phase. Most likely, this means that ovulation did not occur.
An example of an anovulatory BT schedule.
What manifestations indicate an anovulatory cycle?
It is not always possible to suspect an anovulatory cycle on your own. Sometimes women learn about chronic anovulation only after consulting a doctor with a problem of infertility. However, there are several signs indicating malfunctions in the reproductive system.
First of all, attention is drawn to the change in the nature of menstrual bleeding. In the case of hyperestrogenism, menstrual-like reactions will be characterized by an increase in the duration of blood loss, as well as the volume of blood lost. In some cases, the anovulatory cycle occurs against the background of hypoestrogenism - a reduced concentration of estrogen. This condition is characterized by scanty menstrual bleeding, but a short break between them.
In other cases associated with the pathology of hormone-producing organs, such as Itsenko-Cushing's disease, prolactinoma, hypothyroidism, hypothalamic syndrome, there is an increase in body weight not associated with nutrition, fat deposition in the abdominal area, increased hair growth, the appearance of stretch marks on the skin - bright purple stretch marks.
Signs of anovulation
Often this pathology is asymptomatic. The girl has a regular monthly cycle and in general nothing bothers her. Some women may experience the following symptoms:
- Cycle failure: it is irregular, periods are scanty or, conversely, too abundant;
- In the middle of the cycle there are no characteristic signs of ovulation: mucous discharge, abdominal discomfort;
- Excessive hair growth and weight problems (this happens with polycystic ovary syndrome);
- Increased emotionality, fatigue.
How to confirm that there is no ovulation?
There are several ways to determine the anovulatory cycle. The simplest method for determining ovulation is to measure the temperature in the rectum, or otherwise - basal temperature. In the first phase of the cycle, this temperature is 37 degrees. During ovulation, which is accompanied by a peak in LH concentration, the temperature rises to 37.4 - 37.7 degrees, then decreases to the previous level. The absence of fluctuations in the measured temperature indicates a monophasic cycle.
Another diagnostic method that can be performed at home is an ovulation test system. Similar to a pregnancy test, an ovulation test consists of several paper strips on which a special reagent is applied. By dipping such a strip into urine, you can determine whether there has been an increase in the level of luteinizing hormone, which in turn portends the imminent onset of ovulation.
Of the instrumental diagnostic methods that help in determining anovulation, the most informative and accessible is ultrasound. According to the study, it is possible to trace the absence of a dominant follicle.
Laboratory determination of the levels of LH, FSH, and estrogens helps to find out whether ovulation is occurring, whether there are hormonal disorders in a woman’s body, and also to suspect some kind of endocrine pathology.
The decisive criterion is the histological examination of the endometrium obtained as a result of diagnostic curettage. However, this research method is not used to diagnose anovulation only. Curettage of the uterine cavity is prescribed for strict indications (bleeding, hyperplasia or endometrial polyps), but the result of histology allows us to detect the absence of ovulation due to altered endometrium.
Diagnosis of absence of ovulation
- BT charts.
- Ovulation tests.
- Functional tests - fern phenomenon, pupil symptom.
- Colpocytological examination, hormonal mirror.
- Analysis for hormones (estradiol, FSH, progesterone, thyroid hormones, prolactin).
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and folliculometry.
- Diagnostic curettage.
- MRI of the pituitary gland.
Due to the possibility of alternating ovulatory cycles with anovulatory ones, diagnostics should be carried out over several cycles.
Treatment approaches
If you suspect you have symptoms of an anovulatory cycle, you should definitely consult a doctor. Only an obstetrician-gynecologist can understand the reasons, select the appropriate treatment for the anovulatory cycle and give recommendations. Therapeutic tactics will depend on the reasons that caused the menstrual cycle disorder.
- Hormonal therapy is based on identified abnormalities in hormone levels. The fundamental difference in the choice of drugs and regimens of their use will depend on the degree of estrogen saturation. If there is a lack of estrogen, medications containing low doses of this hormone will be indicated. For hyperestrogenism, it is advisable to use progestins. If the reason lies in increased production of prolactin, the goal of treatment in such a situation will be to suppress the production of this hormone. It is important to remember that you can start or stop taking medications only with a doctor’s prescription.
- Vitamin therapy is a great help in the treatment of irregular menstrual cycles. In addition to vitamin D, which is involved in the formation of follicles, B vitamins are of great importance. They are auxiliary elements in the formation of sex hormones. Sometimes eliminating vitamin deficiency is enough to restore fertility.
- Herbal medicine and traditional medicine are not the main methods of treating anovulation, but can be used as an auxiliary component. Decoctions and infusions of boron uterus, sage, and adonis are very popular. In general, herbal decoctions have a general strengthening and tonic effect, increasing the body's adaptive powers and helping to fight stress. However, before starting herbal medicine, you should consult your doctor.
Physiological anovulation is not a painful condition and does not require any treatment.
Prevention of monophasic cycle
Measures to prevent the anovulatory cycle are as follows:
- It is necessary to maintain a healthy lifestyle (balanced diet, moderate exercise, enough sleep)
- Minimize stressful situations
- If possible, prevent all kinds of intoxication, as well as infectious diseases
- Regularly undergo examinations by a gynecologist (at least twice a year) and take care of timely treatment of diseases of the reproductive system
Treatment of the anovulatory cycle in our clinic is selected individually, taking into account the specific diagnosis of each patient. Do not put off taking care of your health until later, because it is its timeliness that will help you fulfill the main female function and experience all the joys of motherhood!
Make a choice in favor of professional medicine!