Pregnancy is one of the most difficult and exciting stages in a woman’s life. Active hormonal and psychological changes, anticipation of meeting a child and the frightening unknown of the last trimester... This is an incomplete list of thoughts and processes that worry a young mother. Paying attention to thematic forums, we can conclude that one of the problems that frightens women at 8–9 months of pregnancy is discharge before childbirth.
Yellowish and white discharge with flakes in late pregnancy
Such secretion indicates leakage of amniotic fluid. The presence of flakes is a normal phenomenon, indicating that particles of lubricant that protect the fetus during the prenatal period have entered the liquid substance.
Amniotic fluid is the baby's natural habitat for 9 months. The processes of its formation, breathing, and movement actively take place in it. The presence of amniotic fluid around the maturing embryo protects it from external influences on the abdomen (blow, push), acting as a shock absorber. The release of the substance is a physiological process that precedes the onset of contractions and foretells their increase in frequency.
As a rule, the outflow of water is accompanied by dilation of the uterus by 2–4 cm. The amount of liquid can vary from a glass to 1.5 liters. The substance is transparent and odorless, but the presence of sweetish shades is normal.
During pregnancy, a woman can be diagnosed with both low and high water levels. The presence of such pathologies requires observation in a hospital setting.
The outflow of water is provoked by the rupture of the amniotic sac and indicates the imminent onset of labor. The presence of feces in the substance and the presence of an unpleasant odor indicate a threat to the life and health of the fetus. A child may swallow liquid, which will lead to the development of infections and pathologies of the respiratory tract.
An incomplete rupture is often diagnosed, which leads to leakage of the substance. It is worth talking about a disruption in the course of pregnancy only if the process has intensified long before the expected due date.
How to detect water leakage?
It is possible to diagnose constant leakage of liquid secretion at home:
- It is necessary to carry out hygiene of the intimate area. It is recommended to perform a similar procedure with baby soap or a special gel that has a mild antimicrobial effect;
- Treat the surface of the genitals with a towel or napkin;
- Lie down on a dry white sheet;
- Stay in a horizontal position for at least 15–20 minutes.
Watery, light yellow discharge Watery discharge
If during these manipulations several wet spots appear on the surface of the sheet, we can safely talk about water leakage.
Why does my water break but contractions don't start?
In the uterus, the fetus is surrounded by about 1.5 liters of amniotic fluid. It protects the child from mechanical damage and infectious processes. Immediately before the onset of labor, the fertilized egg ruptures and the fetal fluid exits through the woman's genital tract. This is a sign that labor pains will begin soon.
However, it happens that several hours pass without contractions appearing. This is not always a deviation from the norm. According to observations, in healthy women, on average, 8-24 hours pass between the breaking of water and the onset of contractions. At this time, the body is preparing for childbirth, so there is no point in rushing things.
Problems arise if the water breaks and there are no contractions for more than 24 hours. The danger is that the risk of infections entering the uterus and the development of complications in the child after birth increases. The following reasons can most often contribute to this:
- uterine fibroids;
- changes in the level of sex hormones;
- premature pregnancy;
- decreased sensitivity of uterine receptors to oxytocin;
- multiple pregnancy;
- concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- infectious diseases;
Taking hormonal medications in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy can also cause premature breaking of water.
Causes
Contractions are rhythmic contractions of the uterine muscles, the task of which is to lead to the dilatation of the cervix. This process is painful and quite long. The cervix needs to expand by 10-12 centimeters so that the baby's head can pass through. Often the period of contractions is accompanied by the manifestation of various discharges, including bloody ones, associated with the discharge of the mucus plug.
A clot of mucus streaked with blood tightly closes the cervical canal of the cervix throughout pregnancy. But when the female body begins to actively prepare for childbirth, the cervix becomes softer, smoothes out, and the plug may begin to come off either entirely or in parts.
It may appear as light, yellowish, or pink mucus with small streaks of blood. Such discharge can appear not only at the “precursor” stage, but also during contractions.
There is no need to be scared - there is a completely natural and physiological process of opening the cervix for the subsequent release of the baby. It is only important to make sure that the discharge does not intensify and does not turn into scarlet blood.
Small bloody or brown discharge may appear when contractions begin and after examination by a gynecologist. After a woman arrives at the maternity hospital, she will definitely be examined, and therefore such discharge should also not frighten or alarm.
Scarlet blood during contractions, heavy bleeding - a more alarming situation. This may result in premature placental abruption. Normally, the “baby place” leaves its place after the birth of the baby, in the subsequent period of childbirth. If earlier detachment occurs, this is fraught with bleeding, a state of acute hypoxia for the child, which can lead to irreversible changes in his brain and the entire central nervous system. The baby may die.
Bright red, scarlet blood during labor is not considered normal. Its appearance is a reason to call an ambulance if the woman is still at home, or immediately inform the medical staff about it if the woman in labor is already in a maternity facility.
How long until I give birth?
In obstetrics, it is believed that after the waters break, labor will begin within 24 hours. At the same time, doctors do not advise rushing to hospitalize a pregnant woman. It is optimal for a woman to arrive at the maternity hospital when her contractions are already beginning. This allows you to protect her from excessive stress and infections that exist inside the walls of a medical institution.
If the amniotic fluid is opaque or has a greenish tint, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible. These are signs of infection or fetal hypoxia.
The doctor may warn the patient in advance that she will need to come to the hospital immediately after her water breaks. This makes sense in the following situations:
- multiple pregnancy;
- presence of concomitant diseases;
- impossibility of childbirth without caesarean section;
- fetal distress syndrome.
The listed factors significantly increase the risk of complications during childbirth, and therefore require additional examination and monitoring of the pregnant woman’s health.
Actions
If heavy bleeding appears with the first contractions or a little later, you need to immediately go to the maternity hospital and immediately report this unpleasant news to the medical staff.
If placental abruption occurs, the woman will urgently undergo a cesarean section, since delay is unacceptable.
For moderate bloody (do not confuse with blood!) discharge, use pads, avoid getting water into the vagina, for example, while showering at home before going to the maternity hospital or in the emergency department of the maternity hospital.
Without a mucus plug, the baby has no mechanical barrier protection against viruses, bacteria and fungi. If aggressive flora or microorganisms enter the uterine cavity, an internal infection can develop quite quickly, which is extremely dangerous for the baby and the mother.
If bloody or scarlet discharge is accompanied by the release of a large amount of fluid, premature rupture of water is possible. In such a situation, you should also go to the maternity hospital as soon as possible, without waiting until the contractions become stronger. In the emergency department, you also need to immediately say that the fluid flowing out was bloody, pink, brown, or some other color. This will help doctors quickly choose the right tactics for labor management.
The main thing is not to panic or get nervous. Doctors have many ways to cope with one or another emergency situation that arises during childbirth. Trust them.
For information on discharge, contractions and other precursors of labor, watch the following video.
medical columnist, psychosomatic specialist, mother of 4 children
Throughout her pregnancy, the woman had to deal more than once with changes in the nature of vaginal discharge. Firstly, it is greatly influenced by the hormonal background of the pregnant woman, which constantly changes over time. Secondly, very often it is during this period that thrush worsens or first manifests itself, annoying with cheesy discharge with a characteristic sour odor. Thirdly, it is likely that there was a threat of failure, which is indicated by spotting during pregnancy. And it is precisely this discharge that expectant mothers fear most.
Now, at the end of the term, you can almost breathe easy: the release of blood before labor in the vast majority of cases will mean its imminent onset. But it’s still too early to completely relax: even on the eve of the baby’s birth, premature placental abruption may begin.
What to do if there are no contractions
If the patient had no problems during pregnancy and does not require a cesarean section, doctors recommend staying at home until labor begins. At this time, it is advisable to limit physical activity and avoid stressful situations.
Nutrition should be as complete as possible. With normal functioning of the kidneys and heart, you can drink 1.5-2 liters of liquid per day. Preference should be given to juices, weak teas and still mineral water.
It is not advisable to limit yourself in food, since the body will need strength during the birth process.
If 24 hours after the water breaks, contractions have not begun, then after consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, you need to come to the hospital. Here it is possible to conduct cardiotocography to examine the condition of the fetus and decide on a strategy for further management of the patient.
If a woman has weak contractions or are completely absent, they can be stimulated with medication. To do this, use the drug oxytocin, a hormone produced in the hypothalamus. It increases the tone of the smooth muscle fibers of the uterine wall, which promotes their regular contraction.
After the administration of oxytocin, labor contractions develop within 10 minutes and last up to 3-4 hours. The drug can be used repeatedly.
There are a number of situations in which the use of oxytocin is contraindicated:
- development of allergic reactions after using the drug;
- fetal distress detected during cardiotocography;
- transverse position of the baby in the uterus;
- partial or complete placenta previa;
- umbilical cord prolapse;
- addition of a secondary infectious process;
- heart failure.
Such pregnant patients are recommended to have a cesarean section. This method of birth is also preferred if stimulation with oxytocin is insufficient.
Physiological contractions begin within 24 hours after the water breaks. If they do not appear on time, or are not strong enough, the doctor may decide on drug stimulation with oxytocin. If it is ineffective, it is necessary to carry out the birth through cesarean section.
Many pregnant women may encounter a situation where the amniotic fluid has broken, but there are no contractions, what to do in this case? No one is immune from such a situation, but you still shouldn’t be afraid of premature outflow of water. If a woman acts correctly at this moment, everything will end well.
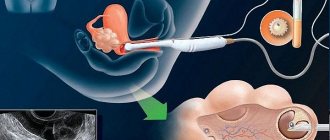
What is amniotic fluid?
Amniotic fluid, or amniotic fluid, is a biologically active medium that creates the necessary conditions for the proper growth and development of the fetus while it is in the womb. Amniotic fluid protects the unborn child from various external negative influences: noise, infections, mechanical damage, sudden changes in pressure and temperature.
In the absence of pathologies of gestation and deviations in the development of the unborn child, the amniotic fluid can be completely transparent or slightly cloudy. Has a sweetish odor. It includes:
- distilled water;
- vitamins;
- proteins;
- glucose;
- salt;
- hormones;
- fats;
- small fragments of the epidermis;
- waste products of the embryo.
Amniotic fluid regulates the metabolism of the small organism, providing it with necessary nutrients and fluid, which in the early stages of pregnancy is absorbed through the pores of the skin and later swallowed in small quantities. With the help of amniotic fluid, the possibility of free movement of the fetus within the fetal membrane is also ensured.
If any pathology is suspected, analysis of fetal fluid allows us to identify:
- Genetic abnormalities or diseases of the fetus.
- Disturbances in the normal course of pregnancy.
- The degree of maturity of the entire small organism or its individual organs.
- The blood type of the embryo.
- Features of pregnancy.
- The need to induce premature labor.
- Indications for cesarean section or abortion.
Abnormal discharge of amniotic fluid
In general, leakage of amniotic fluid can occur at any stage of gestation. Therefore, expectant mothers should familiarize themselves in advance with some of the features of this process so as not to miss an important moment when urgent medical care is needed.
A slight leakage of amniotic fluid can begin at any stage of gestation.
This may be due to some characteristics of the mother’s body, the nature of the pregnancy and some other factors. Therefore, if the expectant mother notices that unusual vaginal discharge has reappeared, she should consult a doctor. This will prevent miscarriage, premature birth or the development of various pathologies in the unborn child.
The volume of amniotic fluid is an individual indicator that depends on many factors. Its amount can vary from 1,000 to 2,500 milliliters. As a rule, the water breaks immediately and completely when there is a significant rupture of the amniotic sac. A woman cannot help but notice this fact. During the daytime, in addition to the underwear getting wet even through the pad, the expectant mother feels heaviness in the lower abdomen. In this case, immediately at the moment of outflow of amniotic fluid, you can feel an internal rupture or cotton. At night, the outpouring does not cause any sensations. Therefore, the main factor indicating that a discharge has occurred is wet bedding and nightwear.
If the ruptures of the bubble are insignificant and appear in its upper part, the water leaves little by little and without any special sensations. Therefore, they are often mistaken for urinary incontinence or severe vaginal discharge. In this case, it is better to independently check using appropriate tests purchased at a pharmacy, or contact a gynecologist who monitors the expectant mother during pregnancy.
Typically, amniotic fluid is colorless and clear. However, when the fetus is deprived of oxygen, meconium accumulates in it. This gives the liquid a black, brown or pale green color. Another dangerous sign is the presence of blood in the water. This indicates placental abruption. In these cases, delay can be dangerous for the life and health of the unborn child. You need to immediately call an ambulance to take the pregnant woman to the maternity hospital.
Discharge before childbirth - what it is, causes and consequences
Discharge during the prenatal period is not always a bad sign.
Most often, this is a natural and understandable phenomenon, so there is no need to rush to the hospital immediately and worry. Each stage of pregnancy has its own type: from mucous to amniotic fluid. Most often, normal discharge tells the expectant mother that the long-awaited baby will be born very soon.
But few people know which ones are normal and which ones signal health problems.
Types of discharge
According to statistics, the following discharge appears before childbirth:
- habitual mucous membranes;
- amniotic fluid;
- discharge after the plug comes out;
- curdled white discharge before childbirth;
- yellow, purulent with an unpleasant odor;
- bloody (for example, pinkish or brown discharge before childbirth).
During pregnancy, discharge of different colors and nature may appear.
Some of them are signs of pathological processes in the body, others are a completely natural phenomenon that indicates a woman’s preparation for the birth process.
Normal discharge
All normal discharge from women in labor should be clear or white, but odorless, in small quantities, and of a thick texture. In medicine they are called mucus.
The mucus plug accompanies pregnancy until the onset of delivery, since its function is to protect the fetus from infections from the outside. Gradually it becomes unnecessary and superfluous, so it comes out. We can say with complete confidence that heavy mucous discharge before childbirth indicates that there is no more than a week left before the baby is born.
Important! After the mucus has receded, the expectant mother needs to be very careful: do not take a bath, do not have an intimate life, and carefully monitor hygiene so as not to introduce harmful microbes into the uterus.
During contractions or immediately before them, water pours out. This is also a normal physiological process that directly signals the onset of labor. Water can drain like this:
- all at once, that is, the woman acutely feels a transparent stream flowing out of her;
- gradual “smudges” during the day.
Mucus plug
The liquid should be odorless and colorless, but may contain some white mucus. If the waters are green - this is a bad sign, immediate contact with a specialist is required.
Pathological discharge
Other discharges that are not mentioned above are considered pathological in medicine, that is, they indicate abnormal physiological processes in the body that can threaten the health of a pregnant woman or her child.
What should you pay special attention to?
- spotting, including brown discharge before childbirth;
- watery brown with an unpleasant odor;
- gray with the smell of rotten fish;
- watery green;
- light, cheesy consistency (while the pregnant woman experiences constant itching in the perineum);
- yellow mucus;
- green slime.
Important! Pink discharge before childbirth is not always considered bloody; if there are a few drops of blood in the discharge, this is a variant of the norm when capillaries in the reproductive organ burst when the mucus plug is released. If there is a lot of blood in the discharge, this is a very bad sign that requires hospitalization. But first things first.
Brown discharge appears in two cases:
- microtrauma of the uterus;
- placental abruption.
The most dangerous are discharges that are bloody or have an unpleasant odor.
The first option is practically not dangerous; it may be associated with a trip to the gynecologist, where the woman was examined in a gynecological chair. In addition, the mucus turns brown if a woman is sexually active in the last months of pregnancy.
Bleeding occurs for one reason - placental abruption. This case threatens the life of both the mother and her unborn child. If a woman notices blood from the vagina, she should immediately call an ambulance or get to the hospital herself as soon as possible.
The opaque color of leaking water, as well as their unpleasant odor, indicates that the fetus is experiencing hypoxia, that is, a lack of oxygen. If there is no smell, then there is a possibility that the baby has emptied in the womb.
The main sign of thrush is itching and light discharge, similar to cottage cheese. This disease needs to be treated urgently so that there is no risk of infection of the fetus, because candidiasis passes through the birth canal.
Another infectious disease is bacterial vaginosis, the color of the mucus is gray and the smell is very unpleasant.
Any yellow discharge is a symptom of sexually transmitted infections. A woman should urgently consult a doctor so that he can prescribe an examination, make a diagnosis and begin timely treatment. Otherwise, the child may also become infected through the birth canal.
Thrush discharge looks like cottage cheese
Reasons for appearance
Brown discharge before childbirth at the 38th week of pregnancy after a full examination by a gynecologist of the woman in labor is not dangerous and is due to the fact that the cervix has already fully matured, softened and become ready for delivery. Droplets of blood appear in the discharge a couple of hours after ingestion.
A woman may feel the release of the mucus plug, which was already mentioned above, or may not notice it at all. The mucus may also be a little pink, but this has nothing to do with the risk of miscarriage.
If the color of the discharge is orange, this is a signal from the body that the expectant mother is abusing vitamin-mineral complexes and there is an excess of such things in the body. Vitamin intake should be reduced or eliminated altogether.
You can judge a woman's health by the color of her discharge.
Any normal physiological discharge has virtually no color (transparent or light - cream, white) or odor. In all other cases, an infection is possible that can easily be transmitted to the child during childbirth from the mother. Therefore, it is so important to visit a doctor on time and cure the disease before giving birth.
What discharge indicates the onset of labor?
It is the discharge that is the first harbinger of labor, which appears even before contractions. What discharge before labor signals the onset of labor?
- A clot of mucus or partial profuse discharge of a mucus plug. In this case, labor can begin in a couple of hours, or in a few days, but not later than in a week. The passage of the plug occurs when the cervix is completely ready for the birth of the baby.
- Watery discharge, clear and odorless, slightly mixed with non-colored mucus. This happens just before contractions begin or even during them. Sometimes the bubble does not burst on its own, then it is punctured by a doctor in the maternity ward, when it becomes clear that the contractions are regular and not training. If the water is leaking, and there have been no contractions for a long time, you need to urgently go to the maternity hospital, otherwise the baby will begin to lack oxygen. If this happens, the liquid will be green or yellow.
A drooping belly is a sign of imminent labor
We can say with confidence that labor begins:
- drooping tummy;
- a feeling of increasing pressure in the lower abdomen, as if something were pressing on the intestines with great force;
- stopping weight gain;
- changes in mood;
- the appearance of frequent and painful spasms;
- bowel movement.
Does not indicate the onset of labor:
- irregular spasms;
- if you change your position or start walking, the spasms stop;
- movement of the fetus during spasms (this is reported to the doctor).
Important! By the 38th week, a woman should have her bags ready for the maternity hospital. If a woman doubts whether labor has begun or not, it is better to still get to the hospital; this is better than later giving birth at home or on the way to the maternity hospital.
When is hospitalization required?
If a woman has a pathological case, then the ambulance team should be called without delay. Critical situations include:
- blood spots on the pad in the last month of pregnancy (these are not two or three drops that appear after an examination by a gynecologist);
- leakage of liquid that has a green tint;
- severe pain in the lower abdomen and lower back.
If you experience severe pain in the back and lower back, consult a doctor immediately
If a woman in labor notices yellow or curdled discharge on her panties before giving birth at 8-9 months, you should not call an ambulance, nor should you treat yourself (especially with traditional medicine, which causes an allergic reaction in the fetus), it is enough to visit a doctor as soon as possible . If this is not done, a possible infection will complicate childbirth and be transmitted to the baby either after the mucus plug comes out or during delivery.
Discharge before childbirth always tells a woman what processes are occurring in the body at a specific period of time.
Is pathology developing or do you need to pack your bags for the maternity hospital? Do you need to call an ambulance to save the life of yourself and your child, or can you simply make an appointment with a doctor in the near future, who will prescribe treatment if necessary and tell you in more detail what is happening in the body.
The most dangerous are the bloody and green watery ones, as they directly indicate a problem that is occurring at that moment. Only transparent or light odorless ones are considered normal; they are harbingers of labor.
Source: https://nashirody.ru/vydeleniya-pered-rodami.html
What to do if there is premature rupture of amniotic fluid?
If the water breaks and there are no contractions, many expectant mothers are at a loss, not knowing what to do in such a situation. First of all, you need to calm down. If there is no blood or other impurities in the gushing waters, you can stay at home for a while.
Unless, of course, the woman suffers from any infectious or other disease that can be transmitted to a baby not protected by amniotic fluid.
However, it should be remembered that if the water breaks and there are no contractions, this creates a certain risk for the successful outcome of the birth process. After all, a prolonged waterless period creates a number of dangers for the health and life of the unborn child. Although amniotic fluid is constantly produced by the walls of the amniotic sac, it is still not enough to ensure absolute protection of the child from external influences.
Therefore, it would still be wiser to immediately go to the maternity hospital after the amniotic fluid has completely drained. There, the expectant mother will be examined by specialists, and she will undergo the necessary tests to determine the general condition of her and the child. The expectant mother must be examined in a gynecological chair. This makes it possible to detect prolapse of the upper or lower limbs of the fetus or the umbilical cord. In the first case, various complications of childbirth are possible. In the second case, the fetus may die due to lack of oxygen, so an urgent caesarean section may be necessary.
After this, the issue of inducing labor, taking antibiotics to protect the fetus from possible infection, etc. will be decided. If inducing labor with the help of special drugs does not give the expected result, resolution of labor by cesarean section may be indicated.
Brown, brown, dark brown discharge at 37–41 weeks
Discharge before childbirth of brown or dark brown shades of low intensity and volume is not evidence of a disruption in the natural course of pregnancy.
Brown discharge Brown discharge
Such substances in small quantities indicate the readiness of the cervical muscle for the passage of the fetus.
In such a situation, it is worth listening to your own feelings. A sharp muscle tone in the lower abdomen, combined with copious discharge of brown or dark brown shades, indicates a sharp contraction of the cervical muscle. This phenomenon is fraught with one-time or multiple rupture of the amniotic sac.
Spotting in late gestation
The presence of a bloody clot or small spotting should cause concern. If such a phenomenon finds a woman in labor at home, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance and go to the maternity hospital. Bloody spotting before birth may indicate premature placental abruption and previa.
Bloody issues
These phenomena can cause bleeding, which directly threatens not only the safety of the fetus, but also the life of the woman.
Bloody and pink mucous discharge before childbirth
Sticky pink mucous discharge during pregnancy in the third trimester, whose consistency resembles mucus or, as many mothers say, “snot,” is considered a physiological phenomenon and does not indicate abnormalities during pregnancy.
Discharge mixed with blood Discharge pink mucus Yellow-brown mucus discharge
This process is associated with the beginning of the passage of the mucous plug, which protects the fetus from infection throughout the entire period and the active preparation of the woman’s body for childbirth. The color is due to the entry of blood cells into it during the formation. This phenomenon does not indicate a disruption in the natural course of pregnancy and the possibility of a threat to the life of the fetus.
Physiological plug is a thick mucous substance. Its withdrawal is an individual phenomenon and can take from several minutes to days. The result of this process is the softening of cartilage tissue in the pelvis and the beginning of active labor. By the way, it is the increased uterine contractions at this time that cause false contractions.
The assessment of risks to the health of the fetus and the woman in labor should be carried out by a practicing gynecologist. If no threats are identified, you should follow some simple recommendations to protect yourself from unwanted consequences:
- Regardless of the amount and intensity of discharge, the use of tampons is strictly prohibited! Their surface is a fertile environment for the development of microorganisms.
- Refrain from visiting public swimming pools, baths and saunas.
- Avoid taking a bath. Perform personal hygiene using a shower.
- To get rid of secretion, it is strictly forbidden to use solutions and syringes.
- Refrain from active sex life. After the release of protective mucus, the uterine cavity, and therefore the child, is easily infected.
- When choosing underwear, try to focus on seamless models made from natural, hypoallergenic, breathable fabrics.
Similar article - Diet number 5 for pancreatitis of the pancreas
A little about the anhydrous process
The duration of safe anhydrous existence of the fetus on the eve of birth is a subject of debate and discussion among practicing obstetricians and gynecologists around the world. Experts have not yet come to a consensus. In Russia, obstetricians and gynecologists generally begin induction of labor 12-13 hours after premature rupture of amniotic fluid.
Some experts believe that induction of labor can begin after 24-36 hours. Sometimes the water-free period can be extended to 72 hours. The issue remains open for now, but over time it will be resolved.
Amniotic fluid performs several important functions, but first of all, it provides the baby with protection and absorbs its movements inside the mother's womb. In normal labor, the waters usually break during the first phase. The ideal option is the release of amniotic fluid after contractions, when the cervix is fully dilated. But sometimes labor begins not with contractions, but with the rupture of the fetal sac and the release of water. What to do if your water breaks but there are no contractions, we will tell you in this article.
Discharge during contractions
Discharge that bothers a woman in labor in the last months of pregnancy may appear directly during labor and accompany childbirth. Such a phenomenon should not cause concern in a woman.
Such discharge often has a smearing mucous consistency and a brown or brown tint. Sometimes a woman in labor may notice blood inclusions, more like veins, in light yellow clots rejected by the body. To eliminate unnecessary anxiety, it is worth understanding the physiological processes of this stage.
Contractions are a sharp contraction of the muscles of the uterus, starting at the top and spreading along the walls. Accompanied by sharp, throbbing pain radiating to the lumbar spine and groin area. Contractions not only contribute to the advancement of the fetus, but also prepare the birth canal for this. Contractions in the first period are less intense and help dilate the cervix.
With the onset of labor, the lining of the uterus and blood vessels experience severe pressure. Injuring them during childbirth provokes the appearance of bloody spotting. It is on the basis of the presence of such clots, rejected by the uterus, that obstetrician-gynecologists establish the expected time interval in which the child will be born.
Brownish discharge in small quantities with bright bloody streaks indicates possible delivery in a few hours.
Attention! The volume of physiological secretions that do not indicate abnormalities in the development and presentation of the fetus does not exceed 2–3 tablespoons!
Another possible reason for the appearance of specific brown discharge during contractions is the release of the mucus plug immediately at the moment of the onset of delivery. During the clogging process, this protective secretion can contain blood cells resulting from injury or the approach of the menstrual period. When rejected, before the active start of the birth process, the “plug” may lose its structure and the released particles, interacting with air, acquire a brown tint.
The appearance of bloody-scarlet discharge shortly or directly during contractions indicates the emergence of a situation requiring urgent medical intervention! The presence of large blood clots in the mucus may indicate the onset of internal bleeding or premature placental abruption. Such deviations require immediate medical intervention in the birth process.
Briefly about the main thing
The 9th month is the most stressful and exciting time for an expectant mother. The sudden appearance of various discharges can provoke “prenatal jitters” and seriously alarm the woman in labor. But it is worth remembering that liquids of various colors and consistencies not only signal danger, but also foreshadow an imminent birth, being natural female assistant guides.
Similar article - Curettage for adenomyosis
For example, brown spotting in small quantities indicates the onset of active labor 2–5 days after the appearance of the first “smears” . Colorless, watery mucus makes it clear to the expectant mother that there are several days left before meeting the baby, but abundant dark mucous substances, released in parallel with frequent contractions, are considered harbingers of the birth of the baby in a few hours.
The process of labor pains does not always proceed in strict accordance with textbook descriptions in medical textbooks. Much depends on the individual characteristics of the woman and her pregnancy.
Therefore, the appearance of bloody discharge already at the stage of contractions is not at all uncommon. Is this normal and what to do if they appear, we will tell you in this article.
Causes and signs of rupture of water
According to statistics, 10% of pregnant women who carried their baby to term experience premature rupture of water. In almost half of the cases of premature birth, the process of giving birth to a baby also begins not with contractions, but with the discharge of amniotic fluid. It is noteworthy that in women in labor whose first pregnancy ended with the breaking of water before the development of labor, in 35% of cases the scenario is exactly repeated during the subsequent pregnancy.
The outpouring of amniotic fluid can be massive, when a lot of it is poured out at once, or it can be gradual, when water gradually leaks due to a small rupture of the membranes. It can be difficult to determine such discharge on your own, and therefore women are strongly recommended to inform their doctor if the nature of the discharge changes.
Before giving birth, a woman’s body produces special enzymes that soften the membrane of the fetal sac. It can burst prematurely due to numerous reasons.
- Ascending infections in the mother (genital tract infections) are the most common cause of premature pregnancy.
- A narrow pelvis and incorrect position of the fetus in the uterus are more common in cases of full-term pregnancy. In this case, there is no tight fit of the presenting part of the child’s body to the pelvis, no division into the so-called anterior and posterior waters is created, almost the entire volume of amniotic fluid accumulates below and leaves. But the risks for the fetus and the woman for this reason are minimal.
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency - this reason usually accompanies premature birth, but can also become the first signal about the onset of the birth of a full-term baby.
Why does bleeding occur before childbirth?
The birth of a baby is a joyful event that you don’t want to overshadow with anxious thoughts.
But knowledge about the complications that can accompany childbirth is necessary - first of all, in order not to get confused at a critical moment and to meet them fully armed. After all, the calmer a woman behaves, and the better she understands her condition, the greater the likelihood of a successful birth outcome for both mother and child. In this article we will talk about one of the most dangerous complications - bleeding. It can develop during childbirth, in the early postpartum period, and even in the last weeks of pregnancy.
The onset of bleeding poses a serious danger to the health (and sometimes to the life) of the mother and the unborn child.
Causes of bleeding
Most often, the immediate cause of bleeding is problems related to the condition of the placenta.
. Predisposing factors for them are:
- Chronic inflammatory diseases of the uterine mucosa (endometritis), especially untreated or undertreated.
- “Old” injuries of the pelvic organs and scars on the uterus (regardless of their origin).
- A large number of abortions, miscarriages and (or) childbirth in a woman’s life, especially if they were complicated by inflammation. (If we take all cases of placenta previa as 100%, then 75% of them occur in multiparous women and only 25% in primiparous women).
- Hormonal disorders, endocrine diseases.
- Uterine fibroids and other diseases of the internal genital organs.
- Severe cardiovascular diseases, some kidney and liver diseases.
- Injuries during pregnancy.
- The woman is over 35 years old.
So what placental problems can cause bleeding?
- Incorrect separation of a normally located placenta
- Premature abruption of a normally located placenta
. Placental abruption can occur in various areas. If the placenta detaches from the edge, then blood flows out of the external genital tract. In other words, in this case there is external bleeding; in such a situation, pain in the lower abdomen is insignificant or absent altogether. Placental abruption can also occur in the middle, then blood accumulates between the placenta and the wall of the uterus and a hematoma is formed; in this case, the pain syndrome is more pronounced.
Premature abruption of a normally located placenta is accompanied by signs of blood loss: heart rate increases, blood pressure decreases, and cold sweat appears. Since this sharply reduces the amount of blood flowing to the fetus, fetal hypoxia develops, so this situation can be life-threatening for both mother and child.
Depending on the period of labor, the condition of the woman and the fetus, childbirth can be completed through the vaginal birth canal or by caesarean section.
- Difficulty in independent and timely separation of the placenta in the third stage of labor (tight attachment or accretion of the placenta - all or partly)
. Normally, after the baby is born, the placenta separates and is delivered. When the placenta separates, a large wound surface forms in the uterus, from which blood begins to ooze. This physiological (normal) bleeding stops very quickly due to contraction of the walls of the uterus and compression of the vessels located in them, from which, in fact, the blood flowed. If the process of placenta rejection is disrupted, then bleeding begins from the surface of the mucous membrane, which has already been freed from the placenta, and tightly attached fragments of the placenta do not allow the uterus to contract and compress the vessels. If a tight attachment of the placenta is suspected, a manual examination of the uterine cavity is performed. This is an operation that is performed under general anesthesia. If the placenta cannot be separated manually, it is said to be placenta accreta. In this case, an emergency hysterectomy is performed. - Incorrect placement of the placenta
:- Placenta previa
, when they partially or completely block the internal os of the cervix. - Low location of the placenta
, when its edge is located closer than 5-6 cm from the internal os of the cervix. - Cervical placenta previa
is a rather rare location of the placenta, when, due to the slightly open internal os of the cervix, it can partially attach to the mucous membrane of the cervix.
With the onset of labor (if not earlier, even during pregnancy), the incorrect location of the placenta definitely develops into its premature detachment.
This occurs due to more intense stretching of the lower (compared to the upper and middle segments) parts of the uterus as pregnancy progresses and their rapid contraction during dilatation of the cervix during childbirth. Complete and cervical placenta previa are more complex and severe complications.
The lower parts of the uterus are less adapted by nature to fully provide the baby with everything necessary. The developing fetus suffers more from a lack of primarily oxygen and, naturally, nutrients.
When the placenta is completely or cervically attached, bleeding can begin spontaneously in the second trimester of pregnancy and be extremely intense. It should be especially emphasized that with complete placenta previa there is no need to talk about independent childbirth at all, since the placenta tightly blocks the “exit”, i.e. cervix.
In this case, a planned caesarean section is performed at 38 weeks of pregnancy. If bleeding occurs, an emergency caesarean section is performed. In case of marginal placenta previa, full labor activity, light bleeding and good condition of the mother and the newborn child, it is possible to carry out delivery through the natural birth canal.
However, the decision on the form of delivery always remains with the doctor. In rare forms of placenta previa, when it affects areas of the cervix, preference is given to cesarean section; Moreover, this situation may even result in the removal of the uterus, since this location of the placenta is PURELY combined with its ingrowth into the wall of the cervix.
Bleeding is also accompanied by another, more rare complication - uterine rupture.
. This extremely serious condition can occur both during pregnancy and directly during childbirth.
Obstetricians specifically determine for themselves the time characteristics of the rupture (threatening, beginning and completed rupture) and its depth, i.e.
how severe is the damage to the uterine wall (it can be a crack, an incomplete rupture, or the most dangerous - complete, when a through defect is formed in the uterine wall with penetration into the abdominal cavity).
All these conditions are accompanied by varying degrees of severe bleeding and severe pain that does not stop between contractions. The contractions themselves become convulsive or, conversely, weaken; The shape of the abdomen changes, signs of child hypoxia increase, and the fetal heartbeat changes.
At the moment of complete rupture of the uterus, the pain sharply intensifies, becoming “dagger-like,” but the contractions stop completely. A false impression of decreased bleeding may appear, since the blood no longer flows out as much as it enters the abdominal cavity through the rupture.
The abdominal deformity remains, the child can no longer be felt in the uterus, but next to it, and there is no heartbeat. This is a critical condition: only immediate surgery and resuscitation measures can save the mother and baby (if he is still alive). The operation usually ends with the removal of the uterus, since the torn, thinned, blood-soaked walls of the uterus are almost impossible to sew up.
The risk group for the probable occurrence of uterine rupture includes:
- Pregnant women with an existing scar on the uterus (regardless of its origin: trauma, cesarean section, removed fibroids, etc.). It should be noted that modern cesarean section techniques are aimed at minimizing the risk of the above-described complications during repeated pregnancies. For this, a special technique is used to cut the body of the uterus (transverse, in the lower segment), which creates good conditions for subsequent wound healing and minimal blood loss in the event of a possible rupture during childbirth.
- Multiparous women with complicated previous births.
- Women who have had multiple abortions.
- Women with complications after an abortion.
- Patients with chronic endometritis.
- Women in labor with a narrow pelvis.
- Pregnant women with a large fetus.
- Pregnant women with abnormal position of the fetus in the uterus
- Women in labor with discoordinated labor (a condition when, instead of a simultaneous contraction during a contraction, each fragment of the uterus contracts in its own way).
If a woman knows that she belongs to one of these categories, she should warn her doctor at the antenatal clinic and the obstetricians at the maternity hospital about this.
Why is bleeding dangerous?
Why do obstetric hemorrhages remain so dangerous today, despite all the achievements of modern medicine, the development of resuscitation techniques and a fairly large arsenal of means to replenish blood loss?
Source: https://sfmggu.ru/pochemu-otkryvaetsya-krovotechenie-pered-rodami/
When should labor start?
If your water does break, there is no need to panic. Normally, contractions should begin within about 3-4 hours. This period is considered optimal. But the limits of the permissible latent period are quite wide.
- If your gestation is between 24 and 28 weeks, it may take a month before your water breaks before delivery. Naturally, if the doctors decide to wait, the woman will have to spend this entire period on bed rest in a ward with increased sterility measures. An important condition is that not all water must recede.
- During pregnancy from 29 to 37 weeks , contractions develop independently within 24 hours in approximately half of the women; for the rest, the waiting period may be longer - up to a week, which, again, provided that the discharge is incomplete and the mother has no infections, the woman will have to spend in hospital ward under the supervision of a doctor.
- From the 38th week, from the moment of effusion to the onset of contractions, usually no more than 12 hours pass in half of the women. For others, the latent period can last from 24 to 72 hours.
After an amniotomy (puncture of the amniotic sac), there is usually less time before contractions begin. Without stimulation they begin within 3-9 hours.
Another question is that waiting a long latent period is sometimes downright dangerous. The risks for a baby deprived of protective waters are too high. Therefore, the question of delivery is raised head-on almost a few hours after a woman goes to the hospital.
During a normal birth, after the timely release of amniotic fluid, the child remains without water for some time. In this case, nature has provided a number of compensatory mechanisms. But a baby cannot be without water for more than 12 hours without health consequences. The safest period is considered to be 6 hours. After this time, doctors need to decide what to do next to save the child and his mother.
Bloody discharge before labor is a sign of its onset
One of the most reliable signs of the onset of labor is the release of the mucous plug, which is always accompanied by discharge. The plug may come off during childbirth (then the woman will not notice it) or come out all at once as a whole clot, for example, while taking a shower, which may also go unnoticed.
But also often the mucus plug comes off in parts, gradually, and at the same time the woman notices a white-yellow mucous discharge on the underwear, which may contain streaks of blood - pinkish, brown or brown. This is a sure sign that there is very little time left before meeting the most desirable creature. From the moment the mucus plug begins to come off, the mother should stop any activities that could lead to infection entering the womb (sexual relations, taking a bath and swimming in stagnant bodies of water).
>
Danger
Why is the waterless period so dangerous for the baby and the woman in labor, why can’t we calmly wait for the end of the latent period and the start of independent contractions?
The most important and most formidable danger lies in the development of an infection that will affect the baby and the inner lining of the uterus. This complication occurs in about a third of cases if the baby remains in the uterus without water for more than 12-24 hours. For the child, this threatens with serious consequences, often death. For the mother, this condition threatens the removal of the reproductive organ and the inability to subsequently conceive, bear and give birth to a child on her own. Infections do not enter the uterus during pregnancy due to the mucus plug and amniotic fluid, which create an almost sterile environment. If there is no water or plug, the likelihood of infection with staphylococcus, streptococcus and other bacteria and viruses is high.
For premature babies, if the water breaks before the 37th week of pregnancy, the situation is complicated by the likelihood of respiratory distress syndrome. In 70% of cases, it is this complication that causes the death of a premature baby.
To avoid such a complication, doctors need to determine with great precision the limits of what is reasonable - to extend the latent period as long as necessary to stimulate hormone production of surfactant in the baby’s lungs, at the same time they need to not overdo it and not lead to infection of the fetus.
An equally dangerous complication of the anhydrous period is fetal hypoxia. It occurs due to compression of the umbilical cord and placental abruption, which occurs quite often. The danger of acute oxygen starvation lies in the likelihood of damage to the brain, central nervous system, and death of the child. Often, after a long anhydrous period, a child develops cerebral palsy, ischemic brain damage, the degree of consequences of which is commensurate with the degree of hypoxia and the duration of the anhydrous period.
Often, labor after the water breaks occurs with anomalies. In itself, early discharge of amniotic fluid is considered a complication of pregnancy and the birth process. However, the lack of water very often leads to the development of contractions, but very weak ones, insufficient to dilate the cervix and give birth to the baby. Another common complication of childbirth after the rupture of water is rapid labor, fast, in which the likelihood of birth trauma is very high.
The formation of cords inside the uterus during a long anhydrous stay is extremely dangerous for the baby. These thin and strong threads can lead to self-amputation of the fetal limbs.
Removal of the mucus plug
The situation when a woman at 37-40 weeks of pregnancy has abundant mucous discharge before childbirth indicates the release of the mucous plug, which clogs the cervix during the entire gestation. Intense secretion of thick mucus signals that labor is about to occur. A woman needs to call an ambulance or go to the maternity hospital on her own, regardless of the presence of contractions. For many women, the release of the plug and the onset of contractions are recorded simultaneously.
The cork is not white or transparent, but yellowish in color; due to blood streaks, it can turn pinkish.
The consistency is also ambiguous - from thick, gradually coming out mucus to several lumps. If immediately after the mucus plug has moved away, the discharge becomes liquid and transparent, leakage of amniotic fluid is diagnosed.
How do doctors act?
Immediately after you are brought to the hospital, doctors will have to quickly make the right decision on what to do next - induce contractions and stimulate labor, perform a caesarean section, or enter into a latent period and try to prolong the pregnancy as much as possible.
First, they will confirm the fact of rupture of the membranes. The woman will be examined, have an ultrasound with changes in the amniotic fluid index, and tested. Today the PAMG-1 test (Amnishur) is used for diagnosis; its accuracy is over 99%.
If the fact is not confirmed, the woman will be reassured and sent home, since it is too early for her to give birth. If the diagnosis confirms rupture of the membranes, they proceed to assess the condition of the woman and child.
It is important to find out as accurately as possible the estimated weight and height of the fetus, the size of its head, the size of the woman’s pelvis, and the degree of readiness of her cervix for labor.
If the pregnancy is less than 36 weeks, most often they try to do everything possible to wait at least a little, to give the baby the opportunity to accumulate surfactant in the lungs. If there are contraindications to expectant management, the issue of delivery is immediately resolved.
If the pregnancy is full-term, and this is considered the gestational age from the 37th week and above, the waters are clear, the woman is sent to the antenatal ward and waits for several hours. During this time, she will be examined for infections, and the baby’s condition will also be monitored using CTG.
If the contractions are too weak or there are no contractions after 6 hours, this is a reason to induce labor. The woman is given a drip of oxytocin, a hormone that enhances uterine contractions. If after another 6 hours full dilatation of the cervix has not occurred, a decision is made to perform an emergency caesarean section.
If doctors decide that giving birth now could be fatal for the child (risk of respiratory distress syndrome) and a decision is made to prolong the pregnancy, they place the woman in a separate room equipped with working bactericidal lamps. It is cleaned 4-5 times a day, linen on the bed is changed once a day, diaper pads are changed to clean and sterilized ones every 3 hours. Strict bed rest and round-the-clock monitoring of the fetal condition are prescribed.
conclusions
Doctors will continue pregnancy after the water breaks only if there is no contraindication for staying in the latent period. Such contraindications include infections, inflammatory processes, various complications and pathologies of pregnancy.
All women whose babies have reached a weight of 2600-2700 g or more at a period of 37 weeks of pregnancy and above are trying to give birth without waiting for many days. Women whose children weigh less and have a shorter term will also have to give birth as soon as possible (usually by caesarean section), provided that there are signs of infection or suspicion of fetal distress - Rh conflict, hypoxia, signs of CHT abnormalities.
The rupture of amniotic fluid can have serious consequences for both the baby and his mother. That is why it is important to act without panic, but clearly and quickly.
Just in case, a woman from 32-34 weeks should prepare a bag with the necessary things and documents for hospitalization, place it in the corridor, not far from the exit. If the water breaks, the outcome of pregnancy and childbirth depends on how quickly she ends up in the hospital and is examined.
From 32 weeks you should not wear colored underwear or sleep on colored bedding. The very fact of water draining or leaking on them can be detected, but it will be almost impossible to determine the color or shade of water when pouring onto blue, green or red bed linen. It is best to use white underwear and panty liners, which will help determine the nuances of the color scheme of the amniotic fluid.
There is not a single harbinger of water breaking. Not a single symptom will appear and indicate that the amniotic sac will burst soon. This happens all of a sudden, unexpectedly, sometimes even without apparent reasons or prerequisites. A woman needs to be extremely prepared for such an event. With the correct actions of the woman in labor and the correct medical tactics (active or passive, expectant), everything ends well, and completely healthy children are born. The likelihood of complications will increase as time is lost.
To see how the onset of labor occurs and your waters break, see the following video.
Which discharges before childbirth are not dangerous, and which require hospitalization
During pregnancy, the female body requires increased attention - especially in the first and last trimesters. Just before childbirth, discharge may appear, which worries many expectant mothers. Whether they are physiological or signal a problem depends on the color, consistency of the secretion, time of appearance and accompanying symptoms.
Blood after intimate contact
Doctors do not prohibit pregnant women from continuing their intimate life if there are no direct contraindications, which include placenta previa detected by ultrasound, increased tone of the uterine walls and diagnosed pathologies of fetal development. It is better to abstain from sexual intercourse, starting from the 35th week of gestation, if immediately after intercourse a woman begins to have spotting dark brown discharge and pain in the lower abdomen.
Experts insist on sexual abstinence for the last two months of pregnancy if you have the following health problems:
- multiple pregnancy (the patient is carrying two or more children);
- leakage of amniotic fluid;
- pronounced discharge of the mucus plug;
- unexpected dilatation of the uterine cervix, which occurred long before the expected date of birth;
- cervical canal insufficiency (a pathology in which the cervix is unable to remain closed, and the risk of premature birth increases);
- discharge from the genital tract with an unpleasant odor and unnatural color, with foreign inclusions - yellow, brown, greenish, white with a cheesy consistency;
- false contractions.
If the discharge began during pregnancy just before childbirth, immediately after sexual intercourse, it means that the partners chose an uncomfortable position that traumatized the cervix. You should seek medical help and find out whether the discharge really warns of the onset of labor and labor, or whether it will go away with sexual rest.
Many experts even advise intimate intercourse for women carrying a child longer than 39-40 weeks. Sexual contact promotes the release of hormones that have a positive effect on the condition of the fetus.
In many cases, immediately after sex, a woman experiences spotting, and after a few hours the process of labor begins with active contractions.
Discharge after examination by a gynecologist
To monitor the future woman in labor over time, doctors recommend undergoing examinations in a gynecological chair once every 1-2 weeks, and the last weeks of gestation, from 36 to 40, are no exception. If labor has not begun at this stage, the patient is prescribed rest, excluding further examinations.
Many women who visit a gynecologist in their last stages experience unpleasant symptoms. Brown vaginal discharge just before childbirth, after examination by a doctor, may be accompanied by nagging pain in the lower abdomen. This clinical picture is explained by the special sensitivity of the mucous membrane in the vaginal lining, cervix and uterine walls at the last stage of gestation.
Permeated with overcrowded blood vessels, the mucous membrane reacts painfully to medical intervention, which is why unnatural discharge appears.
If the bloody mucus stops leaking after 1-2 days, there is no cause for concern. If pain in the pubic area, back and lower abdomen increases, if there is more secretion, you should leave home to see a doctor or call an ambulance.
Discharge during contractions
In the later months of pregnancy, at 38-40 weeks, the fetus is fully term.
The mucous secretion leaking from the genital tract at this time should not frighten the woman - it signals the impending birth.
During the first contractions, the woman in labor begins to experience bloody mucous discharge - before birth, it is brown to brown in color and may include inclusions similar to yellow veins.
Contraction is a process of contraction of the uterus, which begins at the top point and then spreads to the walls.
Associated symptoms include sharp pain in the lower abdomen, spreading to the lower back. The contractions that occur in the first period are not so intense, thanks to them the fetus moves down, the birth canal prepares for the active process of delivery.
As soon as the first contractions begin, the woman may notice a brownish fluid with the presence of clots.
It appears due to increasing pressure on the uterus, which is stuffed with swollen blood vessels.
It is by the presence of these clots that doctors can determine the approximate duration of labor and the time of birth of the child.
The volume of bloody secretion that appears during contractions should not exceed 50-70 ml. An increase in the number allows one to suspect that premature placental abruption has begun.
Removal of the mucus plug
The situation when a woman at 37-40 weeks of pregnancy has abundant mucous discharge before childbirth indicates the release of the mucous plug, which clogs the cervix during the entire gestation.
Intense secretion of thick mucus signals that labor is about to occur. A woman needs to call an ambulance or go to the maternity hospital on her own, regardless of the presence of contractions.
For many women, the release of the plug and the onset of contractions are recorded simultaneously.
The cork is not white or transparent, but yellowish in color; due to blood streaks, it can turn pinkish.
The consistency is also ambiguous - from thick, gradually coming out mucus to several lumps. If immediately after the mucus plug has moved away, the discharge becomes liquid and transparent, leakage of amniotic fluid is diagnosed.
Leakage of amniotic fluid
The moment when the amniotic fluid is completely poured out, a woman cannot help but notice.
The normal volume of amniotic fluid ranges from 500 ml to 1.5 liters.
The liquid itself has a sweetish aroma, and along with it, particles of lubricant are rejected from the uterus, intended to prevent injury to the child when passing through the birth canal.
Complete rupture of amniotic fluid occurs when a woman suddenly changes her body position or strains while going to the toilet.
More often, water leakage occurs gradually, the speed of its drainage depends on the location of the bubble rupture.
Amniotic fluid leakage can be diagnosed as follows:
- wash the external genitalia using a neutral detergent;
- dry the skin with a clean towel or napkin;
- lie down on a clean bed;
- lie down for a quarter of an hour and examine the sheet.
If there are wet spots on the bed, it can be said that the bladder has opened and the water has begun to break.
The flow of amniotic fluid, colored yellow or green, indicates the presence of problems - fetal hypoxia (oxygen starvation), placenta previa or untimely abruption. If a large amount of blood is released along with amniotic fluid, you need to urgently call a medical team and stop trying to get to the hospital on your own.
Types of discharge before childbirth
Not all women experience unusual vaginal fluids before giving birth; according to statistics, the symptom is observed in four out of ten patients.
Sweating a small amount of secretion at 36-40 weeks is normal if it is not accompanied by pathological signs - fever, severe abdominal pain, bleeding.
What kind of discharge should be normal before childbirth depends on the term, full-term birth of the baby, the presence or absence of problems with pregnancy (increased uterine tone, placenta previa). There are several types of discharge - the secretion may differ in color, consistency, and have a distinct odor; its varieties can be assessed in the photo.
Yellow and whitish discharge in later stages
The discharge of amniotic fluid is a natural process that precedes childbirth. If a woman suddenly experiences white, flocculent discharge just before giving birth, the process signals that labor is about to begin and should not be a cause for concern. The expectant mother has to slowly get ready and go to the maternity hospital; the first contractions will probably appear soon.
Greenish secret
In a situation where a greenish secretion is released from the genital tract along with the amniotic fluid, immediate medical attention is necessary, especially if the substance contains fecal particles and the fluid smells unpleasant. Symptoms indicate fetal hypoxia, when meconium (original feces) of the baby is released into the fetal bladder. He can swallow a particle of it and suffocate.
Brown and dark brown discharge
The natural course of gestation should not be overshadowed by the appearance of brown dark discharge before childbirth - a meager amount of such secretion indicates that the cervix is ready for the upcoming passage of the fetus.
The expectant mother needs to be taught to focus on her own feelings.
If the leakage of dark brown liquid, even in a small volume, is accompanied by nagging pain in the groin and lower back, or a general deterioration in health, you should seek medical help.
With a sudden increase in uterine tone, rapid labor and single or multiple rupture of the amniotic sac often occur.
It is important to distinguish brown secretion, which does not pose a threat to the health of the woman and child, from cervical spotting before childbirth with the presence of blood clots. Such daubing with lumps can be caused by abruption or placenta previa.
The secret of pink
Shortly before labor begins, a woman's mucus plug begins to come off. It is viscous, thick, and according to many patients, it resembles snot. The physiological color of cork is transparent, slightly whitish.
And intense pink thick discharge before childbirth also indicates that mucus has begun to leave the cervical canal, preparing the pelvic organs for the upcoming process of expulsion of the fetus.
The pink color of the mucus gives a small amount of brown discharge of a natural character.
White discharge
Normally, secretion leaking from the vagina and being whitish in color should not cause concern in late pregnancy. It is recommended to visit a doctor immediately if you have additional symptoms:
- curdled consistency of the secretion;
- the appearance of itching and burning in the labia area;
- the presence of a pronounced smell of sour milk in the secretion.
Signs indicate infection with the yeast-like fungus Candida; a woman can become infected with thrush from a sexual partner, or provoke the pathology by leading an incorrect lifestyle. In the later stages, immunity is significantly reduced, so it is recommended to protect yourself from general and local hypothermia, eat a balanced diet, do not overindulge in sweets and baked goods, and maintain hygiene.
It is imperative to treat thrush in the later stages, since the disease poses a threat of a bacterial infection occurring after childbirth and infecting the baby as it passes through the birth canal.