Sometimes in vitro fertilization can be accompanied by some complications for the woman's health. In this case, the most serious problem is ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome during IVF. This phenomenon can occur due to the administration of a large volume of the drug to stimulate the ovaries.
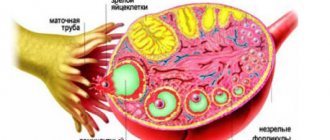
Typically, OHSS develops immediately before the embryo is transferred to the uterus. With ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, instead of one egg, up to 30 germ cells can mature. Of course, this is very good for the IVF protocol, since the likelihood of conception increases, but in this condition the level of estradiol also increases, which impairs the permeability of blood vessels and capillaries. Symptomatic phenomena include the appearance of edema.
What is ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
OHSS is called a reaction of the ovaries in response to a high dosage of hormonal therapy drugs (Gonal) prescribed during reproductive technology. Medicines stimulate an increase in the number of oocytes maturing during 1 cycle. As a result, the patient produces an increased amount of estradiol, which entails an increase in blood clotting and capillary permeability. The accumulated fluid in the tissues causes swelling.
Doctors believe that ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is a severe complication of in vitro fertilization. The likelihood of a woman encountering it is quite high, especially when carrying out a long protocol and hereditary predisposition.
OHSS can appear in a patient both before implantation of the embryo into the uterine wall and at the onset of the gestational period. If the symptoms begin early and intensely, the course of the disease is more severe compared to a late and gradual onset.
During pregnancy
Implantation of a fertilized egg provokes aggravation of the syndrome, so pregnant girls require hospitalization and supportive care. They are prescribed symptomatic treatment, as well as drugs that allow them to maintain pregnancy:
- antispasmodics – relieve tone (tension) of the uterus, relax its walls;
- hormones – stabilize hormonal levels, support pregnancy;
- hepatoprotectors – improve liver function.
During pregnancy, doctors try not to prescribe antibacterial drugs, as they can negatively affect the development of the baby.
Who is at risk for OHSS during IVF?
After performing in vitro fertilization, it is impossible to predict whether the patient will develop pathology or not. However, there is a category of people who have a certain predisposition to hyperstimulation syndrome.
These include:
- Women with light hair color (a feature of the genotype).
- Under 35 years of age.
- Having low weight.
- Prone to allergic reactions.
- Suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Patients with high levels of estradiol activity in plasma.
- Ladies who are on a GnRH protocol.
- Women who receive luteal phase support with increased or repeated doses of hCG drugs.
- Patients with double stimulation.
Considering the presence of risk factors, the attending physician is able to predict and timely identify the pathological process in the patient.
Cancer development
There is an opinion that IVF increases the risk of developing cancer. This is especially associated with cancer of the brain, breast, ovaries and endometrium, since such cases have become quite common among famous people.
At the moment, science does not have a sufficient evidence base on the direct connection between the increase in the occurrence of cancer in women who have undergone IVF.
Proven facts include the connection between the development of cancer pathology and genetic predisposition, the influence of ionizing radiation, and substances that have a carcinogenic effect. It is worth understanding that in cases of cancer detection after IVF protocols, this process may already exist. And tissues in the corresponding localizations of a malignant nature are hormonally dependent.
Hormonal stimulation is a complex process that is accompanied by the exogenous administration of large doses of hormones. It is precisely this combination of circumstances that may be the reason for the connection between IVF and cancer. Currently, this issue has not been fully studied and requires further research.
Forms of the disease
Experts distinguish 2 forms of OHSS:
- Early ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. This type of pathology develops immediately after the maturation of the eggs has occurred. When the embryo is attached to the uterine wall, immediate treatment of the disease is required to avoid its transformation into a later form. If the patient does not become pregnant, the disease disappears on its own after the next menstruation.
- Late OHSS. Is detected at 5-12 weeks of the gestational period. It is characterized by a severe course and requires timely treatment.
Cancel transfer
If the risk of OHSS is high, many follicles have grown in the ovaries, there is high estradiol in the blood, and even more so if the first symptoms begin after the puncture, it makes sense to suspend the protocol. By this time, eggs have already been received. They can be fertilized. Embryos are grown until day 5 and frozen. The highest quality ones can be transferred to the next cycle.
This approach virtually eliminates the risk of moderate or severe OHSS. Because pregnancy does not occur in the current cycle. This means that OHSS can only be early. It is usually mild and clinically manifests only by mild abdominal discomfort. In a cryocycle, stimulation is not performed at all. Accordingly, there cannot be hyperstimulation.
Symptoms
Considering the severity of the signs of hyperstimulation syndrome, doctors distinguish several degrees of pathology.
Let us consider in detail the main manifestations of each of them.
Mild severity
The general condition is not cause for concern. At first, the disease manifests itself in the form of nagging pain in the lower abdomen, a feeling of fullness in it. Women note that their waist circumference becomes 2-3 cm larger and their weight increases slightly.
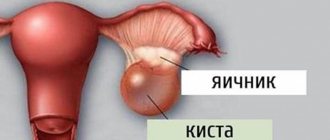
Pain appears, as during menstruation, and urination becomes more frequent. Such changes are explained by an increase in the size of the ovaries due to the appearance of formations in them (follicular, luteal cysts), circulatory disorders with the accumulation of fluid in the chest cavity and abdomen (ascites).
Average degree
The woman's health is deteriorating. The pain intensifies and becomes intense due to the continued growth of the ovaries in size and the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, which causes irritation of the peritoneum.
The patient complains of the appearance of digestive disorders - nausea with vomiting, stool disorders. The abdomen increases in circumference, and ultrasound diagnostics visualizes ascitic fluid in the abdominal cavity. Body weight gain progresses. The frequency of respiratory movements and heart contractions increases.
Severe degree
The woman's general condition is serious. A feeling of fear appears, headaches and dizziness occur. Organ dysfunction develops - cardiac and respiratory failure, which forces the patient to sit or take a lying position with the head end of the bed highly elevated. Shortness of breath, tachycardia appear, body temperature rises, as with a cold, and blood pressure decreases.
On palpation, the abdomen is enlarged in circumference due to ascites. The face, lower extremities and external genitalia swell; anasarca (swelling of the subcutaneous tissue) develops extremely rarely.
Critical degree
The woman's condition is assessed as extremely serious. Subjective complaints remain the same as in the severe form of hyperstimulation syndrome. There is a significant decrease in the volume of excreted urine: no more than 1000 ml.
During a doctor's examination, the patient is diagnosed with shortness of breath and tachycardia. This degree is characterized by a positive symptom of peritoneal irritation, and palpation reveals an enlarged liver and pronounced ascites with fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity of up to 5-6 liters. The ovaries are greatly enlarged and can be easily identified by palpating the lower abdomen. Manifestations of cardiac and respiratory failure are pronounced.
Causes
Normally, after the follicle ruptures, a temporary gland is formed at the site of damage - the corpus luteum. It releases specific substances that affect the woman’s body, preparing it for pregnancy.
The permeability of the capillary wall increases, blood vessels dilate, active blood components (interleukins, tumor necrosis factors, etc.) are activated.
Due to these changes, a small amount of the liquid component of the blood (plasma) leaks into the peritoneal cavity, irritating it.
Usually this process is not accompanied by changes in the woman’s condition; particularly sensitive patients may experience minor discomfort. However, when several corpora lutea are formed in the appendages at once, the effect on the body increases several times.
Because of this, more fluid enters the peritoneum, in severe cases more than a liter of plasma. As a result, the woman’s condition worsens, and the clinical picture of hyperstimulation syndrome develops.
How is OHSS diagnosed?
To make a correct diagnosis and then prescribe therapy, the doctor conducts a complete examination of the woman.
Diagnostics includes:
- Conducting a gynecological and general examination of the patient.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs - the size of the ovaries is determined, how much ascitic fluid has accumulated.
- Clinical and biochemical blood tests, analysis of hormones in plasma.
- OAM.
- Cardiac echocardiography and ECG: if heart failure occurs, signs of pathology are determined.
- X-ray of the OGK: to determine fluid in the cavities of the pleura and pericardium.
Depending on the course and clinical manifestations of OHSS, the list of diagnostic procedures is supplemented. When severe and critical degrees develop, an examination by a cardiologist, pulmonologist and gastroenterologist is required.
Blood and urine tests
In mild forms of the syndrome, blood and urine counts are normal. The average degree of OHSS is characterized by a hematocrit content of no more than 45%.
A severe degree is accompanied by reduced daily diuresis and an increase in hematocrit over 45%. Leukocytosis exceeding 15×10⁹/l is observed. Biochemical analysis visualizes an increase in the content of ALT, AST, and a decrease in the level of total protein. In OAM, urine density increases and proteinuria is observed.
A critical degree of OHSS is characterized by an increase in hematocrit over 55%, leukocytosis (over 25x10⁹/l). Biochemical analysis determines the imbalance of electrolytes and blood coagulation with the development of its thickening. A test for sex hormones records their high levels in plasma. Urinalysis reveals protein in the biological fluid, a decrease in its excretion (oliguria) and an increase in specific gravity.
Treatment options
The initial symptoms of OHSS do not require special treatment of the patient in a hospital setting. Usually it is possible to get rid of the disease after 2-3 weeks.
Treatment for mild hyperstimulation syndrome includes:
- Compliance with the drinking regime: a woman needs to drink a significant amount of liquid, excluding alcohol and drinks with gas. It is advisable to consume mineralized water to avoid electrolyte imbalance.
- Follow a balanced diet that includes foods containing high amounts of protein. It is necessary to refrain from eating foods rich in fiber.
- Avoid sexual contact and any physical activity.
- Monitor urine output and changes in body weight.
Treatment of moderate and severe OHSS is carried out in an inpatient setting, since the patient’s condition can deteriorate very quickly. The hospital must be specialized and equipped with a department or intensive care unit.
To combat hyperstimulation syndrome, doctors carry out the following treatment regimen:
- Drugs that replenish blood volume and improve its properties. The doctor prescribes droppers with crystalloid solutions (Ringer's solution, Trisol, Yonosteril), and then colloidal plasma-substituting solutions (Infucol, Volucam, Refortan).
- Anticoagulants – Fraxiparine, Clexane. They are necessary to prevent blood clots.
- Antibiotics (cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones) to prevent the addition of bacterial microflora.
- Antispasmodics (No-shpa, Papaverine) and NSAIDs to reduce abdominal pain.
To improve blood composition, it is necessary to do plasmapheresis. If severe tense ascites is observed with OHSS, unnecessary fluid is evacuated from the abdominal cavity. To do this, an abdominal or transvaginal puncture is performed.
If a woman is pregnant, but she develops a critical degree of hyperstimulation syndrome, an artificial termination of pregnancy is necessary.
Thrombotic complications
According to various authors, 1-4% of all cases of OHSS are severe. They are most dangerous due to thrombotic complications.
Stimulation of ovulation always leads to an increase in estrogen levels. As a result, a state of hypercoagulation is formed - increased blood clotting ability. Blood clots easily form in blood vessels, which can block vital arteries.
The situation is aggravated after the introduction of hCG or its formation after pregnancy. An increase in the concentration of this hormone in the blood activates the hemostasis system. There is an increase in the levels of fibrinogen, factors II, V, VII, VIII and IX. After another 2 days, fibrinolytic mechanisms are launched. Their peak activity is observed after 8 days.
Pathogenetic mechanisms of thrombotic complications:
- compression of the pelvic veins;
- state of hypercoagulation (increased clotting) of blood;
- thrombophilic conditions;
- impaired vascular reactivity.
Thrombotic complications develop in one in 128 women who develop OHSS. But severe - only 0.04% of those diagnosed with hyperstimulation syndrome.
The risk of thrombosis is 30 times higher than the average incidence of these diseases in the population. Among patients with hyperstimulation syndrome, thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities, subclavian and internal jugular veins predominate. 70% of complications occur after pregnancy. The remaining 30% occurs in early OHSS.
Thrombotic complications can develop at a variety of times. On average, this occurs a month after ovulation is stimulated. But early complications are possible already in the luteal phase. They can also be delayed - one and a half months after ovulation. A case of thrombotic complications after IVF at 20 weeks of pregnancy is described.
Usually blood clots appear only after the symptoms of OHSS disappear. However, most cases are venous thrombosis, not arterial. If arterial thrombosis develops, they appear earlier: on average 2 weeks after embryo transfer.
Assessing the risk of thrombotic complications
Your doctor may anticipate an increased risk of thrombotic complications in some patients and take steps to minimize it. Factors that increase the likelihood of this group of complications are as follows:
- age after 40 years;
- thrombophilic conditions;
- family history;
- obesity;
- multiple IVF.
Thrombophilias are found much more often in patients with infertility. Among those who undergo IVF, antiphospholipid syndrome is detected in at least 10% of cases, while on average in the population it occurs only with a frequency of 1-3%.
Possible consequences
Complications of the disease depend on timely detection and treatment. The higher the degree of OHSS, the greater the likelihood of adverse effects.
In severe forms of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, various diseases are often associated:
- ascites;
- heart and respiratory failure;
- acute renal failure due to a decrease in the volume of circulating blood and its increased coagulability;
- torsion and rupture of the ovary with the formation of massive blood loss;
- ectopic pregnancy: attachment of the embryo outside the uterine cavity;
- exhausted ovarian syndrome (considered the most dangerous complication of OHSS, in which there is an early cessation of the functioning of these organs before menopause - oocytes stop maturing, menstruation disappears. When the syndrome affects both ovaries, the woman becomes infertile).
If OHSS occurs in a woman during pregnancy, it often occurs with adverse consequences. Thus, in the early stages the risk of miscarriage increases, and at the end of gestation - premature birth. Throughout pregnancy, there is a high probability of fetoplacental insufficiency, hypoxia of the baby in the womb and delayed development of the baby inside the womb.
Prevention
It is easier to prevent any pathology than to deal with the consequences later. To avoid complications of IVF in the form of ovarian hyperstimulation, you should resort to several tips:
- plan your pregnancy carefully and undergo examination;
- when choosing stimulation drugs, take into account previous IVF attempts and response to medications;
- maintain psychological and physical calm, eat right;
- reduce the concentration of the hormonal substance that is introduced into ovulation;
- freeze the embryos, thereby postponing implantation to the next cycle, and, if necessary, wait several months;
- remove tumors in the appendages in a timely manner, be under constant supervision of a specialist;
- monitor follicle growth.
If there is a high risk of developing OHSS, you can completely abandon stimulation. In this case, only one egg can be extracted and fertilized from the ovary, so the chance of getting pregnant will be somewhat reduced.
But on the other hand, the woman’s body will not tolerate the hormonal shock and will be ready for a new IVF procedure in the next cycle.
How to avoid illness - preventive measures
To prevent ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, the doctor determines the existing risk factors for each patient.
In addition, the specialist takes the following measures:
- Initial hormonal therapy begins with a reduced dose.
- Does not use an ovulatory dose of hCG.
- Use Doxinex on the day you are taking a medication that triggers ovulation (Menopur).
- Stimulation should last for a short time. For this, late administration of hormones or early administration of hCG is used.
- Performs puncture of available follicles.
- To maintain the luteal phase, it uses progesterone instead of hCG.
- Constantly monitors the estrogen content in the in vitro fertilization cycle.
- Conducts dynamic monitoring of the well-being and general condition of the woman.
Doctor's comment on the topic of ovarian hyperstimulation:
Risks
A low risk of developing hyperstimulation syndrome is possible in the following group of patients:
- over 36 years old;
- when ovulation was stimulated with clomiphene;
- those who are overweight;
- with estradiol levels less than 4000 lg.ml;
- when the second phase is supported with progesterone.
High - women with the presence of the following factors:
- under 36 years old;
- those suffering from PCOS;
- with the support of phase II of the menstrual cycle of hCG;
- when ovulation is stimulated by gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists;
- body weight is less than the physiological norm;
- estradiol level above 4000 log.ml;
- pregnancy;
- the result of stimulation in the form of many follicles.
If ovarian hyperstimulation occurs during IVF, symptoms can be of varying degrees of intensity and have a wide range of laboratory and clinical signs.