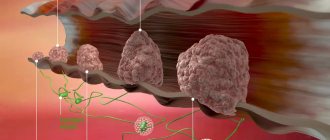
As a rule, stage 1 cancer is diagnosed in cases where the malignant tumor is located within the organ in which it originated, does not grow into neighboring structures, has not spread to regional lymph nodes and has not given distant metastases. At this stage, the chances of achieving remission are high, but cancer is difficult to diagnose because it usually does not manifest any symptoms. Regular preventive examinations and screening tests help detect cancer in its early stages.
Our expert in this field:
Sergeev Pyotr Sergeevich
Deputy chief physician for medical work, oncologist, surgeon, Ph.D.
Call the doctor
Treatment for stage 1 cancer consists mainly of surgical removal of the malignant tumor. Often this is the limit, after which remission occurs. If the risk of recurrence is high (for example, with large, aggressive tumors), chemotherapy or radiation therapy may be given before or after surgery.
Even if cancer is diagnosed at an early stage, treatment cannot be delayed. Some tumors progress rapidly; they can grow into neighboring tissues, spread to lymph nodes, and metastasize. After this, the prognosis worsens. The fight against the disease must begin as soon as it is identified. At the Medicine 24/7 clinic you can quickly receive all the necessary types of treatment. Our doctors work in accordance with the latest versions of international protocols.
Accurate staging
To determine the stage, doctors use a number of tests:
- The physical exam involves gathering information about the cancer. The doctor examines the body so as not to miss the unusual condition of the body. A physical exam can determine the tumor's size and likelihood of spreading.
- Imaging studies provide visual information about the condition of internal organs and include x-rays, computer scans, magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography.
- Laboratory tests and tests for cancer cells determine the health of the blood, urine, and other body fluids and tissues.
- Pathology test reports indicate the size of the tumor, its growth and spread to other organs or systems.
Stage 1 cancer is a localized cancer. In many cases, it has partially penetrated the membrane - a thin, fibrous tissue - but has not spread further.
Symptoms
Many types of cancer are accompanied by clinical manifestations that help make a timely diagnosis.
Common signs of cancer:
- Loss of body weight that cannot be explained by obvious reasons (lifestyle changes or other identified diseases).
- Weakness, fatigue.
- Sweating, which cannot be explained by obvious reasons, worsens at night.
- Itchy skin that is not associated with other obvious causes, such as seasonal allergies or food allergies.
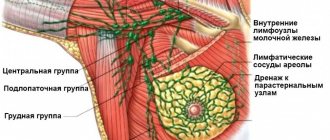
Signs of breast cancer:
- The occurrence of asymmetry in the size of the glands (one is larger than the other in size).
- A change in the size or shape of the glands that is not related to age (i.e., occurring in adulthood).
- The appearance of a “nodule” of increased density in the mammary gland, which increases over time.
- Inflammatory changes (like mastitis or breastfeeding) on the gland that cannot be explained by breastfeeding: swelling, hyperthermia of the gland, redness.
- Nipple changes: retraction, redness, abnormal discharge (often containing blood).
- Retractions of the skin of the gland, the appearance of swelling or compaction on any part of it.
Signs of lung cancer:
- Shortness of breath, feeling of suffocation.
- A prolonged, persistent cough that does not improve over time and cannot be explained by infections (colds, flu).
- The appearance of abnormal impurities in the sputum, including bloody ones.
Symptoms of stomach, intestinal, and pancreatic cancer:
- A sudden change in food preferences (often an aversion to meat and other high-calorie foods), loss of appetite.
- Constant nausea.
- Heaviness in the abdominal cavity after eating.
- Abdominal pain of unknown origin.
- Difficulty swallowing, a feeling of “stagnation” of food inside the esophagus, frequent choking.
- Blood in feces, black stools with a “tarry” appearance.
- Constipation or diarrhea that cannot be explained by changes in diet, lifestyle, infections, etc.
- Ulcers in the mouth.
- Increase in abdominal size.
Signs of skin cancer:
- The appearance of a previously non-existent mole or changes in an existing one, such as increasing its asymmetry, increasing size, changing shade.
- The appearance of long-term non-healing skin “wounds” and ulcers for no apparent reason.
- Yellowing of the skin.
- Unexplained pale skin.
- “Bumps” are cutaneous and subcutaneous, including painless ones, including ones that increase in size and remain motionless when trying to displace them.
Signs of brain cancer:
- Constant pain in the head.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Seizures of an epileptic nature.
- Progressive memory impairment.
- Balance imbalance.
- Dizziness.
- Unsteady gait.
- Difficulty speaking.
- Loss of sensitivity or paralysis of some muscles.
- Deterioration of vision.
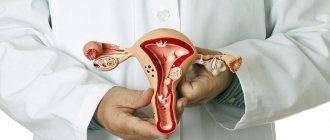
Signs of cancer of the ovaries, uterus, testicles, penis:
- Abnormal genital discharge, particularly bloody discharge, unless caused by menstruation.
- Increased testicular size, increased density, inflammation.
Signs of kidney cancer:
- Blood or other abnormal impurities in the urine.
- A persistent change in the color of urine without obvious reasons.
- Difficulty urinating, pain when urinating.
This list is not complete, since the signs of different types of cancer vary and are determined by the location of the tumor and the extent of metastases. All of the above symptoms can be caused by other pathologies that are not associated with malignant tumors. However, if such symptoms arise or worsen, or if they persist for a long time (for at least several weeks), you need to seek medical help to determine their cause. The timeliness of cancer detection determines how long people live with a cancer diagnosis.
Stage 1 cancer: signs that men ignore
There are certain early symptoms of cancer that indicate the possibility of cancer in men. These include:
- Problems with urination:
This may include the need to go to the toilet more often than usual, sudden leakage of urine, or discomfort. These circumstances often indicate an enlarged prostate. However, it is better to consult a doctor quickly to exclude the possibility of developing a malignant process.
- Changes in the condition of the testicles:
The feeling of heaviness, pain, or unusual appearance of an organ should cause concern.
Damage to the digestive organs
A tumor of the esophagus characterizes a malignant process with an aggressive course. The size of the tumor body increases rapidly, metastasis begins in a matter of time. Tissue atypicality is difficult to cure due to complicated diagnostics. The earliest diagnosis helps to increase the patient's life expectancy by more than 5 years. At the final stage, an unfavorable outcome is predicted. A person rapidly loses weight, his voice changes, and discomfort appears in the sternum. Survival rate is reduced to 6 months.
Stomach cancer is at the top of the list of cancer diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The reasons that provoke atypia are genetic predisposition, bad habits, the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, consumption of low-quality and harmful products containing carcinogens. Gastric tumors can be successfully treated in the initial stages. The neoplasm has not yet spread into the deep layer of the epidermis. The survival prognosis for gastric damage at stage 1 guarantees 100% recovery.
Pathology is difficult to detect. Symptoms may indicate the presence of a common bowel or rectal disorder. A person, pointing out indigestion and other pathologies, triggers the condition, increasing the likelihood of a sad outcome. At stage 3, the disease is accompanied by severe pain in the abdominal cavity. At grade 4, the following signs are noted:
- anemia;
- severe pain;
- intoxication of the body;
- weight loss;
- feverish condition.
At the final stage, patients live less than 6 months.
Common signs of stage 1 cancer
There are characteristic symptoms for both sexes, complaints of which should immediately consult a doctor. These include:
- Skin changes or moles:
Dangerous human condition. If you have the slightest concern, you should consult a doctor.
- Blood in the stool:
The main symptom of hemorrhoids, but can also indicate colon, bladder or kidney cancer.
- Changes in the lymph nodes:
Sometimes provoked by leukemia or lymphoma.
- Swallowing problems:
May be caused by a malignant process of the throat or stomach.
- Cough:
A cough that lasts more than 4 weeks, especially when smoking or shortness of breath, may raise suspicion of cancer. If there is a cough with blood, a person should immediately consult a doctor!
- Painful sensations:
Cancer pain that lasts for quite a long time can signal cancer of the bone, brain, and other cancerous processes.
If you experience severe weight loss, heartburn, or fatigue that does not go away for a long time, it is also advisable to consult a doctor. These symptoms often help identify stage 1 cancer.
Superficial tumor type
With certain types of superficial type oncology, the patient is able to determine the pathology independently. Skin cancer is characterized by the formation of atypical spots and nodes on the epidermis, occurring in the early stages without severe discomfort. If suspicious manifestations do not go away after using medications, it is recommended to undergo a medical examination. A tongue tumor is often asymptomatic. Suspicion may be caused by ulcerative formations, cracks and seals, which are considered a possible signal of a precancerous condition or the initial stage of the oncological process.
Among the superficial varieties, lip damage is also distinguished. The disease is diagnosed in rare cases. The risk group includes people who use tobacco products for a long time. Characteristic signs include cracks, peeling and ulcers that last a long time. However, people neglect the symptoms, which is why oncology is detected in an advanced state. Throat cancer in its early stages develops with symptoms similar in appearance to the standard cold. These types of tumors are localized on the tissues of the lips, tongue and larynx. The general name for pathologies is damage to the oral cavity.
Modern treatment of stage 1 cancer
Therapeutic methods for treating stage 1 tumors include:
Surgery:
Used in cases where the cancer forms a solid tumor. The malignant formation is removed from the affected organ. If necessary, regional lymph nodes are also excised.
Radiation therapy:
It is used as the main method of treatment for oncology that does not form a seal, and also as an adjunct to surgery.
Chemotherapy:
It prevents relapses of the malignant process, therefore it is an important method of treating stage 1 cancer. Cancer drugs attack abnormal cells in the body. However, the possibility of side effects should be taken into account.
Additional treatments for stage 1 cancer
Some types of cancer require increased therapeutic measures. They are carried out using:
Hormonal therapy:
For oncological processes that depend on hormonal factors (cancer of the mammary glands, uterus, ovaries in women; prostate cancer in men; thyroid cancer in both sexes).
Targeted therapy:
Influencing the causes of cancer known to oncologists.
Classification according to the TNM system
The TNM system for determining a cancerous malignant disease is the current classification of oncological diseases, which was adopted by the National Health Committee to classify the stages of development and growth of a cancerous tumor; it is used to more accurately determine the image of the malignant formation itself.
This system was developed by Pierre Denoit in 1952. With the development of oncology, the system itself improved and evolved every year. At the moment, the publication of 2009 is relevant. It contains standards and a clear classification of oncological diseases.
We will begin to look at the system itself, starting from three components:
T is short for the Latin word Tumor. This indicator reflects the size, prevalence, growth of the cancer itself deep into nearby tissues and the location of the tumor. Each tumor has a letter and a number that determines the grade and size of the cancer - from T0 to T4 .
N - comes from the Latin word Nodus - knot. When a cancerous tumor grows, it later begins to overlap and affect nearby lymph nodes. This is exactly what this letter shows. If we have N0 , then the cancerous tumor has not yet invaded the lymph nodes, N3 - maximum damage to the lymph nodes is already underway.
M - comes from the Greek word Metastasis. The presence of metastases to other organs. As in previous cases, the number will determine the gradation of the spread of malignant cells to other organs. M0 - indicates that the cancer does not metastasize. M1 - there is metastasis to nearby organs. But here you need to clarify a small detail; usually after M they write the name of the organ itself where metastasis occurs. For example, M( Mar) - a cancerous tumor has begun to metastasize to the bone marrow, and M( Ski) - metastases have spread to the skin.
| Symbols _ | Organ name |
| Oth | Other organs |
| Pul | Lungs |
| Ski | Leather |
| Oss | Bones |
| Adr | Adrenal glands |
| Hep | Liver |
| Per | Peritoneum |
| Bra | Brain |
| Ple | Pleura |
| Lym | Lymphatic system |
| Mar | Bone marrow |
Blood cancer - leukemia
Additional characters
In addition to using the basic letters TNM, additional markings are used. It helps show exactly when the tumor was discovered.
| Symbol | Decoding |
| c | Non-invasive diagnostic methods were used to determine the stage of cancer. |
| p | The stage was discovered and established during surgery. |
| m | Several tumors were discovered at once. |
| y | Determines tumor after therapy. |
| r | Evaluation of recurrent tumors (recurring) |
| a | Classification of tumor after human autopsy. |
Lung cancer
Forecast
For any type of cancer, a five-year survival rate is first established. This does not mean that the patient will only live five years after the final diagnosis. They simply first study information about patients who remained alive after five years, then ten, etc.
The prognosis for cancer, in particular stage 1 cancer, includes the following features:
1. Disease-free survival:
This factor takes into account the number of people who achieve complete remission. There is a high probability that the malignant process will not recur.
2. Progression-free survival:
This means that cancer cells and tissues are still present in the body, but have not spread to other parts of the body. In this form, the malignant process can become chronic.
In general, stage 1 cancer has a very good prognosis. The difficulty for this stage lies, first of all, in such an early diagnosis.
Causes
Medicine does not know for certain why benign tumors develop into stage 1 cancer in the human body. However, research is underway to suggest that cancers arise from:
- Behavioral factors. Basically, the wrong way of life. This can include bad habits (smoking, alcoholism), unhealthy diet with an abundance of fried and fatty foods, lack of exercise.
- External factors. This section includes what surrounds a person that can cause him to develop cancer: the environmental situation, radiation exposure and “harmful” production, when a person is exposed to the risk of cancer in the workplace.
- Internal factors. This type of factors includes disorders in the body, the development of diseases and inflammations, against the background of which a tumor is formed, heredity, and atypical abnormalities.
How long do they live?
Cancer detected at such an early stage, with proper and timely treatment, has a very good chance of a complete cure (remission). For example, for many types of cancer, the five-year survival rate becomes 100%. If after this time the tumor does not recur, this means in 85% of cases that the malignant process will not return.
Based on the survival rates and overall prognosis, being diagnosed with “ stage 1 cancer ” with proper treatment is not a death sentence for a person at all.
Prevention
Prevention helps reduce the likelihood of cancer. When diagnosing oncology, preventive measures facilitate the treatment of pathology. Group of medical recommendations:
- healthy eating.
- refusal to use alcohol and tobacco products.
- systematic intake of vitamins.
- Regular examinations and medical examinations.
- sports, physical activity.
- avoid stressful situations.
- when working in hazardous industries, increase the number of inspections to three times a year.
Diagnostics
Reliable tumor markers include a blood test, the main purpose of which is to determine the amount of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) contained in it. It refers to a protein compound produced by the prostate gland. It is responsible for several functions, including liquefying the ejaculate.
If laboratory data indicate an amount of PSA that exceeds standard values, then there is reason to suspect an oncological process. The standard amount of antigen depends on the patient’s own age - the threshold for the upper level of concentration increases in accordance with the years lived:
- Interval 40-50 years – 2.5 units;
- 50-60 years – 3.5 units;
- 60-70 – 4.5 units;
- After the 70th birthday - 6.5 units.
The peculiarity is associated with the enlargement of the prostate gland over the years; accordingly, there is an increase in the secretion of the antigen and its level in the bloodstream. More accurate data is obtained by assessing the rate of change in PSA.
Non-standard PSA values are the basis for performing an organ biopsy. After the manipulation, the next test is carried out no earlier than a month and a half later.
Biopsy
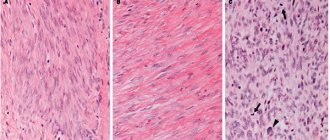
The diagnostic method is considered one of the most effective options for studying the cellular structures of tissues. A biopsy allows you to confirm the presence of malignant neoplasms in problem areas. The obtained histological material from the body of the prostate gland makes it possible to identify the stage of the ongoing disease and select appropriate treatment tactics.
The analysis relates to traumatic procedures; serious reasons are required for its implementation. A biopsy is prohibited in the acute phase of inflammatory processes, the patient’s serious condition, or exacerbation of prostatitis.
The manipulation is performed in an outpatient setting; before the procedure, the patient is given a list of recommendations for preliminary preparation:
- The prohibition includes taking medications that affect the level of blood clotting - anticoagulants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Be sure to take all prescribed medications, especially those related to antibiotics;
- Do not engage in any type of sexual contact for two days before the appointed time of analysis;
- Before the analysis, the patient must do a cleansing enema.
The technique is carried out under local anesthesia, the collection of problematic tissues is carried out under the control of ultrasound equipment, using specialized hollow needles. The injection zone is the rectum, less often the puncture is carried out through the perineum.
The resulting material is studied in the laboratory under a microscope. There is a special Gleason table that allows you to assess the level of damage to the structures of the prostate gland. The index determines deviations in cells:
- Structures;
- Forms;
- Size;
- Differentiations.
Stage 1 prostate cancer is characterized by a neoplasm consisting of homogeneous glandular elements, without significant changes in the nuclei. The stage of the disease is determined by the damage to prostate tissue by cancer cells. At the first stage, the indicators are 5%.